Abstract
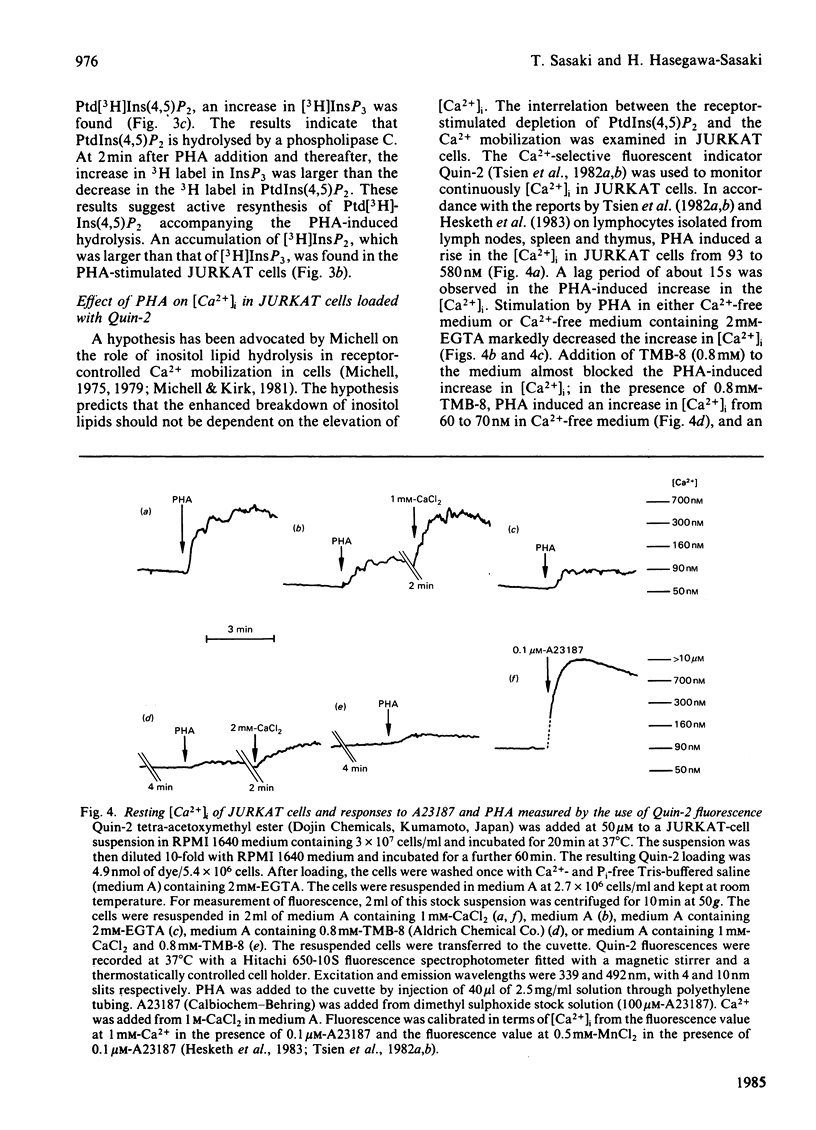
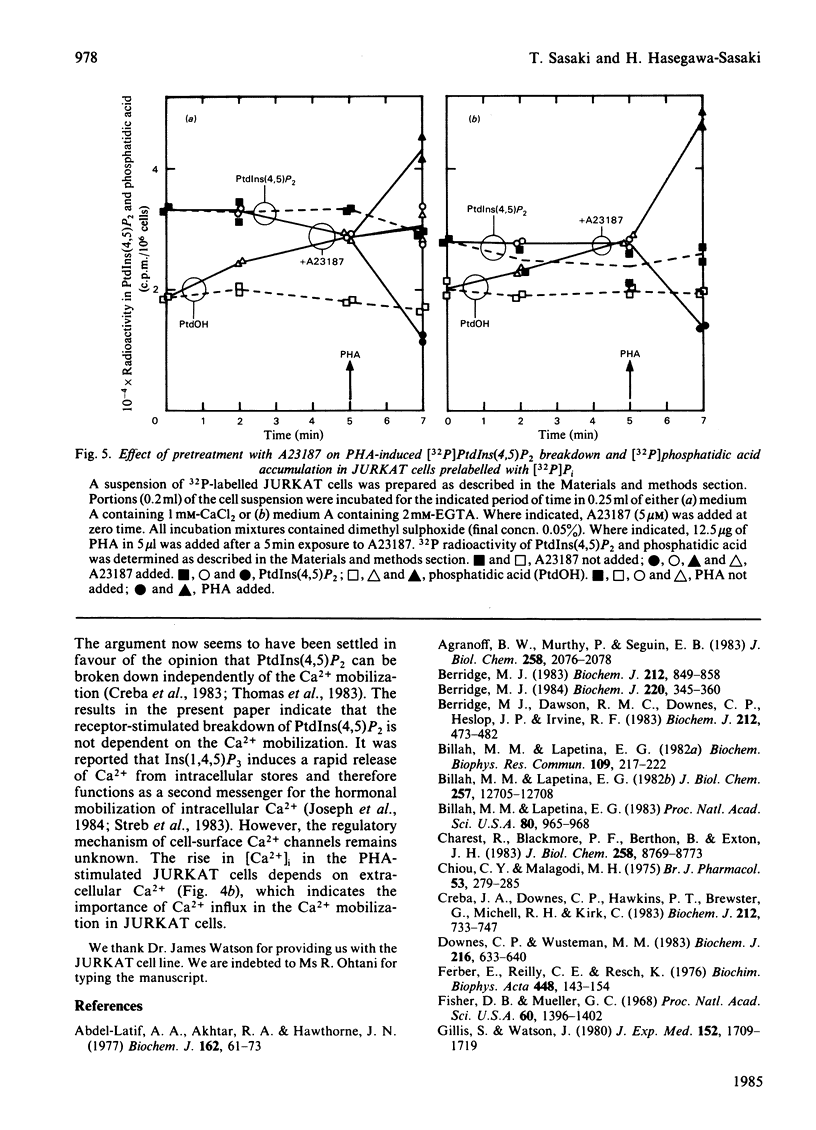
Addition of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) to the [32P]Pi-prelabelled JURKAT cells, a human T-cell leukaemia line, resulted in a decrease of [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] to about 35% of the control value. The decrease was almost complete within 30s after the PHA addition. This decrease was followed by an increase in the 32P-labelling of phosphatidic acid (maximally 2.8-fold at 2 min). The stimulation of myo-[2-3H]inositol-prelabelled JURKAT cells by PHA induced an accumulation of [2-3H]inositol trisphosphate in the presence of 5 mM-LiCl. The result indicates hydrolysis of PtdIns (4,5)P2 by a phospholipase C. The PHA stimulation of JURKAT cells induced about 6-fold increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]i, which was reported by Quin-2, a fluorescent Ca2+ indicator. Studies with partially Ca2+-depleted JURKAT cells, with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187, and with 8-(diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate indicate that the breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 is not mediated through changes of [Ca2+]i. These results therefore indicate that the PHA-induced breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 in JURKAT cells is not dependent on the Ca2+ mobilization.
