Abstract
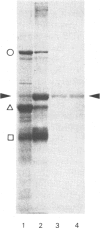
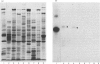
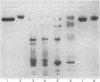
We recently described the tissue distribution of PAS IV (periodic acid/Schiff-positive Band IV), a hydrophobic glycoprotein isolated from bovine milk-fat-globule membrane [Greenwalt & Mather (1985) J. Cell Biol. 100, 397-408]. By using immunofluorescence techniques, PAS IV was detected in mammary epithelial cells, the bronchiolar epithelium of lung, and the capillary endothelium of several tissues, including heart, salivary gland, pancreas, spleen and intestine. In the present paper we describe the specificity of the antibodies used for these studies. Two monoclonal antibodies, E-1 and E-3, were shown by solid-phase immunoassay and immunoaffinity chromatography to be specific for PAS IV (of Mr 76000) in milk-fat-globule membrane and recognize a glycoprotein of slightly higher Mr (85000) in heart. Affinity-purified rabbit antibodies to PAS IV were also shown to recognize components of Mr 76000 and 85000 in fat-globule membrane and heart respectively, by using immunoblotting procedures after sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Additionally, an immunoreactive protein in lung of Mr 85000 was detected. Despite these differences in molecular size, the fat-globule membrane and heart forms of PAS IV were shown to be very similar by peptide-mapping techniques. The possible significance of the expression of similar forms of PAS IV in both epithelial and capillary endothelial cells is briefly discussed.
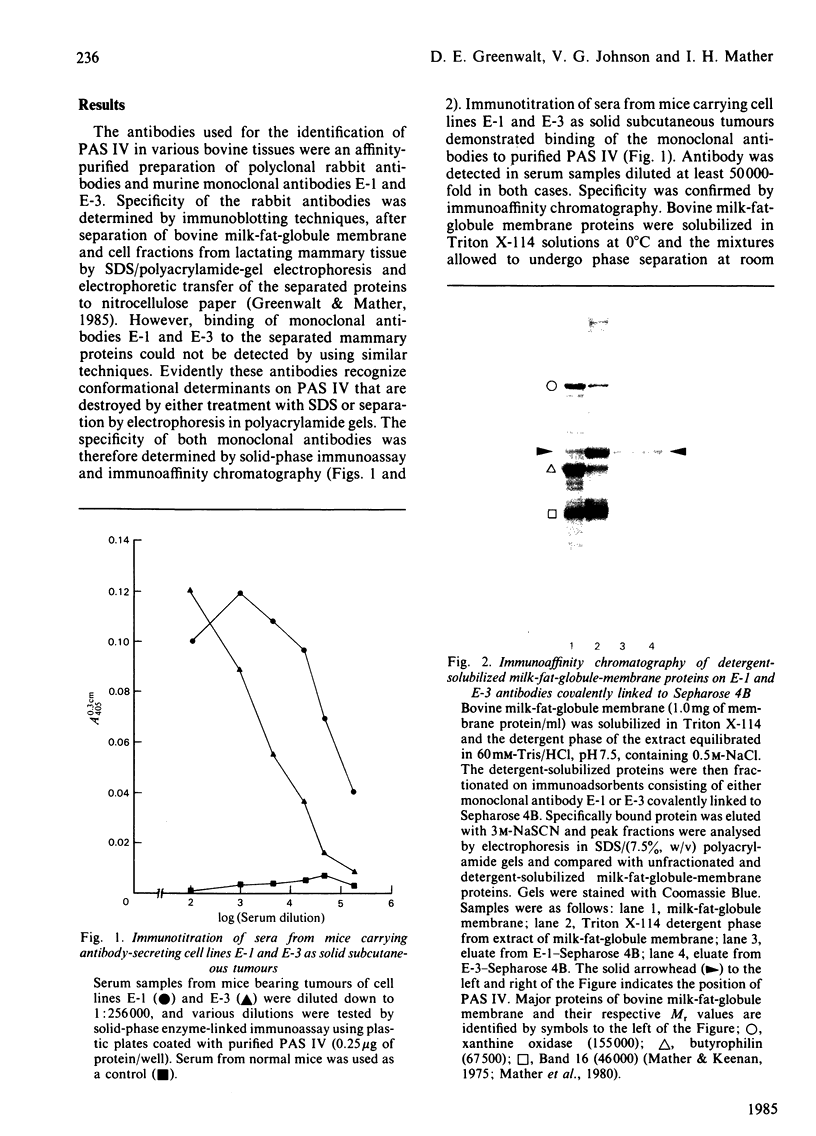
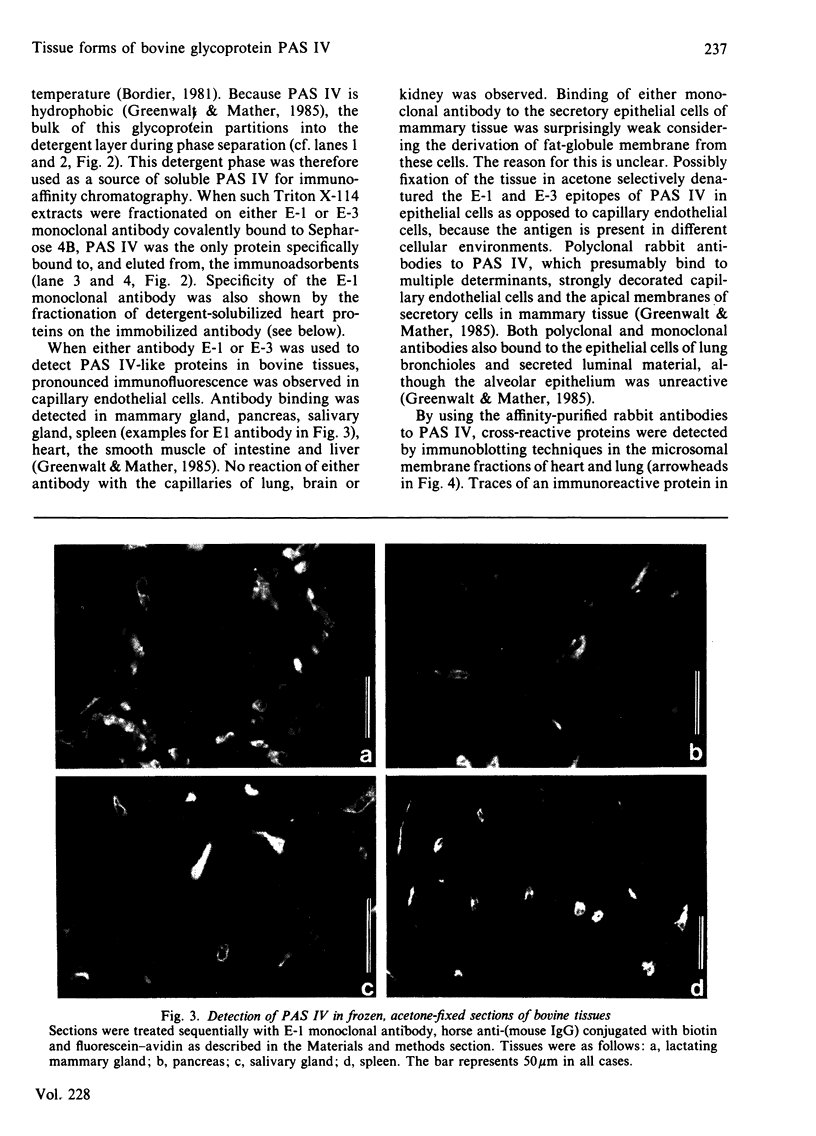
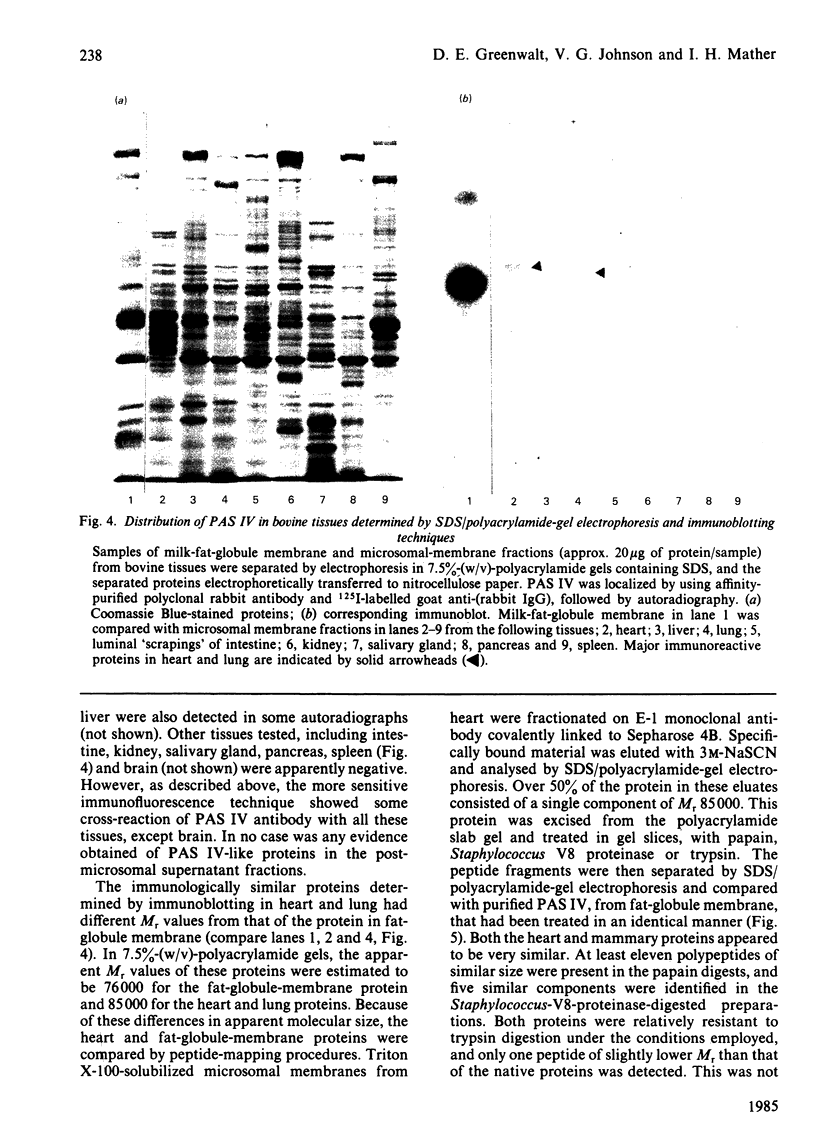
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arklie J., Taylor-Papadimitrious J., Bodmer W., Egan M., Millis R. Differentiation antigens expressed by epithelial cells in the lactating breast are also detectable in breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder G., Heid H., Jarasch E. D., Keenan T. W., Mather I. H. Characteristics of membrane-bound and soluble forms of xanthine