Full text
PDF
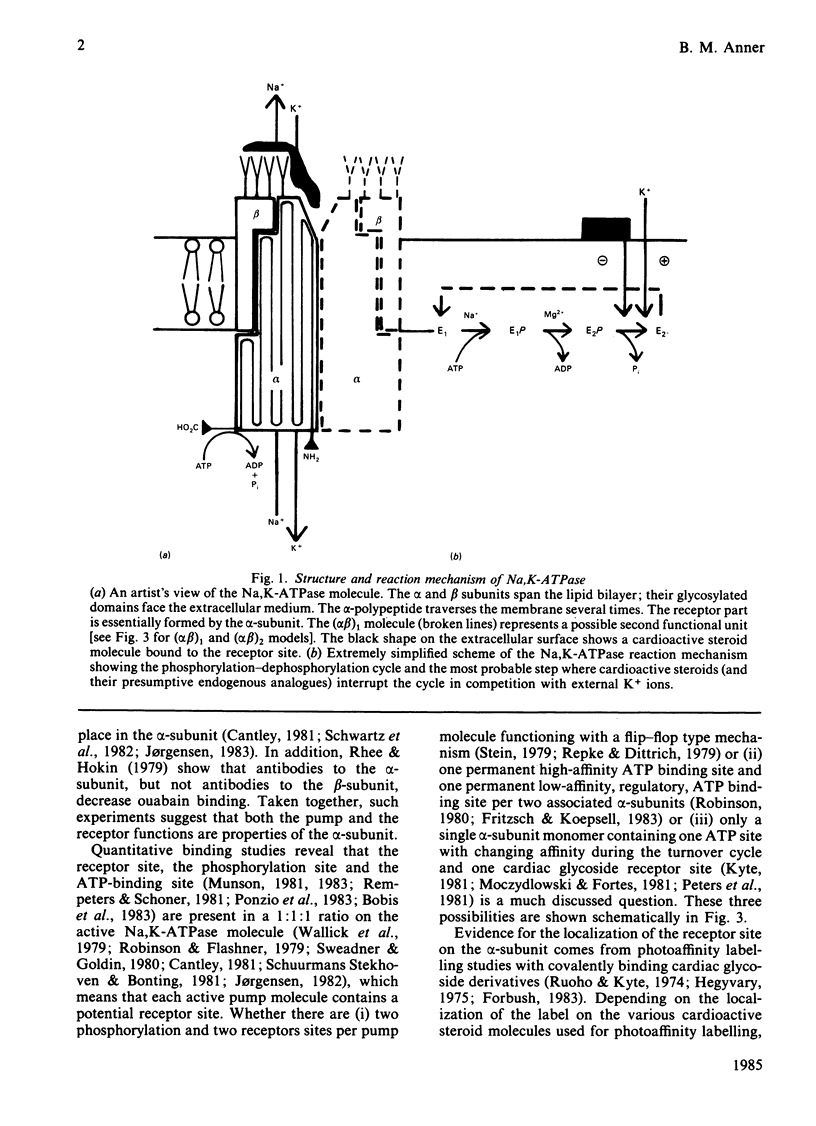
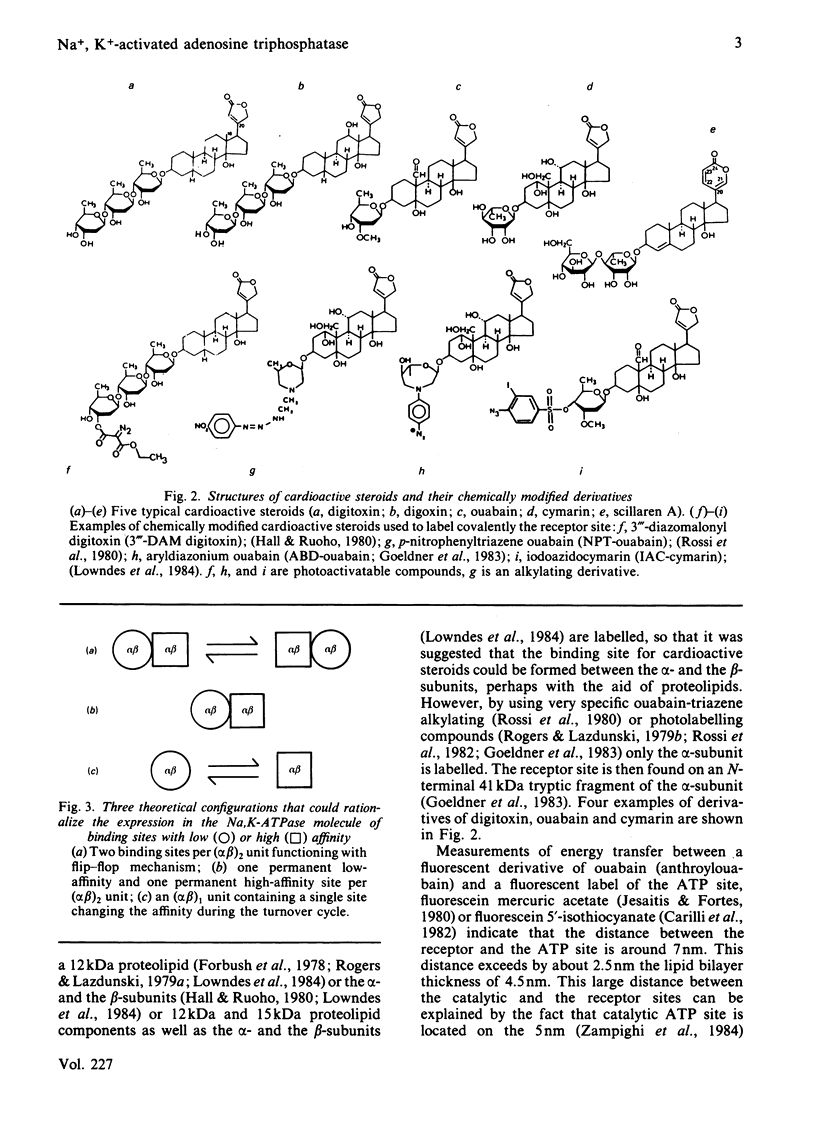




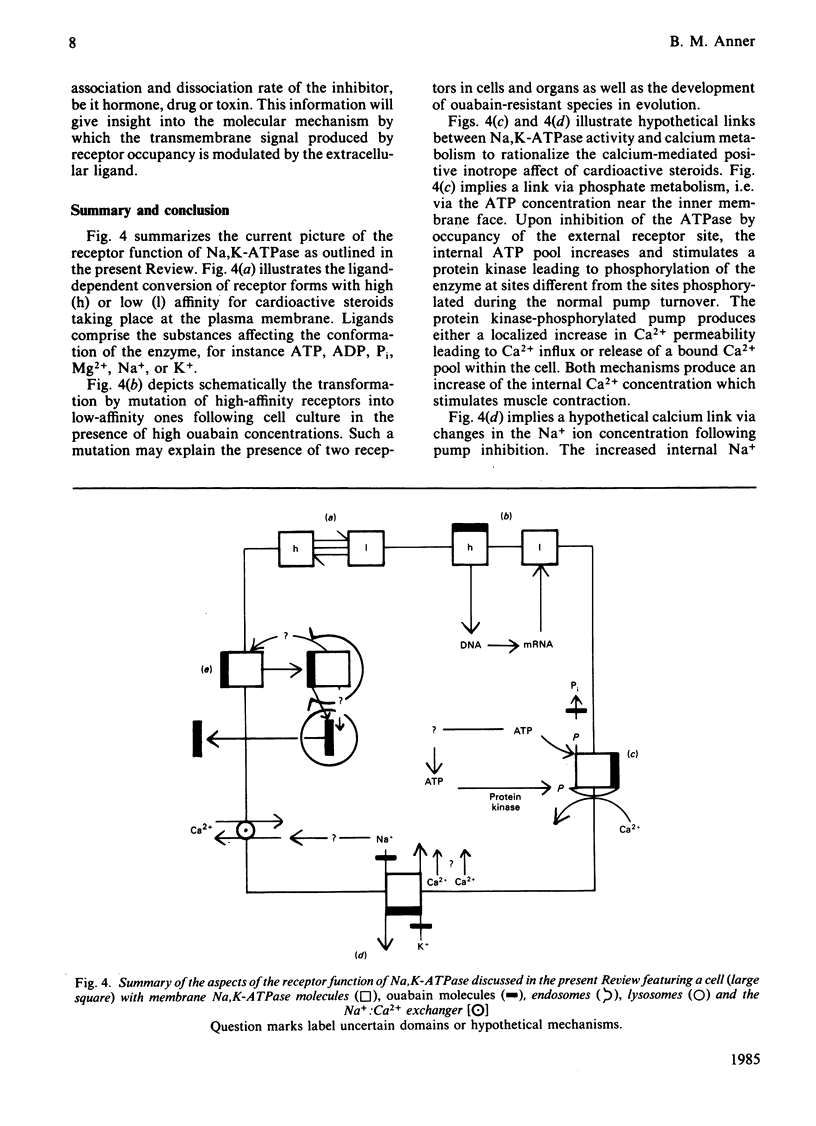



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeywardena M. Y., Charnock J. S. Modulation of cardiac glycoside inhibition of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase by membrane lipids. Difference between species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 23;729(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. J., Schwartz A., Grupp G., Grupp I., Lee S. W., Wallick E. T., Powell T., Twist V. W., Gathiram P. High-affinity ouabain binding site and low-dose positive inotropic effect in rat myocardium. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):167–169. doi: 10.1038/296167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiton J. F., Lamb J. F., Ogden P. Down-regulation of the sodium pump following chronic exposure of HeLa cells and chick embryo heart cells to ouabain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;73(2):333–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akera T., Brody T. M. Myocardial membranes: regulation and function of the sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:375–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anner B. M., Lane L. K., Schwartz A., Pitts B. J. A reconstituted Na+ + K+ pump in liposomes containing purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from kidney medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 16;467(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidard J. N., Rossi B., Renaud J. F., Lazdunski M. A search for an 'ouabain-like' substance from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus which led to arachidonic acid and related fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 11;769(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C165–C173. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium-calcium exchange and the regulation of cell calcium in muscle fibers. Physiologist. 1976 Nov;19(4):525–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman L. J., Lamb J. F., McCall D. Uptake of ( 3 H)ouabain and Na pump turnover rates in cells cultured in ouabain. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(3):619–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., Fishman P. H. Biotransducers of membrane-mediated information. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;50:303–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122952.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Recycling receptors: the round-trip itinerary of migrant membrane proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):663–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckalew V. M., Jr, Gruber K. A. Natriuretic hormone. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:343–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Berthon B., Poggioli J., Burgess G. M., Claret M. The effect of Ca2+ -mobilising hormones on the Na+ --K+ pump in isolated rat liver hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 3;141(1):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carilli C. T., Farley R. A., Perlman D. M., Cantley L. C. The active site structure of Na+- and K+-stimulated ATPase. Location of a specific fluorescein isothiocyanate reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5601–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Reinlib L., Carafoli E. Charge movements during the Na+-Ca2+ exchange in heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Harwood J. P., Aguilera G., Dufau M. L. Hormonal regulation of peptide receptors and target cell responses. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):109–116. doi: 10.1038/280109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlemagne D., Leger J., Schwartz K., Geny B., Zachowski A., Lelievre L. Involvement of tropomyosin in the sensitivity of Na+ + K+ ATPase to ouabain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;29(3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy W. N., Littlefield J. W. Isolation of diploid human lymphoblast mutants presumably homozygous for ouabain resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1101–1105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. S., Tate E. H., Shaffer C. Uptake of [3H]ouabain from the cell surface into the lysosomal compartment of HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jan;110(1):84–92. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deber C. M., Behnam B. A. Role of membrane lipids in peptide hormone function: binding of enkephalins to micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):61–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detweiler D. K. Comparative pharmacology of cardiac glycosides. Fed Proc. 1967 Jul-Aug;26(4):1119–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert K., Grosse R. Incorporation of Na+ - Ca2+ antiporter and of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase into liposomes and demonstration of their non-identity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 22;692(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann E. Cardiac glycoside receptors and positive inotropy. Evidence for more than one receptor? Basic Res Cardiol. 1984;79 (Suppl):7–8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72376-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd, Kaplan J. H., Hoffman J. F. Characterization of a new photoaffinity derivative of ouabain: labeling of the large polypeptide and of a proteolipid component of the Na, K-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3667–3676. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forest C., Ponzio G., Rossi B., Lazdunski M., Ailhaud G. (Na+,K+)ATPase levels in preadipocyte cell lines established from genetically-obese and non-obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):422–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91508-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsch G., Koepsell H. An analysis of biphasic time courses: the inactivation of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase by ATP-analogs. J Theor Biol. 1983 Jun 21;102(4):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K., Gaeggeler H. P., Rossier B. C. Effects of thyromimetic drugs on aldosterone-dependent sodium transport in the toad bladder. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01871096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K., Girardet M., Bron C., Kraehenbühl J. P., Rossier B. C. Hormonal regulation of (Na+,K+)-ATPase biosynthesis in the toad bladder. Effect of aldosterone and 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10338–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., Paraf A., Fedon Y., Charlemagne D. Characterization of a beta-actinin-like protein in purified non-muscle cell membranes. Its activity on (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais A., Lane L. K., Anner B. M., Lindenmayer G. E., Schwartz A. A possible molecular mechanism of the action of digitalis: ouabain action on calcium binding to sites associated with a purified sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase from kidney. Circ Res. 1977 Jan;40(1):8–14. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Rink T. J. Hypertension and inhibition of the sodium pump: a strong link but in which chain? Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):576–577. doi: 10.1038/300576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeldner M. P., Hirth C. G., Rossi B., Ponzio G., Lazdunski M. Specific photoaffinity labeling of the digitalis binding site of the sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase induced by energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4685–4690. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M., Tong S. W. Reconstitution of active transport catalyzed by the purified sodium and potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5907–5915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E., Zambrano F. Possible role of sulphatide in the K+-activated phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 9;728(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy F. J. Humoral factors and the sodium-potassium pump in low renin hypertension. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Oct 1;60(19):1254–1257. doi: 10.1007/BF01716733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy F. J. Natriuretic hormone--the missing link in low renin hypertension? Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3159–3161. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C., Ruoho A. Ouabain-binding-site photoaffinity probes that label both subunits of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4529–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn J. M., Ringel R., Schaeffer J., Levinson P. D., Hamilton B. P., Kowarski A. A., Blaustein M. P. A circulating inhibitor of (Na+ + K+)ATPase associated with essential hypertension. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):650–652. doi: 10.1038/300650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. A biochemical link to digitalis-induced inotropy. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):143–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupert G. T., Jr, Sancho J. M. Sodium transport inhibitor from bovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4658–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyvary C. Covalent labeling of the digitalis-binding component of plasma membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):588–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilden S., Rhee H. M., Hokin L. E. Sodium transport by phospholipid vesicles containing purified sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7432–7440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R. The importance of the endosome in intracellular traffic. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):684–685. doi: 10.1038/304684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossler F. E., Sarras M. P., Jr, Allen E. R. Ultrastructural, cyto- and biochemical observations during turnover of plasma membrane in duck salt gland. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Apr 17;188(2):299–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00222639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inturrisi C. E., Papaconstantinou M. C. Ouabain sensitivity of the Na+, K+-ATPase from rat neonatal and human fetal and adult heart. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):710–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Fortes P. A. Fluorescence studies of the sodium and potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase labeled with fluorescein mercuric acetate and anthroylouabain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):459–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Conformational changes in the alpha-subunit, and cation transport by Na+, K+-ATPase. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:253–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Karlish S. J., Gitler C. Evidence for the organization of the transmembrane segments of (Na,K)-ATPase based on labeling lipid-embedded and surface domains of the alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7435–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Mechanism of the Na+, K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):27–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Sodium and potassium ion pump in kidney tubules. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):864–917. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J. Characterization of conformational changes in (Na,K) ATPase labeled with fluorescein at the active site. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1980 Aug;12(3-4):111–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00744678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazoglou T., Renaud J. F., Rossi B., Lazdunski M. Two classes of ouabain receptors in chick ventricular cardiac cells and their relation to (Na+,K+)-ATPase inhibition, intracellular Na+ accumulation, Ca2+ influx, and cardiotonic effect. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12163–12170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Molecular considerations relevant to the mechanism of active transport. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):201–204. doi: 10.1038/292201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGER G. A. CALCIUM EXCHANGE IN DOG VENTRICULAR MUSCLE: RELATION TO FREQUENCY OF CONTRACTION AND MAINTENANCE OF CONTRACTILITY. Circ Res. 1965 Jul;17:78–89. doi: 10.1161/01.res.17.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Altendorf K., Epstein W. Identification of the structural proteins of an ATP-driven potassium transport system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3216–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. F., Ogden P. Internalization of ouabain and replacement of sodium pumps in the plasma membranes of HeLa cells following block with cardiac glycosides. Q J Exp Physiol. 