Abstract
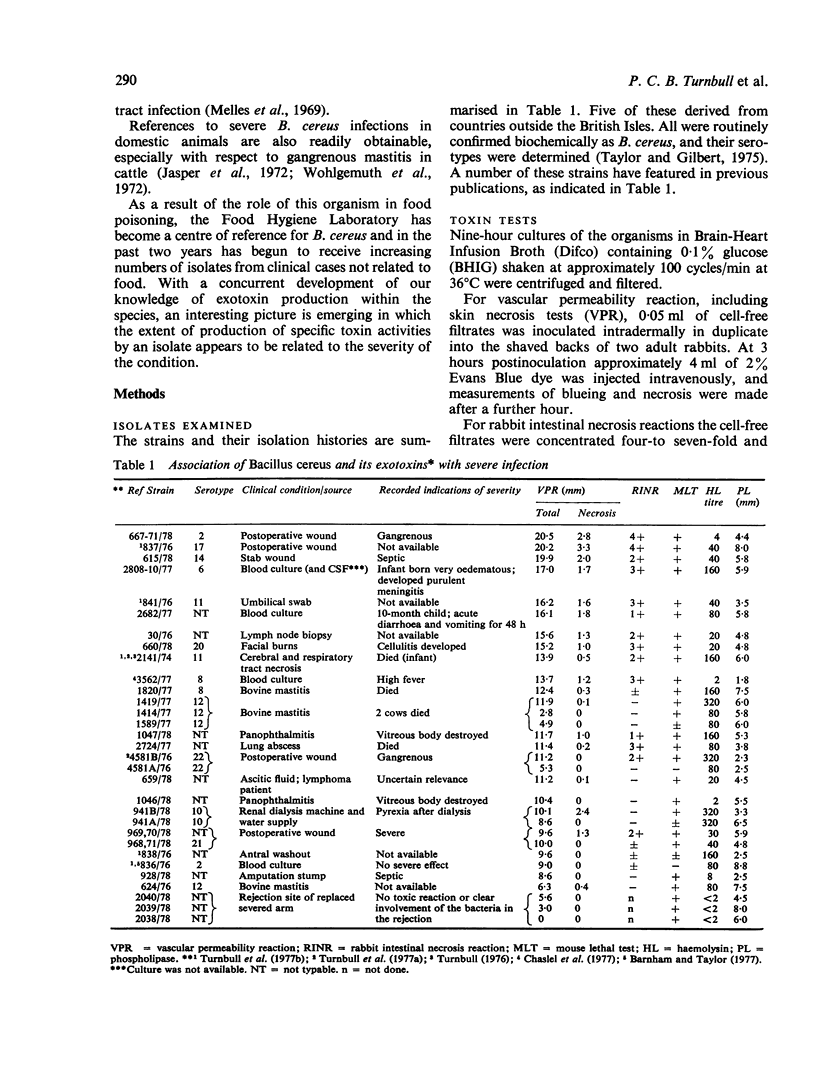
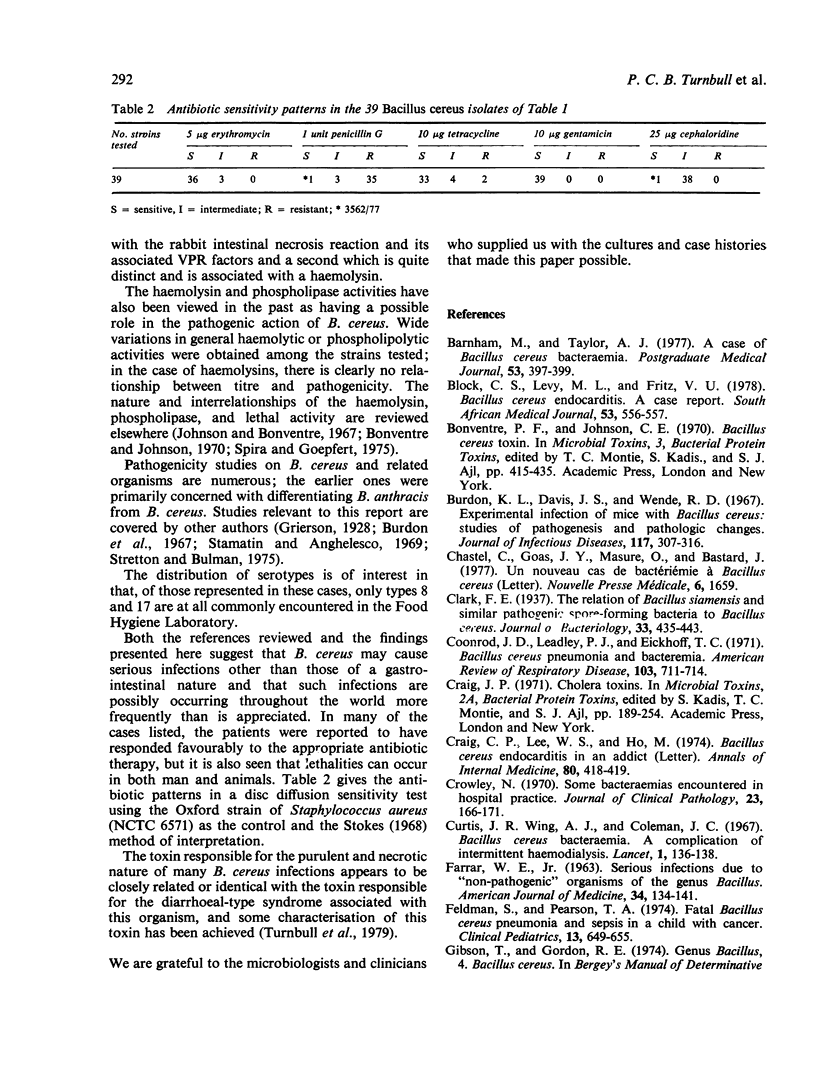
Twenty-one cases of infection with Bacillus cereus are summarised. The histories supplied showed that at least 15 of these were associated with severe or potentially severe symptoms including two deaths. Analysis of the production of exotoxins, including haemolysin and phospholipase, by these strains is given, and the relevance of these metabolites to the severity of the condition is discussed. Three incidents of bovine mastitis resulting from B. cereus and involving three deaths are also included. The observations presented here together with those of previous reports which are reviewed indicate that B. cereus may be of clinical importance, not just an opportunist but also as an agent of potentially severe infections in its own right.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnham M., Taylor A. J. A case of Bacillus cereus bacteraemia. Postgrad Med J. 1977 Jul;53(621):397–399. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.53.621.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block C. S., Levy M. L., Fritz V. U. Bacillus cereus endocarditis. A case report. S Afr Med J. 1978 Apr 8;53(14):556–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon K. L., Davis J. S., Wende R. D. Experimental infection of mice with Bacillus cereus: studies of pathogenesis and pathologic changes. J Infect Dis. 1967 Oct;117(4):307–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. E. The Relation of Bacillus siamensis and Similar Pathogenic Spore-forming Bacteria to Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1937 Apr;33(4):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.33.4.435-443.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Leadley P. J., Eickhoff T. C. Bacillus cereus pneumonia and bacteremia. A case report. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 May;103(5):711–714. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.5.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig C. P., Lee W. S., Ho M. Letter: Bacillus cereus endocarditis in an addict. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Mar;80(3):418–419. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-3-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley N. Some bacteraemias encountered in hospital practice. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;23(2):166–171. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis J. R., Wing A. J., Coleman J. C. Bacillus cereus bacteraemia. A complication of intermittent haemodialysis. Lancet. 1967 Jan 21;1(7482):136–138. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRAR W. E., Jr Serious infections due to "non-pathogenic" organisms of the genus Bacillus. Review of their status as pathogens. Am J Med. 1963 Jan;34:134–141. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S., Pearson T. A. Fatal Bacillus cereus pneumonia and sepsis in a child with cancer. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1974 Aug;13(8):649-51, 654-5. doi: 10.1177/000992287401300806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Pépin H. Une septicémie à Bacillus cereus. Pouvoir pathogène des bactéries du genre Bacillus. Nouv Presse Med. 1974 Nov 9;3(38-40):2490–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel D., Burgress M. A., Bodey G. P., Sr Gas gangrene-like infection with Bacillus cereus in a lymphoma patient. Cancer. 1976 Feb;37(2):988–991. