Abstract
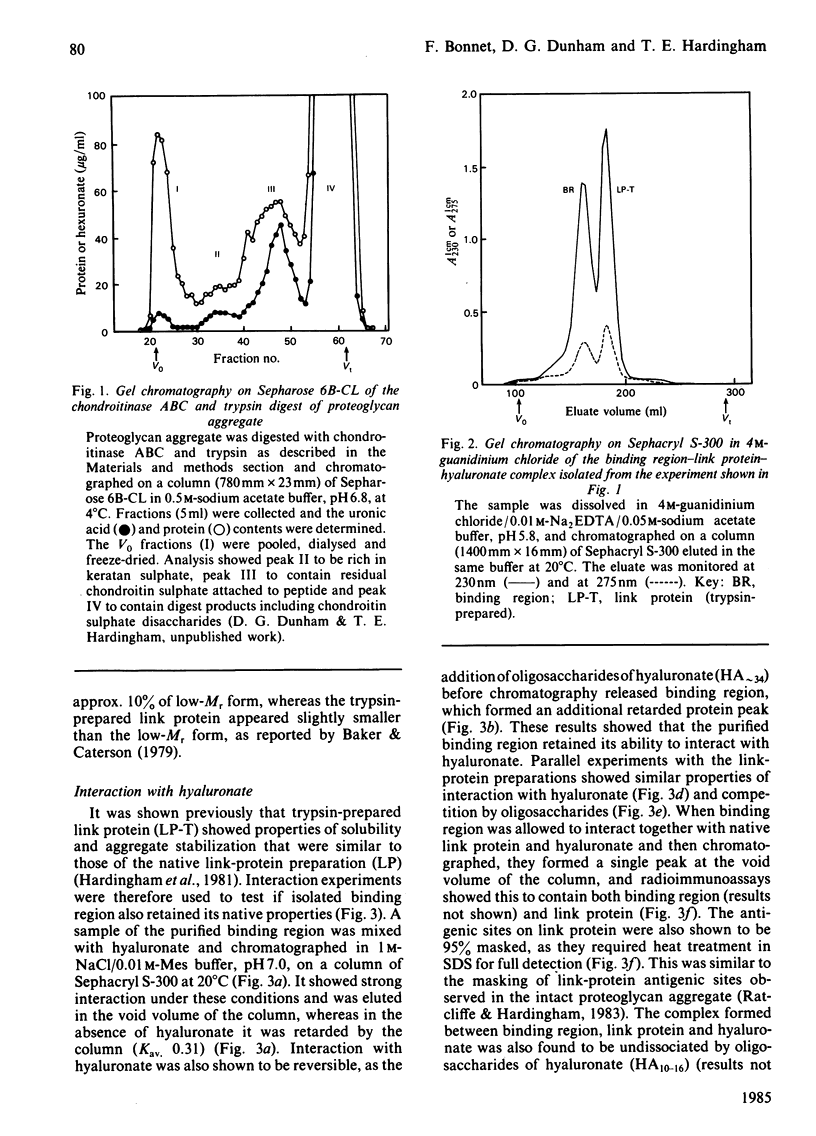
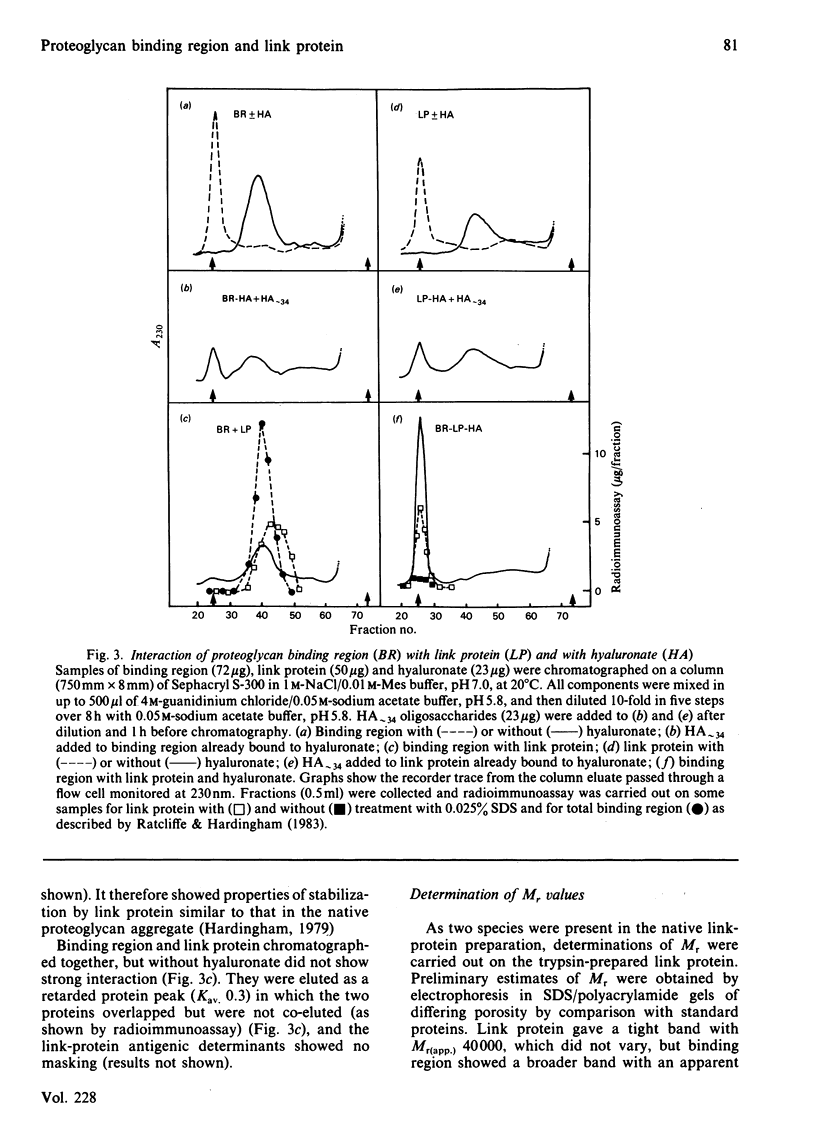
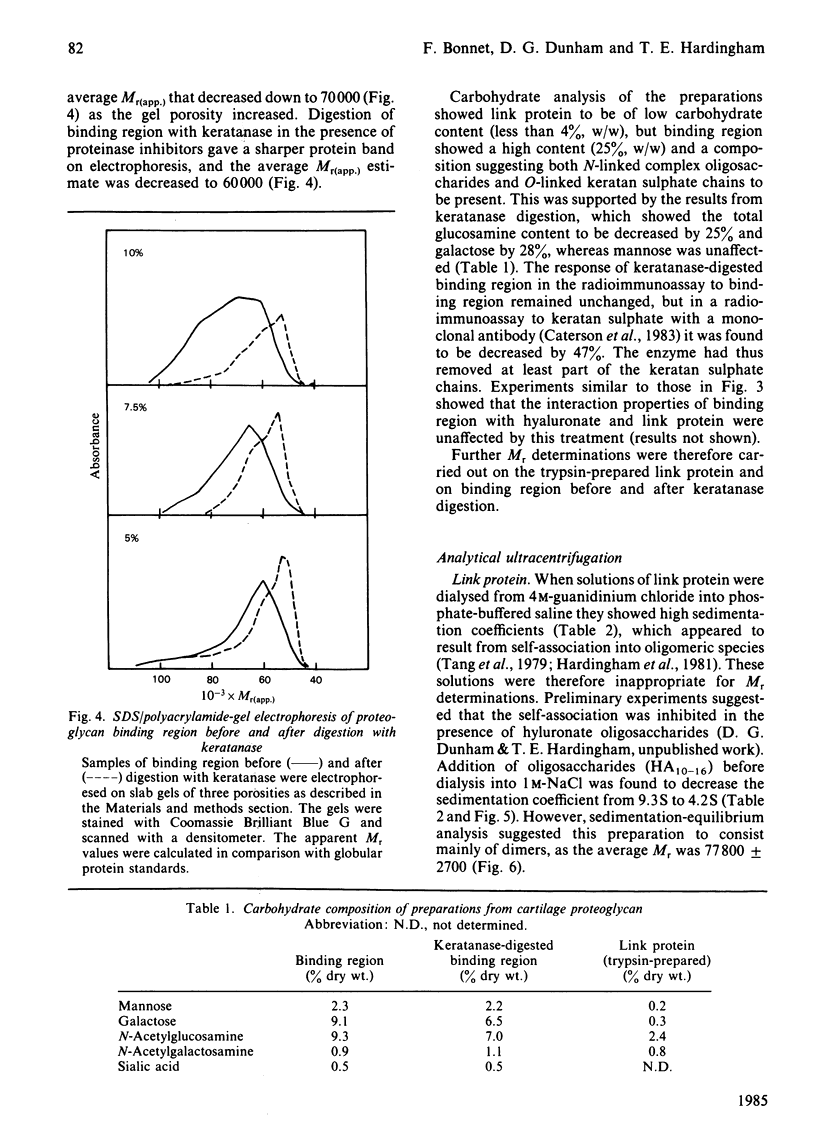
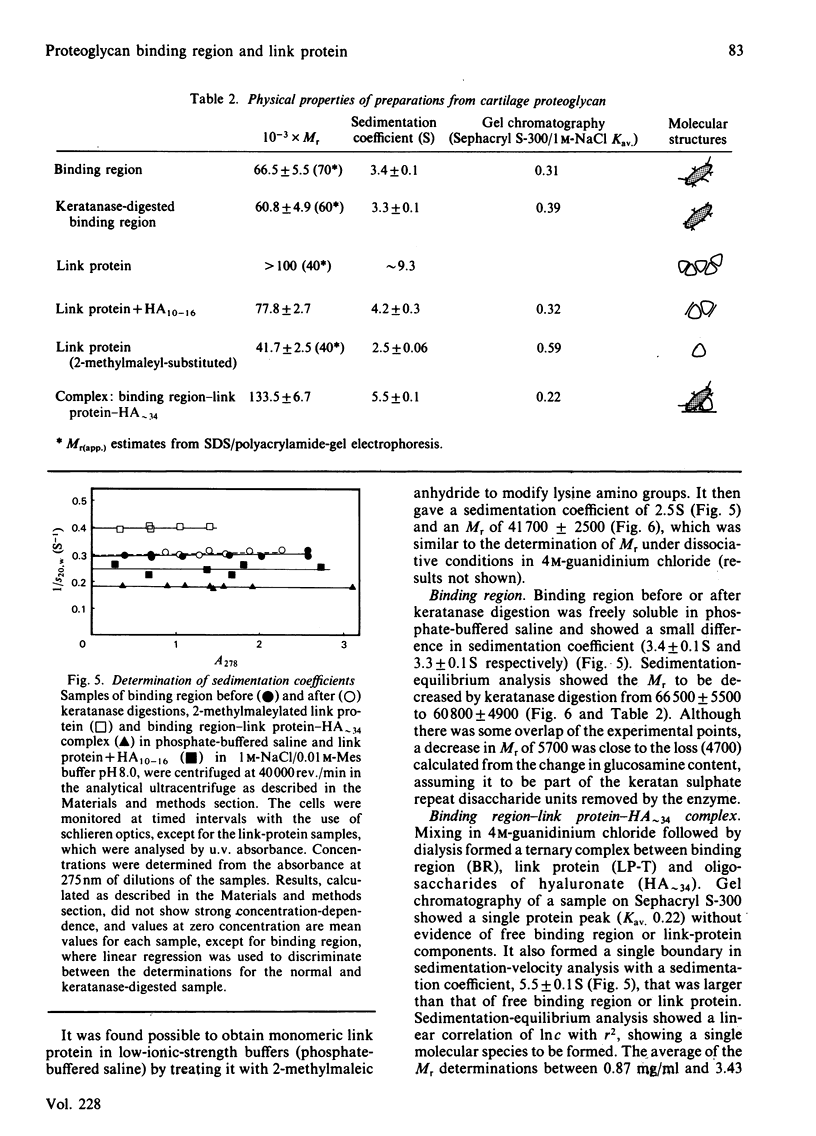
Binding region and link protein were prepared from pig laryngeal cartilage proteoglycans after chondroitinase ABC and trypsin digestion. Experiments on gel chromatography showed the purified binding region to interact reversibly with hyaluronate (HA), and this binding was also shown to be stabilized by native link protein. The trypsin-prepared link protein showed properties of self-association in solution that were partially inhibited by oligosaccharides (HA10-16) and abolished by modification of free amino groups (lysine residues) with 2-methylmaleic anhydride. The Mr (sedimentation equilibrium) of the modified link protein was 41 700. Analysis of binding region showed it to contain 25% (w/w) carbohydrate, mainly in galactose, glucosamine, mannose and galactosamine. It contained some keratan sulphate, as digestion with endo-beta-D-galactosidase (keratanase) removed 28% galactose and 25% glucosamine and the Mr (sedimentation equilibrium) decreased from 66 500 to 60 800. After keratanase digestion the interaction with polyclonal antibodies specific for binding region was unaffected, but the response in a radioimmunoassay with a monoclonal antibody to keratan sulphate was decreased by 47%. Preparation of a complex between binding region, link protein and HA approximately 34 showed a single component (5.5S) of Mr (sedimentation equilibrium) 133 500. In this complex the antigenic determinants of link protein appeared masked, as previously found with proteoglycan aggregates. The isolated binding region and link protein were thus shown to retain properties comparable with those