Summary
Human brain ontogeny is characterized by a considerably prolonged neotenic development of cortical neurons and circuits. Neoteny is thought to be essential for the acquisition of advanced cognitive functions, which are typically altered in intellectual disability (ID) and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Human neuronal neoteny could be disrupted in some forms of ID and/or ASDs, but this has never been tested. Here, we use xenotransplantation of human cortical neurons into the mouse brain to model SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency, one of the most prevalent genetic causes of ID/ASDs. We find that SYNGAP1-deficient human neurons display strong acceleration of morphological and functional synaptic formation and maturation alongside disrupted synaptic plasticity. At the circuit level, SYNGAP1-haploinsufficient neurons display precocious acquisition of responsiveness to visual stimulation months ahead of time. Our findings indicate that SYNGAP1 is required cell autonomously for human neuronal neoteny, providing novel links between human-specific developmental mechanisms and ID/ASDs.
Keywords: human brain development, evolution, cerebral cortex, SYNGAP1, neoteny, neurodevelopmental disease, autism spectrum disorder
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
SYNGAP1 is required cell autonomously for human synaptic neoteny
-
•
SYNGAP1 deficiency leads to precocious sensory responses in human cortical neurons
-
•
ID/ASD are directly linked to disrupted neoteny in human cortical neurons in vivo
-
•
In vivo modeling of a neurodevelopmental disease in human neurons at the circuit level
Vermaercke et al. investigate the mechanisms underlying deficiency in the ID/ASD gene SYNGAP1 in human cortical neurons transplanted in the mouse cortex. They find that SYNGAP1-deficient neurons develop mature synapses and circuit integration months in advance, leading to precocious sensory responsiveness. These data link disrupted neoteny of human neurons to an ID/ASD gene mutation.
Introduction
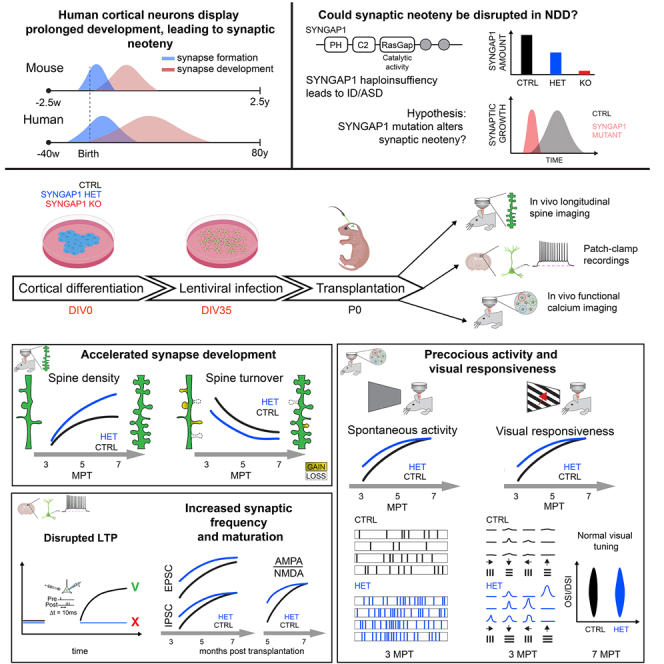
Most neurodevelopmental diseases (NDDs), including intellectual disability (ID) and autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), lead to deficits in cognitive functions. The underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown1,2,3,4 and could involve species-specific features of human brain development.5 One such feature is human-specific neoteny (retention of juvenile properties) of cortical neurons, which display considerably prolonged development compared with other mammals.6 Cortical neoteny has been proposed to be important in the acquisition of human-specific neural functions,7 which could be relevant for NDDs.8 Synapse and dendritic spine formation are increased precociously in some ASD patients,9,10 and early post-natal brain overgrowth is found in many ASD cases.11,12
Some forms of NDDs could thus be causally linked to disruption of human neuronal neoteny, but this has never been tested, given the difficulty accessing live human neurons. Models of xenotransplantation of human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived cortical projection neurons (CPNs) in the neonatal rodent cortex have been recently developed to study their development in vivo.13,14,15,16 Importantly, the xenotransplanted human CPNs retain neotenic properties and can integrate synaptically into the mouse cortical circuits to develop physiological response properties.14,16 Here, we apply xenotransplantation models to study the mechanisms of SYNGAP1 deficiency. SYNGAP1 is ranked among the top 5–6 genes mutated in NDDs: SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency causes up to 1% of non-syndromic ID and is associated with 50% of ASD cases.17,18,19,20,21,22 SYNGAP1 encodes a Ras/Rap-GAP protein that regulates excitatory synapse formation and function23 through regulation of dendritic spine morphology24,25 and AMPA receptor (AMPAR) trafficking.26,27,28
Mouse models for SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency display a transient increase of synapse formation in developing CPNs, possibly reflecting accelerated synaptic maturation.29,30,31 However, given the fast development of mouse cortical circuits (weeks long instead of years long in humans6), it has remained unclear whether cortical neuron neoteny, a human-specific feature, is actually disrupted following SYNGAP1 deficiency. In hPSC in vitro models, SYNGAP1-null mutant neurons were reported to display enlarged dendritic arbors and increased neural circuit activity,32 whereas SYNGAP1-haploinsufficient cortical progenitors were found to undergo precocious neurogenesis.33 However, the impact of SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency on human synaptic developmental timing, function, and plasticity has remained mostly unexplored.
Here, using human-to-mouse cortical xenotransplantation, we found that SYNGAP1-haploinsufficient human CPNs display accelerated synaptogenesis, leading to precocious integration into cortical circuits and acquisition of visual responsiveness months ahead of time. Thus, SYNGAP1 is required for human neuronal neoteny, linking human-specific mechanisms of neuronal development to the pathophysiology of some forms of ID/ASD.
Results
Generating an in vivo model of SYNGAP1 deficiency in human CPNs
We generated isogenic hPSC lines displaying specific SYNGAP1 mutations. We inserted mono- or bi-allelic loss-of-function (LoF) mutations targeting exon 8 (Figures S1A and S1B), which was chosen because it is common to all SYNGAP1-alternate transcripts, is located upstream of the most important functional domains, and is frequently mutated in SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency.23 Several independent clones displaying mutations on only one allele (heterozygote) or two alleles (homozygote) were selected for phenotypic analysis. The hPSC lines were differentiated into CPNs in vitro,13 which confirmed the loss of all SYNGAP1 protein isoforms in SYNGAP1-homozygous mutant (hereafter referred to as KO) neurons and about half a reduction in SYNGAP1-haploinsufficient (hereafter referred to as HET) neurons compared with control (hereafter referred to as CTRL) neurons (Figure S1C). Characterization of the differentiated neurons using canonical cortical fate markers did not reveal detectable differences in SYNGAP1-deficient neurons (Figure S1D).
We next applied a xenotransplantation paradigm in which human CPNs develop and mature in the mouse cortex following their species-specific timeline.16 Cortical progenitors were first differentiated from the hPSCs of each genotype, followed by specific treatments to ensure that xenotransplanted cells correspond mostly to CPNs born shortly before transplantation.16 Specifically, the cells were treated with gamma-secretase inhibitor DAPT (a Notch inhibitor that increases rates of neurogenesis) and antimitotic agent Ara-C34 to enrich for cohorts of newborn neurons prior to transplantation. Ethynyl-labeled deoxyuridine (EdU) pulse labeling at several time points in vitro confirmed that most transplanted CPNs found in the cortex were labeled by EdU 2 days before transplantation, whereas no labeled transplanted CPNs could be found following labeling 4 days before or after transplantation (Figures S2A–S2C). Fate marker analysis confirmed that most of the transplanted cells expressed markers of deep-layer CPN identity (Tbr1/CTIP2, Figures S2D–S2F), and none displayed expression of SATB2 (intratelencephalic [IT] CPNs, Figure S2G) or GAD67 (GABAergic neuron, Figure S2H), as described previously.13,16,35 Cortical cells were infected several days prior to transplantation with ad hoc lentiviral constructs (transducing emerald green fluorescent protein [EmGFP] to enable their identification and morphological analysis or GCaMP for functional analyses) without any detectable infection of the host mouse neurons.16
Differentiated human CPNs of each genotype were transplanted into newborn (P0) mouse pup littermates of the immunodeficient strain, RAG2 −/−, by injecting the cells into the lateral ventricles in the presence of EGTA.36 In this system, transplanted neurons then invade the ventricular zone and migrate along the mouse radial-glial processes to integrate into the cortical gray matter.16
Accelerated dendritic spine development in SYNGAP1-deficient neurons
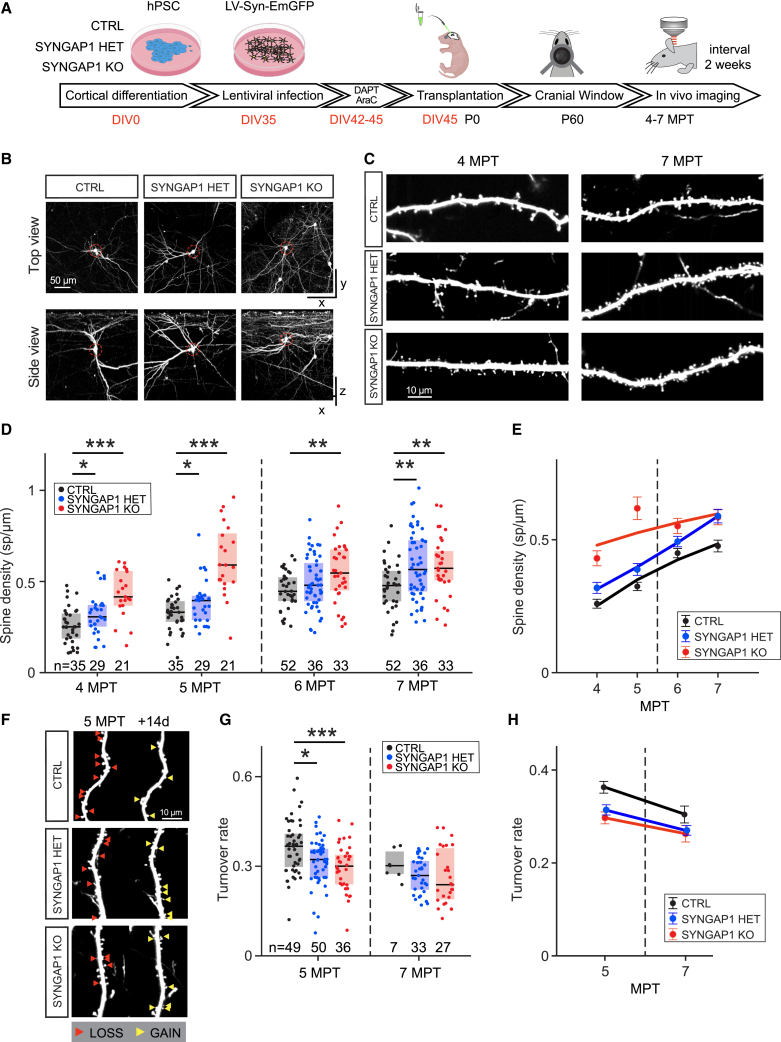
We first examined the morphological development of transplanted SYNGAP1 mutant and CTRL EmGFP-labeled CPNs with longitudinal in vivo multiphoton imaging from 4 to 7 months post-transplantation (MPT) (Figures 1A–1C and S2I). This enabled dendritic spine formation and dynamics to follow in real time as a proxy for post-synaptic formation. It takes up to 6 months for transplanted human CPNs to develop dendritic spines that stabilize and subsequently reach maturity.16 Compared with CTRL neurons, SYNGAP1 KO and HET neurons displayed accelerated dendritic spine formation, leading to increased spine density until 7 MPT (Figures 1D and 1E). We also measured the spine turnover ratio (Figure 1F), which typically decreases as spines mature.16 This revealed decreased dendritic spine turnover ratios in both KO and HET mutant neurons compared with CTRL neurons, indicating that their spines had already reached a high level of stability at least two months earlier (Figures 1G and 1H). Both HET and KO mutant neurons displayed lower spine turnover rates at 5 MPT, whereas KO neurons had much higher spine density at this stage (Figure 1D), suggesting that the observed differences in turnover rates are independent of dendritic spine density.
