Abstract
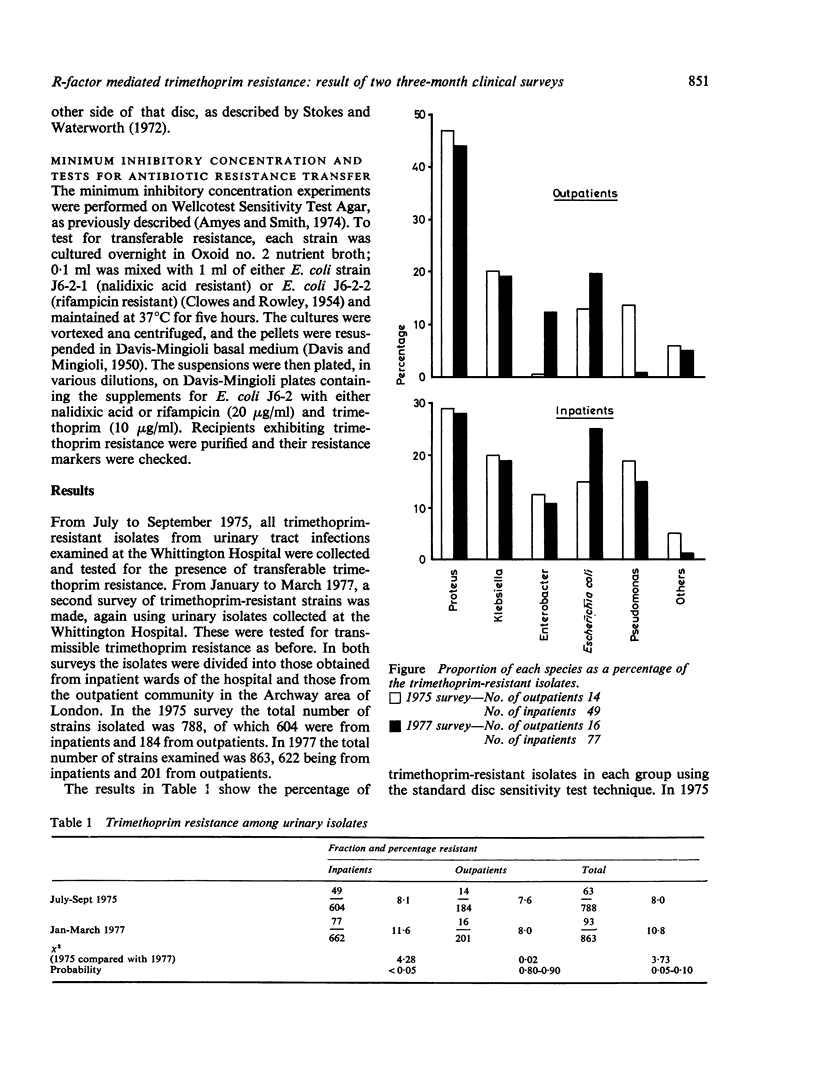
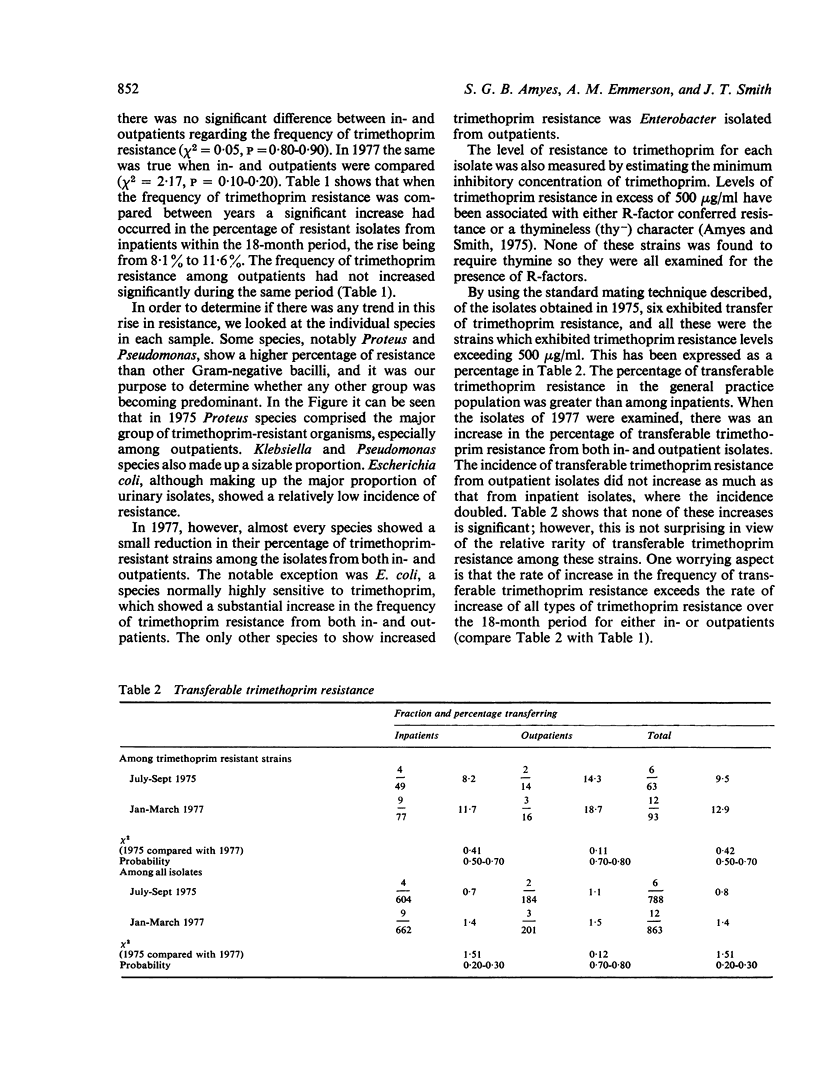
All urinary tract isolates were monitored in the Whittington Hospital, London for trimethoprim resistance over a three-month period in 1975; this survey was repeated 18 months later in 1977. In the later survey the incidence of trimethoprim resistance had increased significantly, and the proportion of strains carrying R-factors conferring trimethoprim resistance had nearly doubled. The pattern of resistances associated with R-factor trimethoprim resistance also changed betweeen these two surveys.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amyes S. G., Smith J. T. Thymineless mutants and their resistance to trimethoprim. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Mar;1(1):85–89. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amyes S. G., Smith J. T. Trimethoprim-sensitivity testing and thymineless mutants. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):143–153. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOWES R. C., ROWLEY D. Some observations on linkage effects in genetic recombination in Escherichia coli K-12. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Oct;11(2):250–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-2-250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Trimethoprim resistance conferred by W plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming M. P., Datta N., Grüneberg R. N. Trimethoprim resistance determined by R factors. Br Med J. 1972 Mar 18;1(5802):726–728. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5802.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg R. N. Susceptibility of urinary pathogens to various antimicrobial substances: a four-year study. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Apr;29(4):292–295. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.4.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIGH D. A., WILLIAMS J. D. METHOD FOR THE DETECTION OF SIGNIFICANT BACTERIURIA IN LARGE GROUPS OF PATIENTS. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Sep;17:498–503. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.5.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. J., Bruten D. M., Speller D. C. Trimethoprim-resistant coliforms. Lancet. 1977 Oct 8;2(8041):774–774. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. H., Whitehead J. E. Antibiotic sensitivity testing: a modification of the Stokes method using a rotary plater. J Clin Pathol. 1974 May;27(5):430–431. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.5.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


