Abstract
PURPOSE
Lorlatinib improved progression-free survival (PFS) and intracranial activity versus crizotinib in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the phase III CROWN study. Here, we report long-term outcomes from CROWN after 5 years of follow-up.
METHODS
Two hundred ninety-six patients with ALK-positive NSCLC were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive lorlatinib 100 mg once daily (n = 149) or crizotinib 250 mg twice daily (n = 147). This post hoc analysis presents updated investigator-assessed efficacy outcomes, safety, and biomarker analyses.
RESULTS
With a median follow-up for PFS of 60.2 and 55.1 months, respectively, median PFS was not reached (NR [95% CI, 64.3 to NR]) with lorlatinib and 9.1 months (95% CI, 7.4 to 10.9) with crizotinib (hazard ratio [HR], 0.19 [95% CI, 0.13 to 0.27]); 5-year PFS was 60% (95% CI, 51 to 68) and 8% (95% CI, 3 to 14), respectively. Median time to intracranial progression was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) with lorlatinib and 16.4 months (95% CI, 12.7 to 21.9) with crizotinib (HR, 0.06 [95% CI, 0.03 to 0.12]). Safety profile was consistent with that in prior analyses. Emerging new ALK resistance mutations were not detected in circulating tumor DNA collected at the end of lorlatinib treatment.
CONCLUSION
After 5 years of follow-up, median PFS has yet to be reached in the lorlatinib group, corresponding to the longest PFS ever reported with any single-agent molecular targeted treatment in advanced NSCLC and across all metastatic solid tumors. These results coupled with prolonged intracranial efficacy and absence of new safety signals represent an unprecedented outcome for patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC and set a new benchmark for targeted therapies in cancer.
Updated results from the CROWN study show unprecedented median PFS of over 5 years with 1L lorlatinib for ALK+ NSCLC
INTRODUCTION
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are the standard first-line therapy recommended for patients with ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).1 Lorlatinib is a brain-penetrant, third-generation ALK TKI that has greater coverage of ALK resistance mutations than second-generation ALK inhibitors.2,3 In the phase III CROWN study, lorlatinib showed improved benefit over crizotinib in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive NSCLC.4,5 At the interim analysis, median progression-free survival (PFS) by blinded independent central review (BICR) was not reached (NR [95% CI, NR to NR]) with lorlatinib and 9.3 months (95% CI, 7.6 to 11.1) with crizotinib, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.28 (95% CI, 0.19 to 0.41; P < .001).4 On the basis of these results, lorlatinib received regulatory approval in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive NSCLC.6-9
CONTEXT
Key Objective
This post hoc analysis of the phase III CROWN study evaluated the long-term outcomes of lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer.
Knowledge Generated
After 5 years of follow-up, lorlatinib continued to show superior efficacy over crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). At a median follow-up of 60.2 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was still not reached with lorlatinib. The PFS benefit with lorlatinib, which exceeds 5 years, corresponds to the longest PFS ever reported with any single-agent targeted treatment not only in advanced NSCLC but across all metastatic solid tumors.
Relevance (T.E. Stinchcombe)
The long term follow-up of the phase III trial revealed an impressive PFS, and no late treatment-emergent adverse events were observed.*
*Relevance section written by JCO Associate Editor Thomas E. Stinchcombe, MD.
In a subsequent post hoc analysis, after approximately 3 years of follow-up, lorlatinib continued to show superior PFS benefit over crizotinib irrespective of the presence or absence of baseline brain metastases.5 At a median 36.7 months of follow-up in the lorlatinib group, median PFS by BICR was still NR (95% CI, NR to NR), and time to intracranial progression by BICR was also longer with lorlatinib than with crizotinib in the overall patient population.5 Only one patient developed intracranial lesions on lorlatinib treatment, suggesting a protective effect of lorlatinib against the development of brain metastases.