Figure 1.
Characterization of dendritic spine development and dynamics of SYNGAP1-deficient neurons
(A) Experimental timeline: differentiated mutant or control cortical neurons are infected with lentivirus (LV)-EmGFP and transplanted into neonatal mouse pups. A cranial window is implanted in adult mice to allow longitudinal imaging of dendritic branches of transplanted cells. Red numbers mark days in vitro preceding transplantation. Postnatal day (P), months post-transplantation (MPT).
(B) Example cell per genotype shown as top and side projection (rows). Red dashed circles mark the soma of each cell in both views. Total volume size shown is 360 × 340 × 400 μm. Data in (B), (C), and (F) show the signal of the green channel (EmGFP) after removing the scaled signal of the red channel.
(C) Representative dendritic branches per genotype at 4 and 7 MPT. SYNGAP1 KO and HET neurons exhibit higher spine density across both time points.
(D) Quantification of spine density for SYNGAP1 CTRL, HET, and KO; both mutants differ from controls at early (4 and 5 MPT) and late (7 MPT) time points. Data from 4 to 5 and 6–7 MPT are taken from the same longitudinally sampled branches; partial overlap exists between branches of both datasets. Medians per genotype/time point (4 MPT: 0.25, 0.31, 0.42; 5 MPT: 0.33, 0.40, 0.59; 6 MPT: 0.45; 0.48, 0.55; 7 MPT: 0.48, 0.57, 0.57). Data collected at 4–5 MPT from CTRL: 16 cells (4 mice); HET: 14 (3); KO: 11 (2). Data collected at 6–7 MPT from CTRL: 17 cells (3 mice); HET: 21 (5); KO: 17 (6). Boxes indicate median and interquartile range (IQR). Statistical comparison was done using rank-sum tests.
(E) Temporal evolution of dendritic spine density for all genotypes. The markers and error bars indicate ± SEMs for each group. The continuous lines are power-law fits. Note the upward shift of the SYNGAP1 KO and HET mutants compared to CTRL.
(F) Example of dendritic spine dynamics at 5 MPT for the 3 genotypes. Branches shown were recorded 2 weeks apart. Red arrow heads indicate spines that were not found at the next time point. Yellow arrows indicated spines that are newly formed relative to the previous time point.
(G) Quantification of spine turnover rate (see STAR Methods). Both mutants differ from controls at 5 MPT; a similar trend is observed at 7 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (5 MPT: 0.37, 0.32, 0.30; 7 MPT: 0.30, 0.27, 0.24). Data collected at 5 MPT from CTRL: 23 cells (5 mice); HET: 23 (5); KO: 17 (5). Data collected at 7 MPT from CTRL: 4 cells (1 mouse); HET: 14 (3); KO: 14 (4).
(H) Summary of turnover data for all 3 genotypes. Note the downward shift of spine turnover values in SYNGAP1 KO and HET neurons compared to controls.
See also Figures S1 and S2.
Accelerated functional synaptogenesis and defective synaptic plasticity in SYNGAP1-deficient neurons
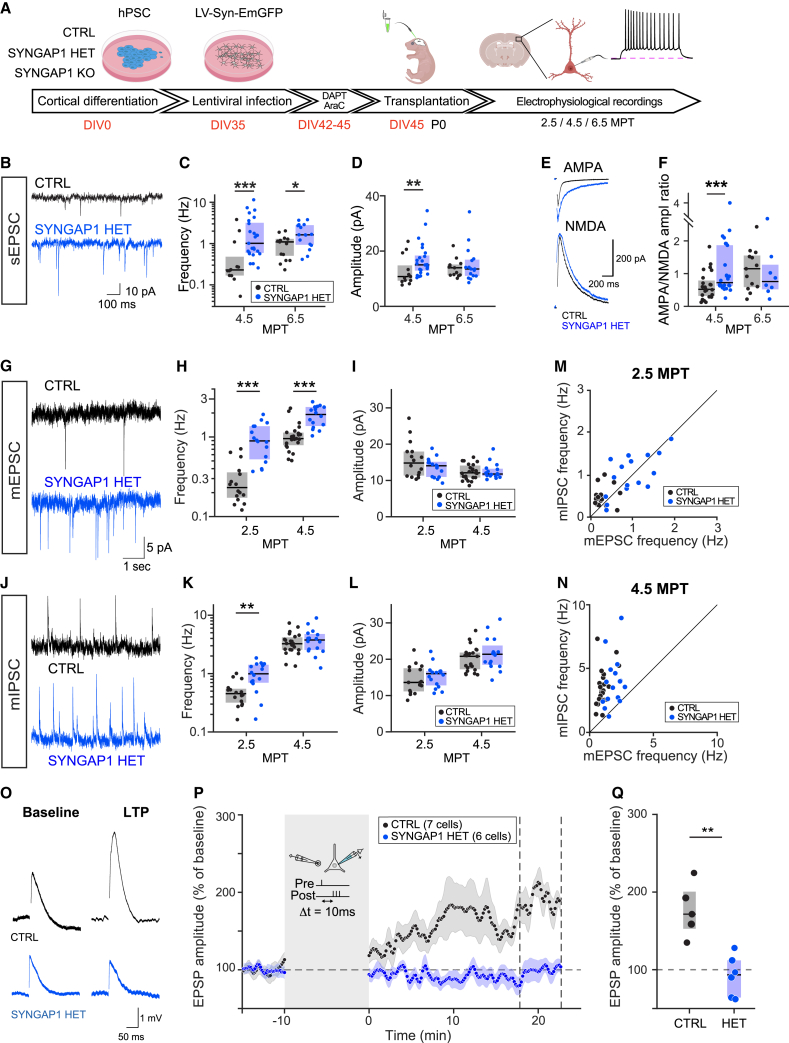
We next determined whether the observed increase in the speed of dendritic spine maturation was reflected in neuronal physiology and synaptic function. To this aim, ex vivo brain slices were prepared from transplanted mice at 4.5 and 6.5 MPT, and EmGFP-labeled transplanted neurons were examined by patch-clamp recordings (Figure 2). We found no differences between the 3 genotypes for all intrinsic properties examined (Figures S3A–S3H and S4F–S4M), suggesting a similar degree of global neuronal development. However, a robust increase in frequency of spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic currents (sEPSCs) was found for both HET and KO mutants (Figures 2C and S4B), and an increased amplitude of sEPSCs in HET neurons was found at early time points (Figure 2D), indicating more numerous synapses in SYNGAP1-deficient transplanted neurons. We next performed mEPSC measurements by including tetrodotoxin (TTX) in the experiments. This revealed an increased mEPSC frequency of SYNGAP1 HET mutant neurons, whereas the mEPSC amplitude was found to be similar across genotypes (Figures 2G–2I).
Figure 2.
Electrophysiological characterization of SYNGAP1-deficient cortical neurons
(A) Experimental timeline: differentiated mutant or control cells are infected with LV-EmGFP and transplanted. Coronal slices are prepared and EmGFP-labeled cells are targeted for patch-clamp experiments.
(B) Recording traces of SYNGAP1 CTRL and HET neurons showing example sEPSCs. Note more and larger inflections in the blue (HET) trace.
(C and D) Quantification of synaptic properties across time: (C) sEPSC frequency at 4.5 and 6.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (4.5 MPT: 0.23, 1.02; 6.5 MPT: 1.10, 1.63). Data collected at 4.5 MPT from CTRL: 13 cells (4 mice); HET: 25 (4). Data collected at 6.5 MPT from CTRL: 13 cells (2 mice); HET: 16 (3). (D) sEPSC amplitude at 4.5 and 6.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (4.5 MPT: 10.8, 15.00; 6.5 MPT: 14.0, 13.5). Data collected from same cells as in (D).
(E) Example AMPA (top) and NMDA (bottom) traces for both CTRL (black) and HET (blue) genotypes. AMPA currents are increased in HET (blue) neurons.
(F) AMPA/NMDA ratio at 4.5 and 6.5 MPT. Medians per genotype (4.5 MPT: 0.52, 0.72; 6.5 MPT: 1.15, 0.76). Data collected at 4.5 MPT from CTRL: 24 cells (4 mice); HET: 26 (5). Data collected at 6.5 MPT from CTRL: 13 cells (2 mice); HET: 8 (1). Boxes indicate median and IQR. Statistical comparison was done using rank-sum tests.
(G–I) Quantification of mEPSC recordings at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. (G) Example mEPSC traces for both genotypes; TTX is applied to isolate spontaneous synaptic events. (H) mEPSC frequency at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (2.5 MPT 0.23, 0.89; 4.5 MPT: 0.95, 1.92). Data collected at 2.5 MPT from CTRL: 16 cells (2 mice); HET: 16 (3). Data collected at 4.5 MPT from CTRL: 23 cells (3 mice); HET: 16 (3). (I) mEPSC amplitude at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (2.5 MPT: 14.8, 14.00; 4.5 MPT: 12.1, 11.8).
(J–L) Quantification of miniature inhibitory post-synaptic currents (mIPSC) recordings at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. (J) Example mIPSC traces for both genotypes, as in (G). (K) mIPSC frequency at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (2.5 MPT: 0.45, 0.99; 4.5 MPT: 3.24, 3.76). Data collected from same cells as (H). (L) mIPSC amplitude at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. Medians per genotype/time point (2.5 MPT: 13.6, 16.00; 4.5 MPT: 20.8, 21.4). Data collected from same cells as (H).
(M and N) E/I frequency at 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. (M) Scatterplot showing miniature excitatory post-synaptic currents (mEPSC) and mIPSC frequency per cell at 2.5 MPT and (N) at 4.5 MPT. In both cases, HET (blue) neurons tend toward higher E/I ratios.
(O–Q) LTP experiments performed at 7–8 MPT. (O) Example traces during baseline (left) and after potentiation (right). (P) Average excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP) per genotype showing deviation from baseline after 10′ pairing protocol (see STAR Methods). CTRL neurons (black) show potentiation, whereas HET neurons (blue) show lack of potentiation. (Q) Quantification of average EPSP levels 20 min after the end of the potentiation protocol. Data collected between 7.5 and 8.5 MPT from CTRL: 5 cells (3 mice); HET: 6 (3).
See also Figures S3 and S4.