1982 Jan;67(1):105–119. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1982.sp002605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski M., Kazazoglou T., Renaud J. F., Rossi B. Digitalis receptors affinity labelling and relation with positive inotropic and cardiotoxic effects. Basic Res Cardiol. 1984;79 (Suppl):110–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72376-6_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. M., Smith A. P. A protein-lipid model of the opiate receptor. Life Sci. 1980 May 5;26(18):1459–1464. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R., Racaniello V., Albritton L., Housman D. Molecular cloning of the mouse ouabain-resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1489–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E., Seegmiller J. E. Ouabain-resistant human lymphoblastoid lines altered in the (Na+ + K+)-dependent ATPase membrane transport system. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jul;88(3):343–352. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. H., Akera T. Increased (Na+,K+)-ATPase concentrations in various tissues of rats caused by thyroid hormone treatment. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):723–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L., Cantley L. The (Na,K)-ATPase of Friend erythroleukemia cells is phosphorylated near the ATP hydrolysis by an endogenous membrane-bound kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4089–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingham R. B., Stewart D. J., Sen A. K. The induction of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in the salt gland of the duck. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 2;601(1):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo C. S., Edelman I. S. Effect of triiodothyronine on the synthesis and degradation of renal cortical (Na+ + k+)-adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7834–7840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes J. M., Hokin-Neaverson M., Ruoho A. E. Photoaffinity labeling of (Na+K+)-ATPase with [125I]iodoazidocymarin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10533–10538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. A., de Wardener H. E. Is a circulating sodium transport inhibitor involved in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension? Clin Exp Hypertens. 1981;3(4):815–830. doi: 10.3109/10641968109033705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansier P., Cassidy P. S., Charlemagne D., Preteseille M., Lelievre L. G. Three Na+, K+-ATPase forms in rat heart as revealed by K+/ouabain antagonism. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80642-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansier P., Lelievre L. G. CA2+-free perfusion of rat heart reveals a (Na+ + K+)ATPase form highly sensitive to ouabain. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):535–537. doi: 10.1038/300535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. Natriuretic hormone linked to hypertension. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1255–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.6262915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto H., Racker E. Solubilization and partial purification of the Ca2+/Na+ antiporter from the plasma membrane of bovine heart. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2656–2658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E. G., Fortes P. A. Inhibition of sodium and potassium adenosine triphosphatase by 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrocyclohexadienylidene) adenine nucleotides. Implications for the structure and mechanism of the Na:K pump. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2357–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. The generation of electric currents in cardiac fibers by Na/Ca exchange. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C103–C110. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson K. B. Light-dependent inactivation of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase with a new photoaffinity reagent, chromium arylazido-beta-alanyl ATP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3223–3230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson K. B. Light-dependent labeling of the active site of sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase with the chromium complex of 3'-O-[3-[(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)amino]-3-tritiopropionyl]adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2301–2308. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh S., Zetterqvist O. Phosphorylation of bovine brain Na + , K + -stimulated ATP phosphohydrolase by adenosine ( 32 P)triphosphate studied by a rapid-mixing technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy S. M., Huang W. H., Askari A. Origins of the different sensitivities of (Na+ + K+)-dependent adenosinetriphosphatase preparations to ouabain. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;76(3):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(83)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy S. M., Lane L. K., Askari A. Ouabain-insensitivity of highly active Na+, K+-dependent adenosinetriphosphatase from rat kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):742–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91775-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. H., Swarts H. G., de Pont J. J., Schuurmans Stekhoven F. M., Bonting S. L. (Na/ + K+)ATPase has one functioning phosphorylation site per alpha subunit. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):338–339. doi: 10.1038/290338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D., Nishimoto A. Y. Na+-Ca2+ exchange is affected by membrane potential in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6880–6882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J. Stoichiometry of sodium-calcium exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Coupling to the sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6232–6235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack L. R., Tate E. H., Cook J. S. Na+, K+-ATPase in HeLa cells after prolonged growth in low K+ or ouabain. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jan;106(1):85–97. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041060110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack L. R., Tate E. H., Cook J. S. Turnover and regulation of Na-K-ATPase in HeLa cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):C173–C183. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.5.C173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzio G., Rossi B., Lazdunski M. Affinity labeling and localization of the ATP binding site in the (Na+,K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8201–8205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPKE K. UBER DEN BIOCHEMISCHEN WIRKUNGSMODUS VON DIGITALIS. Klin Wochenschr. 1964 Feb 15;42:157–165. doi: 10.1007/BF01482616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium ion exchange in cardiac membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rempeters G., Schoner W. Evidence for a Mg2+-induced conformational change at the ATP-binding site of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase demonstrated with a photoreactive ATP-analogue. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;121(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repke K. R., Herrmann I., Portius H. J. Interaction of cardiac glycosides and Na,K-ATPase is regulated by effector-controlled equilibrium between two limit enzyme conformers. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 1;33(13):2089–2099. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90578-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repke K., Est M., Portius H. J. Uber die Ursache der Speciesunterschiede in der Digitalisempfindlichkeit. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Dec;14(12):1785–1802. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee H. M., Hokin L. E. Inhibition of ouabain-binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase by antibody against the catalytic subunit but not by antibody against the glycoprotein subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 16;558(1):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Baker R. M. (Na, K)ATPase activity in membrane preparations of ouabain-resistant HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5163–5168. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D., Flashner M. S. The (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. Enzymatic and transport properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):145–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. B., Lazdunski M. Photoaffinity labeling of the digitalis receptor in the (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):135–140. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. B., Lazdunski M. Photoaffinity labelling of a small protein component of a purified (Na+-K+)ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi B., Ponzio G., Lazdunski M. Identification of the segment of the catalytic subunit of (Na+,K+)ATPase containing the digitalis binding site. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):859–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi B., Vuilleumier P., Gache C., Balerna M., Lazdunski M. Affinity labeling of the digitalis receptor with p-nitrophenyltriazene-ouabain, a highly specific alkylating agent. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9936–9941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A., Kyte J. Photoaffinity labeling of the ouabain-binding site on (Na+ plus K+) adenosinetriphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2352–2356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium- und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(4):346–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Lindenmayer G. E., Allen J. C. The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev. 1975 Mar;27(01):3–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Whitmer K., Grupp G., Grupp I., Adams R. J., Lee S. W. Mechanism of action of digitalis: is the Na,K-ATPase the pharmacological receptor? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:253–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoni Y., Gotsman M., Deutsch J., Kachalsky S., Lichtstein D. Endogenous ouabain-like compound increases heart muscle contractility. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):369–371. doi: 10.1038/307369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderberg K., Rossi B., Lazdunski M., Louvard D. Characterization of ouabain-resistant mutants of a canine kidney cell line, MDCK. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12300–12307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J., Goldin S. M. Active transport of sodium and potassium ions: mechanism, function, and regulation. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):777–783. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation, and difference in affinity for strophanthidin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6060–6067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting-Beall H. P., Holland V. F., Freytag J. W., Lewis W. S., Hastings D. F. Asymmetric mass distribution of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in membranes studied by freeze-fracture-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan G. L., Cook J. S. Regeneration of cation-transport capacity in HeLa cell membranes after specific blockade by ouabain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBRANDT W. Zum Wirkungsmechanismus der Herzglykoside. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1955 Apr 2;85(14):315–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick E. T., Lane L. K., Schwartz A. Biochemical mechanism of the sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:397–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., Longworth J. W., Brake E. T., Cook J. S. Analysis of intracellular drug (ouabain) sequestration as a mechanism of detoxification. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;13(1):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Ling L., English L., Cantley L. Phosphorylation of the (Na,K)-ATPase by a plasma membrane-bound protein kinase in friend erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6567–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampighi G., Kyte J., Freytag W. Structural organization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in purified membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1851–1864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wardener H. E., MacGregor G. A. The natriuretic hormone and essential hypertension. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1450–1454. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



