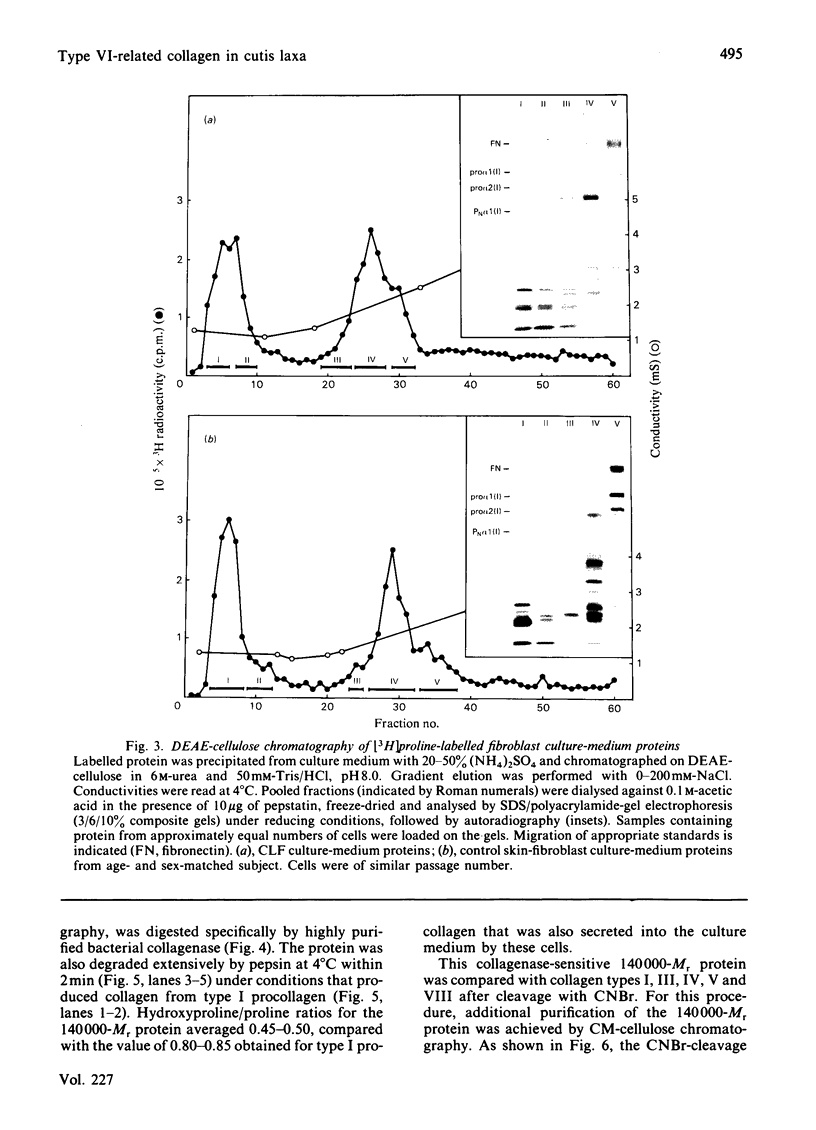
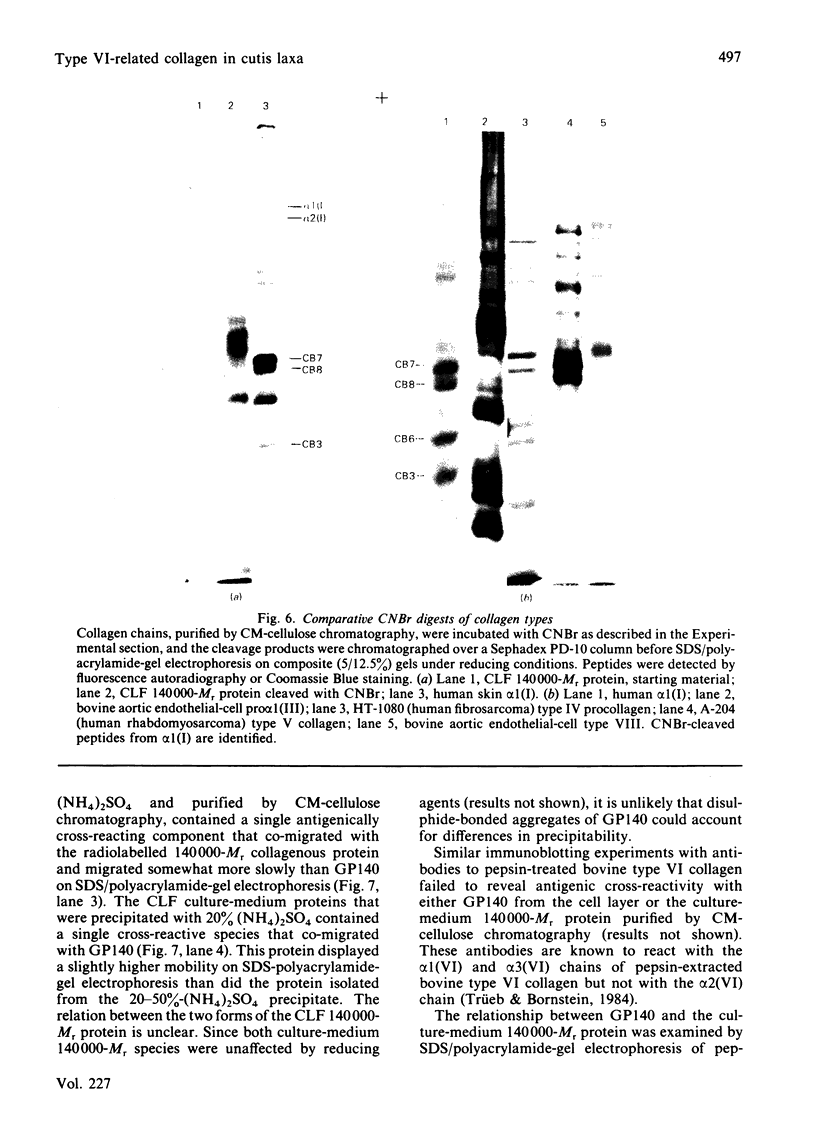
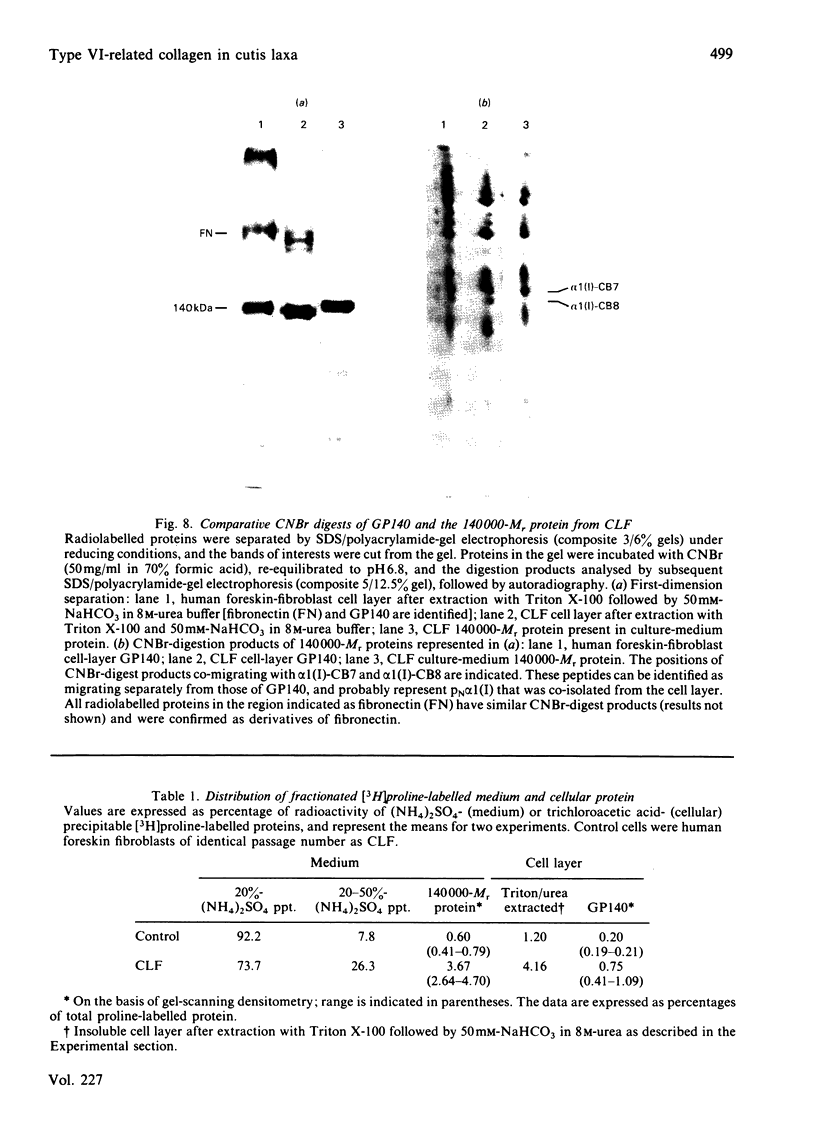
Abstract
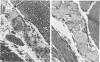
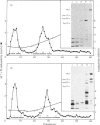
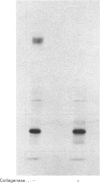
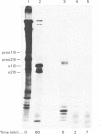
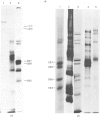
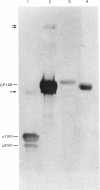
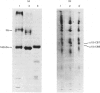
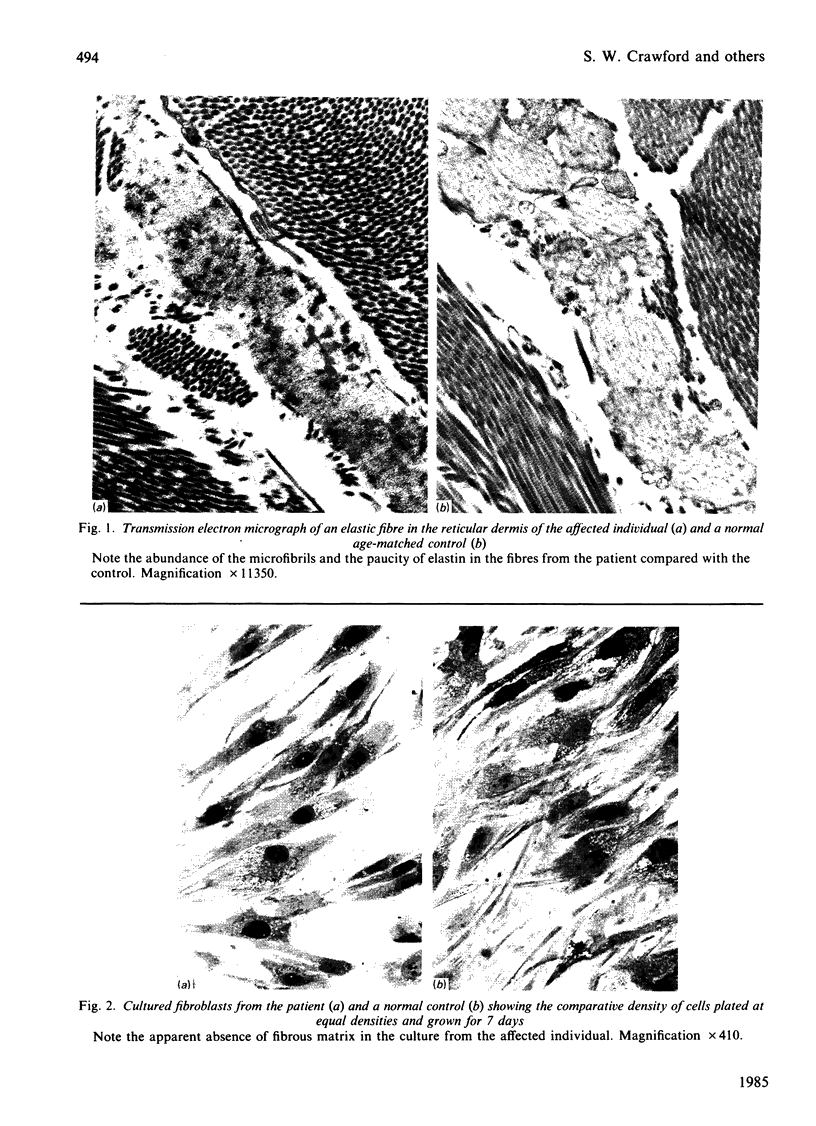
The precise biochemical defects in connective-tissue metabolism that are responsible for the laxity of skin seen in the syndrome of cutis laxa are largely unknown. We have studied fibroblasts cultured from skin explants of a 2-year-old male with the syndrome. Electron-microscopic examination of this skin revealed decreased amounts of amorphous elastin and an increase in elastin-associated microfibrils. Although the cultured fibroblasts were similar to control skin fibroblasts in morphology, growth rate and total protein synthesis, there was a 4-6-fold increase in accumulation of a collagenous protein of Mr 140 000 in both the culture medium and in the cell layer. This protein was structurally distinct from collagen types I, III, IV, V and VIII. It was found to be related to a cell-surface-associated glycoprotein, GP140, by both antigenic cross-reactivity and peptide mapping. Our data support observations that GP140 is a precursor of at least one form of pepsin-extracted type VI collagen.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball M. A., McCullough J. L., Weinstein G. D. Percutaneous absorption of methotrexate: effect on epidermal DNA synthesis in hairless mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79(1):7–10. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12510415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Peterson K. E., Byers P. H. Peptide mapping of collagen chains using CNBr cleavage of proteins within polyacrylamide gels. Coll Relat Res. 1981 Nov;1(6):543–548. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(81)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Siegel R. C., Holbrook K. A., Narayanan A. S., Bornstein P., Hall J. G. X-linked cutis laxa: defective cross-link formation in collagen due to decreased lysyl oxidase activity. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):61–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Hakomori S. A new cell surface, detergent-insoluble glycoprotein matrix of human and hamster fibroblasts. The role of disulfide bonds in stabilization of the matrix. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6953–6960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G. The cooperative role of the transformation-sensitive glycoproteins, GP140 and fibronectin, in cell attachment and spreading. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3249–3257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G. The role of intermolecular disulfide bonding in deposition of GP140 in the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G. Transformation-dependent alterations is glycoproteins of extracellular matrix of human fibroblasts. Characterization of GP250 and the collagen-like GP140. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13805–13815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary E. G., Gibson M. A. Elastin-associated microfibrils and microfibrillar proteins. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:97–209. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Bornstein P. Collagen synthesis by human amniotic fluid cells in culture: characterization of a procollagen with three identical proalpha1(I) chains. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5499–5509. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel F., Grant M. E., Legrand Y. J., Souchon H., Tobelem G., Jackson D. S., Caen J. P. Interaction of blood platelets with a microfibrillar extract from adult bovine aorta: requirement for von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):551–554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. A., Cleary E. G. A collagen-like glycoprotein from elastin-rich tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 29;105(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90926-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller-Harrison R. A., Carter W. G. Pepsin-generated type VI collagen is a degradation product of GP140. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6858–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Holbrook K. A. Calcium regulation of cell-cell contact and differentiation of epidermal cells in culture. An ultrastructural study. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):127–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Engvall E. Type VI collagen. Studies on its localization, structure, and biosynthetic form with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3955–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jander R., Troyer D., Rauterberg J. A collagen-like glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix is the undegraded form of type VI collagen. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3675–3681. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Sear C. H., Grant M. E. An ultrastructural study of fibroblasts derived from bovine ligamentum nuchae and their capacity for elastogenesis in culture. J Pathol. 1980 May;131(1):35–53. doi: 10.1002/path.1711310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. R., Ayad S., Shuttleworth C. A., Grant M. E. A collagenous glycoprotein found in dissociative extracts of foetal bovine nuchal ligament. Evidence for a relationship with type VI collagen. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):395–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2200395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivaniemi H., Peltonen L., Palotie A., Kaitila I., Kivirikko K. I. Abnormal copper metabolism and deficient lysyl oxidase activity in a heritable connective tissue disorder. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):730–733. doi: 10.1172/JCI110503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg S. I., Poppke D. C., Williams B. R. Isolation of elastic tissue microfibrils derived from cultured cells of calf ligamentum nuchae. Connect Tissue Res. 1980;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.3109/03008208009152115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen L., Kuivaniemi H., Palotie A., Horn N., Kaitila I., Kivirikko K. I. Alterations in copper and collagen metabolism in the Menkes syndrome and a new subtype of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6156–6163. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bornstein P. The elastic fiber. I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Bornstein P. Characterization of a novel collagen chain in human placenta and its relation to AB collagen. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3815–3822. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Bornstein P. Preparation and characterization of procollagens and procollagen-collagen intermediates. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):96–127. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Crouch E., Bornstein P. Collagen synthesis by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5433–5442. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Pritzl P., Bornstein P. A unique, pepsin-sensitive collagen synthesized by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5747–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sear C. H., Grant M. E., Jackson D. S. The nature of the microfibrillar glycoproteins of elastic fibres. A biosynthetic study. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):587–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1940587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sear C. H., Kewley M. A., Jones C. J., Grant M. E., Jackson D. S. The identification of glycoproteins associated with elastic-tissue microfibrils. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):715–718. doi: 10.1042/bj1700715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Ventrella G., Field M. J., Hinnie J., Onyezili N. I., Griffiths R. Characterization of a structural glycoprotein from bovine ligamentum nuchae exhibiting dual amine oxidase activity. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5424–5429. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüeb B., Bornstein P. Characterization of the precursor form of type VI collagen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8597–8604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]