We next recorded inhibitory and excitatory synaptic activity in the same control and HET CPNs (Figures 2M and 2N). The frequency of mIPSCs was also increased at early stages (Figures 2J and 2K), in line with the increase of mEPSC frequency (Figure 2H). These data suggest a compensatory mechanism to balance the increased maturation of excitatory synapses, since SYNGAP1 is not present at inhibitory synapses.37 Moreover, this increase in inhibitory innervation could participate in the faster functional development observed in the SYNGAP1 HET mutant neurons.38
We next probed the ratio of AMPA/NMDA currents, which is known to increase over time as synapses mature and is negatively regulated by SYNGAP1 in the mouse.23 We found this ratio to be much increased at 4.5 MPT in both KO (Figure S4E) and HET (Figure 2F), indicative of increased post-synaptic AMPA/NMDA receptor maturation. The differences were more pronounced at 4.5 MPT compared to 6.5 MPT, consistent with accelerated functional synaptic maturation in the mutant neurons.
Finally, we compared the ability of transplanted CTRL and HET CPNs to sustain long-term potentiation (LTP) following a spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) stimulation paradigm (Figure 2P). Although CTRL CPNs displayed robust LTP, it was completely abolished in HET mutant CPNs (Figures 2O–2Q).
Overall, these data indicate that HET mutant CPNs display accelerated rates of synapse formation and maturation and altered synapse plasticity, which is consistent with disrupted neoteny of synaptic development.
Increased spontaneous activity of SYNGAP1 HET neurons in cortical circuits
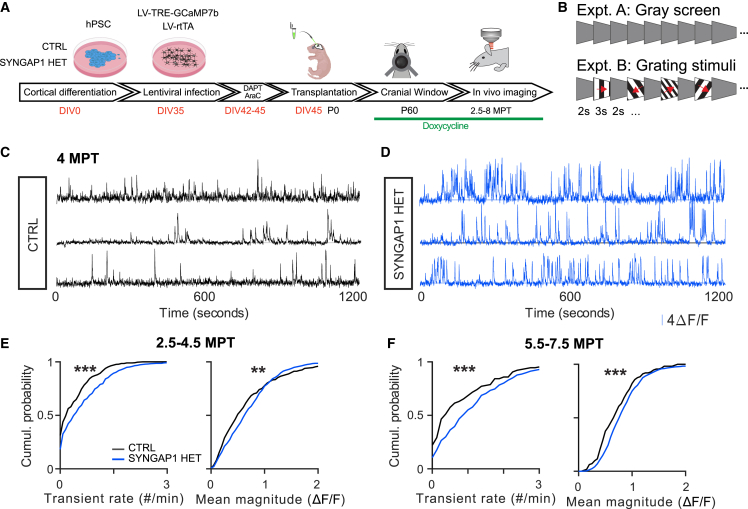
To examine the consequences of SYNGAP1 deficiency at the circuit level, we performed in vivo calcium imaging of transplanted neurons in the visual cortex.16 CPNs were infected in vitro by lentiviral vector constructs enabling conditional expression of GCAMP7b prior to transplantation, followed by two-photon (2P)-imaging at 2.5–8 MPT in vivo (Figure 3A). We focused on SYNGAP1 HET neurons (and not KO neurons) for these analyses, given the challenging nature of the experiments and the clinical relevance of haploinsufficiency. The same virus batches and concentrations were used for both genotypes to ensure similar levels of GCAMP expression (Figures S5A and S5B). We found similar numbers of GCaMP-positive CTRL- and HET- transplanted neurons in the imaged visual cortex (Table S1).
Figure 3.
Spontaneous circuit function in vivo
(A) Experimental timeline: differentiated mutant or control cells are infected with LV-TRE-GCaMP/LV-rtTA and transplanted. A cranial window is implanted to allow longitudinal imaging of cellular calcium responses.
(B) Neurons were stimulated with static gray screen (expt. A) or square-wave drifting gratings of different temporal frequencies, spatial frequencies, spatial orientations, and directions of motion (expt. B).
(C and D) Example calcium traces for 3 SYNGAP1 (C) CTRL and (D) HET neurons recorded at 4 MPT. Note the increased activity and transient magnitude in the HET mutants.
(E) Quantification of calcium transient rates (left) and average transient magnitude (right) for SYNGAP1 CTRL and HET neurons recorded between 2.5 and 4.5 MPT. Medians per genotype (rate: 0.38, 0.45; magnitude: 50.3, 64.6). Data collected between 2.5 and 4.5 MPT from CTRL: 591 cells (10 mice); HET: 701 (12).
(F) Transient rate (left) and transient magnitude (right) for CTRL and mutant neurons recorded between 5.5 and 7.5 MPT. Medians per genotype (rate: 0.40, 0.90; magnitude: 68.7, 78.0). Data collected between 5.5 and 7.5 MPT from CTRL: 127 cells (3 mice); HET: 619 (6). Note the rightward shifted curves consistent with increased values for HET neurons.
See also Figures S5 and S6 and Table S1.
We measured spontaneous activity and responses to drifting gratings visual stimuli (Figure 3B)16 to assess neuronal maturation and circuit integration. The recordings were performed while animals were in a state of quiet wakefulness. Longitudinal observations at 2.5–7.5 MPT allowed developmentally related changes to follow in spontaneous and visually evoked activity of CTRL and HET neurons.
Transplanted human CPNs showed ample spontaneous activity at all stages examined (Figures 3C–3F and S5H–S5I; Table S1). In line with the increased spontaneous synaptic activity observed using patch-clamp recordings, SYNGAP1 HET-deficient neurons showed more pronounced calcium activity than CTRL neurons, including higher transient rates and amplitudes (Figures 3E and 3F). Occasionally, at early stages (before 4.5 MPT), we observed synchronized spontaneous activity in both CTRL and HET neurons (4/13 in CTRL vs. 1/24 in HET-neuron-transplanted animals) (Figures S5E–S5G). This was not correlated with the activity of mouse neurons (Figures S6A–S6C), suggesting it is not inherited from the host cortex but rather reflects intrinsic properties of transplanted neurons. Similar synchronous activity was reported in immature mouse neurons.39
These data indicate that SYNGAP1 HET mutant neurons display increased levels of activity within the live mouse cortical circuits, suggesting precocious synaptic maturation and/or integration.
SYNGAP1-deficient neurons display precocious visual responsiveness
We next analyzed the activity of the transplanted neurons in response to visual stimulation. We previously showed that transplanted human neurons in the visual cortex show tuned responses to visual stimulation, indicative of integration within the host network.16 Following visual stimulation, HET neurons displayed more pronounced visual responses compared to CTRL neurons, including higher calcium transient rates and amplitudes (Figures S6D and S6E). The visual responses of host mouse cortical neurons, recorded with dual-color imaging, did not differ depending on the genotype of the transplanted neurons (Figure S6F).
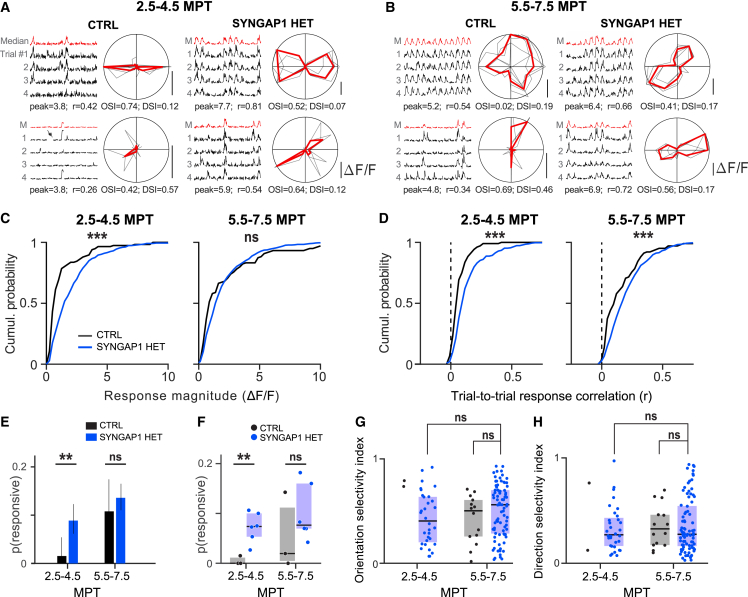
This suggests higher levels of visual responsiveness in the HET neurons but could also reflect the increased levels of activity of HET neurons (Figures 3E and 3F). To distinguish between these possibilities, we examined the recorded signals during visual stimulation, focusing the analysis to epochs of visual stimulus compared to pre-stimulus epochs, to examine the specificity and sensitivity of the neuronal responses. In addition, we correlated the response of each neuron to the direction of moving bars to determine stimulation- and/or orientation-selective responses (Figures 4A and 4B). At early stages (2.5–4.5 MPT), HET neurons responded much more strongly to sensory stimulation than CTRL neurons did (Figures 4C, S7A, and S7C). We next quantified the reliability of the response to repeated presentations of the same set of stimuli (Figures S7A and S7B and STAR Methods). At both time points, HET neurons showed higher trial-to-trial correlation (Figures 4D and S7D–S7F) and a much higher proportion of visually responsive neurons at 2.5–4.5 MPT (Figures 4E and 4F). These data indicate increased robustness of responsiveness in HET neurons (compared with CTRL neurons) at early stages of their development, consistent with acceleration of visual functionality.
Figure 4.
Evoked circuit function in vivo
(A) Example responses for 2 neurons per genotype recorded at the early time point (2.5–4.5 MPT). (Left) Single trial responses (black, in rows) for 12 directions (in columns) for the best combination of spatial frequency-temporal frequency (SF-TF) for each neuron. The median trace is shown in red in the top row. Values for response magnitude (peak, in change in fluorescence divided by basal fluorescence [df/f]) and trial-to-trial response correlation (r) are shown below the panel. (Right) Same data represented as polar plots, single trials shown in gray and the median across trial in red. The values for orientation selectivity index (OSI) and direction selectivity index (DSI) per neuron are reported below each panel.
(B) Same conventions as in (A), for neurons recorded at the later time point (5.5–7.5 MPT).
(C) Quantification of response magnitude to the preferred stimulus for SYNGAP1 CTRL (black) and HET (blue) neurons at both time epochs. Note the large difference in response magnitude at the early time point (left). Medians per genotype/time point (2.5–4.5: 0.76, 1.62; 5.5–7.5: 1.22, 1.62). Data collected between 2.5 and 4.5 MPT from CTRL: 104 cells (3 mice); HET: 337 (6). Statistical comparison was done using rank-sum tests.
(D) Quantification of trial-to-trial correlation for SYNGAP1 CTRL (black) and HET (blue) neurons at both time epochs. SYNGAP1 mutants show increased values at both time points. Medians per genotype/time point (2.5–4.5: 0.01, 0.05; 5.5–7.5: 0.11, 0.18). Data collected between 5.5 and 7.5 MPT from CTRL: 104 cells (3 mice); HET: 337 (6).
(E) Proportion of visually responsive neurons for SYNGAP1 CTRL and HET at both time points. Proportions per genotype/time point (2.5–4.5: 0.02, 0.09; 5.5–7.5: 0.11, 0.14). Statistical comparison was done using a two-proportion chi-square test. Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval (CI) obtained from the binomial fit.
(F) Proportion of responsive neurons per animal for CTRL (gray, n = 3) and HET (blue, n = 6).
(G) Overview of OSI across genotype/time point. We find no difference between HET neurons across time nor between genotypes at the later time point.
(H) Results for DSI values are similar to what is reported in (G).
Finally, we found no difference between CTRL and HET neurons for orientation and direction tuning at 7 MPT (Figures 4G and 4H). This suggests that transplanted neurons inherit their visual tuning through inputs from the host neurons by mechanisms that do not require normal levels of SYNGAP1.
