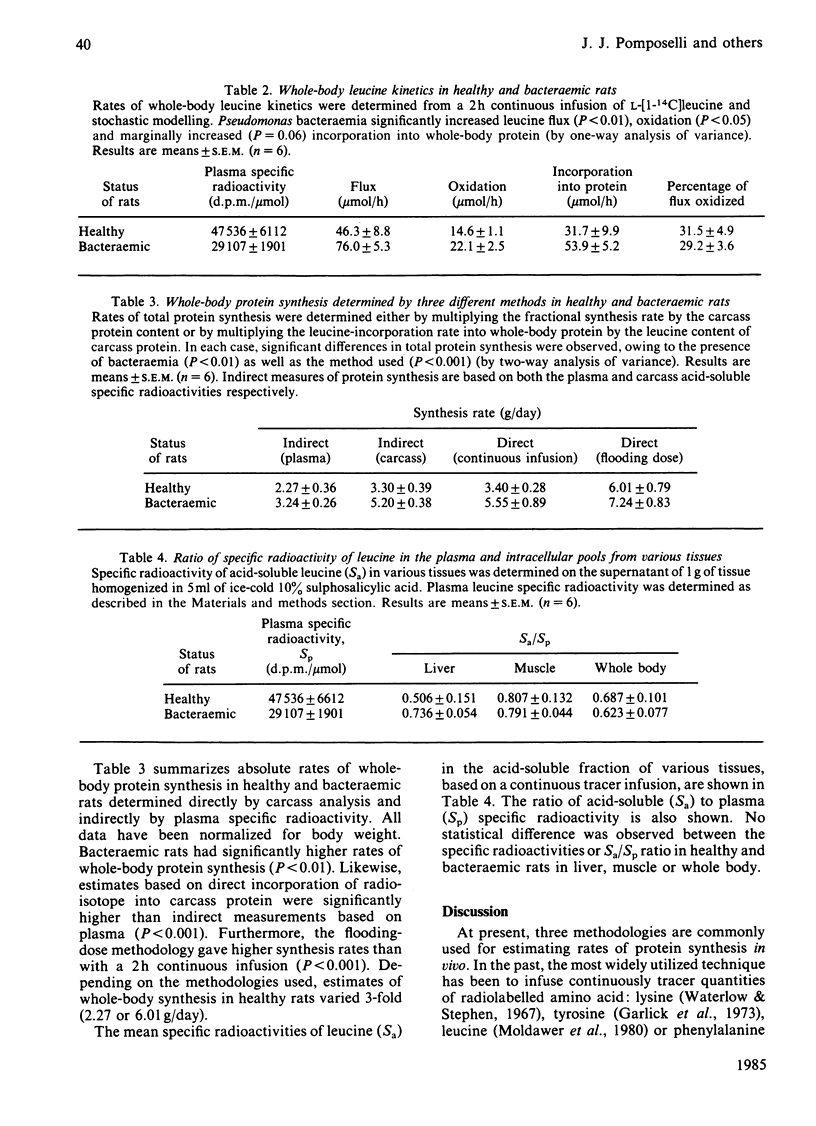
Abstract
Previous studies have reported that use of a flooding dose of radiolabelled amino acid is a more precise technique than the constant infusion of tracer quantities for determining rates of protein synthesis in rapidly turning-over tissues in the rat. However, there has been little direct investigation comparing different methods under comparable conditions. Initially, 12 healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing approx. 100 g, were randomized to receive either a bolus intravenous injection of 100 mumol of L-leucine (containing 30 microCi of [1-14C]leucine)/100 g body wt., or a continuous 2 h tracer infusion of [14C]leucine. In the second phase of the experiment, 12 additional rats were intravenously injected with 1 X 10(8) colony-forming units of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and 16 h later randomized to receive one of two infusions described above. Total protein synthesis as well as fractional synthesis rates were determined in liver, rectus muscle and whole body. Synthesis rates measured in liver, muscle and whole body were significantly higher in bacteraemic rats than in healthy rats. The flooding-dose methodology gave significantly higher estimates of protein synthesis in the liver, skeletal muscle and whole body than did the continuous-infusion method using direct measurement of the acid-soluble fraction from the respective tissue. Indirect estimates of whole-body protein synthesis based on plasma enrichments and stochastic modelling gave the lowest values.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beisel W. R., Sawyer W. D., Ryll E. D., Crozier D. Metabolic effects of intracellular infections in man. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):744–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUMER H. D., KOBLET H., WOODARD C. Phenylalanine metabolism in the phenylpyruvic condition. II. An attempt to calculate the daily incorporation of phenylalanine into proteins. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:61–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI104467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J. An analysis of errors in estimation of the rate of protein synthesis by constant infusion of a labelled amino acid. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):402–405. doi: 10.1042/bj1760402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Marshall I. A technique for measuring brain protein synthesis. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P. The diurnal response of muscle and liver protein synthesis in vivo in meal-fed rats. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):935–945. doi: 10.1042/bj1360935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Fern E. B., London D. R. Identification in skeletal muscle of a distinct extracellular pool of amino acids, and its role in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):817–827. doi: 10.1042/bj1210817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. P., Garlick P. J., Millward D. J. The assessment of intestinal protein turnover in the rat by three techniques. Gut. 1971 Jun;12(6):495–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Fern E. B., Garlick P. J. Failure of leucine to stimulate protein synthesis in vivo. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):831–838. doi: 10.1042/bj2040831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Garlick P. J. Contribution of rat liver and gastrointestinal tract to whole-body protein synthesis in the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):381–383. doi: 10.1042/bj1860381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Tomkins A. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat liver and small intestine. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1780373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Kawamura I., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. The contribution of phenylalanine to tyrosine metabolism in vivo. Studies in the post-absorptive and phenylalanine-loaded rat. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):811–817. doi: 10.1042/bj2100811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., O'Keefe S. J., Bothe A., Jr, Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. In vivo demonstration of nitrogen-sparing mechanisms for glucose and amino acids in the injured rat. Metabolism. 1980 Feb;29(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan N. T. Metabolic adaptations for energy production during trauma and sepsis. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Oct;56(5):1073–1090. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Moldawer L. L., Palombo J. D., Desai S. P., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. Alterations in tyrosine and protein kinetics produced by injury and branched chain amino acid administration in rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Mar;64(3):321–331. doi: 10.1042/cs0640321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik O. A. In vivo rate of translation by ribosomes of normal and regenerating liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3876–3883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein T. P., Leskiw M. J., Buzby G. P., Giandomenico A. L., Wallace H. W., Mullen J. L. Measurement of protein synthesis rates with [15N]glycine. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):E294–E300. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.4.E294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallyn C. S., Vidrich A., Airhart J., Khairallah E. A. Analysis of the specific radioactivity of valine isolated from aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid of rat liver. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):545–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1400545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterlow J. C., Stephen J. M. The measurement of total lysine turnover in the rat by intravenous infusion of L-[U-14C]lysine. Clin Sci. 1967 Dec;33(3):489–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Burke J. F. Effect of burn trauma on glucose turnover, oxidation, and recycling in guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Aug;233(2):E80–E85. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.2.E80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


