Abstract
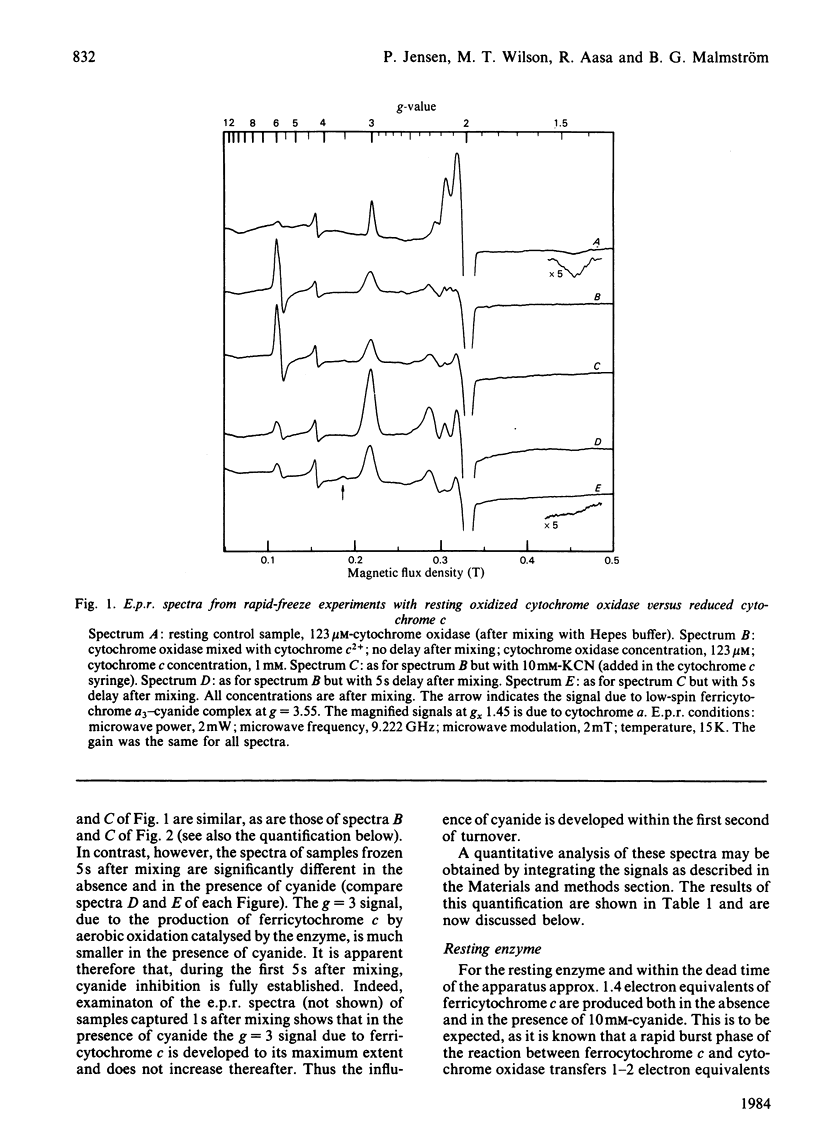
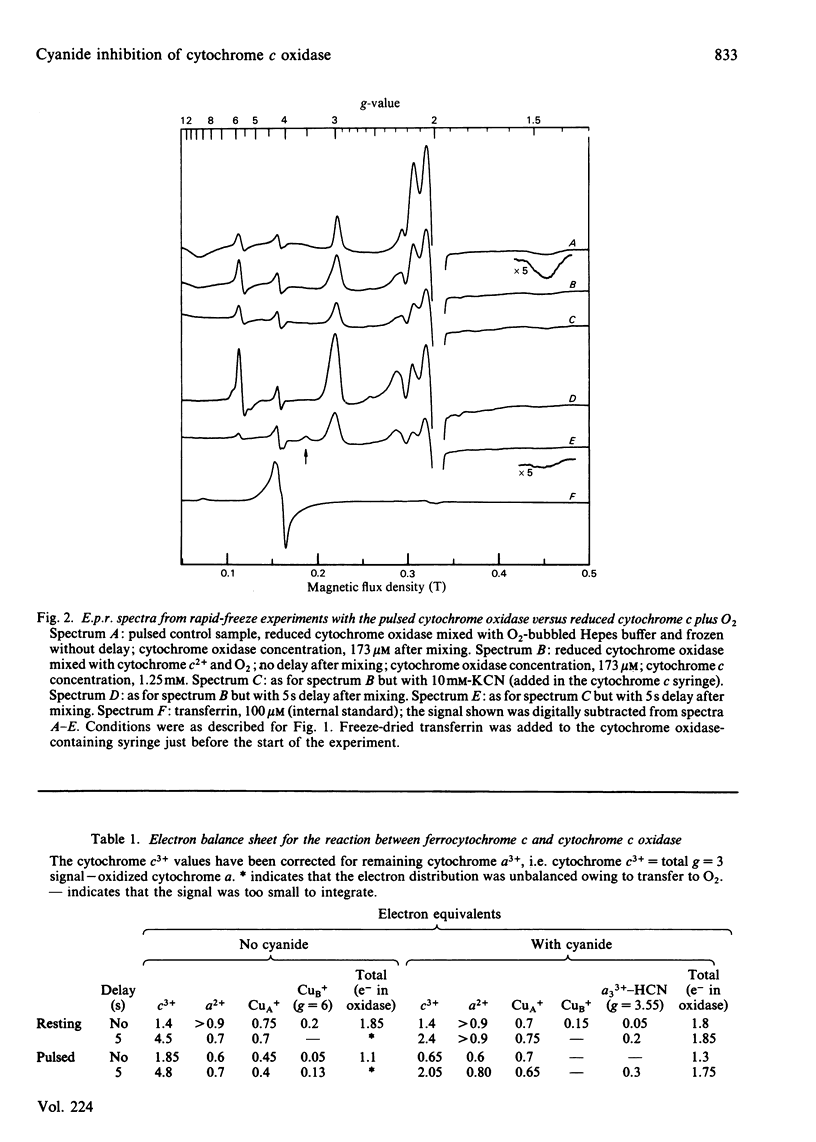
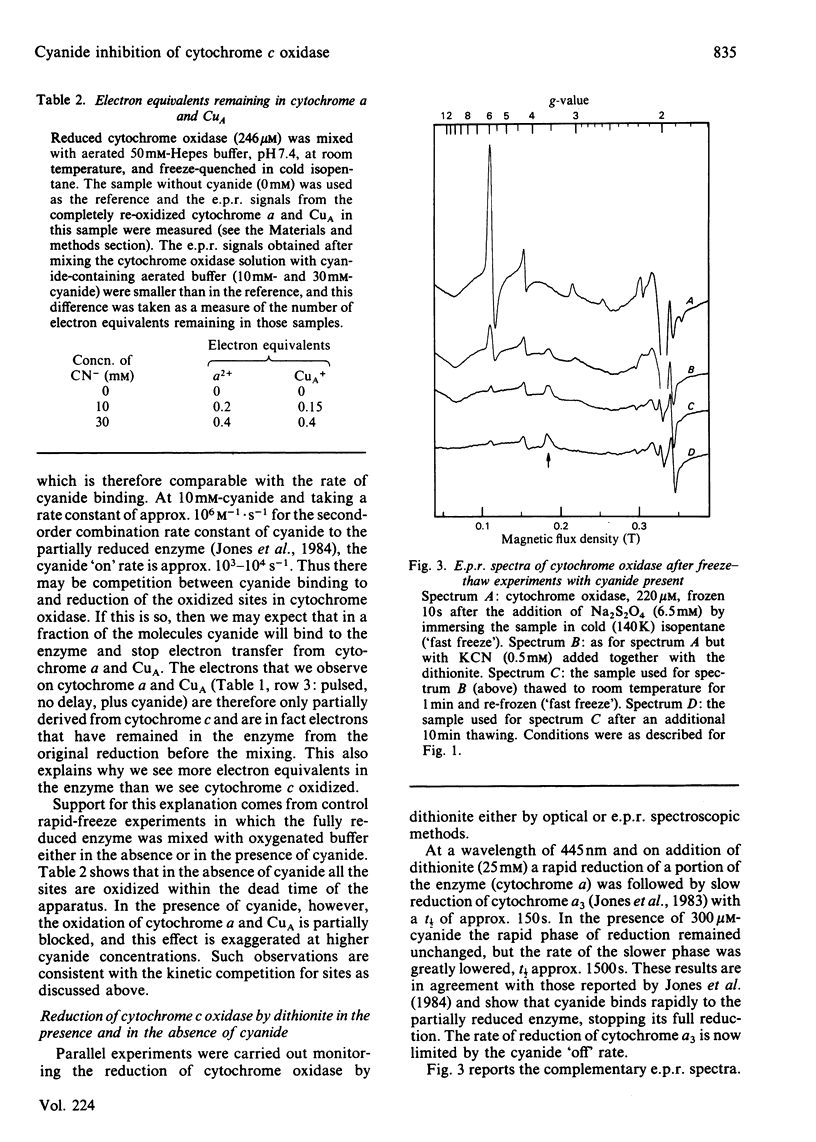
The inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by cyanide, starting either with the resting or the pulsed enzyme, was studied by rapid-freeze quenching followed by quantitative e.p.r. It is found that a partial reduction of cytochrome oxidase by transfer of 2 electron equivalents from ferrocytochrome c to cytochrome a and CuA will induce a transition from a closed to an open enzyme conformation, rendering the cytochrome a3-CuB site accessible for cyanide binding, possibly as a bridging ligand. A heterogeneity in the enzyme is observed in that an e.p.r. signal from the cytochrome a3 3+-HCN complex is only found in 20% of the molecules, whereas the remaining cyanide-bound a3-CuB sites are e.p.r.-silent.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AASA R., MALMSTROEM B. G., SALTMAN P. THE SPECIFIC BINDING OF IRON(III) AND COPPER(II) TO TRANSFERRIN AND CONALBUMIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:203–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90599-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasa R., Albracht P. J., Falk K. E., Lanne B., Vänngard T. EPR signals from cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 13;422(2):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Greenwood C., Wilson M. T. Oxygen "pulsed" cytochrome c oxidase: functional properties and catalytic relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3128–3132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Greenwood C., Malmström B. G., Rotilio G. C. The interaction of cyanide with cytochrome oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):396–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain T., Greenwood