Abstract
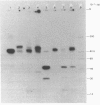
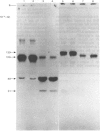
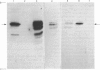
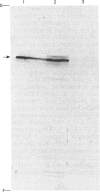
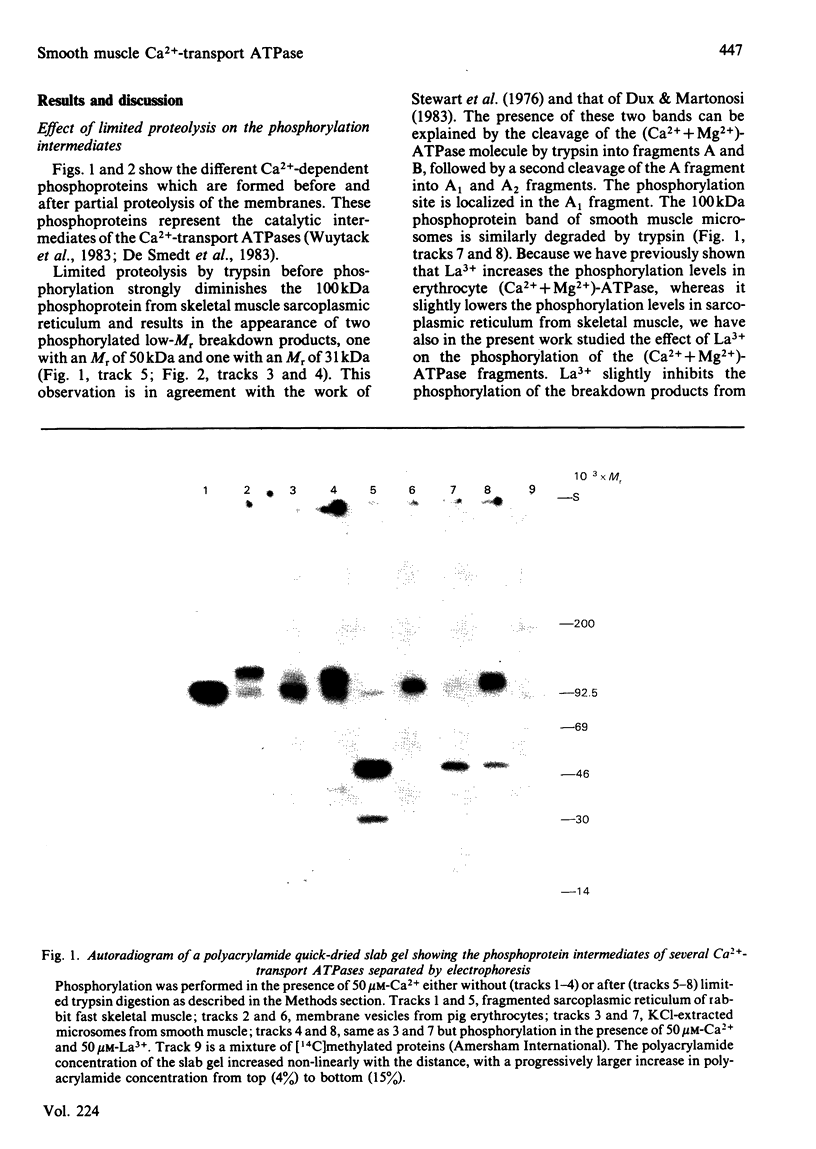
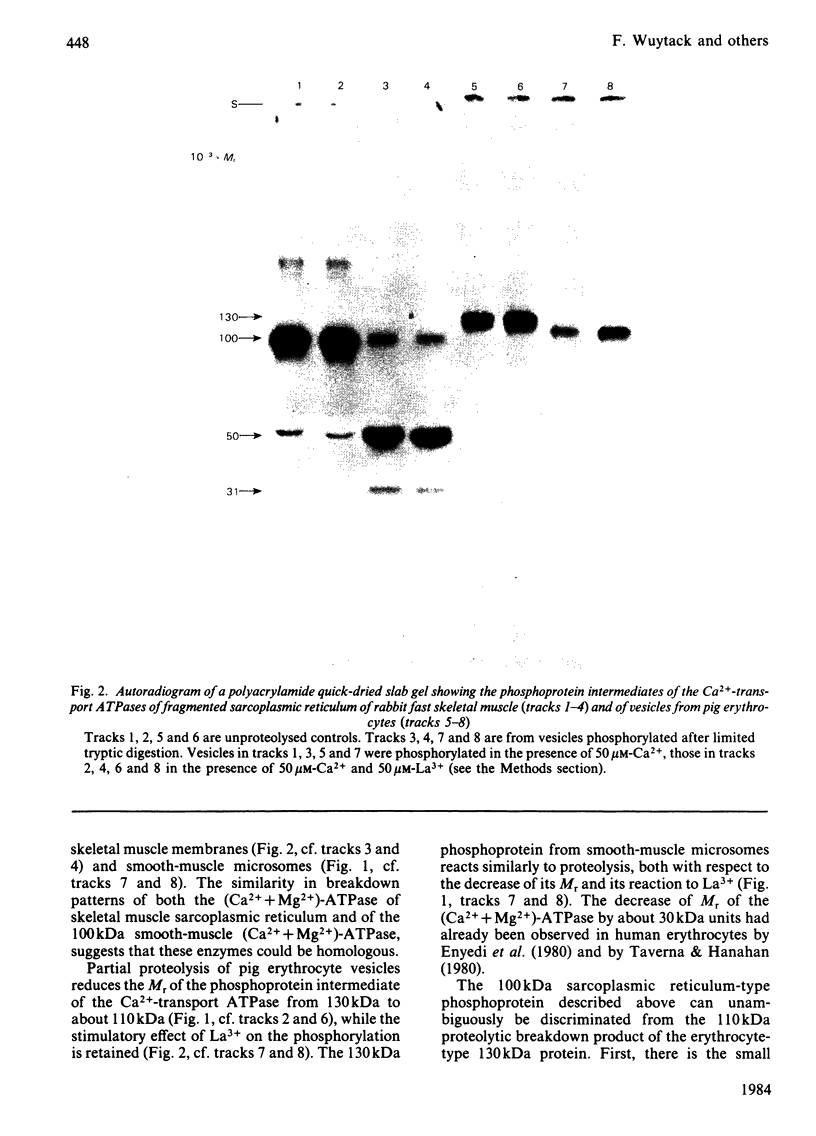
Membrane fractions prepared from smooth muscle of the pig stomach (antral part) contain two Ca2+-dependent phosphoprotein intermediates belonging to different Ca2+-transport ATPases. These alkali-labile phosphoproteins can be separated by electrophoresis in acid medium. The 130 kDa phosphoprotein resembles a corresponding protein in the erythrocyte membrane, whereas the 100 kDa protein resembles that of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. These resemblances are expressed in terms of Mr, reaction to La3+ and in a similar proteolytic degradation pattern. The presence of the calmodulin-stimulated ATPase in mixed membranes from smooth muscle is confirmed by its binding of calmodulin and antibodies against erythrocyte Ca2+-transport ATPase, whereas such binding does not occur with proteins present in the presumed endoplasmic reticulum from smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Schutter G., Wuytack F., Verbist J., Casteels R. Tissue levels and purification by affinity chromatography of the calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+ -transport ATPase in pig antrum smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Smedt H., Parys J. B., Borghgraef R., Wuytack F. Phosphorylated intermediates of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase and alkaline phosphatase in renal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 9;728(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Ca2+-ATPase membrane crystals in sarcoplasmic reticulum. The effect of trypsin digestion. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10111–10115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Sadorf I., Bader H. A model for the regulation of the calmodulin-dependent enzymes erythrocyte Ca2+-transport ATPase and brain phosphodiesterase by activators and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj2070541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Brdiczka D., Nickel E., Pette D. ATPase activities, Ca2+ transport and phosphoprotein formation in sarcoplasmic reticulum subfractions of fast and slow rabbit muscles. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):211–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purified (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Reconstitution and effect of calmodulin and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L. The sarcoplasmic reticulum of smooth muscle fibers. Z Naturforsch C. 1982 May-Jun;37(5-6):481–488. doi: 10.1515/znc-1982-5-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Wuytack F., Eggermont J., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Isolation of a plasma-membrane fraction from gastric smooth muscle. Comparison of the calcium uptake with that in endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):315–322. doi: 10.1042/bj2100315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Wang J. H. Preparation and assay of the Ca2+--dependent modulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:187–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Shuman H. Electron probe analysis of vascular smooth muscle. Composition of mitochondria, nuclei, and cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):316–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. S., MacLennan D. H. Isolation and characterization of tryptic fragments of the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):712–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Hanahan D. J. Modulation of human erythrocyte Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase activity by phospholipase A2 and proteases. A comparison with calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):652–659. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Purification of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from smooth muscle by calmodulin affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 6;129(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., De Schutter G., Verbist J., Casteels R. Antibodies to the calmodulin-binding Ca2+-transport ATPase from smooth muscle. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80901-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Demonstration of the phosphorylated intermediates of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in a microsomal fraction and in a (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase purified from smooth muscle by means of calmodulin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurini M., Krebs J., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Controlled proteolysis of the purified Ca2+-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. A correlation between the structure and the function of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):618–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]