Acquired resistance to ALK TKIs limits the durability of responses in patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC. EML4::ALK variant 3 and/or a TP53 mutation are poor prognostic markers and may influence development of specific secondary ALK resistance mutations.10-12 When lorlatinib was used in the first-line setting, preliminary data indicated that no emerging new ALK resistance mutations were detected in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) collected at the end of treatment,13 consistent with the potent activity of lorlatinib across a broad spectrum of ALK kinase domain resistance mutations, whereas alterations in bypass pathways were more frequent.
Given that median PFS was not reached after 3 years of follow-up, we aimed to further quantify long-term systemic and intracranial outcomes from the CROWN study at the clinically meaningful landmark follow-up of 5 years in this post hoc analysis.
METHODS
Study Design and End Points
The CROWN study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03052608) is an ongoing, international, open-label, randomized phase III trial comparing lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive NSCLC. Full details of the study design were published previously.4,5
Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive lorlatinib 100 mg once daily or crizotinib 250 mg twice daily in 28-day cycles. The primary end point was PFS by BICR per RECIST version 1.1. The key secondary end point was overall survival (OS), which will be assessed at the time of the protocol-specified second interim analysis after at least 139 deaths have occurred (70% information fraction). Other secondary end points include PFS by investigator assessment; objective response, intracranial objective response, time to intracranial progression, duration of response, and duration of intracranial response, both by BICR and investigator assessment; safety; patient-reported outcomes; and biomarker analyses. Per protocol, end point evaluation by BICR stopped after the 3-year analysis. Tumor assessments, including brain magnetic resonance imaging, have been performed every 8 weeks in all patients throughout the study.
The Protocol (online only) and amendments were approved by institutional review boards or independent ethics committees at each site and complied with International Guidelines for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects, Good Clinical Practice Guidelines, the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and local laws. All patients provided written informed consent.
This is a post hoc analysis conducted after 5 years of follow-up to present efficacy by investigator assessment only, safety, and biomarker analyses. Because the primary objective of the study was met at the prespecified interim analysis,4 no further formal comparative analysis of PFS is planned, per protocol, and no formal statistical testing was performed. Full details of statistical analyses were published previously.4,5
Molecular Profiling
ctDNA from plasma collected at screening was analyzed with a validated, commercially available 74-gene ctDNA next-generation sequencing assay (Guardant360 panel version 2.11; bioinformatics pipeline version 3.5.3; Guardant Health, Inc, Redwood City, CA). Details of the molecular profiling were published previously.14
RESULTS
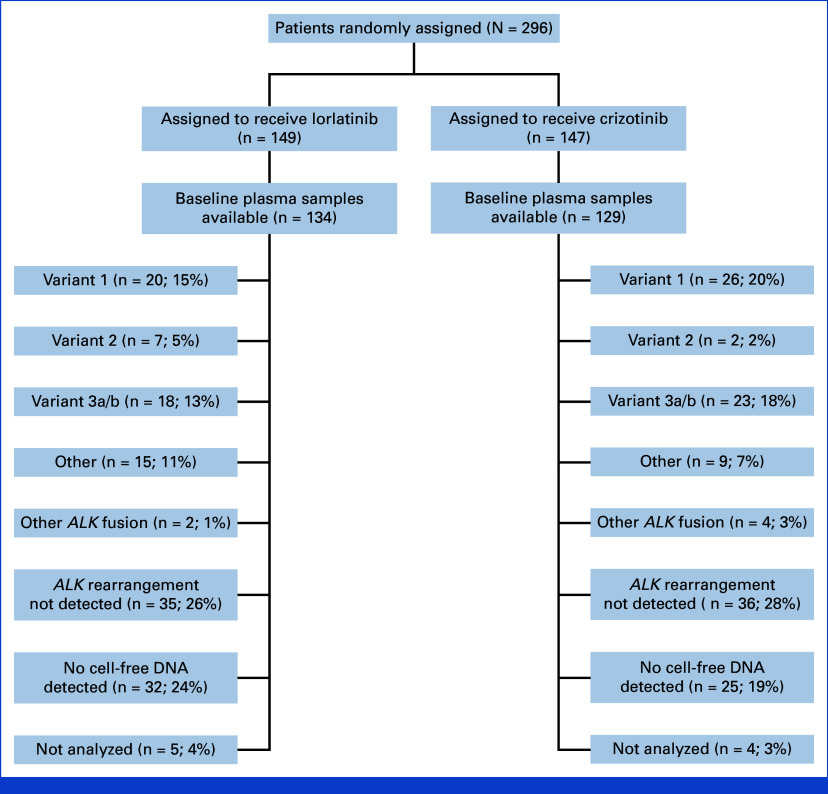
A total of 296 patients were randomly assigned to the lorlatinib group (n = 149) or the crizotinib group (n = 147; Fig 1). Five patients in the crizotinib group did not receive treatment but were included in the intention-to-treat population. At the data cutoff for this analysis (October 31, 2023), 74 of 149 (50%) patients treated with lorlatinib and 7 of 142 (5%) patients treated with crizotinib were continuing to receive the assigned treatment. Baseline characteristics of patients in the treatment groups have been published previously.4,5
FIG 1.