involved in the structure and organization of proteoglycan aggregates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Boezi J. A. A new staining technique for proteins in polyacrylamide gels using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):580–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Périn J. P., Jollès P. Isolation and chemical characterization of two distinct "link proteins" from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90578-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLANAN M. J., CARROLL W. R., MITCHELL E. R. Physical and chemical properties of protamine from the sperm of salmon (Oncorhynchus tschawytscha). J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. Identification of a monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes corneal and skeletal keratan sulfate. Monoclonal antibodies to cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8848–8854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. An assessment of methanolysis and other factors used in the analysis of carbohydrate-containing materials. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1042/bj1251009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner J. E., Brown M. L., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Affinity binding of the cartilage proteoglycan protein-keratan sulfate core to immobilized hyaluronic acid. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland R. L. Binding of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides by cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1140–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltz L. L., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Schrode J., Hascall V. C. Structure of the complex between hyaluronic acid, the hyaluronic acid-binding region, and the link protein of proteoglycan aggregates from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1381–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Glédic S., Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès P. Identity of the protein cores of the two link proteins from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Localization of their sugar moieties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14759–14761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski I. A., Sheehan J. K., Phelps C. F., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Equilibrium-binding studies of pig laryngeal cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronate oligosaccharide fractions. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):107–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1850107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Cooper K. M. An improved automated periodate-resorcinol method for the determination of sialic acid. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike Y., Kimata K., Shinomura T., Nakazawa K., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of chick-embryo cartilage proteoglycan by selective degradation with chondroitin lyases (chondroitinases) and endo-beta-D-galactosidase (keratanase). Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):193–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1910193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Miller A., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Physical properties of the hyaluronate binding region of proteoglycan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Densitometric and small-angle neutron scattering studies of carbohydrates and carbohydrate-protein macromolecules. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):69–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe A., Hardingham T. Cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Radioimmunoassays and the detection of masked determinants in aggregates. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):371–378. doi: 10.1042/bj2130371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L. H., Rosenberg L., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Properties of a soluble form of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10523–10531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A. A comparative study of the binding of cartilage link protein and the hyaluronate-binding region of the cartilage proteoglycan to hyaluronate-substituted Sepharose gel. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):297–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1990297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell B. V., Mankin D. P., Ho P. K., Mankin H. J. Cell-free synthesis of cartilage proteins: partial identification of proteoglycan core and link proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2269–2275. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Vertel B. M., Dorfman A. Translation and characterization of messenger RNAs in differentiating chicken cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4847–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander J., Heinegárd D. Immunochemical analysis of cartilage proteoglycans. Radioimmunoassay of the molecules and the substructures. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):687–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1870687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