Discussion
The neoteny for human brain development has long been hypothesized to underlie the acquisition of some of the enhanced cognitive performance in our species.7 The disruption of human neuronal neoteny could thus in principle partly explain the altered development of cognitive functions in at least some cases of NDDs, but this has never been tested.
SYNGAP1 mutant mouse models were previously shown to display a transient increase of synapse formation in developing CPNs, consistent with accelerated synaptic maturation.29,30,31 However, whether this reflects genuine changes in developmental timing that could lead to disrupted neoteny in human CPNs had remained unknown, given the fast development of mouse CPNs and the difficulties in studying synaptogenesis in human neurons. Moreover, as these observations were made mostly in non-conditional mouse models of SYNGAP1 invalidation, they could have been caused by alterations at the whole circuit level and/or in interneurons or glial cells, in which SYNGAP1 is also expressed.
Using a xenotransplantation system that models haploinsufficiency of SYNGAP1 during human CPN development, we found accelerated synaptogenesis in SYNGAP1 HET mutant neurons, leading to faster integration into cortical circuits and thereby premature visual responsiveness months ahead of time, consistent with disrupted neoteny.
This increased tempo of synaptogenesis may involve two complementary mechanisms, increased rates of synapse formation, and increased maturation rates of AMPA currents, converging to accelerate synaptic integration of human mutant CPNs into cortical circuits. Indeed, we found a strong impact of SYNGAP1 deficiency on dendritic spine and functional synapse formation, as well as on AMPA/NMDA ratios. On the other hand, sEPSC (but not mEPSC) amplitude was increased at early stages, possibly due to increased network-activity-dependent input at this stage. Alternatively, changes in EPSC amplitude could be due to alterations in other physiological features of SYNGAP1 mutant synapses, including developmental differences in AMPA/kainate receptor subunit composition,40 synaptic distribution along the dendrites, or neuromodulation.
SYNGAP1 KO hPSC-induced neurons were previously found to display increased neural circuit activity in vitro.32 Although we find that SYNGAP1 KO neurons display phenotypes to a greater extent than HET mutants, such as accelerated dendritic spine formation, the HET mutants display precocious dendritic spine stabilization and increased rates of synaptic formation almost as strongly as the KO neurons do. This suggests that the neotenic timing of human synaptogenesis depends on absolute levels of SYNGAP1, which are altered following SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency. Our data strongly suggest cell-autonomous effects of SYNGAP1 deficiency on synaptic neoteny, since in this system of xenotransplantation, human CPNs are mostly connected with mouse CPNs,16 which themselves display normal levels of activity. However, there could be additional or secondary non-cell-autonomous phenotypes that could not be uncovered in our reductionist experimental paradigm.
Transplanted SYNGAP1 HET mutants also display disrupted synaptic plasticity. Impaired LTP plasticity was reported previously in mice haploinsufficient for SYNGAP141 but not in mice displaying selective mutations in the SYNGAP1 GAP domain.42 This suggests that SYNGAP1 concentration-dependent changes also lead to plasticity defects. It remains unclear whether this LTP impairment is due to alterations in synaptic developmental timing or function.43 This could be examined by performing a time course of synaptic plasticity but also by determining whether other forms of plasticity, such as sensory deprivation, are altered in the mutant neurons. In any case, a synaptic plasticity defect was, to our knowledge, never demonstrated previously for human cortical neurons in any pathological condition. This illustrates the potential of in vivo xenotransplantation approaches to model human neuronal (dys)function more completely.15
Accelerated postnatal brain growth has been associated with some forms of ASD,9,10,12 and in vitro hPSC models of ASD also point to temporal dysregulation of neuronal development.44,45 In our model, SYNGAP1-haploinsufficient CPNs display precocious synaptic and circuit abnormalities, likely corresponding to early postnatal ages in the human brain. In principle, this could be tested in affected patients by psychophysical and electrophysiological measurements, which could reveal changes indicative of precocious functionality. Altered developmental timing could also lead to miswiring of cortical circuits.46,47 However, in our model, SYNGAP1 HET mutant human neurons display remarkably normal, tuned visual responses. This contrasts with previous observations in adult mouse SYNGAP1 HET mutants that were reported to display impaired cortical sensory responses,48,49 whereas SYNGAP1 mutant patients (at a mean age of 10 years old) display electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns suggestive of altered processing of auditory and visual stimuli.49 The relative contribution of synaptic development vs. function to these phenotypes remains critical to determine in order to assess optimal timing of therapeutic interventions.
In vivo disease modeling using xenotransplanted mutant neurons could be very useful to helping resolve some of these clinically relevant questions. Indeed, while in vitro modeling from hPSCs, whether in two-dimensional (2D) models or organoids, has emerged as a powerful set of tools to study human brain development,50,51,52 they do not yet enable us to capture some fundamental features of neural circuits that were studied here—including dendritic spine dynamics, synaptic plasticity, or physiological responsiveness to sensory stimulation. Here, we provide a key proof of principle that the mechanisms of ID/ASDs can be studied in human neurons at the level of neural circuits in vivo, thus opening novel opportunities to study human brain diseases in the physiologically relevant context of the living brain.
Limitations of the study
Our study is based on SYNGAP1 mutants (KO and HET) generated within a single genetic background of hPSCs. Even if the NDDs caused by SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency are fully penetrant, the impact of SYNGAP1 mutations should be examined in other genetic backgrounds. Although we detect no difference in the tuning properties of the HET neurons, there could be subthreshold or synaptic differences that are not observable at the level of somatic calcium signals measured here.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Chicken polyclonal anti-EGFP | abcam | Cat# ab13970 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-RFP | Rockland | Cat# 600-401-379 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-bIII-Tubulin (Tuj1) | Covance | Cat# MMS-435P |
| Goat polyclonal anti-Sox2 | Santa Cruz | Cat# sc-17320 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-TBR1 [EPR8138(2)] | abcam | Cat# ab183032 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-Ctip2 [25B6] | abcam | Cat# ab18465 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-Human Nuclei [235-1] | MERCK | Cat# MAB1281 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-BF1 (FOXG1) | Takara bio | Cat# M227 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-FOXP2 | abcam | Cat# ab16046 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-SATB2 | abcam | Cat# ab34735 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-CDP (CUX1) | Santa Cruz | Cat# sc-17320 |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Chicken IgY (IgG) (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 703-545-155 |
| Alexa Fluor® 488 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat#: 715-545-150 |
| Cy™3 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 711-165-152 |
| Cy™3 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rat IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 712-165-153 |
| Cy™3 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 715-165-150 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 711-605-152 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 715-605-151 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Goat IgG (H + L) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 705-605-147 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| Lenti-hSynI-EmGFP-WPRE | Linaro et al.16 | N/A |
| Lenti-TRE-GCaMP6s-P2A-nls-dTomato-WPRE | Linaro et al.16 | N/A |
| Lenti-TRE-jGCaMP7b-WPRE | This study | N/A |
| Lenti-UbC-M2rtTA-WPRE | Linaro et al.16 | N/A |
| Lenti-hSynI-TetON3G-WPRE | This study | N/A |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632) | MERCK | Cat# 688000 |
| Recombinant human Noggin | R&D systems | Cat# 1967-NG |
| Doxycycline hydrochloride | MERCK | Cat# D3447 |
| Knockout DMEM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10829018 |
| Knockout Serum Replacer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10828028 |
| Non-essential Amino Acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11140050 |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15070063 |
| 2-Mercaptoenthanol | MERCK | Cat# M6250 |
| L-glutamine | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 25030081 |
| Dispase II, powder | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 17105041 |
| Collagenase, Type IV, powder | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 17104019 |
| Stem-Pro Accutase | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A1110501 |
| Matrigel hES qualified | BD | Cat# 354277 |
| B-27™ Supplement (50X), minus vitamin A | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 12587010 |
| X-tremeGENE HP DNA Transfection Reagent | MERCK | Cat# 6366244001 |
| mFreSR™ | STEMCELL Tech | Cat# 05855 |
| DAPT, gamma-Secretase inhibitor | abcam | Cat# ab120633 |
| Cytarabine | MERCK | Cat# C3350000 |
| Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid | MERCK | Cat# 03777 |
| Fast Green | MERCK | Cat# 210-M |
| CaCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | C5670 |
| Na-ascorbate | Sigma-Aldrich | A4034 |
| Na-pyruvate | Sigma-Aldrich | P8574 |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 71376 |
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | P9541 |
| NaH2PO4 | Sigma-Aldrich | S7907 |
| MgCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 |
| MgSO4 | Sigma-Aldrich | M7506 |
| N-Methyl-D-glucamine | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 |
| Thiourea | Sigma-Aldrich | T8656 |
| D-glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | D9434 |
| NaHCO3 | Sigma-Aldrich | S6297 |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | 54457 |
| SR95531 (Gabazine) | Sigma-Aldrich | S106 |
| Potassium D-gluconate | Sigma-Aldrich | G4500 |
| ATP-Mg | Sigma-Aldrich | A9187 |
| GTP-Na2 | Sigma-Aldrich | G8877 |
| Na2-phosphocreatine | Sigma-Aldrich | P7936 |
| Biocytin | Sigma-Aldrich | B4261 |
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
| Human embryonic stem cell H9 | WiCell | Cat# NIHhESC-10-0062 |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| Mouse: RAG2 KO | Jackson Laboratories | B6(Cg)-Rag2tm1.1Cgn/J |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| pMD2.G | pMD2.G was a gift from Didier Trono | RRID:Addgene_12259 |
| psPAX2 | psPAX2 was a gift from Didier Trono | RRID:Addgene_12260 |
| FUW-M2rtTA | Hockemeyer et al.53 | RRID:Addgene_20342 |
| pCAG-TetON 3G | Hockemeyer et al.53 | RRID:Addgene_96963 |
| pAAV-hSyn1-jGCaMP7b-WPRE | Faedo et al.54 | RRID:Addgene_104489 |
| pAAV-hSyn1-NES-jRCaMP1a | Dana et al.55 | RRID:Addgene_100848 |
| pLenti-hSynI-EmGFP-WPRE | Linaro et al.16 | N/A |
| pLenti-TRE-GCaMP6s-P2A-nls-dTomato-WPRE | Linaro et al.16 | N/A |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| ImageJ | NIH | RRID:SCR_002285 |
| Custom-written MATLAB routines | This study | RRID:SCR_001622 |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to Pierre Vanderhaeghen (pierre.vanderhaeghen@kuleuven.be).
Materials availability
All plasmids generated in this study are available without restriction.
Data and code availability
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request. This paper does not report original code. Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
Experimental model and subject details
Mice
All mouse experiments were performed with the approval of KU Leuven Committee for animal welfare (ECD). Mouse housing, breeding and experimental handling were performed according to the ethical guidelines of the Belgian Ministry of Agriculture in agreement with European community Laboratory Animal Care and Use Regulations. Animals (Rag2−/− mice16) were housed under standard conditions (12 h light:12 h dark cycles) with food and water ad libitum. Data for this study are derived from a total of 134 mice of both sexes.