CONSORT diagram for the CROWN study. AE, adverse event.
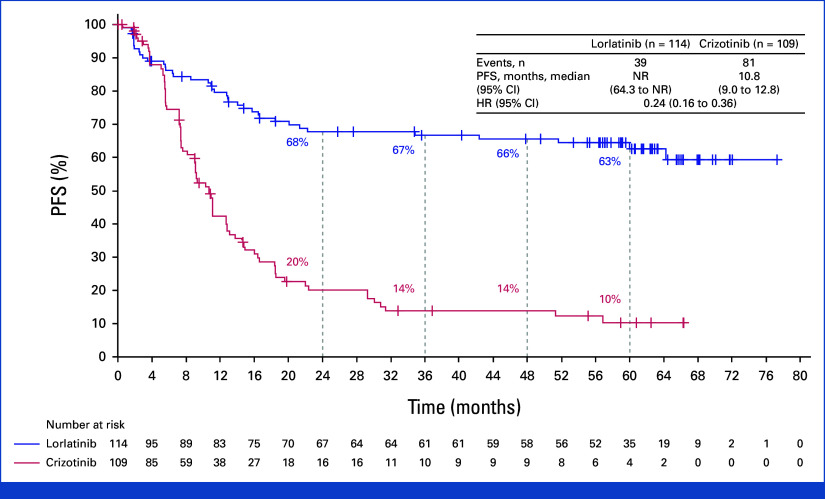
Efficacy
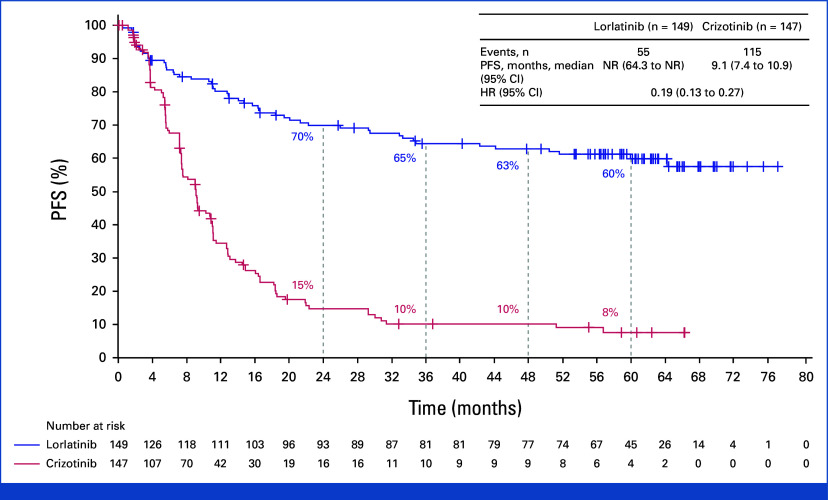
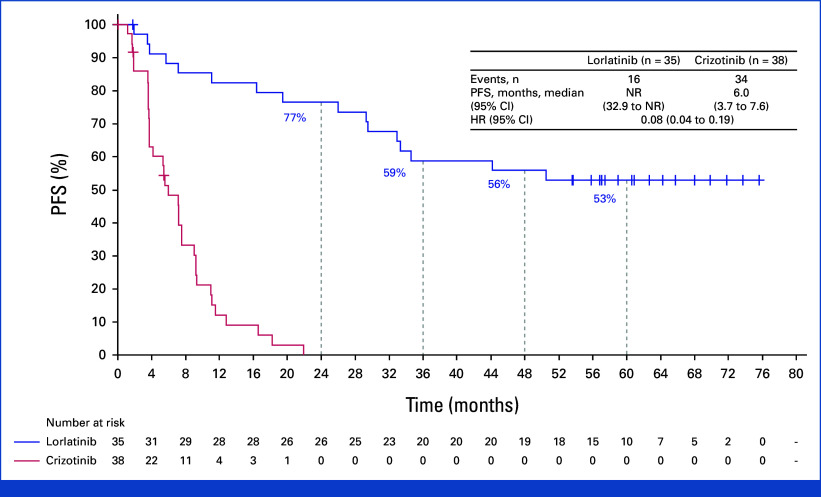
The median duration of follow-up for PFS was 60.2 months (95% CI, 57.4 to 61.6) in the lorlatinib group and 55.1 months (95% CI, 36.8 to 62.5) in the crizotinib group. The HR for disease progression or death with lorlatinib versus crizotinib was 0.19 (95% CI, 0.13 to 0.27). Median PFS was NR (95% CI, 64.3 to NR) with lorlatinib and 9.1 months (95% CI, 7.4 to 10.9) with crizotinib (Fig 2). The 4- and 5-year PFS was 63% and 60% (95% CI, 51 to 68) with lorlatinib, respectively, and 10% and 8% (95% CI, 3 to 14) with crizotinib. Among patients with baseline brain metastases (measurable and/or nonmeasurable; n = 35 in the lorlatinib group and n = 38 in the crizotinib group), the HR for disease progression or death with lorlatinib versus crizotinib was 0.08 (95% CI, 0.04 to 0.19); median PFS was NR (95% CI, 32.9 to NR) with lorlatinib and 6.0 months (95% CI, 3.7 to 7.6) with crizotinib. Five-year PFS was 53% (95% CI, 35 to 68) with lorlatinib and not evaluable with crizotinib as all patients progressed or died or were censored within 2 years (Appendix Fig A1, online only). Among patients without baseline brain metastases, the HR for disease progression or death with lorlatinib versus crizotinib was 0.24 (95% CI 0.16 to 0.36); median PFS was NR (95% CI, 64.3 to NR) with lorlatinib and 10.8 months (95% CI, 9.0 to 12.8) with crizotinib. Five-year PFS was 63% (95% CI, 52 to 71) with lorlatinib and 10% (95% CI, 5 to 18) with crizotinib (Appendix Fig A2).
FIG 2.
PFS by investigator assessment in the intention-to-treat population. HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached; PFS, progression-free survival.
The proportion of patients with a confirmed objective response by investigator assessment was 81% (95% CI, 73 to 87) with lorlatinib and 63% (95% CI, 54 to 70) with crizotinib; median duration of response was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) and 9.2 months (95% CI, 7.5 to 11.1), respectively (Table 1). In patients with measurable and/or nonmeasurable baseline brain metastases, intracranial objective response was also greater with lorlatinib than with crizotinib (60% v 11%, respectively); intracranial complete response was reported in 49% and 5% of patients, respectively. Median duration of intracranial response was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) and 12.8 months (95% CI, 7.5 to NR), respectively.
TABLE 1.