C. Kinetic studies on the binding of cyanide to oxygenated cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):453–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1550453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudvig G. W., Stevens T. H., Morse R. H., Chan S. I. Conformations of oxidized cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3912–3921. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD H., SMITH L. A study of the kinetics of the oxidation of cytochrome c by cytochrome c oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer N. W., Robinson N. C. Characterization of a seventh different subunit of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase. Similarities between the beef heart enzyme and that from other species. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2930–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. C., Brittain T., Eglinton D. G., Gadsby P. M., Greenwood C., Nicholls P., Peterson J., Thomson A. J., Woon T. C. Low-spin ferric forms of cytochrome a3 in mixed-ligand and partially reduced cyanide-bound derivatives of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):57–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2150057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. C., Greenwood C. Kinetic evidence for the re-definition of electron transfer pathways from cytochrome c to O2 within cytochrome oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P., Aasa R., Malmström B. G. Electron redistribution in cytochrome c oxidase during freezing under turnover conditions. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80709-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Eglinton D. G., Gooding P. E., Greenwood C., Thomson A. J. Characterization of the partially reduced cyanide-inhibited derivative of cytochrome c oxidase by optical, electron-paramagnetic-resonance and magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):699–708. doi: 10.1042/bj1930699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. D., Jones M. G., Wilson M. T., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Sarti P. Reactions of cytochrome c oxidase with sodium dithionite. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):175–182. doi: 10.1042/bj2090175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. G., Bickar D., Wilson M. T., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Sarti P. A re-examination of the reactions of cyanide with cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):57–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2200057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Greenwood C., Brunori M., Antonini E. Kinetic studies on the reaction between cytochrome c oxidase and ferrocytochrome c. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):145–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1470145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Jensen P., Aasa R., Malmström B. G., Vänngård T. An investigation by e.p.r. and optical spectroscopy of cytochrome oxidase during turnover. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj2030483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries S., Albracht S. P. Intensity of highly anisotropic low-spin heme EPR signals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 9;546(2):334–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buuren K. J., Nicholis P., van Gelder B. F. Biochemical and biophysical studies on cytochrome aa 3 . VI. Reaction of cyanide with oxidized and reduced enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):258–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