Cell lines
Human H9 embryonic stem cells (WiCell) were routinely propagated on mitotically inactivated mouse embryonic fibroblasts in Knockout DMEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 20% Knockout Serum Replacement (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1X Non-essential Amino Acids (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1X Penicillin/Streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1X 2-Mercaptoethanol (Merck), 2mM L-glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Method details
DNA constructs
pLenti-TRE3G-GCaMP7b-WPRE: The TRE3G fragment (pLenti CMVTRE3G eGFP Puro (w819-1) was a gift from Eric Campeau (Addgene plasmid # 27570; http://n2t.net/addgene:27570; RRID:Addgene_27570)) and the GCaMP7b fragment (pGP-AAV-syn-jGCaMP7b-WPRE was a gift from Douglas Kim & GENIE Project (Addgene plasmid # 104489; http://n2t.net/addgene:104489; RRID:Addgene_104489)) was transferred to lentiviral backbone by restriction enzyme digestion and ligation.
pLenti-hSynI-TetON3G-WPRE: The DNA fragment of TetON3G was amplified from AAVS1-TRE3G-EGFP was a gift from Su-Chun Zhang (Addgene plasmid # 52343; http://n2t.net/addgene:52343; RRID:Addgene_52343) using following primers pair: 5′-GTCGACatgtctagactggacaagag-3’/5′-ACGCGTttacccggggagcatgtcaa-3’. The TetON3G fragment was transferred to lentiviral backbone pLenti-hSynI (human synapsin I promoter)-WPRE.
SYNGAP1 gRNA plasmid: DNA fragment of 5′-TTAGCACATTGTCTACCCGG-3′and 5′- ACGGTACAGATGCAGCCGCA-3′ were transferred to lentiCRISPR v2 plasmid by restriction enzyme digestion and ligation. lentiCRISPR v2 was a gift from Feng Zhang (Addgene plasmid # 52961; http://n2t.net/addgene:52961; RRID:Addgene_52961).
SYNGAP1 donor vector (5′HA-EF1α-EGFP-T2A-tCD8-pA-3′HA): The 5′ homology arm was cloned from H9 hESC DNA using following primers pair: 5′-tGGTACCagcttcctggggctgctata-3’/5′-aACGCGTGGCTGTTGTCCTGGCATGG-3’. The 3′ homology arm was cloned from H9 hESC DNA using following primers pair: 5′- tCCTCGAGGaaaGCCGGGTAGACAATGTGCTA-3’/5′- CCTAGGTCGCGGAATATGAGGTGCTC-3’. The EF1α promoter-EGFP fragment was prepared from pAAV-EF1α-EGFP/nlsCre-WPRE-pA by restriction enzyme digestion. The T2A-tCD8 fragment was amplified from CD8a-EGFP was a gift from Lei Lu (Addgene plasmid # 86051; http://n2t.net/addgene:86051; RRID:Addgene_86051) using following primers pair: 5′- tTGTACAAGGGATCCGGAGAGGGGAGAGGATCACTGCTGACTTGCGGGGATGTGGAAGAGAACCCAGGGCCCATGGCCTTACCAGTGACC-3’/5′- aAGCGCTTCAGTGGTTGCAGTAAAGGGTGATAACCAGTGACAGGAGAAGG-3’. These DNA fragments was transferred to pBlueScript by restriction enzyme digestion and ligation.
Human PSC culture and cortical cell differentiation
Human ESC (hESC) (H9; WiCell Cat # NIHhESC-10-0062; female donor) were grown on irradiated mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in the ES cell medium until the start of cortical cell differentiation. Cortical cell differentiation was performed as described previously. Two days before starting neuronal cell differentiation, hESCs were dissociated with Accutase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#00-4555-56) and plate on Matrigel-coated (BD, Cat#354277) plates at low confluency (5,000 cells/cm2) in hES medium with 10μM ROCK inhibitor (Merck, Cat#688000). On day 0 of the differentiation, the medium was changed to DDM/B27 medium (DMEM/F12 + GlutaMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#10565042) with N2-supplement (1x, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#A1370701), B27 supplement minus Vitamin A (1x, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#12587010), Bovine Albumin Fraction V (0.05%, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#15260037), 2-Mercaptoethanol (100μM, Merck, Cat#M3148), Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution (1x, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#11140050) and Sodium Pyruvate (1mM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat#11360070) with recombinant mouse Noggin (100 ng/ml, R&D systems, Cat#1967-NG). The medium was changed every other day until day 6. From day 6, the medium was changed every day until day 16. At day 16, medium was changed to DDM/B27 medium and changed every day until day 25. At day 25, the differentiated cortical cells were dissociated using Accutase and cryopreserved in mFreSR (STEMCELL technologies, Cat#05855). Cortical cells were validated for neuronal and cortical markers by immunostaining using antibodies for TUBB3 (1:2,000; BioLegend, Cat#MMS-435P), TBR1 (1:1,000; Abcam, Cat#ab183032), CTIP2 (1:1,000; Abcam, Cat#ab18465), FOXG1 (1:1,000; Takara, Cat#M227), SOX2 (1:2,000; Santa Cruz, Cat#sc-17320), FOXP2 (1:500; Abcam, Cat#ab16046), SATB2 (1:2,000; Abcam, Cat#ab34735), and CUX1 (1:1,000; Santa Cruz, Cat#sc-13024).
Establishment of SYNGAP1 mutant cell lines
Establishment of SYNGAP1 KO cell lines
hESC were dissociated with Accutase and suspended in Human Stem Cell Nucleofector Kit 2 (Lonza, Cat#VPH-5022) with SYNGAP1 gRNA plasmids (5′-TTAGCACATTGTCTACCCGG-3′and 5′-ACGGTACAGATGCAGCCGCA-3′ into lentiCRISPR v2). DNA transfer was performed using Nucleofector II (Lonza) following manufacturer’s instructions. The nucleofected cells were plated on irradiated DR4 MEF (ThermoFisher, Cat#A34966) coated 5cm dishes. At three days after nucleofection, cells were selected with puromycin (500 ng/mL, ThermoFisher, Cat#A1113803) for 72h. At 9–11 days after Puromycin selection, single colony isolation was performed. At 5–7 days after mechanical colony pick-up, expanded cells were cryopreserved in mFreSR and used for DNA extraction. The extracted genomic DNA were used for sequence by MiSeq (Illumina).
Establishment of SYNGAP1 HET cell lines
hESC were dissociated with Accutase and suspended in Human Stem Cell Nucleofector Kit 2 (Lonza, Cat#VPH-5022) with following mixture: SYNGAP1 donor vector, crRNA/tracrRNA duplex (Integrated Dna Technologies, crRNA sequence: TTAGCACATTGTCTACCCGG) and Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 (Integrated Dna Technologies, Cat#1081060). DNA/RNA/protein transfer was performed using Nucleofector II (Lonza) following manufacturer’s instructions. The nucleofected cells were plated on irradiated DR4 MEF coated 5cm dishes. At seven days after nucleofection, cells were used for CD8+ magnetic cell sorting (MACS). The dissociated hESCs were incubated with magnetic beads conjugated anti-human CD8 (Miltenyi Biotec, Cat#130-045-201) in MACS buffer, mixture of autoMACS Rinsing Solution (Miltenyi Biotec, Cat#130-091-222) and MACS BSA Stock Solution (Miltenyi Biotec, Cat#130-091-376), at 4°C for 10 min. CD8 positive selection was carried out with MS column (Miltenyi Biotec, Cat# 130-042-201) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sorted cells were plated on irradiated MEF coated plate. At 5–7 days after MACS, expanded cells were cryopreserved in mFreSR and used for DNA extraction. The extracted DNA was used for genomic PCR validation of SYNGAP1 HET/HOMO combined with following primers pair: 5′- TGCAGGACTTTCCAGTTCCC-3’/5′- ATCAAGCTGTGGAAGGGTGG-3’.
Lentiviral preparation
HEK293T cells were transfected with the packaging plasmids, psPAX2, a gift from Didier Trono (Addgene plasmid # 12260; http://n2t.net/addgene:12260; RRID:Addgene_12260) and pMD2.G, a gift from Didier Trono (Addgene plasmid # 12259; http://n2t.net/addgene:12259; RRID:Addgene_12259), and a plasmid of the gene of interest in the lentiviral backbone: pLenti-hSynI-EmGFP-WPRE; pLenti-hSynI-tdTomato-WPRE; pLenti-UbC promoter-M2rtTA-WPRE (a gift from Rudolf Jaenisch (Addgene plasmid # 20342; http://n2t.net/addgene:20342; RRID:Addgene_20342)); pLenti-hSynI-TetON3G-WPRE (this study); pLenti-TRE-GCaMP6s-P2A-nls-dTomato-WPRE; pLenti-TRE3G-GCaMP7b-WPRE (this study). Three days after transfection, the culture medium was collected and viral particles were enriched by filtering (Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifuge Filters, Merck, Cat#UFC910008). Titer check was performed on HEK293T cell culture for every batch of lentiviral preparation.
Xenotransplantation
Human neuron xenotransplantation was performed as described previously.16 Human cortical cells (frozen at day 25) were thawed and plated on Matrigel-coated plates using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium at 37°C with 5% CO2. At seven days after thawing (day 32), cells were dissociated using Accutase and plated on Matrigel-coated plate at high confluency (450,000–700,000 cells/cm2) with lentiviral vector: LV-hSynI-EmGFP-WPRE or LV-hSynI-tdTomato-WPRE for spine imaging; LV-UbC-M2rtTA-WPRE/LV-TRE-GCaMP6s-P2A-nls-dTomato-WPRE or LV-hSynI-TetON3G-WPRE/LV-TRE3G-GCaMP7b-WPRE for functional imaging. Next day (day 33), the lentivirus-containing medium was removed and rinsed three times using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. The medium was changed every three days. Eight days later (day 41), the medium was changed to DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium with 10μM DAPT (Abcam, Cat#ab120633) and cultured for two additional days. At day 43, the cells were treated with 5μM Cytarabine (Merck, Cat#C3350000) and 10μM DAPT for 24h. On the following day, the cortical cells were dissociated using NeuroCult Enzymatic Dissociation Kit (STEMCELL technologies, Cat#05715) following manufacturer’s instructions and suspended in the injection solution containing 20mM EGTA (Merck, Cat#03777) and 0.1% Fast Green (Merck, Cat#210-M) in PBS at 100,000–200,000 cells/μL. Approximately 1-2μL of cell suspension was injected into the lateral ventricles of each hemisphere of neonatal (postnatal day 0 or 1) immunodeficient mice (Rag2−/−) using glass capillaries pulled on a horizontal puller (Sutter P-97). The absence of infection of the host cells by the lentiviruses was confirmed by co-staining for lentiviral marker and human nuclear antigen, which revealed 100% co-labeling.16
EdU labeling
Human cortical cells (frozen at day 25) were thawed and plated on Matrigel-coated plates using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium at 37°C with 5% CO2. At seven days after thawing (day 32), cells were dissociated using Accutase and plated on Matrigel-coated plate at high confluency (450,000–700,000 cells/cm2) with lentiviral vector: LV-hSynI-EmGFP-WPRE. Next day (day 33), the lentivirus-containing medium was removed and rinsed three times using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. The medium was changed every three days. Seven days later (day 40) the medium was changed to DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium with 10μM DAPT and cultured for two additional days. At day 43, the cells were treated with 10μM DAPT and 5μM Cytarabine for 24h. At day 44, the cortical cells were dissociated using NeuroCult Enzymatic Dissociation Kit and suspended in the injection solution containing 20mM EGTA and 0.1% Fast Green in PBS at 200,000 cells/μL. Approximately 1-2μL of cell suspension was injected into the lateral ventricles of each hemisphere of neonatal (postnatal day 0) Rag2−/− mice. At P6, mice were anesthetized and intracardiac perfusion was performed using 4% paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Cat#15714-S) in PBS. Brains were isolated and incubated overnight in the 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS solution at 4°C. The brains were then washed in PBS and sectioned along the coronal plane at 100 μm using a vibrating. The sections were blocked in blocking buffer (5% horse serum, 3% BSA, and 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS) for 1 h at room temperature and then incubated for two overnights at 4°C with the chicken anti-GFP antibody (Abcam, Cat#ab13970) in blocking buffer. The stained slices were then washed in PBS and incubated with the Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-chicken antibody with DAPI (Thermo Fisher, Cat#D1306) in PBS. The sections were used for EdU labeling using Click-iT EdU Cell Proliferation Kit (Thermo Fisher, Cat#C10340) following manufacturer’s instruction and subsequently mounted on glass slides in Glycergel Mounting Medium (Dako, Cat#C0563). The slides were imaged on a Zeiss LSM 880 confocal microscope using 10x objective.