Summary of Overall and Intracranial Response by Investigator Assessment
| Response/Duration | Lorlatinib | Crizotinib |
|---|---|---|
| Intention-to-treat population, No. | 149 | 147 |
| Confirmed ORR, % (95% CI) | 81 (73 to 87) | 63 (54 to 70) |
| Best overall response, No. (%) | ||
| Complete response | 15 (10) | 3 (2) |
| Partial response | 105 (70) | 89 (61) |
| Stable disease | 16 (11) | 38 (26) |
| Progressive disease | 8 (5) | 7 (5) |
| Not evaluable | 5 (3) | 10 (7) |
| ORR for lorlatinib v crizotinib, OR (95% CI) | 2.43 (1.43 to 4.43) | |
| Duration of response, months, median (95% CI) | NR (NR to NR) | 9.2 (7.5 to 11.1) |
| Duration of response ≥2 years, n/N (%) | 89/120 (74) | 14/92 (15) |
| Patients with measurable and/or nonmeasurable baseline brain metastases, No. | 35 | 38 |
| Confirmed intracranial ORR, % (95% CI) | 60 (42 to 76) | 11 (3 to 25) |
| Best overall response, No. (%) | ||
| Complete response | 17 (49) | 2 (5) |
| Partial response | 4 (11) | 2 (5) |
| Stable disease | 0 | 4 (11) |
| Noncomplete response or nonprogressive disease | 13 (37) | 22 (58) |
| Progressive disease | 1 (3) | 5 (13) |
| Not evaluable | 0 | 3 (8) |
| ORR for lorlatinib v crizotinib, OR (95% CI) | 12.02 (3.23 to 54.92) | |
| Duration of intracranial response, months, median (95% CI) | NR (NR to NR) | 12.8 (7.5 to NR) |
