Abstract
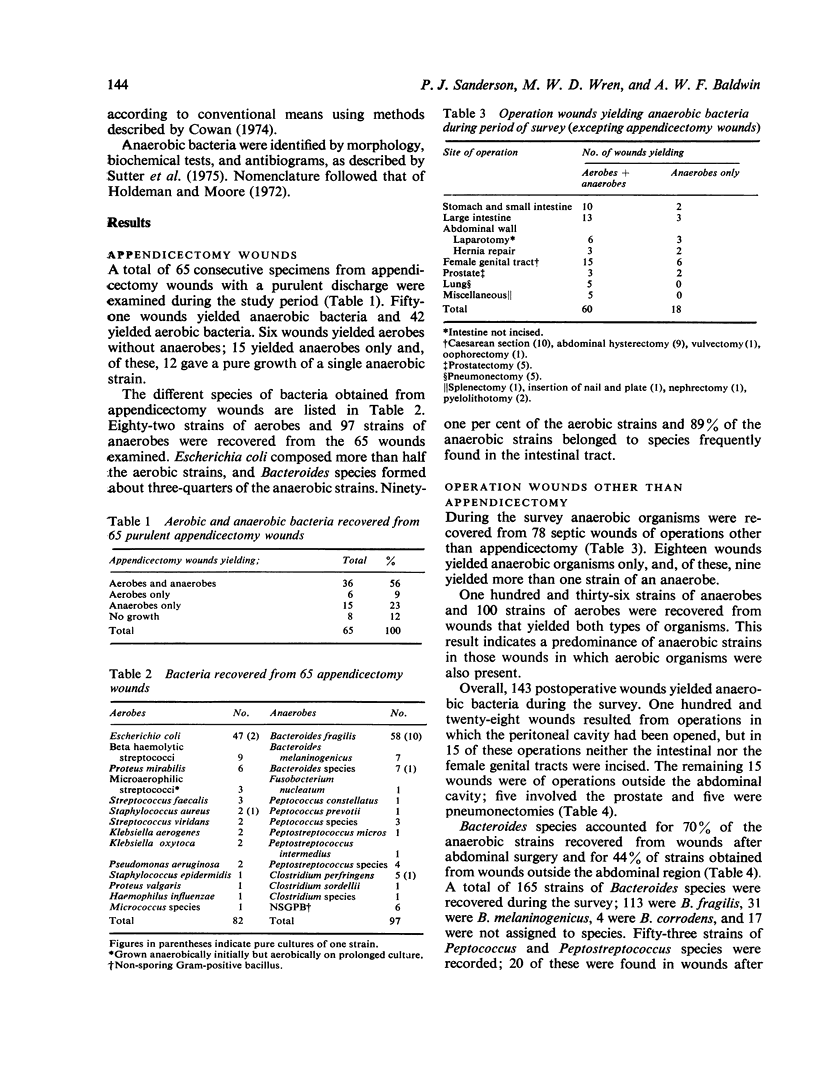
A survey of the bacteria found in postoperative wounds was undertaken during a 14-month period. The yields of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in 65 appendicectomy wounds were compared; 42 wounds yielded aerobes and 51 anaerobes. Seventy-eight other operation wounds yielded anaerobes, and, overall, 33 wounds yielded anaerobes only. Bacteroides sp were the most common anaerobic organisms isolated from all operation sites except the lung.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. W. An improved catalyst sachet for anaerobic jars. Med Lab Technol. 1975 Oct;32(4):329–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARY S. G., BLAIR E. B. NEW TRANSPORT MEDIUM FOR SHIPMENT OF CLINICAL SPECIMENS. I. FECAL SPECIMENS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:96–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.96-98.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore O. J., Sanderson P. J. Prophylactic interparietal povidone-iodine in abdominal surgery. Br J Surg. 1975 Oct;62(10):792–799. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800621011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta U., Talwar J. R., Hingorani V. Anaerobic bacteria isolated from pyogenic lesions. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Nov;60(11):1557–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann K., Gierhake F. W. Postoperative infection of wounds by anaerobes. Ger Med Mon. 1969 Jan;14(1):31–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Sisson P. R., Tharagonnet D., Selkon J. B., Codd A. A. Inhibition of phagocytosis in vitro by obligate anaerobes. Lancet. 1977 Dec 17;2(8051):1252–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J., Warren R. E. The value of an operative wound swab sent in transport medium in the prediction of later clinical wound infection: a controlled clinical and bacteriological evaluation. Br J Surg. 1978 Feb;65(2):81–88. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh D. A., Simmons K., Norman E. Bacterial flora of the appendix fossa in appendicitis and postoperative wound infection. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Dec;27(12):997–1000. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.12.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Anaerobic bacteria of the gastrointestinal flora and their occurrence in clinical infections. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):641–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach S., Hayek L. The isolation of anaerobic bacteria from wound swabs. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jul;27(7):578–582. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.7.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadepalli H., Gorbach S. L., Broido P., Norsen J. A prospective study of infections in penetrating abdominal trauma. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1405–1408. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. T. A view of bacteroides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Sep;1(3):254–255. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren M. W., Baldwin A. W., Eldon C. P., Sanderson P. J. The anaerobic culture of clinical specimens: a 14-month study. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):49–61. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren M. W. The culture of clinical specimens for anaerobic bacteria: a comparison of three regimens. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):195–201. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


