Abstract
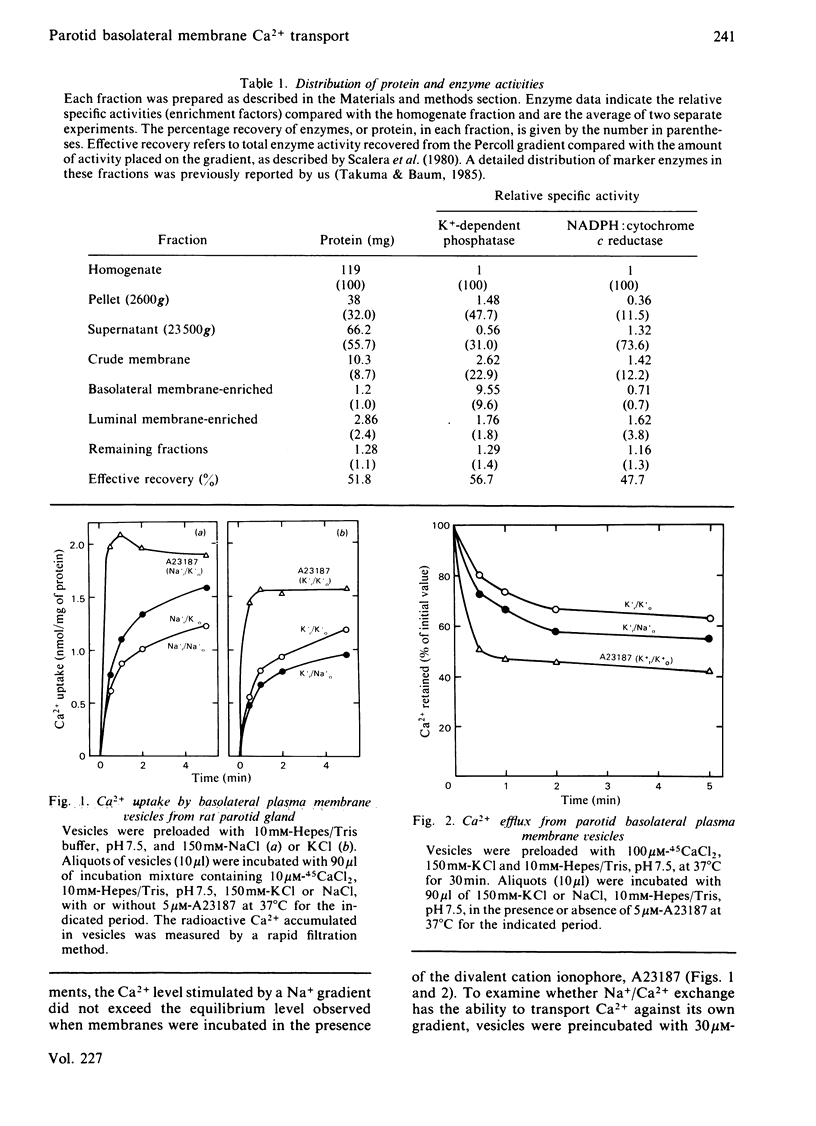
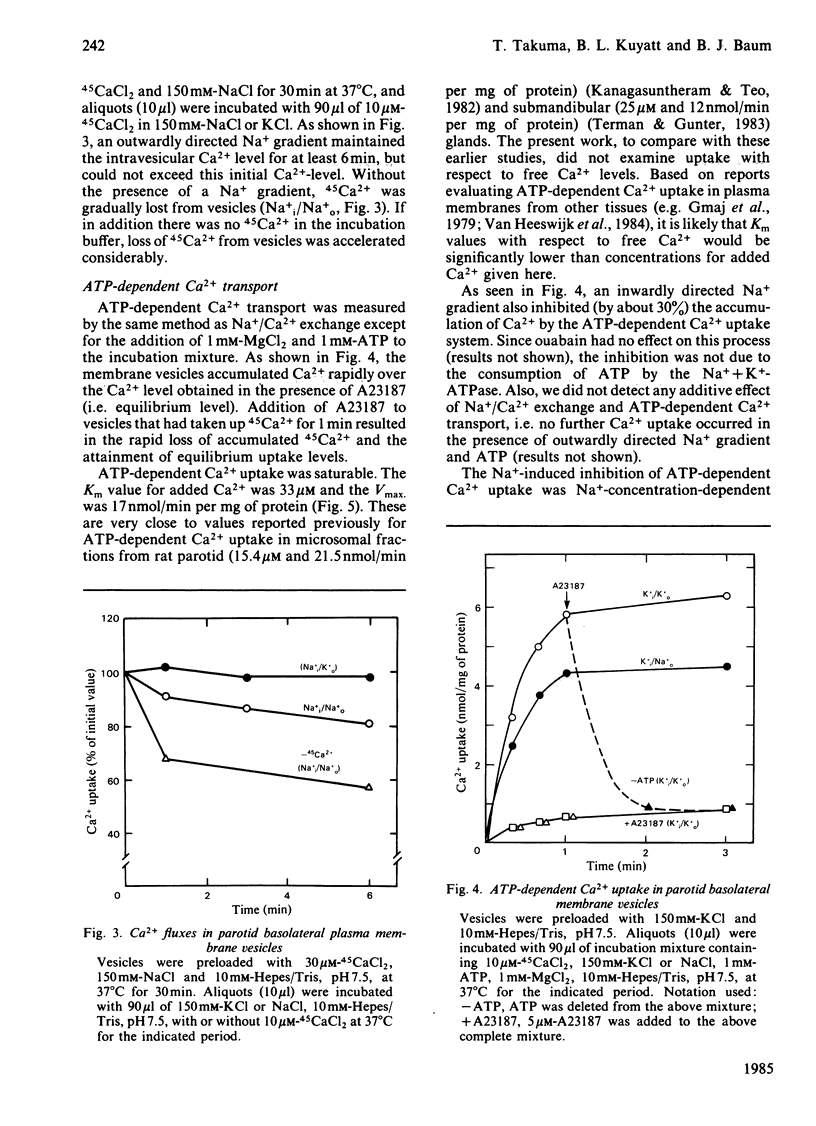
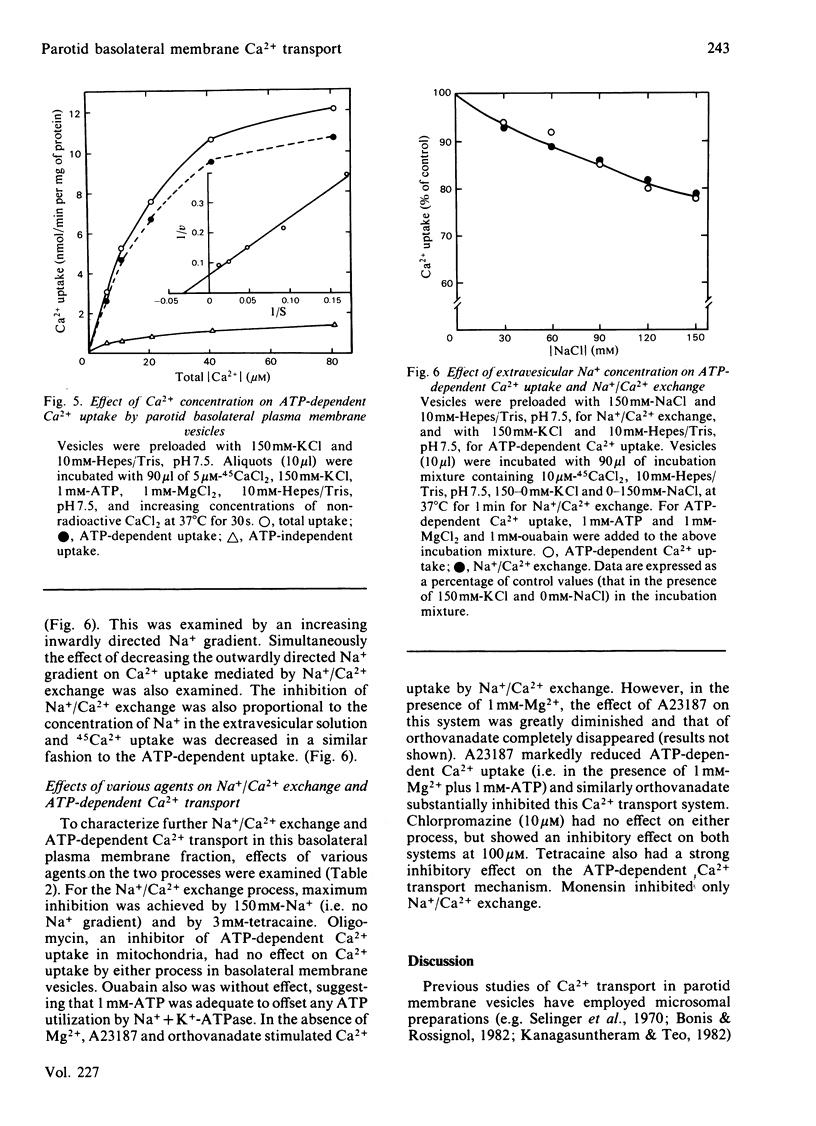
Ca2+ transport was studied by using basolateral plasma membrane vesicles from rat parotid gland prepared by a Percoll gradient centrifugation method. In these membrane vesicles, there were two Ca2+ transport systems; Na+/Ca2+ exchange and ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport. An outwardly directed Na+ gradient increased Ca2+ uptake. Ca2+ efflux from Ca2+-preloaded vesicles was stimulated by an inwardly directed Na+ gradient. However, Na+/Ca2+ exchange did not show any 'uphill' transport of Ca2+ against its own gradient. ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport exhibited 'uphill' transport. An inwardly directed Na+ gradient also decreased Ca2+ accumulation by ATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake. The inhibition of Ca2+ accumulation was proportional to the external Na+ level. Na+/Ca2+ exchange was inhibited by monensin, tetracaine and chlorpromazine, whereas ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport was inhibited by orthovanadate, tetracaine and chlorpromazine. Oligomycin had no effect on either system. These results suggest that in the parotid gland cellular free Ca2+ is extruded mainly by an ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport system, and Na+/Ca2+ exchange may modify the efficacy of that system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvan P., Castle J. D. Plasma membrane of the rat parotid gland: preparation and partial characterization of a fraction containing the secretory surface. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):8–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonis D., Rossignol B. Effect of sodium and potassium on ATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake in rat parotid microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher F. R., Putney J. W., Jr Regulation of parotid gland function by cyclic nucleotides and calcium. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:215–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. The regulation of the Na+ -Ca2+ exchanger of heart sarcolemma. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):451–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly E., Nånberg E., Nedergaard J. Na+-dependent, alpha-adrenergic mobilization of intracellular (mitochondrial) Ca2+ in brown adipocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):187–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulski K. S., Carafoli E. Calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation and calcium uptake in rat-liver microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):15–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghijsen W. E., De Jong M. D., Van Os C. H. Kinetic properties of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in basolateral plasma membranes of rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 21;730(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmaj P., Murer H., Kinne R. Calcium ion transport across plasma membranes isolated from rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1780549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa M., Aoki H., Terao N., Abiko Y., Takiguchi H. Vitamin D-mediated decrease of Ca2+-pump activity in the rat parotid gland. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(9):1175–1178. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildmann B., Schmidt A., Murer H. Ca++-transport across basal-lateral plasma membranes from rat small intestinal epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1982;65(1-2):55–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01870469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasuntheram P., Teo T. S. Parotid microsomal Ca2+ transport. Subcellular localization and characterization. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):789–794. doi: 10.1042/bj2080789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Kraus-Friedmann N. Hepatic microsomal Ca2+-dependent ATPase. Calmodulin-dependence and partial purification. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):69–75. doi: 10.1042/bj2140069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N., Godfraind T. Sodium/calcium exchange in smooth-muscle microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2180421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Stimulus-permeability coupling: role of calcium in the receptor regulation of membrane permeability. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Jun;30(2):209–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium ion exchange in cardiac membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalera V., Storelli C., Storelli-Joss C., Haase W., Murer H. A simple and fast method for the isolation of basolateral plasma membranes from rat small-intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1860177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Naim E., Lasser M. ATP-dependent calcium uptake by microsomal preparations from rat parotid and submaxillary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 21;203(2):326–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoo A. E., Ambudkar I. S. Regulation of calcium transport in cardiac cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;62(1):9–22. doi: 10.1139/y84-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Gunter T. E. Characterization of the submandibular gland microsomal calcium transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 21;730(1):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90327-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T. Na+-Ca2+ exchange activity in rabbit lymphocyte plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 12;734(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A. Na+ dependence of in vitro pancreatic amylase release. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):1023–1026. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heeswijk M. P., Geertsen J. A., van Os C. H. Kinetic properties of the ATP-dependent Ca2+ pump and the Na+/Ca2+ exchange system in basolateral membranes from rat kidney cortex. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(1):19–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01868523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