oxidase from milk and endothelial cells of capillaries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 4;701(3):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster C. S., Edwards P. A., Dinsdale E. A., Neville A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the human mammary gland. I. Distribution of determinants in non-neoplastic mammary and extra mammary tissues. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;394(3):279–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00430671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Heid H. W., Grund C., Winter S., Freudenstein C., Schmid E., Jarasch E. D., Keenan T. W. Antibodies to the major insoluble milk fat globule membrane-associated protein: specific location in apical regions of lactating epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):485–494. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giloh H., Sedat J. W. Fluorescence microscopy: reduced photobleaching of rhodamine and fluorescein protein conjugates by n-propyl gallate. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1252–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.7112126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwalt D. E., Mather I. H. Characterization of an apically derived epithelial membrane glycoprotein from bovine milk, which is expressed in capillary endothelia in diverse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):397–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heid H. W., Winter S., Bruder G., Keenan T. W., Jarasch E. D. Butyrophilin, an apical plasma membrane-associated glycoprotein characteristic of lactating mammary glands of diverse species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb;728(2):228–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarasch E. D., Grund C., Bruder G., Heid H. W., Keenan T. W., Franke W. W. Localization of xanthine oxidase in mammary-gland epithelium and capillary endothelium. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaetzel C. S., Mather I. H., Bruder G., Madara P. J. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to bovine xanthine oxidase. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):917–925. doi: 10.1042/bj2190917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather I. H., Keenan T. W. Studies on the structure of milk fat globule membrane. J Membr Biol. 1975 Apr 23;21(1-2):65–85. doi: 10.1007/BF01941062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather I. H. Separation of the proteins of bovine milk-fat globule membrane by electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather I. H., Sullivan C. H., Madara P. J. Detection of xanthine oxidase and immunologically related proteins in fractions from bovine mammary tissue and milk after electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulphate. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2020317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather I. H., Tamplin C. B., Irving M. G. Separation of the proteins of bovine milk-fat-globule membrane by electrofocusing with retention of enzymatic and immunological activity. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(2):327–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather I. H., Weber K., Keenan T. W. Membranes of mammary gland. XII. Loosely associated proteins and compositional heterogeneity of bovine milk fat globule membrane. J Dairy Sci. 1977 Mar;60(3):394–402. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(77)83878-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Switzer R. C., Van Keuren M. L. Trace polypeptides in cellular extracts and human body fluids detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis and a highly sensitive silver stain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4335–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Walter G., Singer S. J. On the nature of crossreactions observed with antibodies directed to defined epitopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton S., Keenan T. W. The milk fat globule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):273–309. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]