| Duration of intracranial response ≥2 years, n/N (%) | 17/21 (81) | 0 |
| Patients with measurable baseline brain metastases, No. | 12 | 6 |
| Confirmed intracranial ORR, % (95% CI) | 92 (62 to 100) | 33 (4 to 78) |
| Best overall response, No. (%) | ||
| Complete response | 7 (58) | 0 |
| Partial response | 4 (33) | 2 (33) |
| Stable disease | 0 | 4 (67) |
| Progressive disease | 1 (8) | 0 |
| Not evaluable | 0 | 0 |
| ORR for lorlatinib v crizotinib, OR (95% CI) | 15.00 (0.99 to 786.47) | |
| Duration of intracranial response, months, median (95% CI) | NR (NR to NR) | 10.2 (7.5 to NR) |
| Duration of intracranial response ≥2 years, n/N (%) | 8/11 (73) | 0 |
Abbreviations: NR, not reached; OR, odds ratio; ORR, objective response rate.
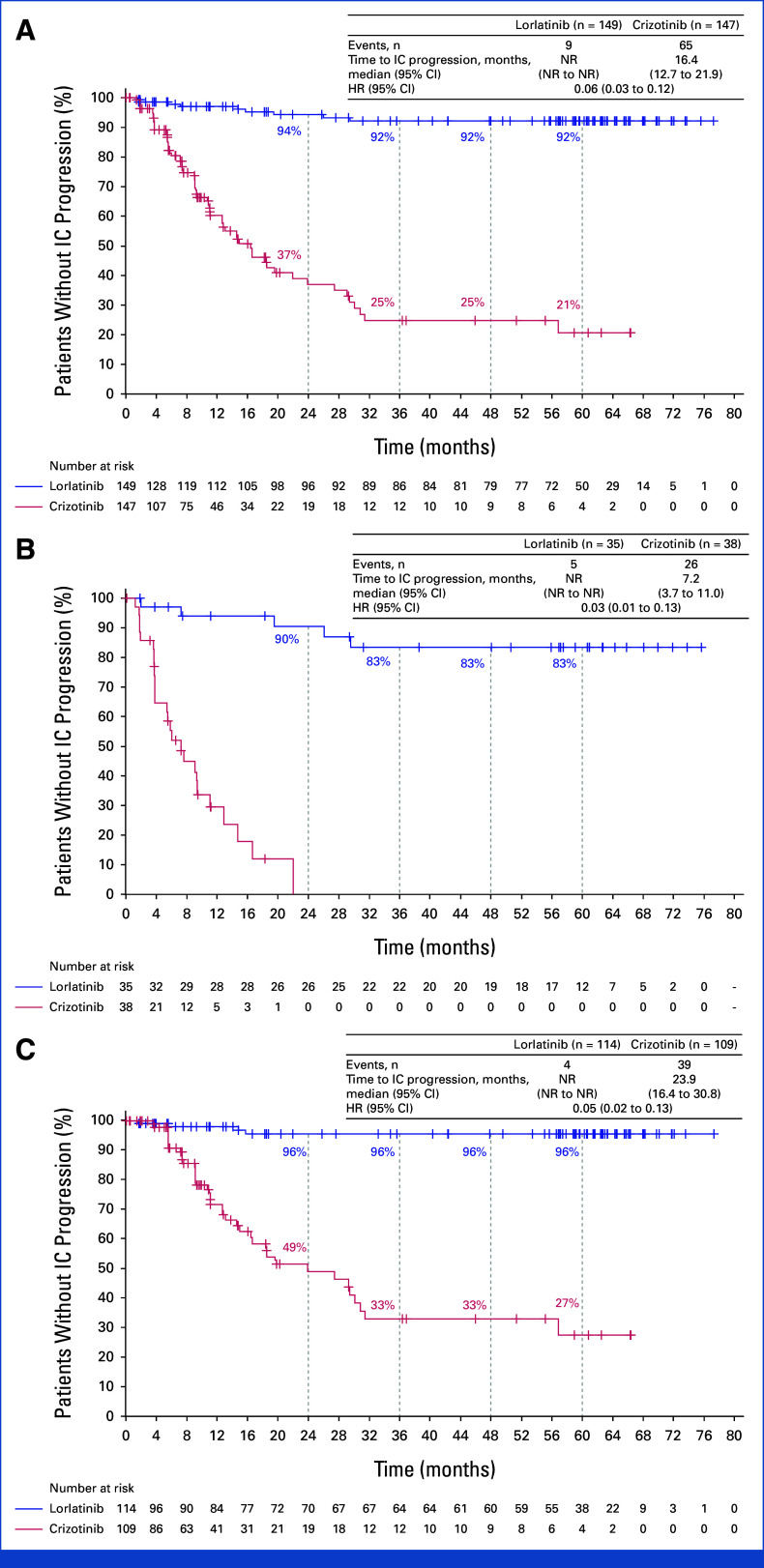
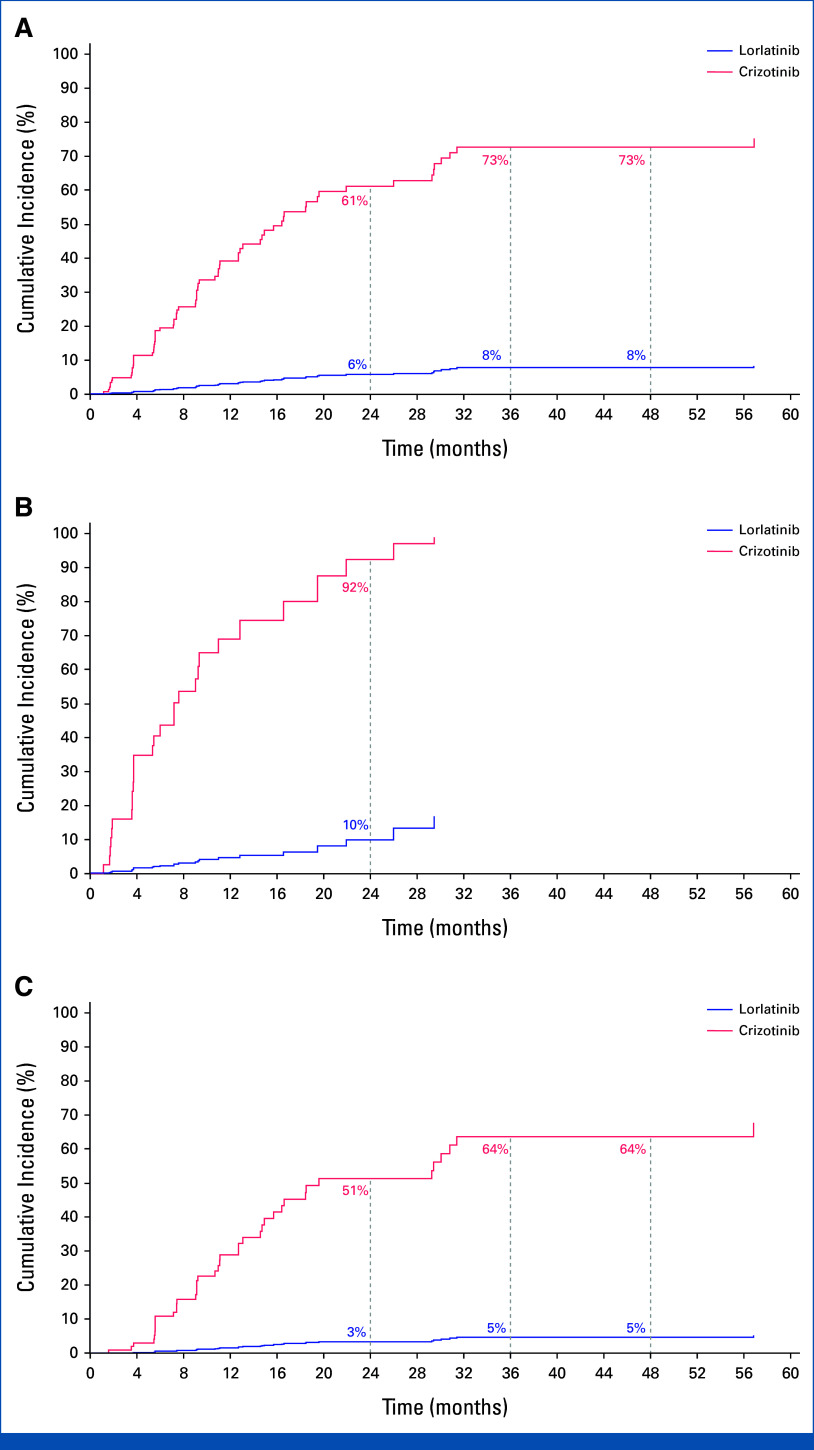
The time to intracranial progression by investigator assessment was longer with lorlatinib than with crizotinib, with an HR of 0.06 (95% CI, 0.03 to 0.12). Median time to intracranial progression was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) with lorlatinib and 16.4 months (95% CI, 12.7 to 21.9) with crizotinib. The probability of being free of intracranial progression was 92% (95% CI, 85 to 96) with lorlatinib and 21% (95% CI, 10 to 33) with crizotinib at 5 years (Fig 3A). Among patients with baseline brain metastases, the HR for time to intracranial progression favored lorlatinib over crizotinib at 0.03 (95% CI, 0.01 to 0.13). At 5 years, the probability of being free of intracranial progression was 83% (95% CI, 64 to 93) with lorlatinib and not evaluable with crizotinib as all the patients progressed in the brain or were censored within 2 years (Fig 3B). In patients without baseline brain metastases, the HR for time to intracranial progression was 0.05 (95% CI, 0.02 to 0.13), favoring lorlatinib over crizotinib. The probability of preventing development of brain metastases was 96% (95% CI, 89 to 98) with lorlatinib versus 27% (95% CI, 14 to 43) with crizotinib (Fig 3C). The cumulative incidence of progression of brain metastases as the first event, with adjustment for the competing risks of progression other than brain metastases and death, was lower in the lorlatinib group than in the crizotinib group (Appendix Fig A3). In the lorlatinib group, according to investigator assessment, only 4 of 114 patients without baseline brain metastases developed intracranial lesion(s), which occurred during the first 16 months of treatment. Additional information on these four patients is presented in Appendix 1, Results.