Full text
PDF

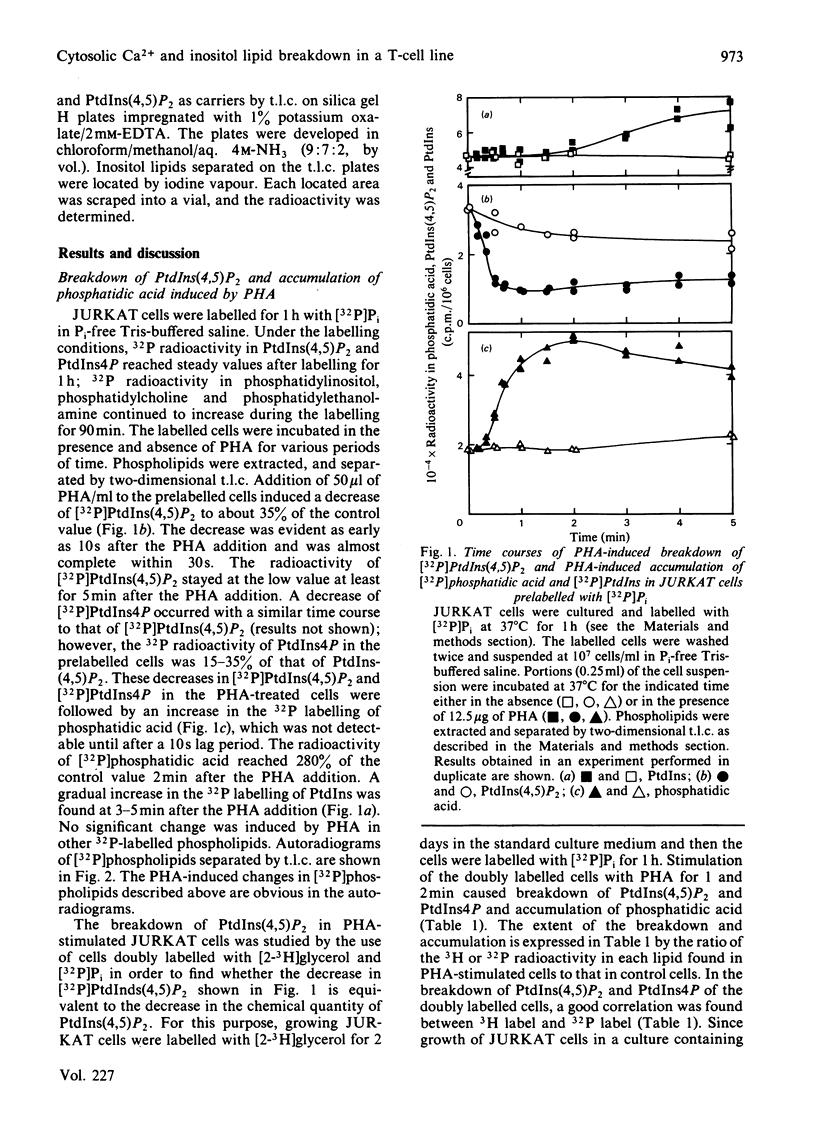


Images in this article
Selected References
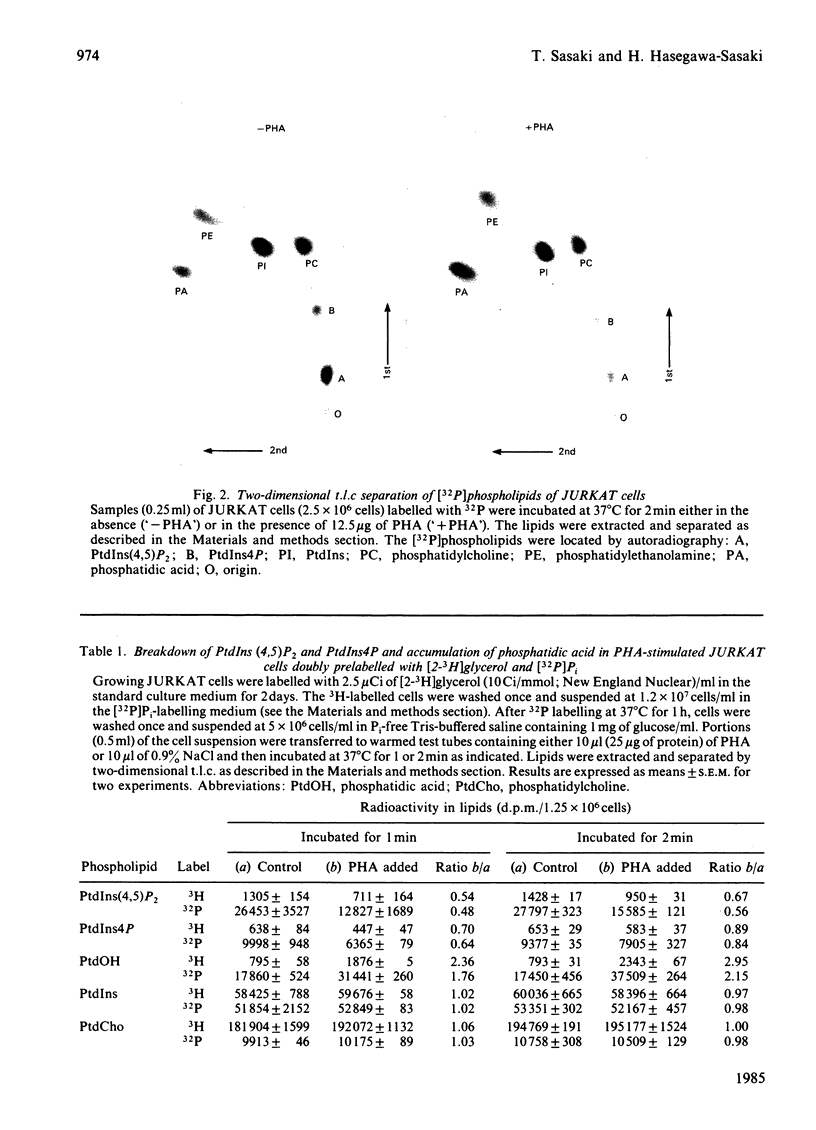
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A., Akhtar R. A., Hawthorne J. N. Acetylcholine increases the breakdown of triphosphoinositide of rabbit iris muscle prelabelled with [32P] phosphate. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):61–73. doi: 10.1042/bj1620061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is insensitive to CA2+ mobilization in stimulated platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Platelet-activating factor stimulates metabolism of phosphoinositides in horse platelets: possible relationship to Ca2+ mobilization during stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):965–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Berthon B., Exton J. H. Changes in free cytosolic Ca2+ in hepatocytes following alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation. Studies on Quin-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8769–8773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou C. Y., Malagodi M. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of a new Ca-2+ antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)octyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride in smooth and skeletal muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):279–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber E., Reilly C. E., Resch K. Phospholipid metabolism of stimulated lymphocytes. Comparison of the activation of acyl-CoA:lysolecithin acyltransferase with the binding of concanavalin A to thymocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 21;448(1):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Mueller G. C. An early alteration in the phospholipid metabolism of lymphocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1396–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
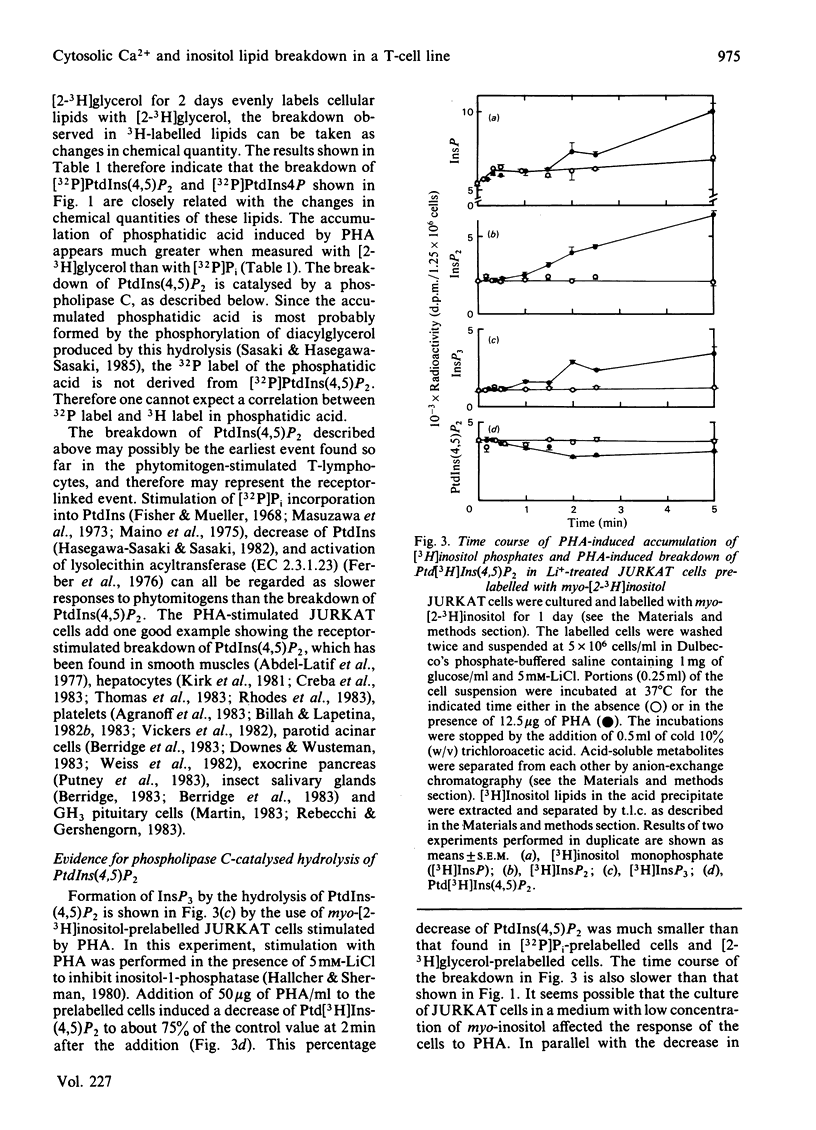
