Abstract
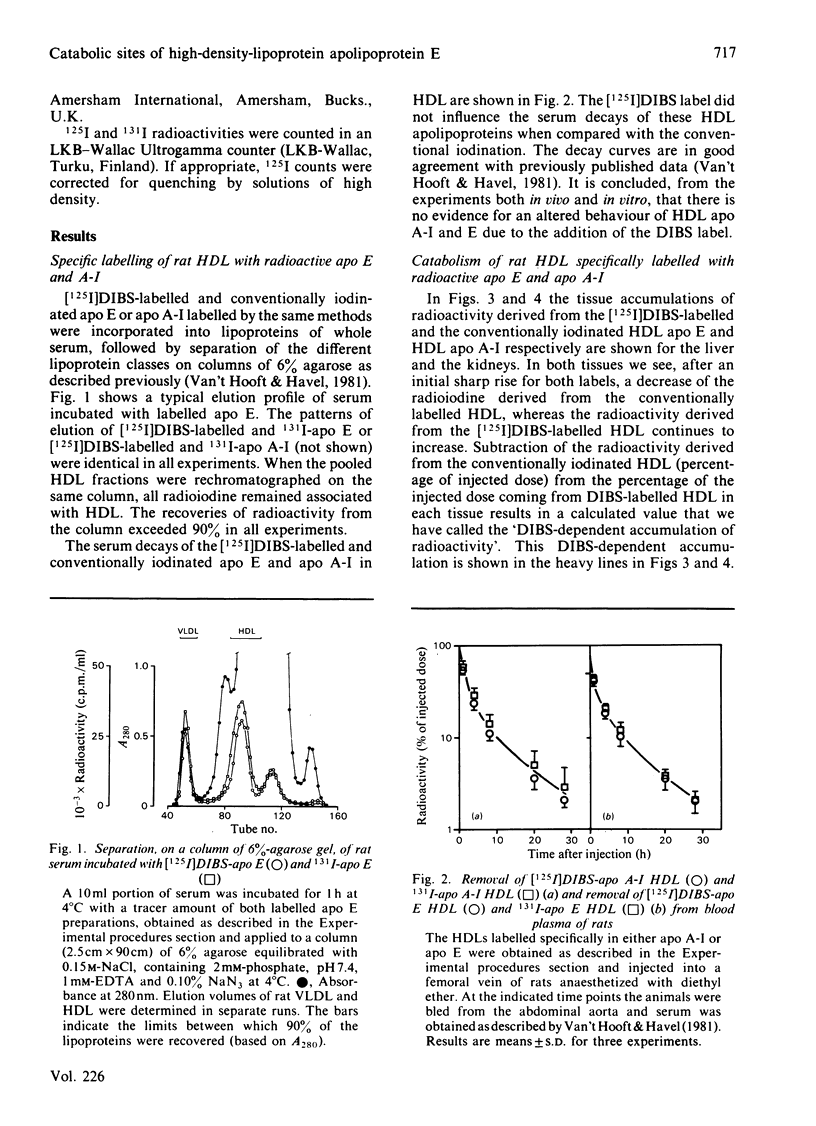
O-(4-Diazo-3-[125I]iodobenzoyl)sucrose ([125I]DIBS), a novel labelling compound specifically designed to study the catabolic sites of serum proteins [De Jong, Bouma, & Gruber (1981) Biochem. J. 198, 45-51], was applied to study the tissue sites of degradation of serum lipoproteins. [125I]DIBS-labelled apolipoproteins (apo) E and A-I, added in tracer amounts to rat serum, associate with high-density lipoproteins (HDL) just like conventionally iodinated apo E and A-I. No difference is observed between the serum decays of chromatographically isolated [125I]DIBS-labelled and conventionally iodinated HDL labelled specifically in either apo E or apo A-I. When these specifically labelled HDLs are injected into fasted rats, a substantial [125I]DIBS-dependent 125I accumulation occurs in the kidneys and in the liver. No [125I]DIBS-dependent accumulation is observed in the kidneys after injection of labelled asialofetuin or human low-density lipoprotein. It is concluded that the kidneys and the liver are important sites of catabolism of rat HDL apo E and A-I.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAUFAY H., BENDALL D. S., BAUDHUIN P., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 12. Intracellular distribution of some dehydrogenases, alkaline deoxyribonuclease and iron in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:623–628. doi: 10.1042/bj0730623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges K., Harford J., Ashwell G., Klausner R. D. Fate of receptor and ligand during endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins by isolated hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):350–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. S., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. O-(4-Diazo-3,5-di[125I]iodobenzoyl)sucrose, a novel radioactive label for determining organ sites of catabolism of plasma proteins. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):45–51. doi: 10.1042/bj1980045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelot P., Bos C. J. Studies on plasma membranes. 3. Mg2+-ATPase,(Na+-K+-Mg2+)-ATPase and 5'-nucleotidase activity of plasma membranes isolated from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 13;120(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Pittman R. C., Keller G. A., Steinberg D. Tissue sites of degradation of apoprotein A-I in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7161–7167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C., Pittman R. C., Weinstein D. B., Steinberg D. Dissociation of tissue uptake of cholesterol ester from that of apoprotein A-I of rat plasma high density lipoprotein: selective delivery of cholesterol ester to liver, adrenal, and gonad. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5435–5439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. S., Hamilton R. L., Ostwald R., Havel R. J. Secretion of nascent lipoproteins and apolipoproteins by perfused livers of normal and cholesterol-fed guinea pigs. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):543–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman W., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. Involvement of thiol enzymes in the lysosomal breakdown of native and denatured proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 24;297(1):98–109. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munniksma J., Noteborn M., Kooistra T., Stienstra S., Bouma J. M., Gruber M., Brouwer A., Praaning-van Dalen Dalen D., Knook D. L. Fluid endocytosis by rat liver and spleen. Experiments with 125I-labelled poly(vinylpyrrolidone) in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):613–621. doi: 10.1042/bj1920613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Otto P. S., Whayne T. F. Proteolysis of canine apolipoprotein by acid proteases in canine liver lysosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 13;422(2):380–389. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Van Herle A. J., Naruse R. T., Fierer G., Costin A. In vivo quantification of receptor-mediated uptake of asialoglycoproteins by rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):990–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Attie A. D., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Tissue sites of degradation of low density lipoprotein: application of a method for determining the fate of plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Simons L. A., Myant N. B., Pflug J. J., Mills G. L. The lipids and lipoproteins of human peripheral lymph, with observations on the transport of cholesterol from plasma and tissues into lymph. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):313–329. doi: 10.1042/cs0450313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röschlau P., Bernt E., Gruber W. Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamt-Cholesterins im Serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1974 Sep;12(9):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson G., Noel S. P., Havel R. J. Catabolism of the apoprotein of low density lipoproteins by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):628–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein Y., Dabach Y., Hollander G., Halperin G., Stein O. Metabolism of HDL-cholesteryl ester in the rat, studied with a nonhydrolyzable analog, cholesteryl linoleyl ether. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 16;752(1):98–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zile J., Henderson L. A., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. [3H]Raffinose, a novel radioactive label for determining organ sites of catabolism of proteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3547–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Hooft F., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoprotein E in plasma high density lipoproteins from normal and cholesterol-fed rats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10996–11001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Hooft F., Havel R. J. Metabolism of chromatographically separated rat serum lipoproteins specifically labeled with 125I-apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3963–3968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