For “Before DAPT group” (Timeline 1), add 5μM EdU (Thermo Fisher, Cat#C10340) in the culture medium and incubate for 1 h on day 40. After incubation, the EdU-containing medium was removed and rinsed three times using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. After rinsing, add DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium with 10μM DAPT. For “During DAPT group” (Timeline 2), add 5μM EdU in the culture medium and incubate for 1 h on day 42. After incubation, the EdU-containing medium was removed and rinsed three times using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. After rinsing, add DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium with 10μM DAPT and 5μM Cytarabine. For “After DAPT group” (Timeline 3), add 5μM EdU in the culture medium and incubate for 1 h on day 44. After incubation, the EdU-containing medium was removed and rinsed three times using DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. After rinsing, add DDM/B27+Nb/B27 medium. For “After xenotransplantation group” (Timeline 4), 5 mg/kg EdU in PBS was used by oral administration.
Western blot
Human cortical cells were collected and lysed in RIPA buffer (Cell Signaling Technology, Cat#9806) with 1x Protease inhibitor (Roche, Cat#11873580001) at 4°C with rotation. Protein concentration was measured using Bradford assay (Thermo Fisher). The sample were run in a NuPAGE 4–12% Bis-Tris Gel (Thermo Fisher, Cat#NP0321) at 90 V for 2h and then transferred to Immun-Blot PVDF Membrane (BioRad) at 100 V for 2h. The membrane was blocked in TBS supplemented with 5% skim milk and 0.1% TWEEN 20 (Sigma-Aldrich) for 1h at room temperature and subsequently incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies (SYNGAP1 (1:1,000, Thermo Fisher, Cat#PA1-046) and GAPDH (1:5,000, Sigma-Aldrich, Cat#G8795)) diluted in the blocking solution. The membrane was washed three times and incubated with adequate HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1h at room temperature. The signal was detected by Western Lightning Plus-ECL, Enhanced Chemiluminescence Substrate (PerkinElmer).
Electrophysiological recordings
Whole cell patch-clamp recordings were performed on acute coronal slices prepared from 4.5 to 6.5 months old mice with xenotransplanted PSC-derived human neurons. Briefly, animals were anesthetized intraperitoneally with Nembutal and transcardially perfused with ∼25 mL of ice-cold NMDG-based slicing solution. Brains were rapidly extracted and placed in ice-cold NMDG-based slicing solution containing (in mM): 93 N-Methyl-D-glucamine, 2.5 KCl, 1.2 NaH2PO4, 0.5 CaCl2, 10 MgSO4, 30 NaHCO3, 5 Na-ascorbate, 3 Na-pyruvate, 2 Thiourea, 20 HEPES and 25 D-glucose (pH adjusted to 7.35 with 10 N HCl, gassed with 95% O2/5% CO2). Coronal slices (250 μm) were cut in ice-cold NMDG-based slicing solution (using a Leica VT1200) and subsequently incubated for ∼6 min in the NMDG solution at 34°C. Slices were then transferred into holding aCSF, containing (in mM): 126 NaCl, 3 KCl, 1 NaH2PO4, 1 CaCl2, 6 MgSO4, 26 NaHCO3 and 10 D-glucose (gassed with 95% O2/5% CO2). Slices were stored at room temperature for ∼1 h before experiments. We focused our recordings on slices of parietal (somatosensory) cortex.
During experiments brain slices were continuously perfused with recordings acsf in a submerged chamber (Warner Instruments) at a rate of 3–4 mL/min with 127 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM KCl, 1.25 mM NaH 2 PO 4, 25 mM NaHCO 3, 1 mM MgCl 2, 2 mM CaCl 2, 25 mM glucose at pH 7.4 with 5% CO 2/95% O 2. For sEPSC, AMPA/NMDA ratio and long-term potentiation recordings we added 20 μM bicuculline. Whole cell patch clamp recordings were done using borosilicate glass recording pipettes (resistance 3.5–5 MΩ, Sutter P-1000). For sEPSC and AMPA/NMDA recordings we used the following internal solution: 115 mM CsMSF, 20 mM CsCl, 10 mM HEPES, 2.5 mM MgCl 2, 4 mM ATP, 0.4 mM GTP, 10 mM creatine phosphate and 0.6 mM EGTA (pH 7.25). For LTP the following intracellular was used: 135 mM K-Gluconate, 4 mM KCl, 10 mM HEPES, 4 mM Mg-ATP, 0.3 mM Na2-GTP, 10 mM Na2-phosphocreatine and 3 mg/mL biocytin (pH 7.25). For mEPSC & mIPSC recordings 1 μM TTX and 100 μM AP-5 was added to the recording acsf and the following internal solution was used: 126 mM CsMSF, 10 mM HEPES, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 4 mM Na2-ATP, 0.4 mM Na-GTP, 10 mM creatine phosphate, 0.6 mM EGTA, 5 mM QX-314 and 3 mg/mL biocytin (pH 7.25). For each cell mEPSCs and mIPSCs were recorded at −90 mV and 0 mV, respectively. Visually identifiable fluorescently labeled transplanted neurons were selected for recording. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were done using a double EPC-10 amplifier under control of Patchmaster v2 x 32 software (HEKA Elektronik, Lambrecht/Pfalz, Germany). Currents were recorded at 20 Hz and low-pass filtered at 3 kHz when stored. The series resistance was compensated to 75–85%. Spontaneous input was recorded using whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings (Vm = -70 mV). An extracellular stimulation pipette (borosilicate theta glass, Hilgenberg) was placed near the recorded neuron and used for initiating evoked responses during AMPA/NMDA-ratio and LTP experiments (80–120 μA, 1ms (Isoflex, A.M.P. Instruments LTD)). AMPAR-mediated evoked EPSCs were measured in whole-cell voltage clamp at a holding potential of −70 mV, while the NMDAR-mediated component was measured at +40 mV immediately after the initial AMPAR/NMDAR-mediated current (100–150 ms after electrical stimulation). During LTP experiments cell were held in whole cell current clamp and extracellular stimulation was used to induce stable eEPSPs of 2–4 mV (50–80 μA, 0.3 ms (Isoflex, A.M.P. Instruments LTD)). After baseline recording (30 single stimulations, 10 s interval), long-term potentiation was induced using a repeated pre- and postsynaptic paired activation protocol: 10 ms after a single eEPSP, three action potentials were induced in the recorded cell using 1 ms pulses with an interspike frequency of 50 Hz. This pairing protocol was repeated 60 times, using 10 s intervals. Single extracellular stimulations were reinitiated immediately after paired stimulation (180 single stimulations, 10 s interval). Evoked data were analyzed using Fitmaster (HEKA Elektronik, Lambrecht/Pfalz, Germany), spontaneous and miniature input were analyzed using Mini Analysis program (Synaptosoft).
Immunostaining
Differentiated cortical cells were validated for neuronal and cortical markers by immunostaining using primary antibodies for TUBB3 (1:2,000; BioLegend, Cat#MMS-435P), TBR1 (1:1,000; Abcam, Cat#ab183032), FOXG1 (1:1,000; Takara, Cat#M227). For immunocytochemistry, coverslips were fixed with 4% PFA in PBS 1h at 4°C. The coverslips were transferred into PBS, then blocked using PBS with 3% horse serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat# 16050122) and 0.3% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat#T9284) during 1 h, and incubated overnight at 4°C with the primary antibodies. After three washes with PBS/0.1% Triton X-100, the coverslips were incubated in PBS for 5 min at room temperature and incubated 2 h at room temperature with the appropriate secondary antibodies with DAPI (Merck, Cat#D9542). The coverslips were again washed three times with PBS for 5 min. The coverslips were mounted on a Superfrost slide (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using Glycergel mounting medium (Dako, Cat#C0563).
Surgical procedures
Standard craniotomy surgeries were performed to gain optical access to the visual cortex through a set of cover glasses.56 Rag2KO mice aging between 2 and 6 months were anesthetized (isoflurane 2.5%–3% induction, 1%–1.25% or a mix of ketamine and xylazine 100 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively). A custom-made titanium head plate was mounted to the skull, and a craniotomy over the visual cortex was made for calcium imaging. The cranial window was covered by a 5 mm cover glass. Buprenex and Cefazolin were administered postoperatively (2 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg respectively) when the animal recovered from anesthesia after surgery.
Widefield calcium imaging
Widefield fluorescent images were acquired through a 2x objective (NA = 0.055, Mitutoyo, Edmund Optics). Illumination was from a blue LED (479nm, ThorLabs), the green fluorescence was collected with an sCMOS camera (PCO edge 3.1, PCO) via a bandpass filter (510/84 nm filter, Semrock). The image acquisition was controlled with customized software written in Python. We used widefield imaging of flavoprotein to obtain functional maps of visual cortex. We only recorded transplanted human neurons that were located within visual cortex.
Two-photon calcium imaging
A customized two-photon microscopy (Neurolabware) was used which was controlled by Scanbox software written in MATLAB (Mathworks). GCaMP6s/dTomato and GCaMP7b were excited at 920 nm wavelength with a Ti:Sapphire excitation laser (MaiTai eHP DeepSee, Spectra-Physics). The emitted photons were split by a dichroic beamsplitter (centered at 562 nm) and collected with a photomultiplier tube (PMT, Hamamatsu) through a bandpass filter (510 ± 42 nm, Semrock) for the green fluorescence of GFP or GCaMP6s/GCaMP7b and a bandpass filter (607 ± 35 nm, Semrock) for the red fluorescence of nls-dTomato. For dual color imaging, we coupled a 1073 nm fixed wavelength red laser (Fidelity 2, Coherent) to our microscope. Both beams were aligned to have focal points overlap. The combined power of the two beams was kept below 100 mW at the sample.
In vivo structural imaging
Animals were aneasthetised using a mix of ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) at 1% ml/g of their body weight. They were placed on a sterilized plexiglass platform and protective eye ointment was applied to both eyes.
The high NA objective (25x Olympus, 1.05 NA) was aligned to be orthogonal to the surface of the top coverslip. All imaging was performed by moving the motorised stages of the microscope along a virtual axis parallel to the optical axis of the objective. For each neuron, we collected a 3D overview stack spanning 360 × 340 × 450 μm. We then bi-weekly acquired high resolution anatomical stacks from anesthetized mice. The imaged area spanned 127 x 110 μm. Typical stacks consisted of 200–300 optical section spaced 1 μm apart. We recorded both green and red channels which allows us to separate EmGFP signals from endogenous fluorescence which typically emits in both red and green channels. To reduce effects of shot noise, we averaged 50 frames collected per section. Using these preprocessed stacks, we traced branches of interest using a custom MATLAB GUI. We then extracted 3D sub-volumes (28 x 20 x X μm, where X is the length of the branch, ranging 50–120 μm) by extracting vertical section centered on the traced coordinates to closely fit each branch. These sub-volumes were used for subsequent analysis.