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H., Sasaki T. Phytohemagglutinin induces rapid degradation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and transient accumulation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol in a human T lymphoblastoid cell line, CCRF-CEM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 20;754(3):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H., Sasaki T. Phytomitogen-induced stimulation of syntheses de novo of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol in rat and human lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 23;666(2):252–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H., Sasaki T. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol accompanied by accumulation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol in rat lymphocytes stimulated by concanavalin A. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):463–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. The role of mitogenic lectins in T-cell triggering. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):239–241. doi: 10.1038/280239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maino V. C., Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Relationship between enhanced turnover of phosphatidylinositol and lymphocyte activation by mitogens. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):247–252. doi: 10.1042/bj1460247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagodi M. H., Chiou C. Y. Pharmacological evaluation of a new Ca++ antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)octyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride (TMB-8): studies in skeletal muscles. Pharmacology. 1974;12(1):20–31. doi: 10.1159/000136517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly activates the phosphodiester hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in GH3 pituitary cells. Evidence for the role of a polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14816–14822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa Y., Osawa T., Inoue K., Nojima S. Effects of various mitogens on the phospholipid metabolism of human peripheral lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Takeshige K., Minakami S. Inhibition of phagocytotic metabolic changes of leukocytes by an intracellular calcium-antagonist 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):974–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Mechanism of T cell activation: role and functional relationship of HLA-DR antigens and interleukins. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:73–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Phosphatidylinositol breakdown induced by vasopressin and epinephrine in hepatocytes is calcium-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11323–11331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Burgess G. M., Halenda S. P., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P. Effects of secretagogues on [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in the exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2120483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Gershengorn M. C. Thyroliberin stimulates rapid hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by a phosphodiesterase in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. Evidence for an early Ca2+-independent action. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in hepatocytes by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2770–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Deykin D. The activation by Ca2+ of platelet phospholipase A2. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate and 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):409–422. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Inhibition by neomycin of polyphosphoinositide turnover in subcellular fractions of guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1119–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Ruscetti F. W. T-cell growth factor and the culture of cloned functional T cells. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:137–175. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60920-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Changes in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 10 seconds after stimulation of washed rabbit platelets with ADP. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1247–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Receptor-mediated net breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):555–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2060555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]