Abstract
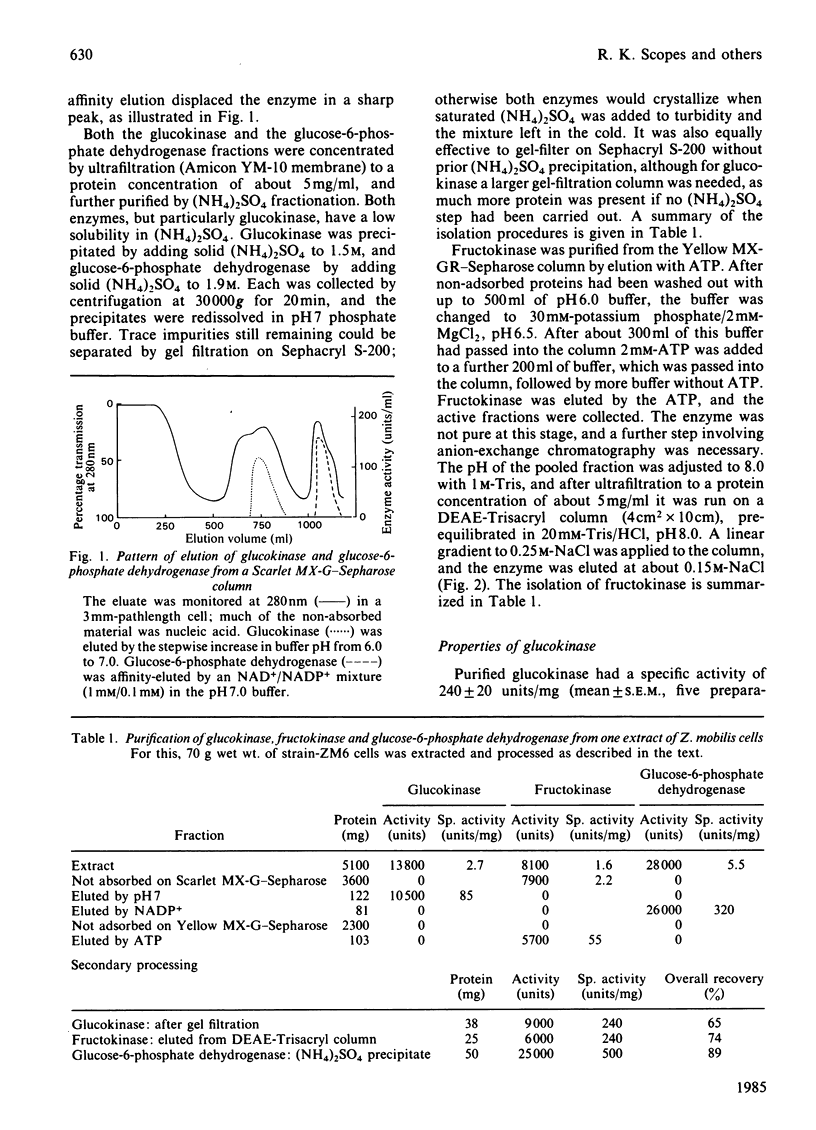
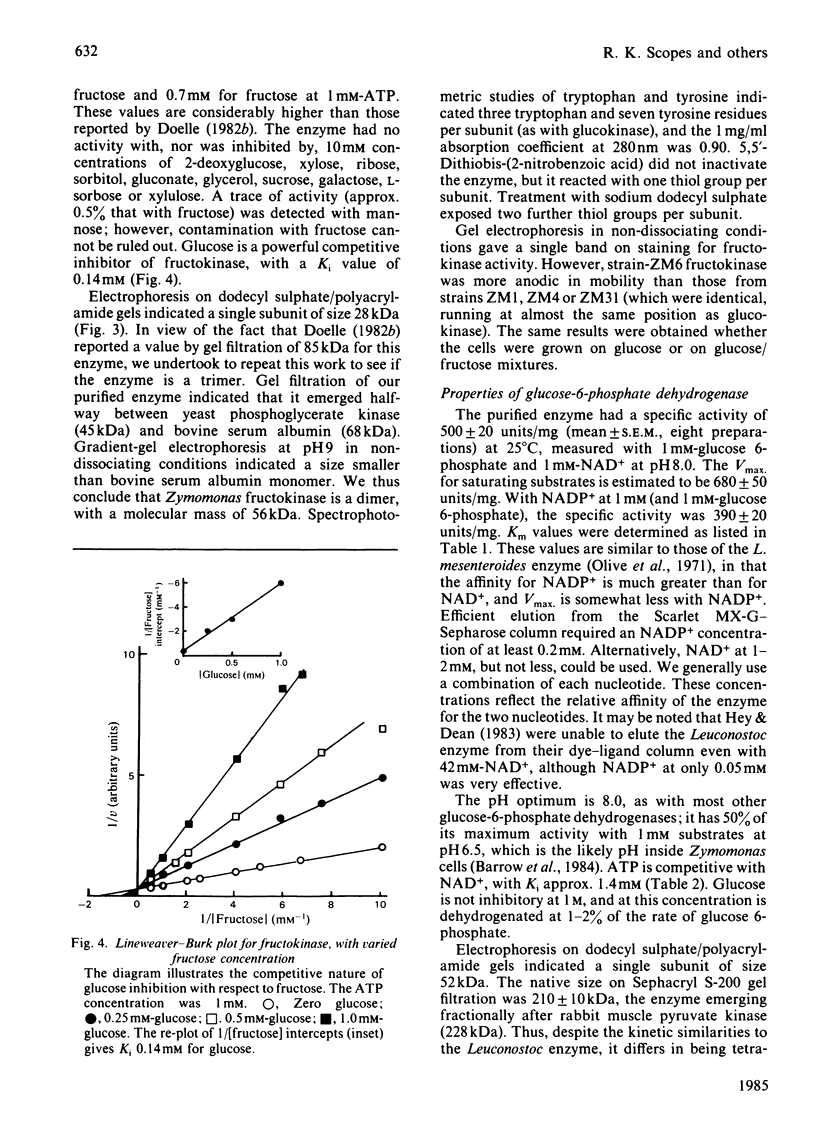
The three enzymes glucokinase (EC 2.7.1.2), fructokinase (EC 2.7.1.4) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) were isolated in high yield from extracts of Zymomonas mobilis. The principal steps in the isolation procedures involved the use of selected dye-ligand adsorbent columns, with affinity elution of two of the three enzymes. Glucokinase and fructokinase are dimeric proteins (2 X 33000 Da and 2 X 28000 Da respectively) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is a tetramer (4 X 52000 Da). Some similarities in the structural and kinetic parameters of the two kinases were noted, but they have absolute specificity for their substrates. Fructokinase is strongly inhibited by glucose; otherwise non-substrate sugars had little effect on any of the three enzymes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson T., Hammond P. M., Hartwell R. D., Hughes P., Scawen M. D., Sherwood R. F., Small D. A., Bruton C. J., Harvey M. J., Lowe C. R. Triazine-dye affinity; chromatography. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Aug;9(4):290–293. doi: 10.1042/bst0090290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow K. D., Collins J. G., Norton R. S., Rogers P. L., Smith G. M. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the fermentation of glucose to ethanol by Zymomonas mobilis. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5711–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich J. P., Senez J. C., Murgier M. Microcalorimetric study of glucose permeation in microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1750–1757. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1750-1757.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes E. A., Ribbons D. W., Large P. J. The route of ethanol formation in Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):795–803. doi: 10.1042/bj0980795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS M., DEMOSS R. D. Anaerobic dissimilation of C14-labeled glucose and fructose by Pseudomonas lindneri. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):689–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner H., Zuber H. Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic glucokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey Y., Dean P. D. Tandem dye-ligand chromatography and biospecific elution applied to the purification of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):363–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2090363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel M. Y., Allison D. P., Anderson R. L. Stereospecific D-glucokinase of Aerobacter aerogenes. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):690–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. R., Small D. A., Atkinson A. Some preparative and analytical applications of triazine dyes. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive C., Geroch M. E., Levy H. R. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2047–2057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive C., Levy H. R. The preparation and some properties of crystalline glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):730–736. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M., Holmlund C. E. Partial purification and properties of a mannofructokinase from Streptococcus mutans SL-1. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.43-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M., Holmlund C. E. Purification and kinetic characterization of a specific glucokinase from Streptococcus mutans OMZ70 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 20;709(2):178–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri F., Dean P. D. The use of various immobilized-triazine affinity dyes for the purification of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):53–62. doi: 10.1042/bj1910053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico V., Anderson R. L. An adenosine 5'-triphosphate:hexose 6-phosphotransferase specific for D-mannose and D-fructose from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Purification, properties, and evidence for a single enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5086–5092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scawen M. D., Hammond P. M., Comer M. J., Atkinson T. The application of triazine dye affinity chromatography to the large-scale purification of glycerokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;132(2):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K., Griffiths-Smith K. Use of differential dye-ligand chromatography with affinity elution for enzyme purification: 6-phosphogluconate dehydratase from Zymomonas mobilis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):530–534. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Measurement of protein by spectrophotometry at 205 nm. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Use of differential dye-ligand chromatography with affinity elution for enzyme purification: 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase from Zymomonas mobilis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki M. L., Warr R. G., Goodman A. E., Lee K. J., Rogers P. L. High-productivity alcohol fermentations using Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1983;48:53–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly L. I., Doelle H. W. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in cell free extracts of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(3):197–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00412836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swings J., De Ley J. The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):1–46. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.1-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