In vivo functional imaging
To enable functional imaging of transplanted human cells, these were infected in vitro with both LV-TRE-GCaMP6s-P2A-nls-dTomato-WPRE and LV-UbC-M2rtTA-WPRE or LV-TRE-GCaMP7s and LV-UbC-M2rtTA-WPRE two weeks ahead of transplantation. In these conditions, 50%–70% cells express GCaMP (and nls-dTomato) under doxycycline treatment. We started doxycycline treatment at least two weeks before the imaging experiments. We used a combination of doxycycline pellets (625 mg/kg) and I.P. injections (10 mg/mL) 2 days prior to imaging to boost expression.
Two-photon images (702x796 pixels per frame) were collected at 20 Hz with a 16x objective (Nikon 0.80 NA). Volume imaging was accomplished by using an electro-tunable lens (EL-10-30-TC, Optotune) to move the focal plane using a sawtooth pattern in 4 or 5 steps (∼50 μm separation). We simultaneously recorded neuronal activities in large volumes (1 × 1.5 × 0.20 mm3) of layer 2/3 visual cortex. During imaging, awake mice were head-clamped on a sterile plexiglass platform while viewing the visual stimuli. Eye movements were monitored using a camera (Mako G-32, Allied Vision) and infrared illumination (720–900 nm bandpass filters, Edmund).
Visual stimuli were displayed on a gamma-corrected LCD display (22″, Samsung 2233RZ). The screen was oriented parallel to the right eye and placed 18 cm from the animal (covering 80° in elevation by 105° in azimuth). Spherical correction was applied to the stimuli to define eccentricity in spherical coordinates. Visual stimuli consisted of drifting square wave gratings in 6 combinations of 3 spatial frequencies (SF = 0.04, 0.08, 0.16 cycles per degree) and 2 temporal frequencies (TF = 1, 4 Hz) in 12 directions covering 360°. All 72 stimuli were presented in random order and this block of 72 stimuli was repeated 4 times.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Electrophysiology
All electrophysiological recordings were analyzed using MATLAB (The Mathworks, Natick, MA). Raw voltage traces were filtered at 5 kHz and passive membrane and AP properties were extracted and saved in a database for further analysis and statistics.
In vivo spine imaging
We focused our analysis on apical dendrites of transplanted neurons located within 100–300 μm of the cortical surface. Segmented branches for adjacent time-points were loaded into a custom GUI and all protrusions were marked as spines. During this process we took the 3D structure of the spine into account by scrolling through the axial (Z) dimension the volume. This allowed us to distinguish between actual spines and processes passing above and below the branch of interest. We then annotated spines in both time-points using their location relative to branch landmarks. Spines that were present in both time-points were marked as conserved. Spines present only in the first time-point were marked as lost and, conversely, spines that were found only in the second time-point were marked gained. Spines present on a non-overlapping section of the branch were marked, but only included for the spine density quantification. The spine density was calculated by counting the number of actual spines on each segment and dividing this number by the length of the branch. This length was obtained by summing the distances between adjacent markers used to trace the branch. Spine turn-over was calculated by dividing the sum of gained and lost spines by the sum of spines from both time-points. Spine density for gained and lost spines was calculated by counting gained and lost spines and dividing by branch length.
Calcium imaging
Two-photon movies for all experiments collected during 1 session were motion registered to a common reference image. This image was constructed by registering and then averaging 1200 frames from the middle of the session. No sessions were removed due to excessive sample motion. We manually segmented regions-of-interest (ROIs) using information from both red and green channels. We then extracted cellular time courses for each ROI by averaging all pixels inside each ROI, removing the neuropil signal and correcting for slow baseline drift. We then calculated ΔF/Fo traces by subtracting the baseline fluorescence (Fo) corrected time course and dividing by Fo.
Neurons were considered active if their calcium trace exhibited more than 0.05 transients per minute. We computed average correlation between all simultaneously recorded neurons as the mean pairwise correlation between all ΔF/Fo of active neurons. We label a population of simultaneously recorded neurons as bursting when the average correlation between active neurons exceeds 0.40.
To detect visually responsive neurons, we calculated normalized stimulus responses for each stimulus condition. Specifically, we computed response magnitude by dividing median(STIM-BASE) by std(BASE) where STIM and BASE are the average fluorescence signal respectively during and 1 s preceding presentation of a visual stimulus:
where i refers to the i-th presentation of the stimulus j (i = 1–4 and j = 1–72)
To be deemed visually responsive, the normalized stimulus response for the preferred stimulus needed to exceed a cut-off of 2. Cells responding to the offset of the visual stimulus but not during visual stimulus epochs were excluded from the analysis. We noticed some neuron exhibit both spontaneous and visually driven activity. To account for this, we calculated trial-to-trial response correlation. To do that we concatenated all stimulus epochs (1 s before until 1 s after the visual stimulus) for a single presentation of the stimulus set. This resulted in one vector of stimulus responses for all 72 stimulus conditions (12 directions x 2 TF x 3 SF) for every repeat of the stimulus set (4 repeats in this study). We then calculated the pairwise correlation between all combination of these 4 vectors and computed trial-to-trial response correlation r as the 75th percentile of these cross-trial correlation coefficients.
Neurons were deemed reliably responsive if r exceeded 0.25. Only the neurons that had a normalized response greater than 2 and had a trial-to-trial response correlation greater than 0.25 were included for further analysis (see Figures S7E–S7F). For the orientation tuning experiment, we determined the orientation selectivity index (OSI) and direction selectivity index (DSI) based on circular variance as proposed by.57
General statistical analysis
Results are shown as median and interquartile range. Statistical comparison was done using non-parametric rank sum tests, regardless of whether the data are represented as column scatterplots or cumulative probability curves. Additional statistical details are given in the figure legends and in the main text. The number of samples N can be found in the figures.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the P.V. lab and CBD for helpful discussions and precious help. We thank Alexandre Gehanno, Daan Remans, and Arissa Jokhio for precious help. This work was funded by grants from the European Research Council (NEUROTEMPO), the C1 KU Leuven Internal Funds Program, the EOS Program, the Foundation GENERET, ERANET EPINEURODEVO, NSC-Reconstruct, the Belgian FWO, and the Belgian Queen Elizabeth Foundation (P.V.). The authors gratefully acknowledge the VIB Bio Imaging Core for their support and assistance in this work. R.I. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship of the FRS/FNRS.
Author contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, B.V., R.I., V.B., and P.V.; investigation, B.V. and K.W.; formal analysis, B.V.; writing, B.V. and P.V.; funding acquisition, P.V. and V.B.; resources, P.V. and V.B.; supervision, P.V. and V.B.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Published: August 6, 2024
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2024.07.007.
Contributor Information
Vincent Bonin, Email: vincent.bonin@kuleuven.be.
Pierre Vanderhaeghen, Email: pierre.vanderhaeghen@kuleuven.be.
Supplemental information
Left table: this table summarizes the number of cells recorded during gray screen (Expt. A) per FOV, how many of these are deemed active, and the average correlation between pairs of cells within each FOV. For the sessions where visual stimulation was performed (Expt. B), we present active and responsive neurons and again the average correlations (in bold). Data are grouped per genotype (CTRL vs. HET) and time point (2.5–4.5 vs. 5.5–7.5). Middle table: we present the same data averaged per animal. Right table: we present data averaged per genotype.
Left: representative movie of in vivo calcium imaging recording of a mouse transplanted with GCaMP7b-labeled CTRL human neurons. The image shown at the start and end shows the max projection across all planes. White circles mark all cells that were segmented. Red circles mark cells that are deemed visually responsive. The total duration of the recording is ∼3 min and playback speed is 2x real time. The size of the FOVs shown is ∼930 x 1200 micron. The white square on the top right marks the onset of any of the 72 visual stimuli. Right: same conventions as used in the left, showing GCaMP7b responses recorded from SYNGAP1 HET human neurons.
