Abstract
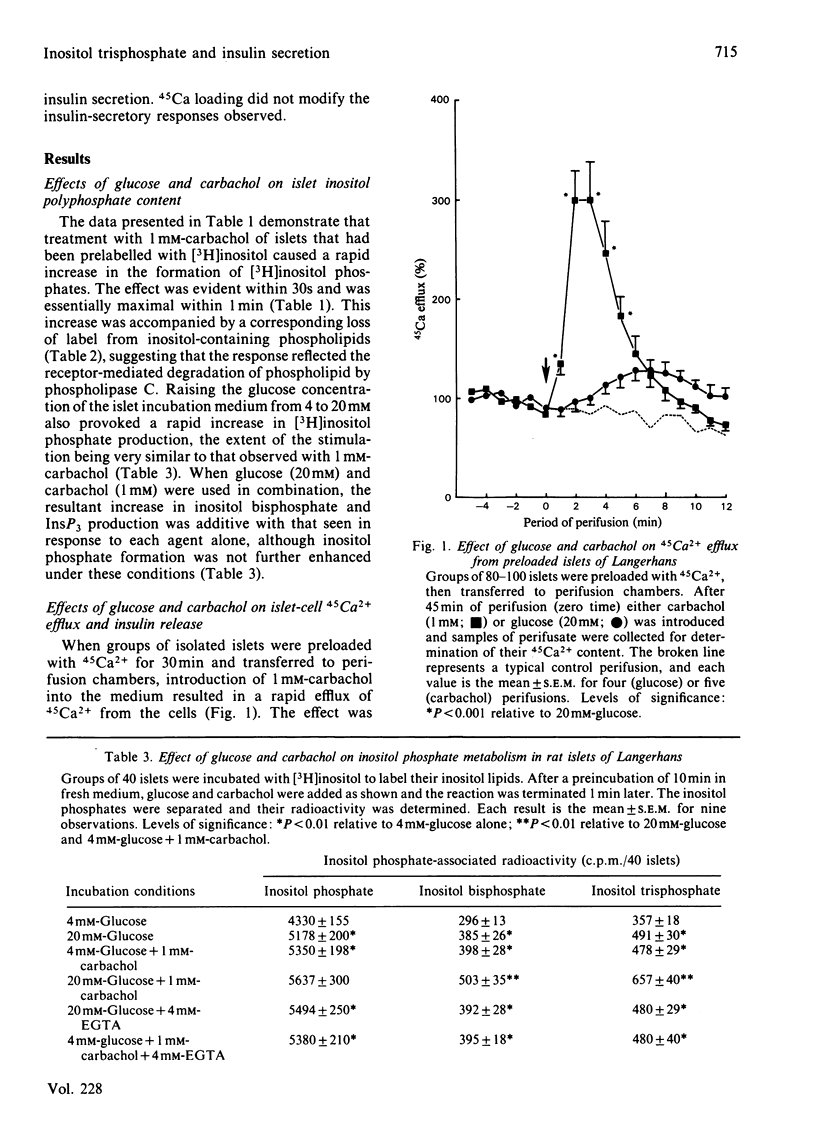
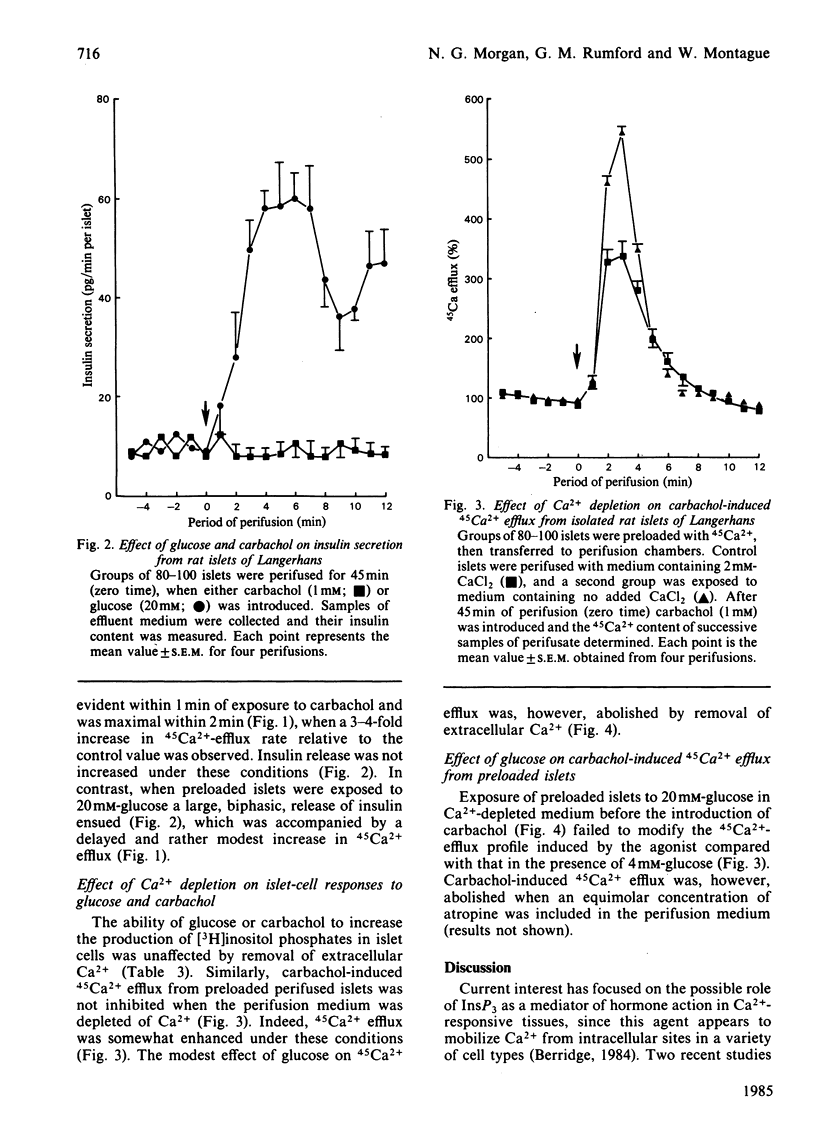
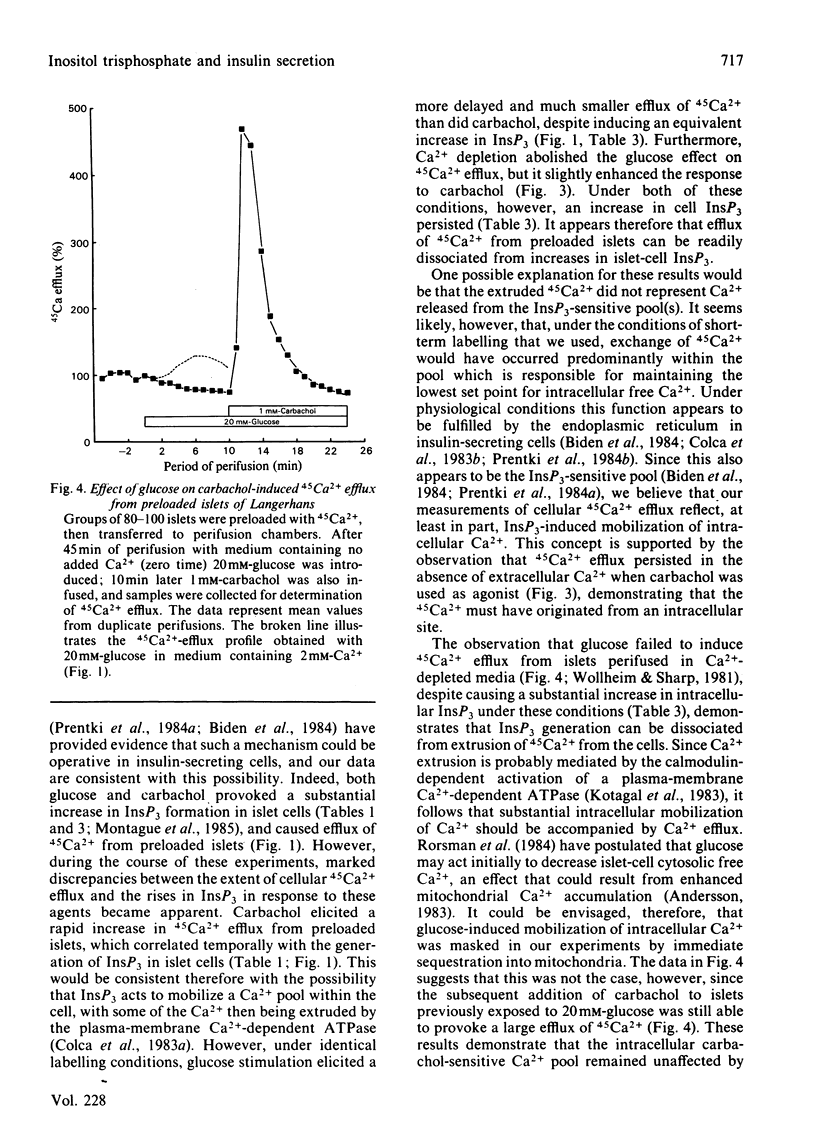
Glucose (20 mM) and carbachol (1 mM) produced a rapid increase in [3H]inositol trisphosphate (InsP3) formation in isolated rat islets of Langerhans prelabelled with myo-[3H]inositol. The magnitude of the increase in InsP3 formation was similar when either agent was used alone and was additive when they were used together. In islets prelabelled with 45Ca2+ and treated with carbachol (1 mM), the rise in InsP3 correlated with a rapid, transient, release of 45Ca2+ from the cells, consistent with mobilization of 45Ca2+ from an intracellular pool. Under these conditions, however, insulin secretion was not increased. In contrast, islets prelabelled with 45Ca2+ and exposed to 20mM-glucose exhibited a delayed and decreased 45Ca2+ efflux, but released 7-8-fold more insulin than did those exposed to carbachol. Depletion of extracellular Ca2+ failed to modify the increase in InsP3 elicited by either glucose or carbachol, whereas it selectively inhibited the efflux of 45Ca2+ induced by glucose in preloaded islets. Under these conditions, however, glucose was still able to induce a small stimulation of the first phase of insulin secretion. These results demonstrate that polyphosphoinositide metabolism, Ca2+ mobilization and insulin release can all be dissociated in islet cells, and suggest that glucose and carbachol regulate these parameters by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T. Glucose-induced retention of intracellular 45Ca in pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C343–C347. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Malaisse W. J. Phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid metabolism in rat pancreatic islets in response to neurotransmitter and hormonal stimuli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 7;750(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation of phosphoinositide breakdown in rat pancreatic islets by glucose and carbamylcholine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 14;116(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Prentki M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ from permeabilized insulin-secreting cells. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2230467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E., McDaniel M. L. Comparison of the properties of active Ca2+ transport by the islet-cell endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 6;729(2):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E., McDaniel M. L. Modulation of active Ca2+ uptake by the islet-cell endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):113–121. doi: 10.1042/bj2120113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells: effect of ions. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. The role of calcium in phospholipid turnover following glucose stimulation in neonatal rat cultured islets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8407–8411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Idahl L. A., Meissner H. P., Täljedal I. B. Insulin release, cGMP, cAMP, and membrane potential in acetylcholine-stimulated islets. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):E493–E500. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.5.E493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I. C., Perrin D., Pedley K. C., Leslie R. D., Pyke D. A. Effect of enkephalins and morphine on insulin secretion from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1980 Aug;19(2):158–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00421864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne J. N. Polyphosphoinositide metabolism in excitable membranes. Review. Biosci Rep. 1983 Oct;3(10):887–904. doi: 10.1007/BF01140658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotagal N., Colca J. R., McDaniel M. L. Activation of an islet cell plasma membrane (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase by calmodulin and Ca-EGTA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4808–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G. Identification and metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in isolated islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):101–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2160101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Evidence for two distinct modalities of CA2+ influx into pancreatic B cell. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):E59–E66. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.1.E59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Mathias P. C., Malaisse W. J. Gating and blocking of calcium channels by dihydropyridines in the pancreatic B-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):1062–1068. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A., Devis G., Somers G., Boschero A. C., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A., Atwater I. J., Duncan G. Regulation of calcium fluxes and their regulatory roles in pancreatic islets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:562–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H., Ashmore J. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic agents upon insulin secretion in vitro. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):975–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Morgan N. G., Rumford G. M., Prince C. A. Effect of glucose on polyphosphoinositide metabolism in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):483–489. doi: 10.1042/bj2270483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Taylor K. W. Pentitols and insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1090333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Stimulation of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans by melittin. Biosci Rep. 1984 Aug;4(8):665–671. doi: 10.1007/BF01121020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Studies on the interaction of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin with isolated islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):111–125. doi: 10.1042/bj2040111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nenquin M., Awouters P., Mathot F., Henquin J. C. Distinct effects of acetylcholine and glucose on 45calcium and 86rubidium efflux from mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Janjic D., Biden T. J., Blondel B., Wollheim C. B. Regulation of Ca2+ transport by isolated organelles of a rat insulinoma. Studies with endoplasmic reticulum and secretory granules. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10118–10123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Dual effects of glucose on the cytosolic Ca2+ activity of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trus M. D., Hintz C. S., Weinstein J. B., Williams A. D., Pagliara A. S., Matschinsky F. M. A comparison of the effects of glucose and acetylcholine on insulin release and intermediary metabolism in rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3921–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. The roles of intracellular and extracellular Ca++ in glucose-stimulated biphasic insulin release by rat islets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):451–458. doi: 10.1172/JCI109146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Sharp G. W. Dependency of acetylcholine-induced insulin release on Ca++ uptake by rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):924–929. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


