Abstract
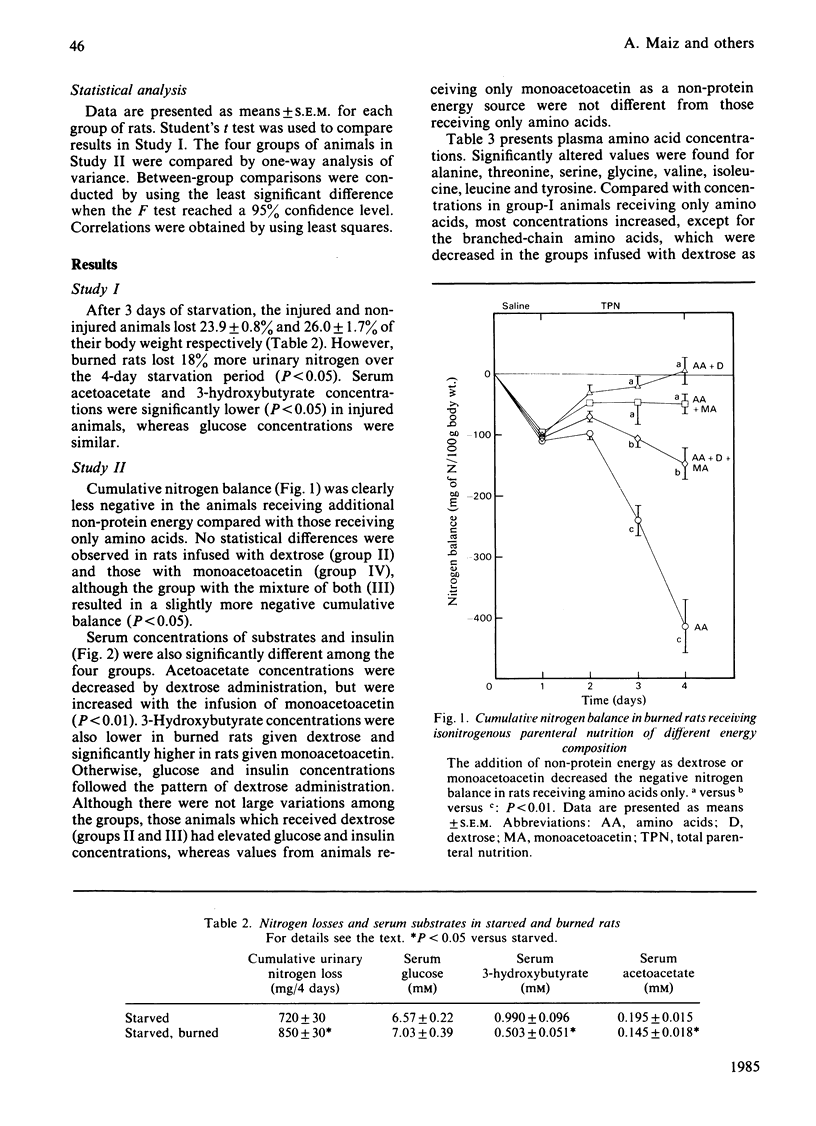
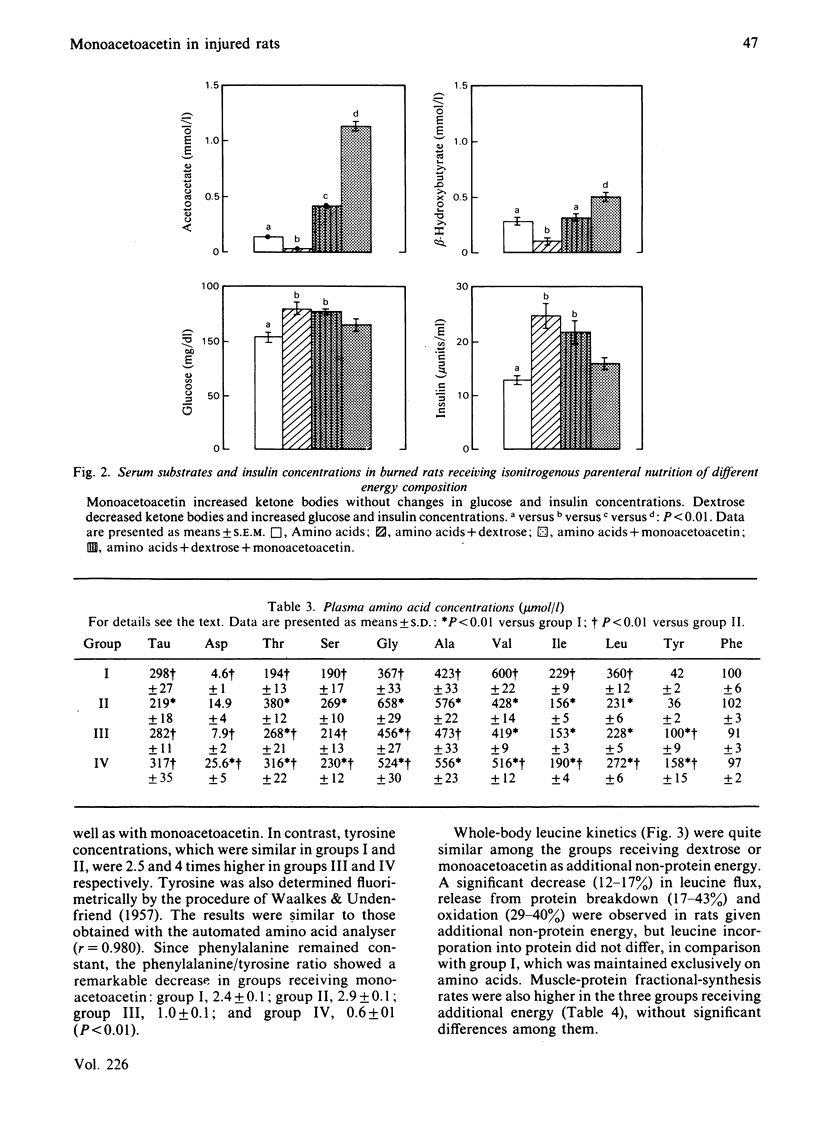
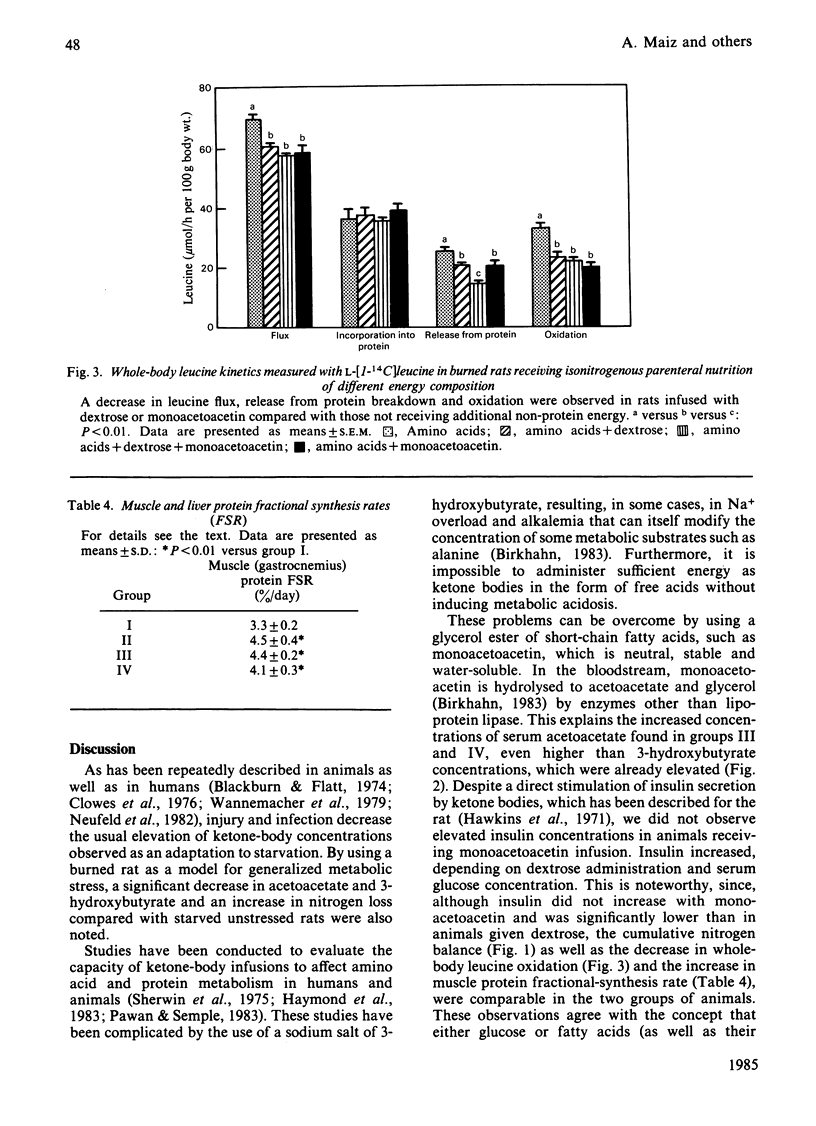
The effect of intravenous infusion of monoacetoacetin (glycerol monoacetoacetate) as a non-protein energy source was evaluated in burned rats. During 3 days of parenteral nutrition, in which animals received 14 g of amino acids/kg body wt. per day exclusively (group I) or with the addition of isoenergetic amounts (523 kJ/kg per day) of dextrose (group II), a 1:1 mixture of dextrose and monoacetoacetin (group III) or monoacetoacetin (group IV), significant decreases in urinary nitrogen excretion and whole-body leucine oxidation were observed in the three groups given additional non-protein energy as compared with group I. Serum ketone bodies (acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate) were decreased in rats given dextrose, whereas glucose and insulin increased significantly. Monoacetoacetin-infused animals (group IV) had high concentrations of ketone bodies without changes in glucose and insulin, whereas animals infused with both monoacetoacetin and glucose (group III) showed intermediate values. On day 4 of nutritional support, whole-body L-leucine kinetics were measured by using a constant infusion of L-[1-14C]leucine. In comparison with group I, the addition of dextrose or monoacetoacetin produced a significant decrease in plasma leucine appearance and release from whole-body protein breakdown. Gastrocnemius-muscle protein-synthesis rates were also higher in the three groups receiving additional non-protein energy. These findings suggest that monoacetoacetin can effectively replace dextrose as an intravenous energy source in stressed rats. Both fuels are similar in decreasing weight loss, nitrogen excretion, leucine release from whole-body protein breakdown and oxidation, in spite of differences in energy substrate and insulin concentrations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T. T., Assal J-P, Manzano F. M., Kozak G. P., Cahill G. F. Plasma and cerebrosponal fluid amino acid levels in diabetic ketoacidosis before and after corrective therapy. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):463–467. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkhahn R. H., Border J. R. Alternate or supplemental energy sources. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1981 Jan-Feb;5(1):24–31. doi: 10.1177/014860718100500124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkhahn R. H., Border J. R. Intravenous feeding of the rat with short chain fatty acid esters. II. Monoacetoacetin. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Mar;31(3):436–441. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkhahn R. H., Long C. L., Fitkin D., Geiger J. W., Blakemore W. S. Effects of major skeletal trauma on whole body protein turnover in man measured by L-[1,14C]-leucine. Surgery. 1980 Aug;88(2):294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes G. H., Jr, O'Donnell T. F., Blackburn G. L., Maki T. N. Energy metabolism and proteolysis in traumatized and septic man. Surg Clin North Am. 1976 Oct;56(5):1169–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK A., MUNRO H. N. THE DETERMINATION OF ORGANIC NITROGEN IN BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS. A REVIEW. Clin Chim Acta. 1965 Jan;11:2–12. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(65)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Owen O. E., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):584–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI106017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P. The diurnal response of muscle and liver protein synthesis in vivo in meal-fed rats. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):935–945. doi: 10.1042/bj1360935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Alberti K. G., Houghton C. R., Williamson D. H., Krebs H. A. The effect of acetoacetate on plasma insulin concentration. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):541–544. doi: 10.1042/bj1250541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejee hoy K. N., Anderson G. H., Nakhooda A. F., Greenberg G. R., Sanderson I., Marliss E. B. Metabolic studies in total parenteral nutrition with lipid in man. Comparison with glucose. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):125–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI108252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Moldawer L. L., Young V. R., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. Whole-body leucine and muscle protein kinetics in rats fed varying protein intakes. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):E444–E451. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.5.E444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., Kawamura I., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. The contribution of phenylalanine to tyrosine metabolism in vivo. Studies in the post-absorptive and phenylalanine-loaded rat. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):811–817. doi: 10.1042/bj2100811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldawer L. L., O'Keefe S. J., Bothe A., Jr, Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. In vivo demonstration of nitrogen-sparing mechanisms for glucose and amino acids in the injured rat. Metabolism. 1980 Feb;29(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld H. A., Pace J. G., Kaminski M. V., Jr, Sobocinski P., Crawford D. J. Unique effects of infectious or inflammatory stress on fat metabolism in rats. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1982 Nov-Dec;6(6):511–521. doi: 10.1177/0148607182006006511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnel T. F., Clowes G. H., Jr, Blackburn G. L., Ryan N. T., Benotti P. N., Miller J. D. Proteolysis associated with a deficit of peripheral energy fuel substrates in septic man. Surgery. 1976 Aug;80(2):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawan G. L., Semple S. J. Effect of 3-hydroxybutyrate in obese subjects on very-low-energy diets and during therapeutic starvation. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):15–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Moldawer L. L., Palombo J. D., Desai S. P., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. Alterations in tyrosine and protein kinetics produced by injury and branched chain amino acid administration in rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Mar;64(3):321–331. doi: 10.1042/cs0640321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R. G., Felig P. Effect of ketone infusions on amino acid and nitrogen metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1382–1390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S. The effect of ketone bodies and dietary carbohydrate intake on protein metabolism. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1981;507:30–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Pace J. G., Beall R. A., Dinterman R. E., Petrella V. J., Neufeld H. A. Role of the liver in regulation of ketone body production during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1565–1572. doi: 10.1172/JCI109617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterlow J. C., Stephen J. M. The measurement of total lysine turnover in the rat by intravenous infusion of L-[U-14C]lysine. Clin Sci. 1967 Dec;33(3):489–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


