Abstract
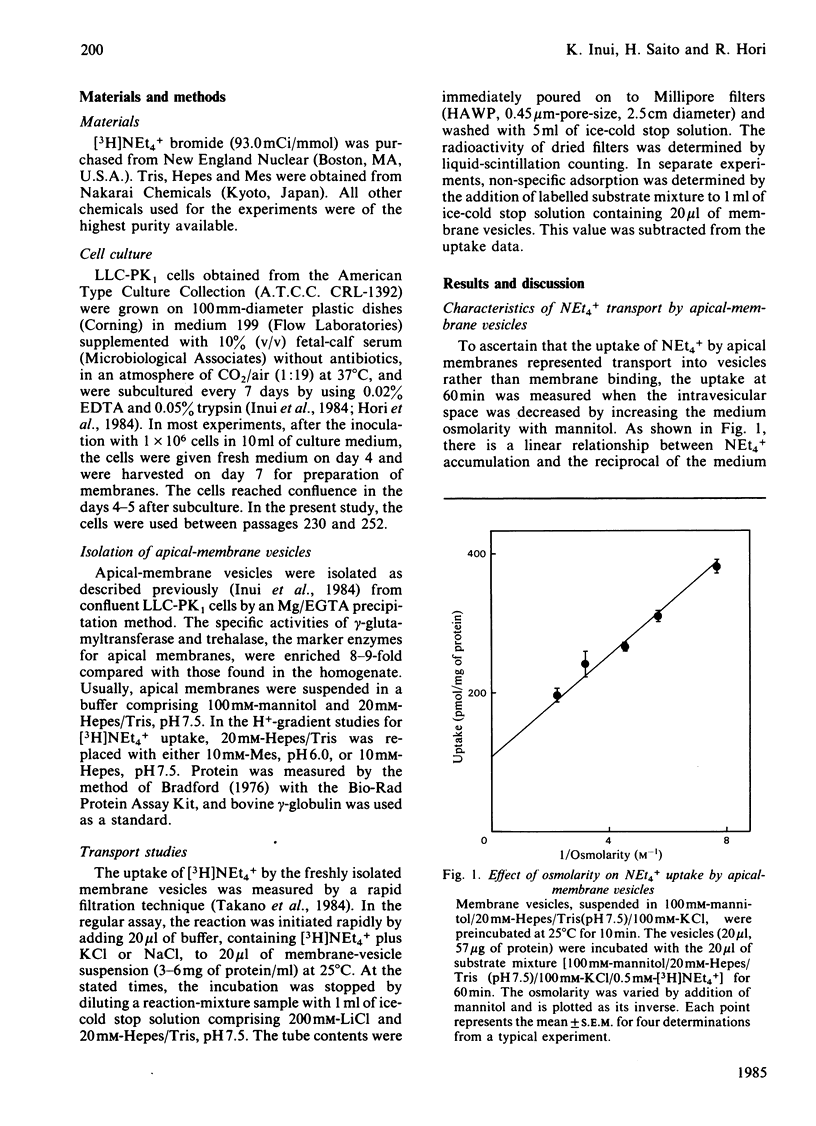
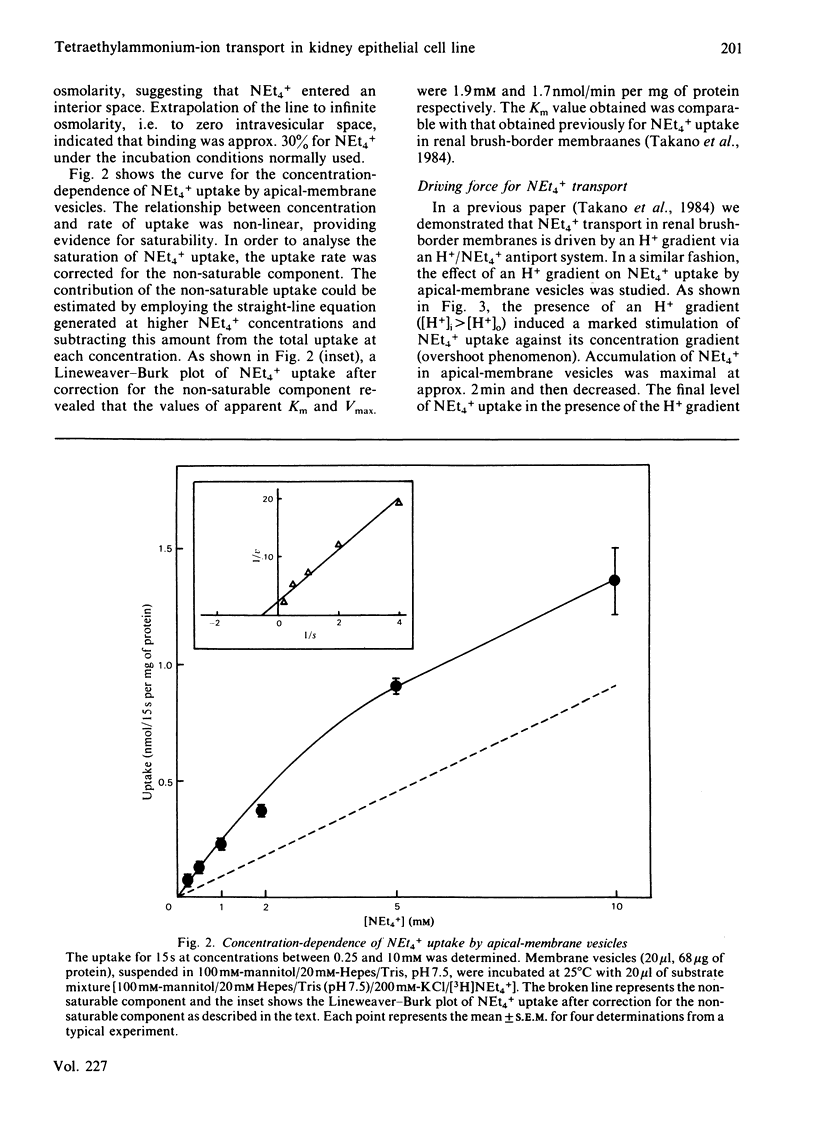
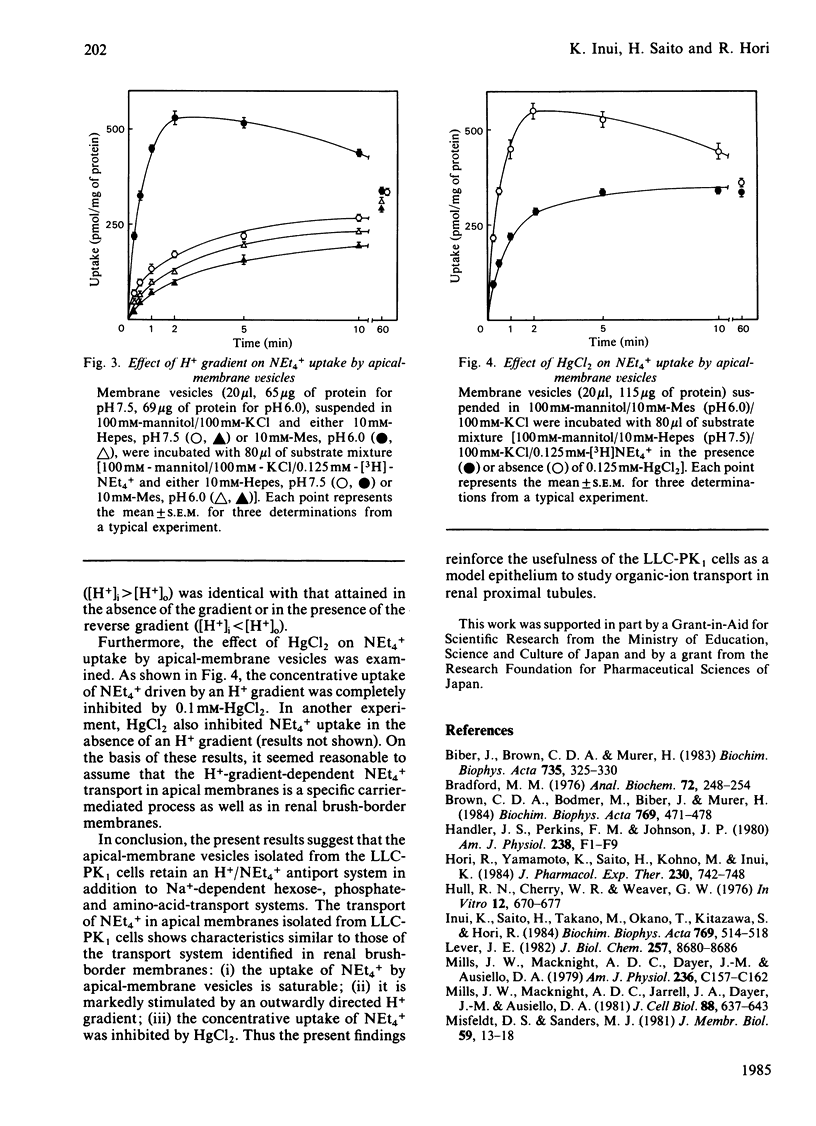
Transport of [3H]tetraethylammonium (NEt4+), an organic cation, has been studied by using apical-membrane vesicles isolated from cultured kidney epithelial cell line LLC-PK1. The uptake of NEt4+ by apical-membrane vesicles was osmotically sensitive, time-dependent and saturable. The presence of an H+ gradient ([H+]i greater than [H+]o) induced a marked stimulation of NEt4+ uptake against its concentration gradient (overshoot phenomenon), and this concentrative uptake was inhibited by HgCl2. These results suggest that apical membranes isolated from the LLC-PK1 cells retain the transport characteristics of NEt4+ similar to those observed in renal brush-border membranes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biber J., Brown C. D., Murer H. Sodium-dependent transport of phosphate in LLC-PK1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 23;735(3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. D., Bodmer M., Biber J., Murer H. Sodium-dependent phosphate transport by apical membrane vesicles from a cultured renal epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S., Perkins F. M., Johnson J. P. Studies of renal cell function using cell culture techniques. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):F1–F9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. N., Cherry W. R., Weaver G. W. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK. In Vitro. 1976 Oct;12(10):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02797469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui K., Saito H., Takano M., Okano T., Kitazawa S., Hori R. Enzyme activities and sodium-dependent active D-glucose transport in apical membrane vesicles isolated from kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):514–518. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Expression of a differentiated transport function in apical membrane vesicles isolated from an established kidney epithelial cell line. Sodium electrochemical potential-mediated active sugar transport. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8680–8686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. W., Macknight A. D., Dayer J. M., Ausiello D. A. Localization of [3H]ouabain-sensitive Na+ pump sites in cultured pig kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C157–C162. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. W., Macknight A. D., Jarrell J. A., Dayer J. M., Ausiello D. A. Interaction of ouabain with the Na+ pump in intact epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):637–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt D. S., Sanders M. J. Transepithelial transport in cell culture: D-glucose transport by a pig kidney cell line (LLC-PK1). J Membr Biol. 1981 Mar 15;59(1):13–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01870816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran A., Handler J. S., Turner R. J. Na+-dependent hexose transport in vesicles from cultured renal epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):C293–C298. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.5.C293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin J. M., Weibel J., Diamond L., Kleinzeller A. Sugar transport in the LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cell line: similarity to mammalian kidney and the influence of cell density. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Sep;104(3):375–389. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041040311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Kinne R. The use of isolated membrane vesicles to study epithelial transport processes. J Membr Biol. 1980 Jul 15;55(2):81–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01871151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller J. V., Sheikh M. I. Renal organic anion transport system: pharmacological, physiological, and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Dec;34(4):315–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito C. A., Ausiello D. A. Na+-dependent sugar transport in a cultured epithelial cell line from pig kidney. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01875374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito C. A., Karish M. V. Polarized amino acid transport by an epithelial cell line of renal origin (LLC-PK1). The apical systems. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2543–2547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito C. A., Karish M. V. Polarized amino acid transport by an epithelial cell line of renal origin (LLC-PK1). The basolateral systems. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6802–6808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito C. A., Kreisberg J. I., Wight D. Alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as polarization markers during the organization of LLC-PK1 cells into an epithelial membrane. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):574–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabito C. A. Phosphate uptake by a kidney cell line (LLC-PK1). Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F22–F31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennick B. R. Renal tubule transport of organic cations. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):F83–F89. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.2.F83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepúlveda F. V., Pearson J. D. Characterization of neutral amino acid uptake by cultured epithelial cells from pig kidney. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):182–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Inui K., Okano T., Saito H., Hori R. Carrier-mediated transport systems of tetraethylammonium in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90556-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


