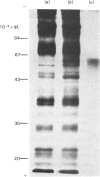
Abstract
A simplified procedure for the production and purification of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) is described. Bowes-melanoma cells were maintained in continuous serum-free culture. The cell nutrient consisted of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with insulin (5 mg/litre), transferrin (5 mg/litre), progesterone (1 nM), cortisol (10 nM), aprotinin (2 X 10(4) units/litre) and a mixture of trace elements. t-PA accumulated in the culture medium at a rate of 40 units/day per ml and was harvested every third day. Cell losses during each harvest, leading to a steady decline of enzyme yields, were compensated for by treating the cells with 5% (v/v) fetal-bovine serum in DMEM every 6-8 weeks. t-PA was rapidly purified by a combination of cation-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. The procedure yielded mainly single-chain t-PA of a specific activity of 80 000 to 100 000 units/mg.
Full text
PDF
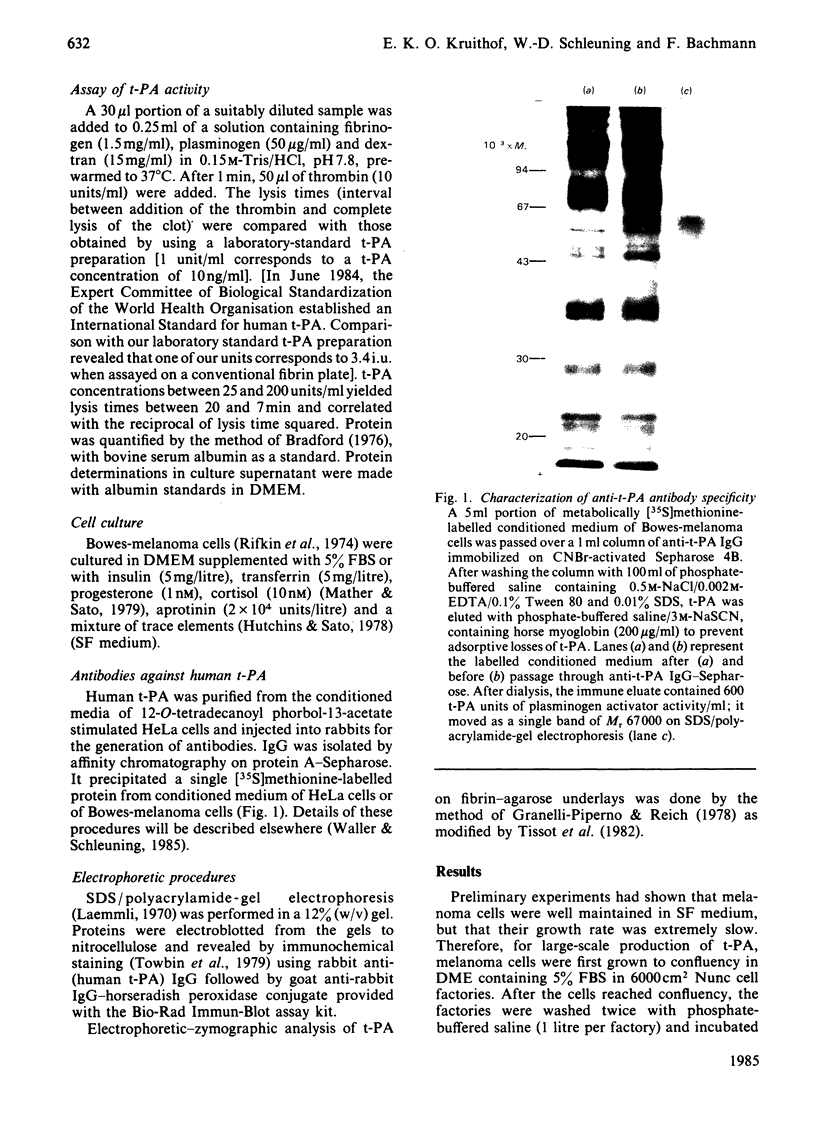
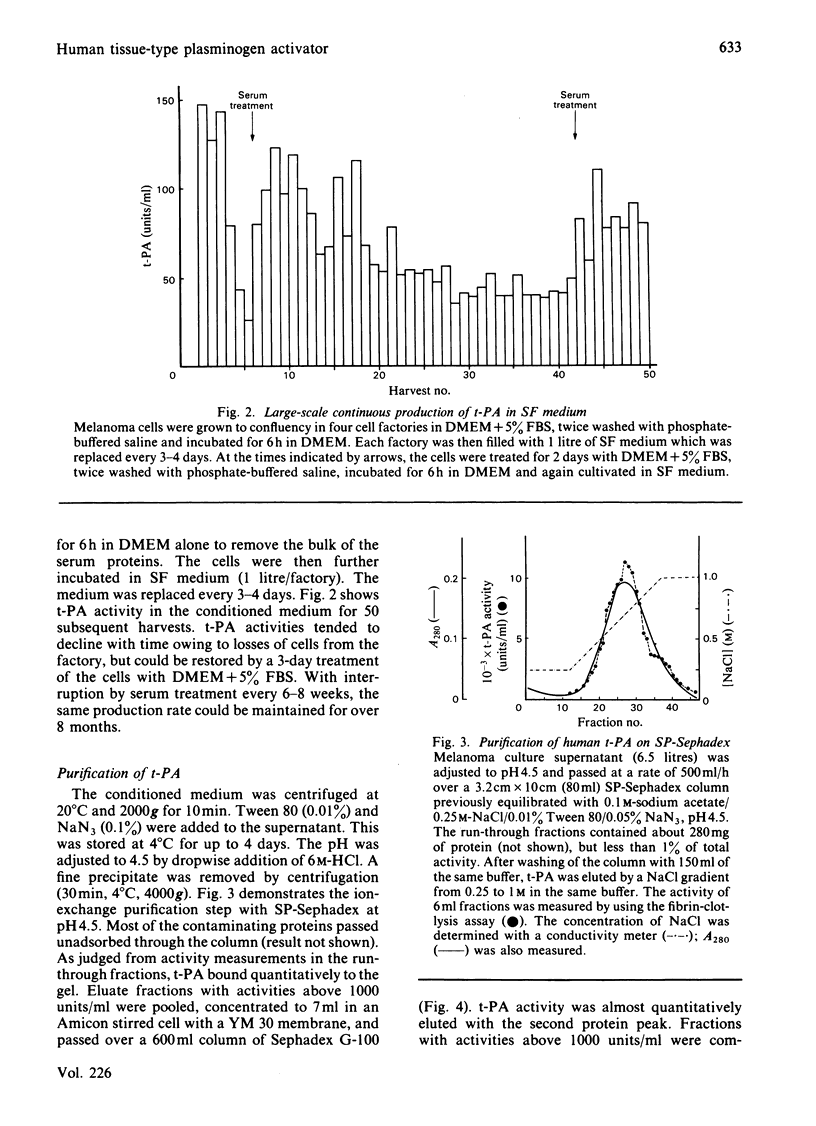


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann F., Kruithof I. E. Tissue plasminogen activator: chemical and physiological aspects. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):6–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann S. R., Fox K. A., Ter-Pogossian M. M., Sobel B. E., Collen D. Clot-selective coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6602378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bányai L., Váradi A., Patthy L. Common evolutionary origin of the fibrin-binding structures of fibronectin and tissue-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Stassen J. M., Verstraete M. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits with experimental jugular vein thrombosis. Effect of molecular form and dose of activator, age of the thrombus, and route of administration. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI110778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Ny T., Rånby M., Hedén L. O., Palm G., Holmgren E., Josephson S. Isolation of cDNA sequences coding for a part of human tissue plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):349–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings S. E., Sato G. H. Growth and maintenance of HeLa cells in serum-free medium supplemented with hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):901–904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Matsuo