Abstract
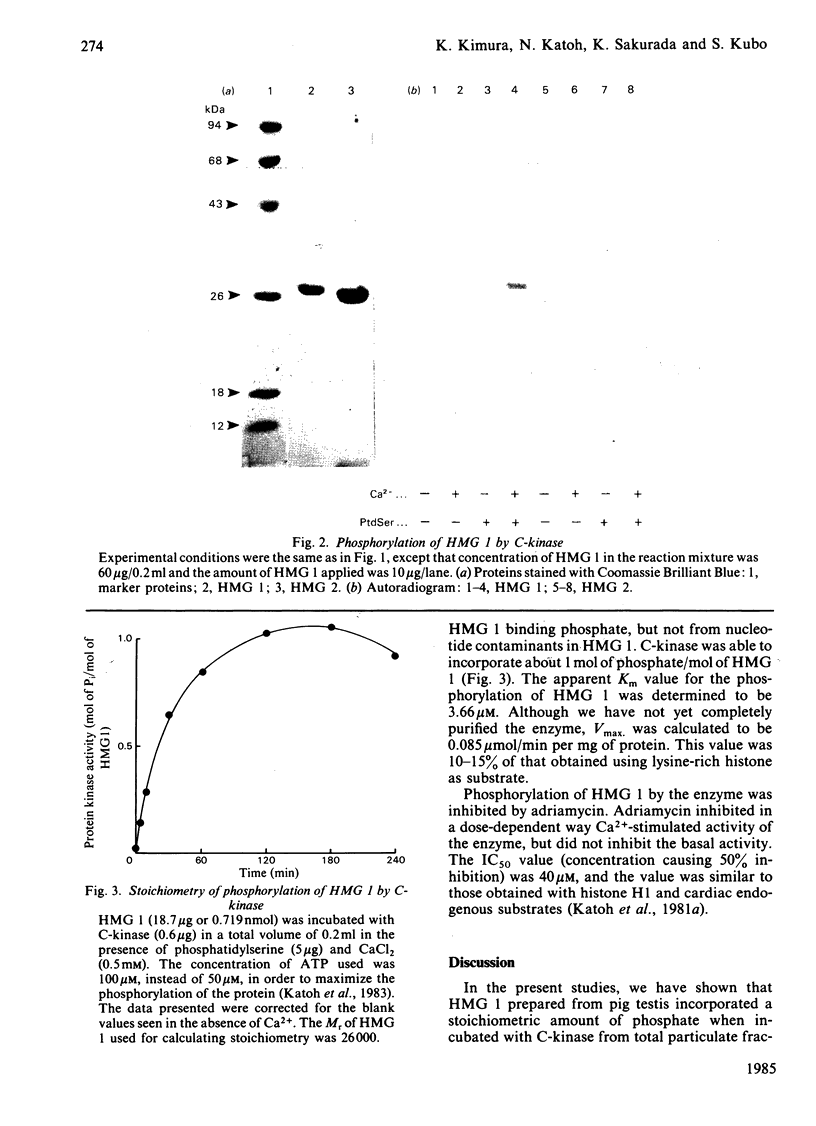
Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase was partially purified from total particulate fraction of pig testis. The enzyme phosphorylated high mobility group 1 protein (HMG 1), one of the major chromatin-associated non-histone proteins. Other HMG proteins (HMG 2, 14 and 17) were not phosphorylated by the enzyme. Exhaustive phosphorylation of HMG 1 revealed that 1 mol of phosphate was incorporated/mol of HMG 1. The apparent Km value for HMG 1 was 3.66 microM. 1,3-Diolein stimulated the phosphorylation at 10 microM-Ca2+ in the presence of phosphatidylserine. The phosphorylation of HMG 1 was inhibited by adriamycin, an inhibitor of spermatogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartfai T. Preparation of metal-chelate complexes and the design of steady-state kinetic experiments involving metal nucleotide complexes. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:219–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhorjee J. S. Differential phosphorylation of nuclear nonhistone high mobility group proteins HMG 14 and HMG 17 during the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Hopkins R. B., Isenberg I. Immunological relatedness of high mobility group chromosomal proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1694–1699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiva M., Mezquita C. Quantitative changes of high mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2 during rooster spermatogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):324–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80781-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Goodwin G. H. Demonstration of an S1-nuclease sensitive site near the human beta-globin gene, and its protection by HMG 1 and 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. O., Staller J. M., Mahsem R. A., Boutwell R. K. Retinoid-binding proteins are phosphorylated in vitro by soluble Ca+2- and phosphatidylserine-dependent protein kinase from mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Clark M. R. Activation of protein kinase in the bovine corpus luteum by phospholipid and Ca2+. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):569–574. doi: 10.1042/bj2140569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg J., Pariset C., Rondard M., Loir M., Lanneau M., Weinman S., Demaille J. Evolution of Ca2+- and cAMP-dependent regulatory mechanisms during ram spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):260–265. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Nicolas R. H., Johns E. W. An improved large scale fractionation of high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):280–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Tei Y., Hasuma T., Yukioka M., Morisawa S. Phosphorylation of HMG 17 by protein kinase NII from rat liver cell nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80915-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Liu J. F., Wang J. C. Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 change the DNA helical structure. Science. 1978 Mar 24;199(4335):1345–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.628842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin inhibitory subunit (troponin I) and tropomyosin-binding subunit (troponin T) by cardiac phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):189–195. doi: 10.1042/bj2090189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wise B. C., Wrenn R. W., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by adriamycin of calmodulin-sensitive and phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous proteins from heart. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):199–205. doi: 10.1042/bj1980199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wrenn R. W., Wise B. C., Shoji M., Kuo J. F. Substrate proteins for calmodulin-sensitive and phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases in heart, and inhibition of their phosphorylation by palmitoylcarnitine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Katoh N., Sakurada K., Kubo S. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase system in testis: localization and endogenous substrates. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2391–2399. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. I., Schjeide O. A. Micro estimation of RNA by the cupric ion catalyzed orcinol reaction. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. C., Meistrich M. L. Cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on mouse testis cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Sep;39(9):3575–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. A method for the fractionation of the high-mobility-group non-histome chromosomal proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):1034–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the beta subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2). FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Fritz R. B., Kuo J. F. Purification to homogeneity, characterization and monoclonal antibodies of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from spleen. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2090435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri K., Isackson P. J., Fishback J. L., Land M. D., Reeck G. R. Influence of nonhistone chromatin protein HMG-1 on the enzymatic digestion of purified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5059–5072. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Interactions of a purified non-histone chromosomal protein with DNA and histone. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Spiess J., Gill G. N. Phosphorylation of high mobility group 14 protein by cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4661–4668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]