Abstract
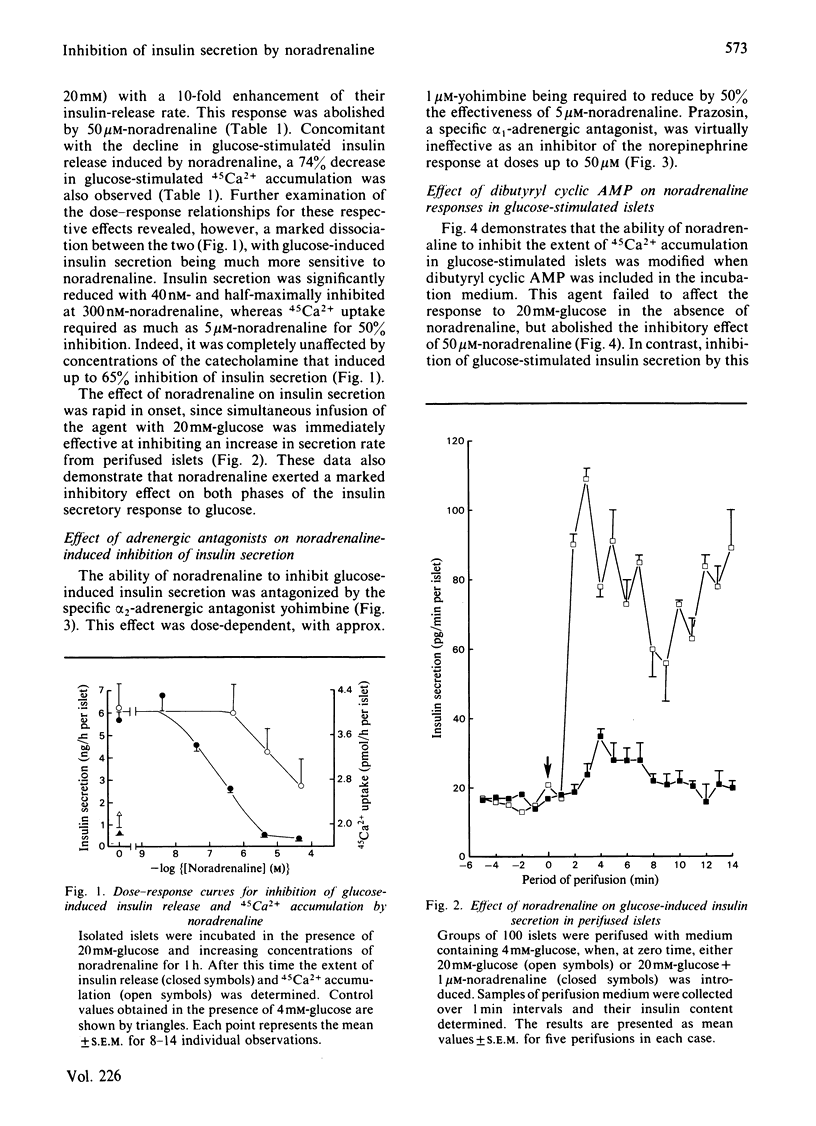
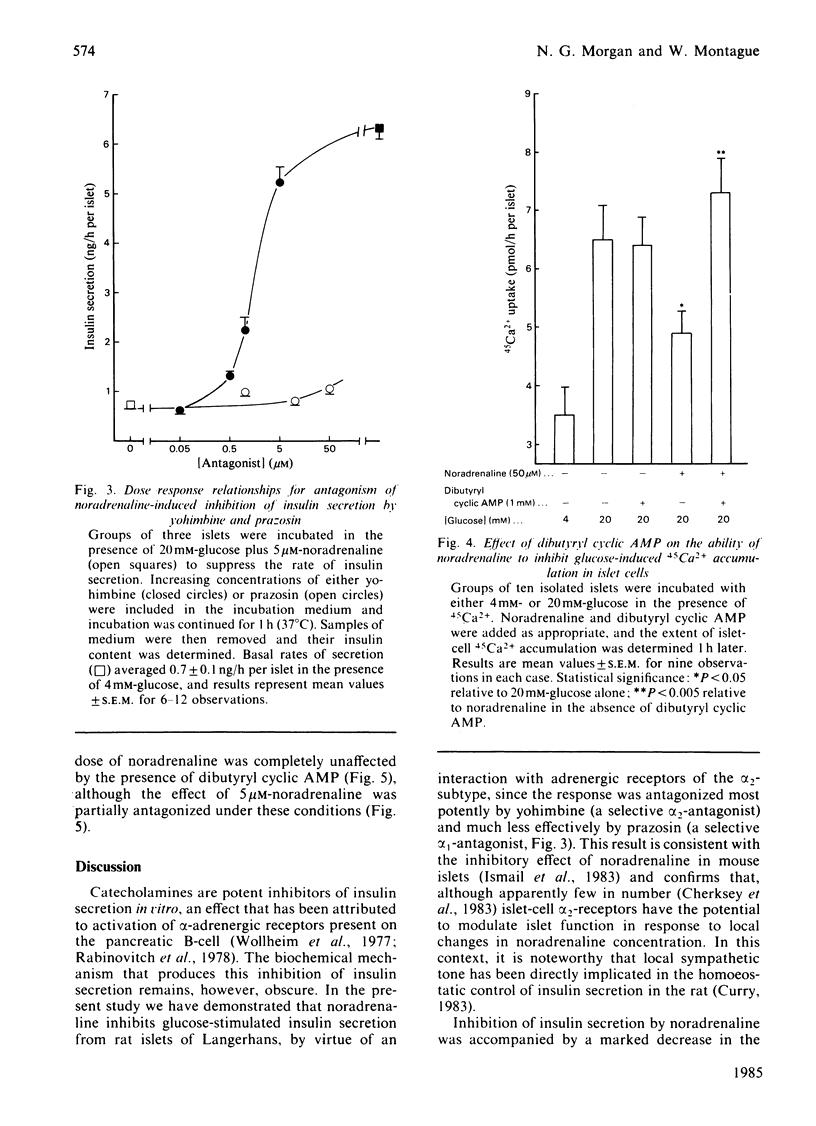
Noradrenaline (norepinephrine) was shown to be a potent inhibitor of glucose-induced insulin release from rat pancreatic islets, with half-maximal inhibition of the secretory response to 20 mM-glucose occurring at approx. 0.3 microM, and complete suppression of the response occurring at 4 microM-noradrenaline. Inhibition of insulin secretion by noradrenaline was antagonized by the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine (half maximally effective dose approximately 1 microM), but was largely unaffected by the alpha 1-adrenergic antagonist prazosin at concentrations up to 50 microM, suggesting that the response was mediated by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Noradrenaline significantly reduced the extent of 45Ca2+ accumulation in glucose-stimulated islets, although as much as 5 microM-noradrenaline was required for 50% inhibition of this response. The ability of noradrenaline to inhibit islet-cell 45Ca2+ uptake was totally abolished in media containing 1 mM-dibutyryl cyclic AMP, suggesting that the response may have been secondary to lowering of islet cyclic AMP. Under these conditions, however, noradrenaline was still able to inhibit insulin secretion maximally. The data suggest that the site(s) at which noradrenaline acts to mediate inhibition of insulin secretion in rat islets lies distal to both islet-cell cyclic AMP accumulation and Ca2+ uptake.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brisson G. R., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XI. Effects of theophylline and epinephrine on Ca efflux from perifused islets. Metabolism. 1973 Mar;22(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherksey B., Mendelsohn S., Zadunaisky J., Altszuler N. Displacement of alpha- and beta-radioligands by specific adrenergic agonists in rat pancreatic islets. Pharmacology. 1983;27(2):95–102. doi: 10.1159/000137840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L. Direct tonic inhibition of insulin secretion by central nervous system. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E425–E429. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Molecular mechanisms involved in alpha-adrenergic responses. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Sep;23(3):233–264. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Insulin secretion and action. Metabolism. 1984 Jul;33(7):672–679. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Dibutyryl cyclic AMP triggers Ca2+ influx and Ca2+-dependent electrical activity in pancreatic B cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91508-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Schmeer W., Meissner H. P. Forskolin, an activator of adenylate cyclase, increases CA2+-dependent electrical activity induced by glucose in mouse pancreatic B cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2218–2220. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N. A., El-Denshary E. S., Idahl L. A., Lindström P., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on insulin secretion, calcium uptake, and rubidium efflux in mouse pancreatic islets. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jun;118(2):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby J. H., Bryce G. F. Monoaminergic modulation of pancreatic endocrine secretion. Gen Pharmacol. 