References
- 1.Zoghbi H.Y., Bear M.F. Synaptic dysfunction in neurodevelopmental disorders associated with autism and intellectual disabilities. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012;4 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ebert D.H., Greenberg M.E. Activity-dependent neuronal signalling and autism spectrum disorder. Nature. 2013;493:327–337. doi: 10.1038/nature11860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Courchesne E., Gazestani V.H., Lewis N.E. Prenatal Origins of ASD: The When, What, and How of ASD Development. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:326–342. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Klingler E., Francis F., Jabaudon D., Cappello S. Mapping the molecular and cellular complexity of cortical malformations. Science. 2021;371 doi: 10.1126/science.aba4517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vanderhaeghen P., Polleux F. Developmental mechanisms underlying the evolution of human cortical circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023;24:213–232. doi: 10.1038/s41583-023-00675-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Libé-Philippot B., Vanderhaeghen P. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Linking Human Cortical Development and Evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2021;55:555–581. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-071719-020705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sherwood C.C., Gómez-Robles A. Brain plasticity and human evolution. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2017;46:399–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anthro-102215-100009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marín O. Developmental timing and critical windows for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Nat. Med. 2016;22:1229–1238. doi: 10.1038/nm.4225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Forrest M.P., Parnell E., Penzes P. Dendritic structural plasticity and neuropsychiatric disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018;19:215–234. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu X., Han D., Somel M., Jiang X., Hu H., Guijarro P., Zhang N., Mitchell A., Halene T., Ely J.J., et al. Disruption of an Evolutionarily Novel Synaptic Expression Pattern in Autism. PLoS Biol. 2016;14 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hazlett H.C., Gu H., Munsell B.C., Kim S.H., Styner M., Wolff J.J., Elison J.T., Swanson M.R., Zhu H., Botteron K.N., et al. Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder. Nature. 2017;542:348–351. doi: 10.1038/nature21369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Courchesne E., Pierce K., Schumann C.M., Redcay E., Buckwalter J.A., Kennedy D.P., Morgan J. Mapping early brain development in autism. Neuron. 2007;56:399–413. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Espuny-Camacho I., Michelsen K.A., Gall D., Linaro D., Hasche A., Bonnefont J., Bali C., Orduz D., Bilheu A., Herpoel A., et al. Pyramidal Neurons Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Integrate Efficiently into Mouse Brain Circuits In Vivo. Neuron. 2013;77:440–456. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Revah O., Gore F., Kelley K.W., Andersen J., Sakai N., Chen X., Li M.-Y., Birey F., Yang X., Saw N.L., et al. Maturation and circuit integration of transplanted human cortical organoids. Nature. 2022;610:319–326. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05277-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vermaercke B., Bonin V., Vanderhaeghen P. Studying human neural function in vivo at the cellular level: Chasing chimeras? Cell. 2022;185:4869–4872. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Linaro D., Vermaercke B., Iwata R., Ramaswamy A., Libé-Philippot B., Boubakar L., Davis B.A., Wierda K., Davie K., Poovathingal S., et al. Xenotransplanted Human Cortical Neurons Reveal Species-Specific Development and Functional Integration into Mouse Visual Circuits. Neuron. 2019;104:972–986.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mignot C., von Stulpnagel C., Nava C., Ville D., Sanlaville D., Lesca G., Rastetter A., Gachet B., Marie Y., Korenke G.C., et al. Genetic and neurodevelopmental spectrum of SYNGAP1-associated intellectual disability and epilepsy. J. Med. Genet. 2016;53:511–522. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wright C.F., Fitzgerald T.W., Jones W.D., Clayton S., McRae J.F., Van Kogelenberg M., King D.A., Ambridge K., Barrett D.M., Bayzetinova T., et al. Genetic diagnosis of developmental disorders in the DDD study: A scalable analysis of genome-wide research data. Lancet. 2015;385:1305–1314. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61705-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Parker M.J., Fryer A.E., Shears D.J., Lachlan K.L., Mckee S.A., Magee A.C., Mohammed S., Vasudevan P.C., Park S.M., Benoit V., et al. De novo, heterozygous, loss-of-function mutations in SYNGAP1 cause a syndromic form of intellectual disability. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2015;167a:2231–2237. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hamdan F.F., Daoud H., Piton A., Gauthier J., Dobrzeniecka S., Krebs M.O., Joober R., Lacaille J.C., Nadeau A., Milunsky J.M., et al. De novo SYNGAP1 mutations in nonsyndromic intellectual disability and autism. Biol. Psychiatry. 2011;69:898–901. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hamdan F.F., Gauthier J., Spiegelman D., Noreau A., Yang Y., Pellerin S., Dobrzeniecka S., Côté M., Perreau-Linck E., Carmant L., et al. Mutations in SYNGAP1 in autosomal nonsyndromic mental retardation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;360:599–605. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Berryer M.H., Hamdan F.F., Klitten L.L., Møller R.S., Carmant L., Schwartzentruber J., Patry L., Dobrzeniecka S., Rochefort D., Neugnot-Cerioli M., et al. Mutations in SYNGAP1 Cause Intellectual Disability, Autism, and a Specific Form of Epilepsy by Inducing Haploinsufficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2013;34:385–394. doi: 10.1002/humu.22248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gamache X.T.R., Araki X.Y., Huganir X.R.L. Twenty Years of SynGAP Research : From Synapses to Cognition. J. Neurosci. 2020;40:1596–1605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0420-19.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Carlisle H.J., Manzerra P., Marcora E., Kennedy M.B. SynGAP regulates steady-state and activity-dependent phosphorylation of cofilin. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:13673–13683. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.4695-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vazquez L.E., Chen H.J., Sokolova I., Knuesel I., Kennedy M.B. SynGAP regulates spine formation. J. Neurosci. 2004;24:8862–8872. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3213-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Araki Y., Zeng M., Zhang M., Huganir R.L. Rapid dispersion of SynGAP from synaptic spines triggers AMPA receptor insertion and spine enlargement during LTP. Neuron. 2015;85:173–189. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krapivinsky G., Medina I., Krapivinsky L., Gapon S., Clapham D.E. SynGAP-MUPP1-CaMKII synaptic complexes regulate p38 MAP kinase activity and NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic AMPA receptor potentiation. Neuron. 2004;43:563–574. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rumbaugh G., Adams J.P., Kim J.H., Huganir R.L. SynGAP regulates synaptic strength and mitogen-activated protein kinases in cultured neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:4344–4351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600084103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Clement J.P., Ozkan E.D., Aceti M., Miller C.A., Rumbaugh G. SYNGAP1 links the maturation rate of excitatory synapses to the duration of critical-period synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:10447–10452. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.0765-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Clement J.P., Aceti M., Creson T.K., Ozkan E.D., Shi Y., Reish N.J., Almonte A.G., Miller B.H., Wiltgen B.J., Miller C.A., et al. Pathogenic SYNGAP1 mutations impair cognitive development by disrupting maturation of dendritic spine synapses. Cell. 2012;151:709–723. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aceti M., Creson T.K., Vaissiere T., Rojas C., Huang W.C., Wang Y.X., Petralia R.S., Page D.T., Miller C.A., Rumbaugh G. Syngap1 haploinsufficiency damages a postnatal critical period of pyramidal cell structural maturation linked to cortical circuit assembly. Biol. Psychiatry. 2015;77:805–815. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Llamosas N., Arora V., Vij R., Kilinc M., Bijoch L., Rojas C., Reich A., Sridharan B., Willems E., Piper D.R., et al. SYNGAP1 controls the maturation of dendrites, synaptic function, and network activity in developing human neurons. J. Neurosci. 2020;40:7980–7994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1367-20.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Birtele M., Del Dosso A., Xu T., Nguyen T., Wilkinson B., Hosseini N., Nguyen S., Urenda J.-P., Knight G., Rojas C., et al. Non-synaptic function of the autism spectrum disorder-associated gene SYNGAP1 in cortical neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2023;26:2090–2103. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01477-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Doetsch F., Manuel J., García-Verdugo G., Alvarez-Buylla A. Regeneration of a germinal layer in the adult mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:11619–11624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Espuny-Camacho I., Michelsen K.A., Linaro D., Bilheu A., Acosta-Verdugo S., Herpoel A., Giugliano M., Gaillard A., Vanderhaeghen P. Human Pluripotent Stem-Cell-Derived Cortical Neurons Integrate Functionally into the Lesioned Adult Murine Visual Cortex in an Area-Specific Way. Cell Rep. 2018;23:2732–2743. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nagashima F., Suzuki I.K., Shitamukai A., Sakaguchi H., Iwashita M., Kobayashi T., Tone S., Toida K., Vanderhaeghen P., Kosodo Y. Novel and robust transplantation reveals the acquisition of polarized processes by cortical cells derived from mouse and human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:2129–2142. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gamache T.R., Araki Y., Huganir R.L. Twenty years of syngap research: From synapses to cognition. J. Neurosci. 2020;40:1596–1605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0420-19.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mòdol L., Moissidis M., Selten M., Oozeer F., Marín O. Somatostatin interneurons control the timing of developmental desynchronization in cortical networks. Neuron. 2024;112:2015–2030.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Golshani P., Gonçalves J.T., Khoshkhoo S., Mostany R., Smirnakis S., Portera-Cailliau C. Internally mediated developmental desynchronization of neocortical network activity. J. Neurosci. 2009;29:10890–10899. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2012-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Henley J.M., Wilkinson K.A. Synaptic AMPA receptor composition in development, plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016;17:337–350. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Llamosas N., Michaelson S.D., Vaissiere T., Rojas C., Miller C.A., Rumbaugh G. Syngap1 regulates experience-dependent cortical ensemble plasticity by promoting in vivo excitatory synapse strengthening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;118:1–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2100579118/-/DCSupplemental. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Araki Y., Rajkovich K.E., Gerber E.E., Gamache T.R., Johnson R.C., Tran T.H.N., Liu B., Zhu Q., Hong I., Kirkwood A., Huganir R. SynGAP regulates synaptic plasticity and cognition independently of its catalytic activity. Science. 2024;383 doi: 10.1126/science.adk1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Huganir R.L., Nicoll R.A. AMPARs and synaptic plasticity: the last 25 years. Neuron. 2013;80:704–717. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Paulsen B., Velasco S., Kedaigle A.J., Pigoni M., Quadrato G., Deo A.J., Adiconis X., Uzquiano A., Sartore R., Yang S.M., et al. Autism genes converge on asynchronous development of shared neuron classes. Nature. 2022;602:268–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04358-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schafer S.T., Paquola A.C.M., Stern S., Gosselin D., Ku M., Pena M., Kuret T.J.M., Liyanage M., Mansour A.A., Jaeger B.N., et al. Pathological priming causes developmental gene network heterochronicity in autistic subject-derived neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2019;22:243–255. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0295-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cossart R., Garel S. Step by step: cells with multiple functions in cortical circuit assembly. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022;23:395–410. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00585-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Klingler E., Tomasello U., Prados J., Kebschull J.M., Contestabile A., Galiñanes G.L., Fièvre S., Santinha A., Platt R., Huber D., et al. Temporal controls over inter-areal cortical projection neuron fate diversity. Nature. 2021;599:453–457. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Michaelson S.D., Ozkan E.D., Aceti M., Maity S., Llamosas N., Weldon M., Mizrachi E., Vaissiere T., Gaffield M.A., Christie J.M., et al. SYNGAP1 heterozygosity disrupts sensory processing by reducing touch-related activity within somatosensory cortex circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2018;21:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0268-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Carreño-Muñoz M.I., Chattopadhyaya B., Agbogba K., Côté V., Wang S., Lévesque M., Avoli M., Michaud J.L., Lippé S., Di Cristo G. Sensory processing dysregulations as reliable translational biomarkers in SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency. Brain. 2022;145:754–769. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Suzuki I.K., Vanderhaeghen P. Is this a brain which i see before me? Modeling human neural development with pluripotent stem cells. Development (Camb.) 2015;142:3138–3150. doi: 10.1242/dev.120568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Arlotta P., Paşca S.P. Cell diversity in the human cerebral cortex: from the embryo to brain organoids. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019;56:194–198. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2019.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lancaster M.a., Knoblich J.a. Organogenesis in a dish: modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science. 2014;345 doi: 10.1126/science.1247125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hockemeyer D., Soldner F., Cook E.G., Gao Q., Mitalipova M., Jaenisch R. A Drug-Inducible System for Direct Reprogramming of Human Somatic Cells to Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:346–353. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Faedo A., Laporta A., Segnali A., Galimberti M., Besusso D., Cesana E., Belloli S., Moresco R.M., Tropiano M., Fucà E., et al. Differentiation of human telencephalic progenitor cells into MSNs by inducible expression of Gsx2 and Ebf1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E1234–E1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611473114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dana H., Mohar B., Sun Y., Narayan S., Gordus A., Hasseman J.P., Tsegaye G., Holt G.T., Hu A., Walpita D., et al. Sensitive red protein calcium indicators for imaging neural activity. Elife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.12727.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Goldey G.J., Roumis D.K., Glickfeld L.L., Kerlin A.M., Reid R.C., Bonin V., Schafer D.P., Andermann M.L. Removable cranial windows for long-term imaging in awake mice. Nat. Protoc. 2014;9:2515–2538. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mazurek M., Kager M., Van Hooser S.D. Robust quantification of orientation selectivity and direction selectivity. Front. Neural Circuits. 2014;8:92. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Left table: this table summarizes the number of cells recorded during gray screen (Expt. A) per FOV, how many of these are deemed active, and the average correlation between pairs of cells within each FOV. For the sessions where visual stimulation was performed (Expt. B), we present active and responsive neurons and again the average correlations (in bold). Data are grouped per genotype (CTRL vs. HET) and time point (2.5–4.5 vs. 5.5–7.5). Middle table: we present the same data averaged per animal. Right table: we present data averaged per genotype.
Left: representative movie of in vivo calcium imaging recording of a mouse transplanted with GCaMP7b-labeled CTRL human neurons. The image shown at the start and end shows the max projection across all planes. White circles mark all cells that were segmented. Red circles mark cells that are deemed visually responsive. The total duration of the recording is ∼3 min and playback speed is 2x real time. The size of the FOVs shown is ∼930 x 1200 micron. The white square on the top right marks the onset of any of the 72 visual stimuli. Right: same conventions as used in the left, showing GCaMP7b responses recorded from SYNGAP1 HET human neurons.
Data Availability Statement
All data reported in this paper will be shared by the lead contact upon request. This paper does not report original code. Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.