Abstract
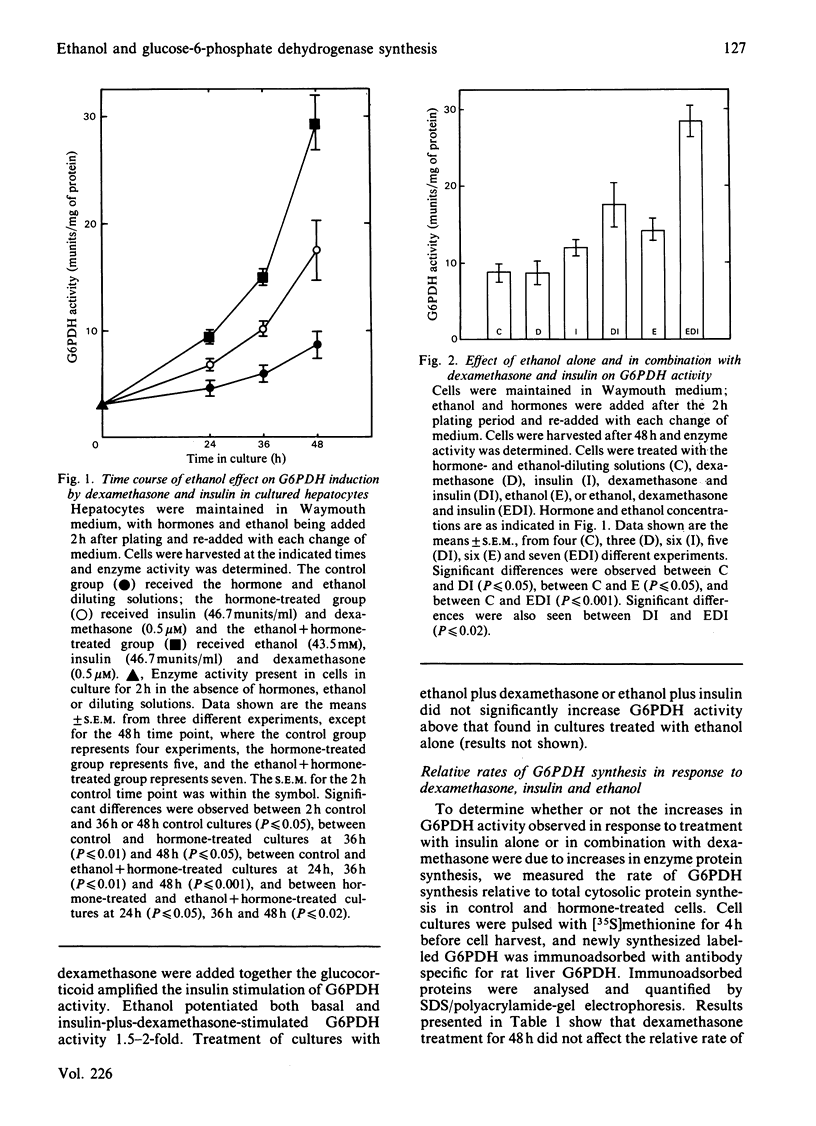
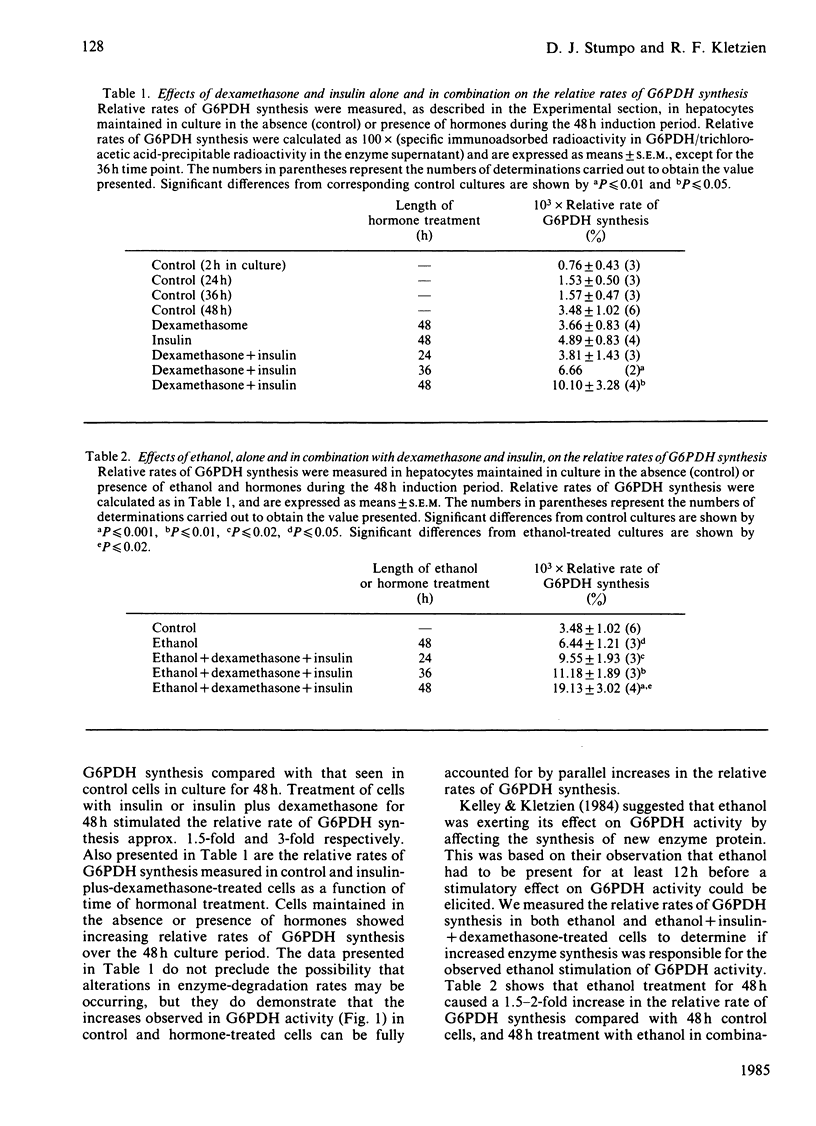
The hormonal regulation of the relative rate of synthesis and mRNA of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH; EC 1.1.1.49) was studied in primary cultures of adult-rat liver parenchymal cells maintained in a chemically defined medium. Maintenance of hepatocytes from starved animals in a culture medium devoid of any hormones resulted in a 4-fold increase in the relative rate of G6PDH synthesis in 48 h. Parallel cultures treated with glucocorticoids alone exhibited a rate of G6PDH synthesis comparable with that in the control cultures, whereas insulin alone caused a 6.5-fold increase in the rate of synthesis in 48 h. However, if the cultures were treated with glucocorticoids and insulin simultaneously, a 13-fold increase in the rate of synthesis was observed. The effect of ethanol, alone and in combination with the hormones, on the relative rate of G6PDH synthesis was studied also. Ethanol alone caused an 8-fold increase in the rate of synthesis in 48 h, whereas the combination of ethanol, glucocorticoid and insulin caused a 25-fold increase. The amount of functional mRNA encoding G6PDH, as measured in a cell-free translation system, was compared with enzyme activity and relative rate of enzyme synthesis. The increases in G6PDH activity and relative rate of synthesis in primary cultures of hepatocytes treated with ethanol, alone and in combination with the glucocorticoids and insulin, were paralleled by comparable increases in G6PDH mRNA. The results of this study show that the glucocorticoids acted in a permissive manner to amplify the insulin stimulation of G6PDH synthesis and that insulin, glucocorticoids and ethanol interact to stimulate synthesis of G6PDH primarily by increasing the concentration of functional G6PDH mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraona E., Lieber C. S. Effects of ethanol on lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1979 Mar;20(3):289–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdanier C. D., Shubeck D. Interaction of glucocorticoid and insulin in the responses of rats to starvation-refeeding. J Nutr. 1979 Oct;109(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1093/jn/109.10.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdanier C. D., Wurdeman R., Tobin R. B. Further studies on the role of the adrenal hormones in responses of rats to meal-feeding. J Nutr. 1976 Dec;106(12):1791–1800. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.12.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., MCLEAN P. A preliminary investigation of the hormonal control of the hexose monophosphate oxidative pathway. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):390–397. doi: 10.1042/bj0610390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia D. R., Holten D. Inhibition of rat liver glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase synthesis by glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3960–3965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. C., Sassoon H. F. Studies on the induction of liver glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the rat. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1967;5:93–106. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(67)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. S., Kletzien R. F. Ethanol modulation of the hormonal and nutritional regulation of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):543–549. doi: 10.1042/bj2170543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. W., Wells W. W. Induction of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Requirement for insulin and dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10870–10875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R. J., Towle H. C. Changes in the rates of synthesis and messenger RNA levels of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases following induction by diet or thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11829–11835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yoshimoto K., Aoyama K., Ichihara A. Hormonal regulations of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and lipogenesis in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):681–693. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepokroeff C. M., Lakshmanan M. R., Ness G. C., Muesing R. A., Kleinsek D. A., Porter J. W. Coordinate control of rat liver lipogenic enzymes by insulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudack D., Chisholm E. M., Holten D. Rat liver glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Regulation by carbohydrate diet and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1249–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Späth P. J., Koblet H. Properties of SDS-polyacrylamide gels highly cross-linked with N,N'-diallyltartardiamide and the rapid isolation of macromolecules from the gel matrix. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Kletzien R. F. Regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA by insulin and the glucocorticoids in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN H. M., TEPPERMAN J. ON THE RESPONSE OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY TO CHANGES IN DIET COMPOSITION AND FOOD INTAKE PATTERN. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1963;1:121–136. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(63)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN H. M., TEPPERMAN J. The hexosemonophosphate shunt and adaptive hyperlipogenesis. Diabetes. 1958 Nov-Dec;7(6):478–485. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.6.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Effects of antecedent food intake pattern on hepatic lipogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Convery H. J. Insulin: inducer of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Life Sci. 1966 Jun;5(12):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L., Holten D. Rat liver glucose-6-p dehydrogenase. Dietary regulation of the rate of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7796–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L., Nakayama R., Wolfe R., Holten D. Regulation of glucose-6-P dehydrogenase activity in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):748–755. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurdeman R., Berdanier C. D., Tobin R. B. Enzyme overshoot in starved-refed rats: role of the adrenal glucocorticoid. J Nutr. 1978 Sep;108(9):1457–1461. doi: 10.1093/jn/108.9.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yugari Y., Matsuda T. [Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from rat liver. II. Effect of diet on enzyme activity in vivo, and inhibition by long chain fatty acids in vitro]. J Biochem. 1967 May;61(5):541–549. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