1978;9(6):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(78)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R., Sharp R., Burr I. M. Effects of calcium, lanthanum, and bicarbonate ion on epinephrine modification of insulin release in vitro. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28(1):52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Erdos J. J. Inhibition of magnesium uptake by beta-adrenergic agonists and prostaglandin E1 is not mediated by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1030–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Robertson R. P. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors reverse alpha-adrenergic inhibition of acute insulin response to glucose. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):E490–E500. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.6.E490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E. Pancreatic neuroendocrinology: peripheral neural mechanisms in the regulation of the Islets of Langerhans. Endocr Rev. 1981 Fall;2(4):471–494. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Taylor K. W. Pentitols and insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1090333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Stimulation of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans by melittin. Biosci Rep. 1984 Aug;4(8):665–671. doi: 10.1007/BF01121020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Studies on the interaction of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin with isolated islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):111–125. doi: 10.1042/bj2040111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Waynick L. E., Exton J. H. Characterisation of the alpha 1-adrenergic control of hepatic cAMP in male rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Ishii K., Kato R. Postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in isolated rat islets of Langerhans: inhibition of insulin release and cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Inhibition of dibutyryl cyclic AMP-induced insulin release by alpha-2 adrenergic stimulation. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 17;32(3):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Cerasi E., Sharp G. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent and -independent inhibitory effects of epinephrine on insulin release in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1733–1740. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes G., Blayac J. P., Loubatieres-Mariani M. M. Differences between the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline on insulin secretion in the dog. Diabetologia. 1983 Feb;24(2):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00297391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M. W., Lee K. C., Jones M. S., Miller R. E. Neural control of pancreatic insulin and somatostatin secretion. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):770–775. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. Islet cyclic AMP levels are not lowered during alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4111–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Somatostatin- and epinephrine-induced modifications of 45Ca++ fluxes and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1165–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S., Katada T., Ui M. Alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin secretion via interference with cyclic AMP generation in rat pancreatic islets. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


