Abstract
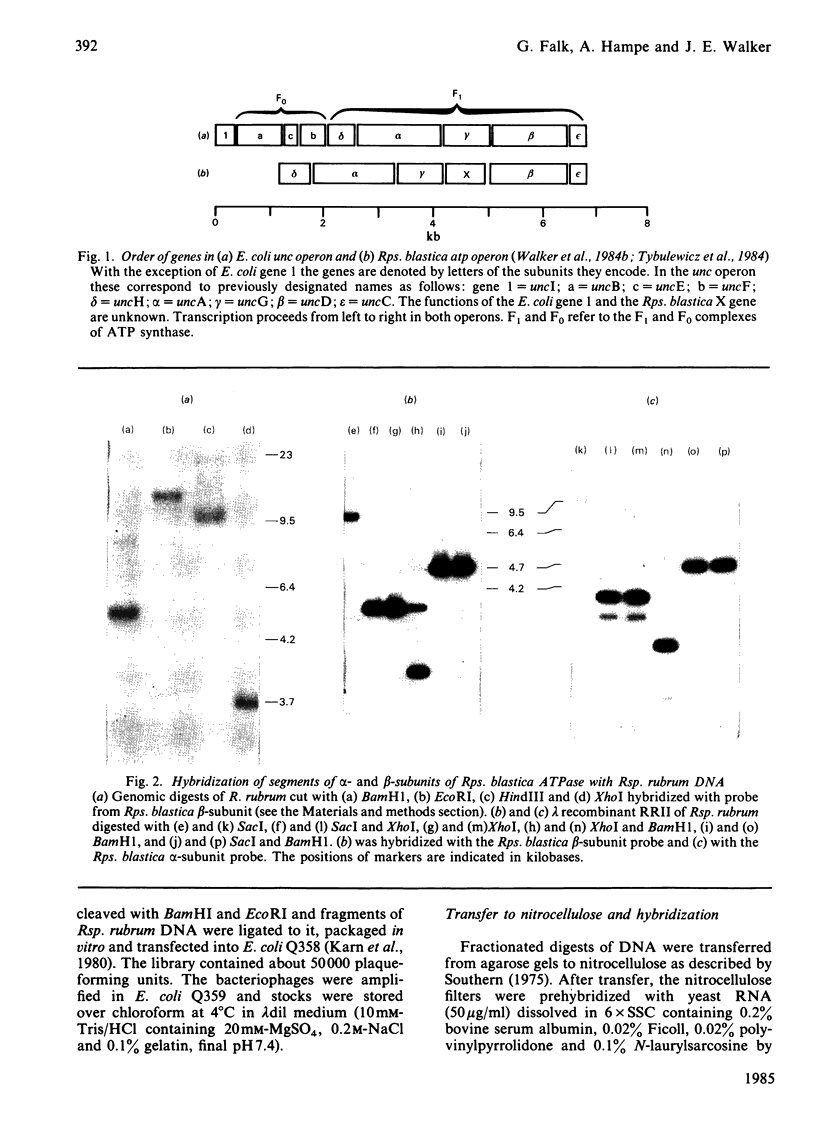
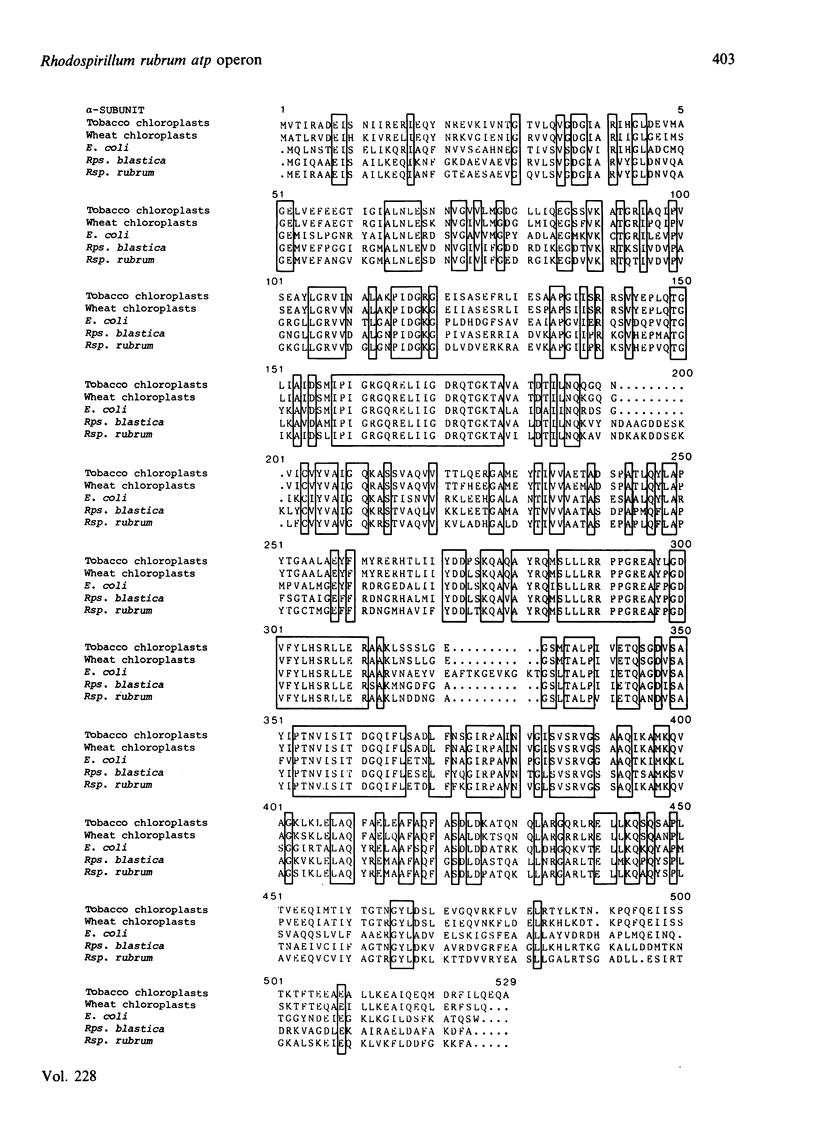
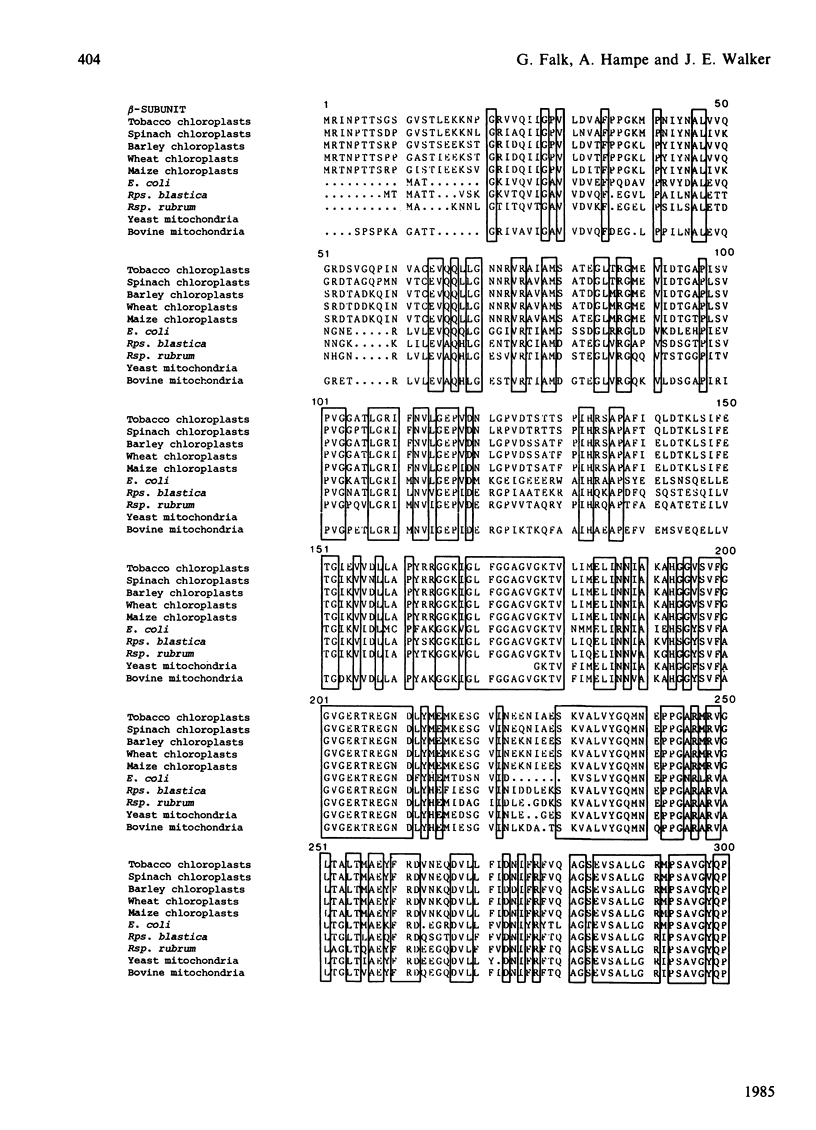
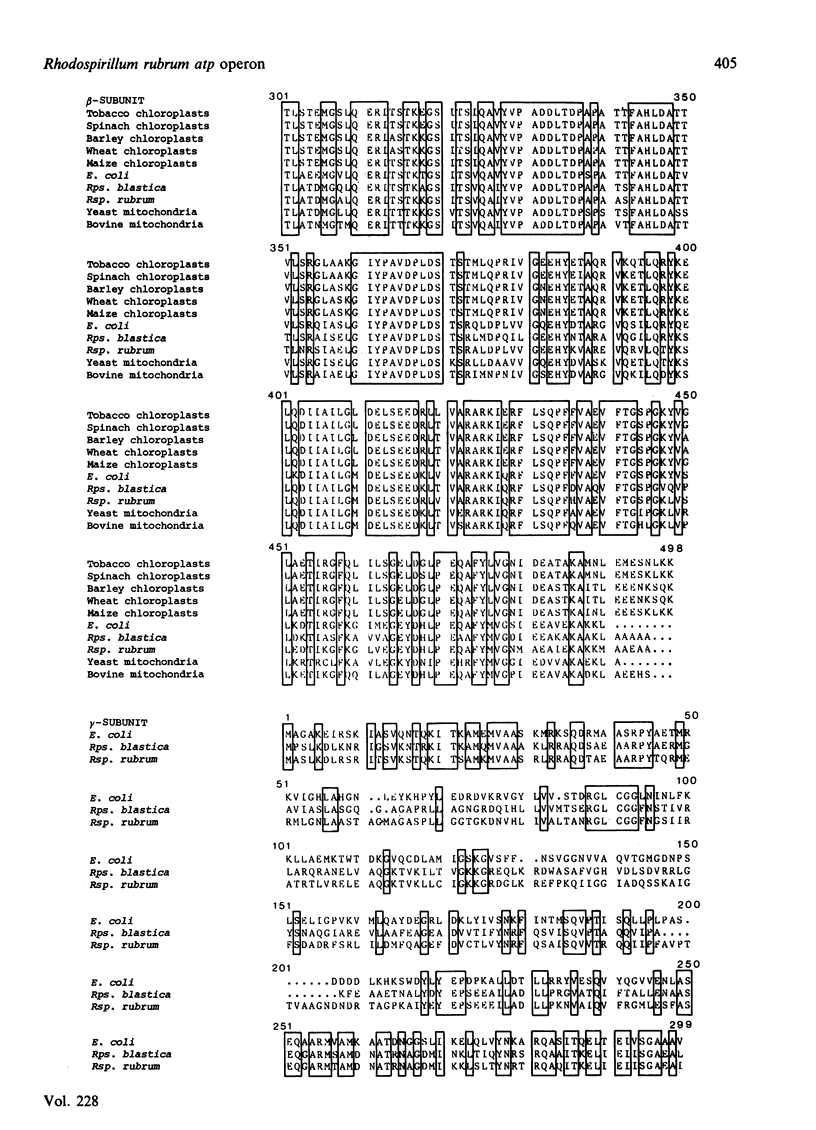
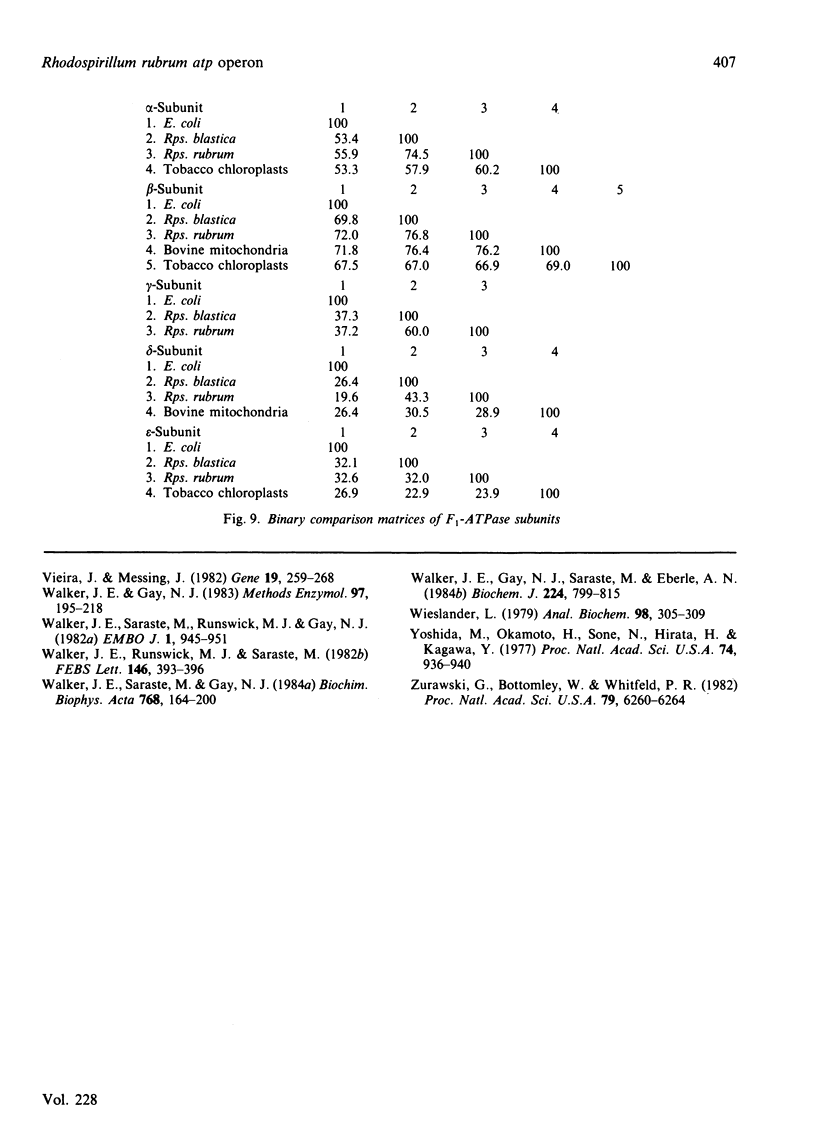
The nucleotide sequence was determined of a 8775-base-pair region of DNA cloned from the photosynthetic non-sulphur bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. It contains a cluster of five genes encoding F1-ATPase subunits. The genes are arranged in the same order as F1 genes in the Escherichia coli unc operon. However, as in the related organism Rhodopseudomonas blastica, neither genes for components of F0, the membrane sector of ATP synthase, nor a homologue of the E. coli uncI gene are associated with this locus, as they are in E. coli.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusilow W. S., Klionsky D. J., Simoni R. D. Differential polypeptide synthesis of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1363–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1363-1371.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno H., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco chloroplast gene for the alpha subunit of proton-translocating ATPase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2185–2191. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Deininger P. L., Bankier A., Barrell B. Homologous upstream sequences near Epstein-Barr virus promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Sternweis P. C., Heppel L. A. Purification and properties of reconstitutively active and inactive adenosinetriphosphatase from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J. Construction and characterization of an Escherichia coli strain with a uncI mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):820–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.820-825.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the genes for the membrane proteins, and the delta subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3919–3926. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F. The Leeuwenhoek Lecture, 1981. The biochemical and genetic approach to the study of bioenergetics with the use of Escherichia coli: progress and prospects. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Apr 22;215(1198):1–18. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. G., Nielsen J., Riise E., von Meyenburg K. The genes for the eight subunits of the membrane bound ATP synthase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):463–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00268766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A. The interactions of coupling ATPases with nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 10;463(3-4):245–273. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Sebald W. The proton conducting F0-part of bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 9;768(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Baltscheffsky M. On the subunit composition of the coupling factor (ATPase) from Rhodospirillum rubrum. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. New bacteriophage lambda vectors with positive selection for cloned inserts. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:3–19. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebbers E. T., Larrinua I. M., McIntosh L., Bogorad L. The maize chloroplast genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of the photosynthetic coupling factor CF1 are fused. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4985–5002. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Modyanov N. N., Grinkevich V. A., Aldanova N. A., Trubetskaya O. E., Nazimov I. V., Hundal T., Ernster L. Amino acid sequence of the oligomycin sensitivity-conferring protein (OSCP) of beef-heart mitochondria and its homology with the delta-subunit of the F1-ATPase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runswick M. J., Walker J. E. The amino acid sequence of the beta-subunit of ATP synthase from bovine heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3081–3089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzgaber-Muller J., Kunapuli S. P., Douglas M. G. Nuclear genes coding the yeast mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase complex. Isolation of ATP2 coding the F1-ATPase beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11465–11470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Deno H., Kato A., Sugiura M. Overlap and cotranscription of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of tobacco chloroplast ATPase. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Sternweis P. C. Purification of membrane attachment and inhibitory subunits of the proton translocating adenosine triphosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):306–311. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
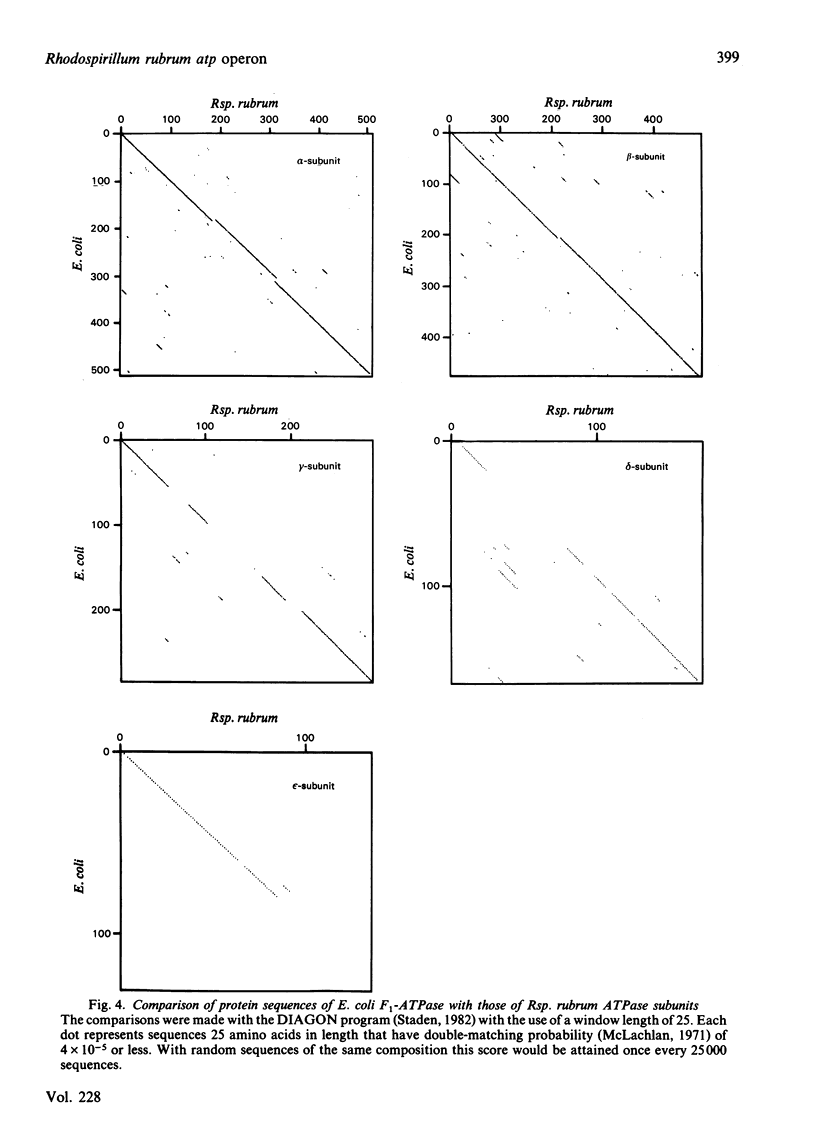
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
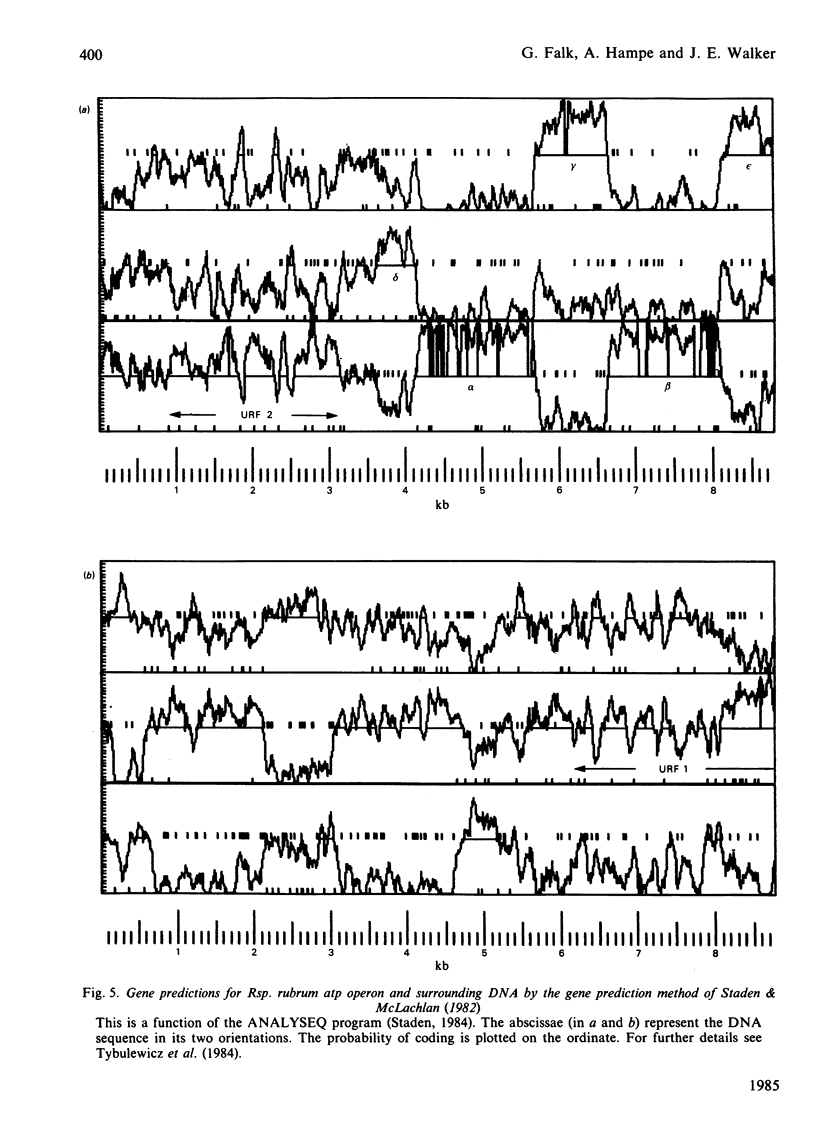
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The epsilon subunit of Escherichia coli coupling factor 1 is required for its binding to the cytoplasmic membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3123–3128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Falk G., Walker J. E. Rhodopseudomonas blastica atp operon. Nucleotide sequence and transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):185–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90465-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Gay N. J. Analysis of Escherichia coli ATP synthase subunits by DNA and protein sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:195–218. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Gay N. J., Saraste M., Eberle A. N. DNA sequence around the Escherichia coli unc operon. Completion of the sequence of a 17 kilobase segment containing asnA, oriC, unc, glmS and phoS. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):799–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2240799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Runswick M. J., Saraste M. Subunit equivalence in Escherichia coli and bovine heart mitochondrial F1F0 ATPases. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 20;146(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80960-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Gay N. J. The unc operon. Nucleotide sequence, regulation and structure of ATP-synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 6;768(2):164–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Okamoto H., Sone N., Hirata H., Kagawa Y. Reconstitution of thermostable ATPase capable of energy coupling from its purified subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Structures of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of spinach chloroplast ATPase indicate a dicistronic mRNA and an overlapping translation stop/start signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