O., Suy R., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in dogs with femoral vein thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):573–580. doi: 10.1172/JCI110483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather J. P., Sato G. H. The growth of mouse melanoma cells in hormone-supplemented, serum-free medium. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Apr;120(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90549-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Rijken D. C., Collen D. Thrombolysis by human tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase in rabbits with experimental pulmonary embolus. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):590–591. doi: 10.1038/291590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson C., Nilsson S., Häggroth L. Human extrinsic plasminogen activator fibrinolytic properties and neutralization in vivo. Thromb Res. 1983 Apr 1;30(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Loeb J. N., Moore G., Reich E. Properties of plasminogen activators formed by neoplastic human cell cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1317–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot J. D., Schneider P., Hauert J., Ruegg M., Kruithof E. K., Bachmann F. Isolation from human plasma of a plasminogen activator identical to urinary high molecular weight urokinase. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1320–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI110733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Werf F., Ludbrook P. A., Bergmann S. R., Tiefenbrunn A. J., Fox K. A., de Geest H., Verstraete M., Collen D., Sobel B. E. Coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator in patients with evolving myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):609–613. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Pohl G., Bergsdorf N., Rånby M., Ny T., Jörnvall H. Purification and characterization of a melanoma cell plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):681–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar W., Stibbe J., van Seyen A. J., Billiau A., De Somer P., Collen D. Specific lysis of an iliofemoral thrombus by administration of extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator. Lancet. 1981 Nov 7;2(8254):1018–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]