Abstract
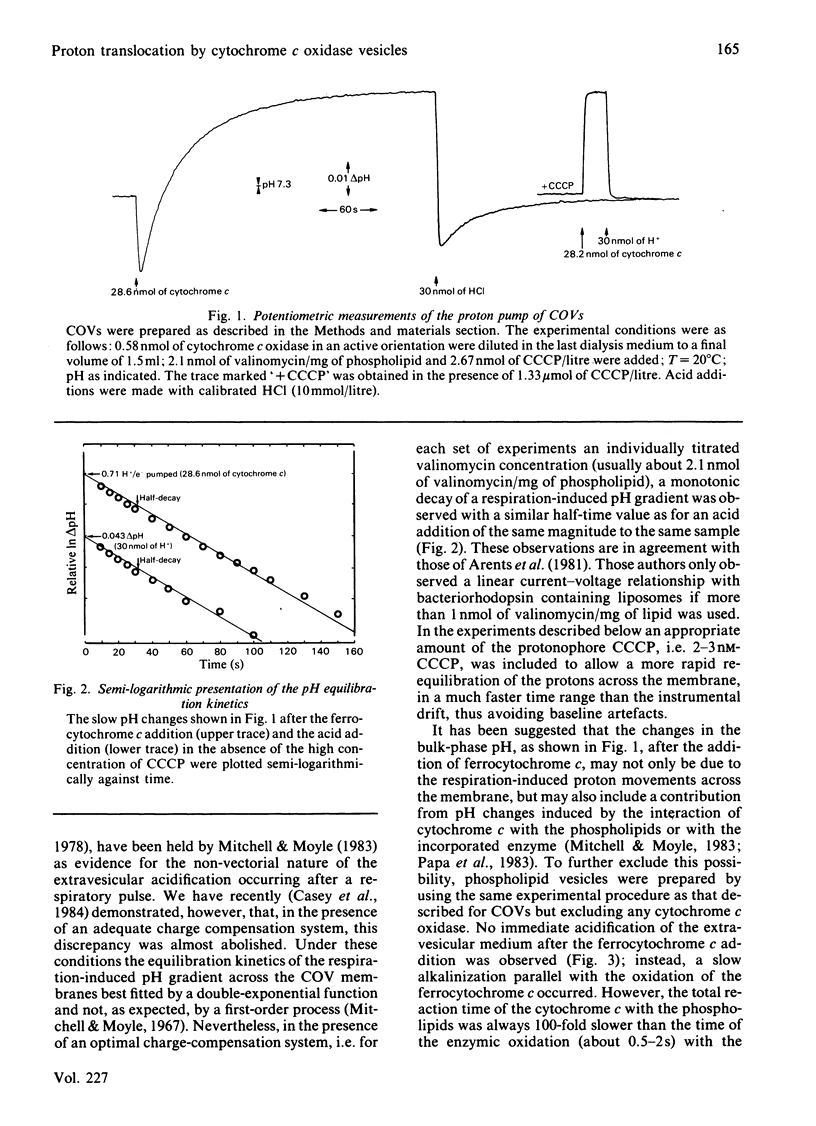
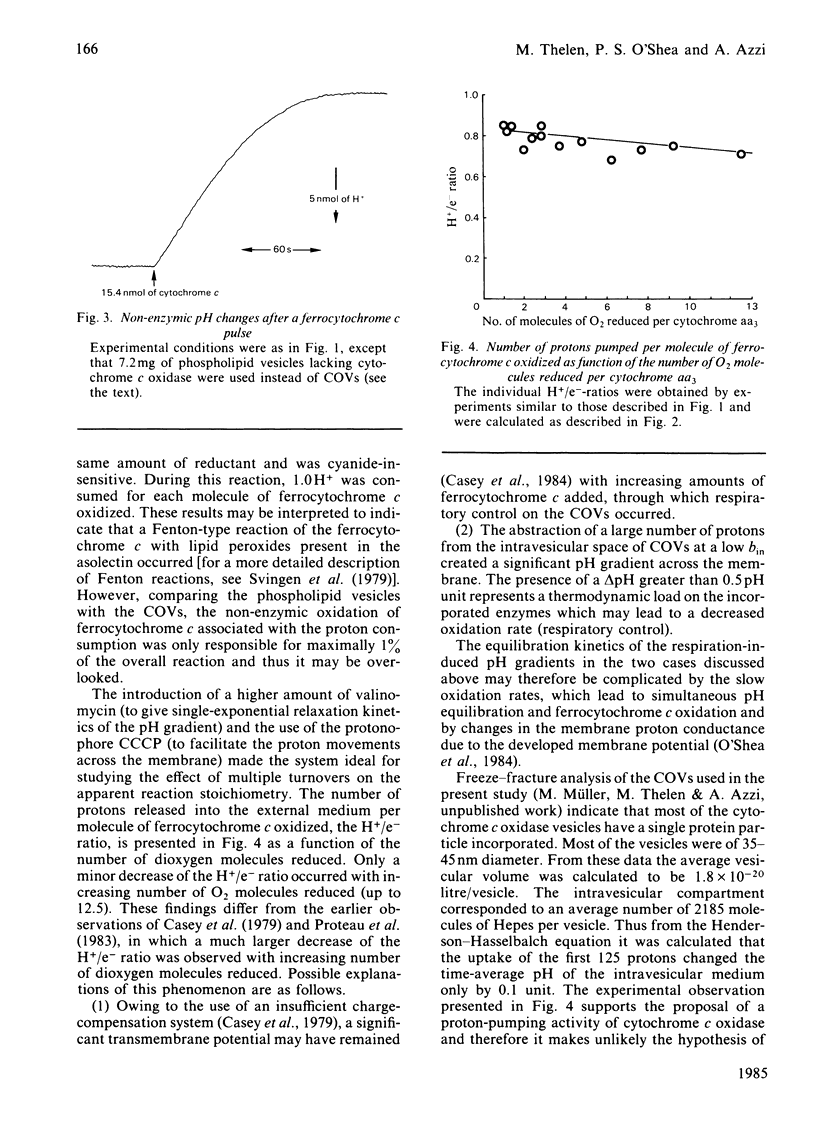
Cytochrome c oxidase vesicles were used to show that, under appropriate experimental conditions: (1) no net deprotonation of the vesicular membrane or of the incorporated enzyme occurs during the oxidation of ferrocytochrome c; (2) the pH equilibration kinetics of a respiration-induced pH gradient across the bilayer are a simple function of the ohmic proton-conductance properties of the membrane; (3) a fairly constant stoichiometry (0.8-0.7) of the numbers of protons pumped per molecule of ferrocytochrome c oxidized, i.e. the H+/e- ratio, over a wide range of dioxygen molecules reduced (1-12) is observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casey R. P., Azzi A. An evaluation of the evidence for H+ pumping by reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase in the light of recent criticism. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Chappell J. B., Azzi A. Limited-turnover studies on proton translocation in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase-containing vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):149–156. doi: 10.1042/bj1820149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., O'Shea P. S., Chappell J. B., Azzi A. A quantitative characterisation of H+ translocation by cytochrome c oxidase vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 26;765(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(84)90153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. C., Kim J. J., Racker E. Ion transport and respiratory control in vesicles formed from cytochrome oxidase and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1338–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krab K., Wikström M. Proton-translocating cytochrome c oxidase in artificial phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 11;504(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Alternative hypotheses of proton ejection in cytochrome oxidase vesicles. Transmembrane proton pumping or redox-linked deprotonation of phospholipid-cytochrome c complex(es). FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea P. S., Petrone G., Casey R. P., Azzi A. The current-voltage relationships of liposomes and mitochondria. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):719–726. doi: 10.1042/bj2190719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Lorusso M., Capitanio N., De Nitto E. Characteristics of redox-linked proton ejection in cytochrome c oxidase reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. New observations support mechanisms different from proton pumping. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska L. J., Bisson R., Capaldi R. A., Steffens G. C., Buse G. Inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase function by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 14;637(2):360–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proteau G., Wrigglesworth J. M., Nicholls P. Protonmotive functions of cytochrome c oxidase in reconstituted vesicles. Influence of turnover rate on 'proton translocation'. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):199–205. doi: 10.1042/bj2100199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svingen B. A., Buege J. A., O'Neal F. O., Aust S. D. The mechanism of NADPH-dependent lipid peroxidation. The propagation of lipid peroxidation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5892–5899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teissie J. Interaction of cytochrome c with phospholipid monolayers. Orientation and penetration of protein as functions of the packing density of film, nature of the phospholipids, and ionic content of the aqueous phase. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1554–1560. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. K., Saari H. T. The mechanism of energy conservation and transduction by mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 17;462(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Cullis P. R. Cytochrome c specifically induces non-bilayer structures in cardiolipin-containing model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