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197602)37:2<988::aid-cncr2820370256>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper D. E., Bushnell R. B., Dellinger J. D., Stang A. M. Bovine mastitis due to Bacillus cereus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Mar 1;160(5):750–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. E., Bonventre P. F. Lethal toxin of Bacillus cereus. I. Relationships and nature of toxin, hemolysin, and phospholipase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):306–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.306-316.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Lourd R., Domec L., Le Lourd F. Pleurésie purulente à Bacillus cereus chez une asthmatique traitée au long cours par les corticoïdes. Sem Hop. 1967 Oct 26;43(44):2730–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff A., Jacobs R., Gooding V., Hauch J., Conte J., Stulbarg M. Bacillus cereus pneumonia. Survival in a patient with cavitary disease treated with gentamicin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jan;115(1):151–154. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffert H. L., Baptist J. N., Gidez L. I. Meningitis and bacteremia after ventriculoatrial shunt-revision: isolation of a lecithinase-producing Bacillus cereus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):547–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lázár J., Jurcsák L. Daten zur Pathogenität des B. cereus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Jan;199(1):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphael S. S., Donaghue M. Letter: Infection due to Bacillus cereus. Can Med Assoc J. 1976 Aug 7;115(3):207–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Goepfert J. M. Biological characteristics of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1236–1246. doi: 10.1139/m75-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatin N., Anghelesco S. Pouvoir pathogène et toxicité de Bacillus cereus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Feb;116(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. J., Gilbert R. J. Bacillus cereus food poisoning: a provisional serotyping scheme. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):543–550. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., French T. A., Dowsett E. G. Severe systemic and pyogenic infections with Bacillus cereus. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 25;1(6077):1628–1629. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6077.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Kramer J. M., Jørgensen K., Gilbert R. J., Melling J. Properties and production characteristics of vomiting, diarrheal, and necrotizing toxins of Bacillus cereus. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):219–228. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Nottingham J. F., Ghosh A. C. A severe necrotic enterotoxin produced by certain food, food poisoning and other clinical isolates of Bacillus cereus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Jun;58(3):273–280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C. Studies on the production of enterotoxins by Bacillus cereus. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Oct;29(10):941–948. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.10.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN L., COLBURN C. G. Bacillus subtilis meningitis and bacteremia; report of a case and review of the literature on subtilis infections in man. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1950 Oct;86(4):585–594. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1950.00230160097009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgemuth K., Kirkbride C. A., Bicknell E. J., Ellis R. P. Pathogenicity of Bacillus cereus for pregnant ewes and heifers. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Dec 15;161(12):1691–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