FIG 3.
Time to intracranial progression by investigator assessment using modified RECIST, version 1.1, in (A) the intention-to-treat population, (B) patients with baseline brain metastases, and (C) patients without baseline brain metastases. HR, hazard ratio; IC, intracranial; NR, not reached.
Safety
The median duration of treatment was 57.0 months (IQR, 13.9-63.3) with lorlatinib and 9.6 months (IQR, 4.7-17.1) with crizotinib. Overall, 49 of 149 patients (33%) treated with lorlatinib and 36 of 142 (25%) treated with crizotinib had at least one dose reduction. The median relative dose intensity was 99% (IQR, 80-100) with lorlatinib and 99% (IQR, 91-100) with crizotinib. All-causality any-grade adverse events (AEs) occurred in all patients in the lorlatinib group and in 140 of 142 patients (99%) in the crizotinib group; grade 3/4 AEs occurred in 77% and 57% of patients, respectively (Table 2). The higher incidence of all-causality grade 3/4 AEs in patients in the lorlatinib group versus crizotinib group was largely due to hypertriglyceridemia (25% v 0%), hypercholesterolemia (21% v 0%), weight gain (23% v 2%), and hypertension (12% v 1%; Appendix Table A1). With lorlatinib, all-causality AEs led to dose reduction in 23% of patients, temporary treatment discontinuation in 62%, and permanent discontinuation in 11%. Treatment-related AEs led to permanent treatment discontinuation in eight patients (5%), which occurred during the first 26 months. With crizotinib, all-causality AEs led to dose reduction in 15% of patients, temporary treatment discontinuation in 48%, and permanent discontinuation in 11%.
TABLE 2.
Summary of AEs
| Safety Population | Lorlatinib (n = 149) | Crizotinib (n = 142) |
|---|---|---|
| All-causality AEs, No. (%) | ||
| Any grade | 149 (100) | 140 (99) |
| Grade 3/4 | 115 (77) | 81 (57) |
| Grade 5 | 14 (9) | 7 (5) |
| Serious | 65 (44) | 45 (32) |
| Leading to temporary drug discontinuation | 92 (62) | 68 (48) |
| Leading to dose reduction | 34 (23) | 21 (15) |
| Leading to permanent drug discontinuation | 16 (11) | 15 (11) |
| Treatment-related AEs, No. (%) | ||
| Any grade | 145 (97) | 133 (94) |
| Grade 3/4 | 99 (66) | 55 (39) |
| Grade 5 | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Serious | 14 (9) | 9 (6) |
| Leading to temporary drug discontinuation | 58 (39) | 51 (36) |
| Leading to dose reduction | 31 (21) | 19 (13) |
| Leading to permanent drug discontinuation | 8 (5) | 8 (6) |
Abbreviation: AE, adverse event.
At 5 years, all-causality any-grade cardiovascular AEs occurred in 42 of 149 patients (28%) in the lorlatinib group and 40 of 142 (28%) in the crizotinib group (Appendix Table A2). Among patients with hyperlipidemia that was either present at baseline or developed during the study, 37 of 134 patients (28%) in the lorlatinib group and 15 of 32 (47%) in the crizotinib group had cardiovascular AEs (Appendix Table A3). The lower incidence of cardiovascular AEs in this patient population in the lorlatinib group versus crizotinib group was largely due to ischemic heart disease (16% v 31%) and embolic and thrombotic events (7% v 19%). All-causality CNS AEs occurred in 42% of patients in the lorlatinib group, the majority of which (86%) were of grade 1/2 severity (Appendix Table A4). Only three patients who experienced treatment-related CNS AEs (two had confusional state and one had nightmares) permanently discontinued lorlatinib. In the lorlatinib group, CNS AEs occurred in six of nine (67%) patients who had prior brain radiotherapy and in 57 of 140 (41%) patients without prior brain radiotherapy (Appendix Table A5).
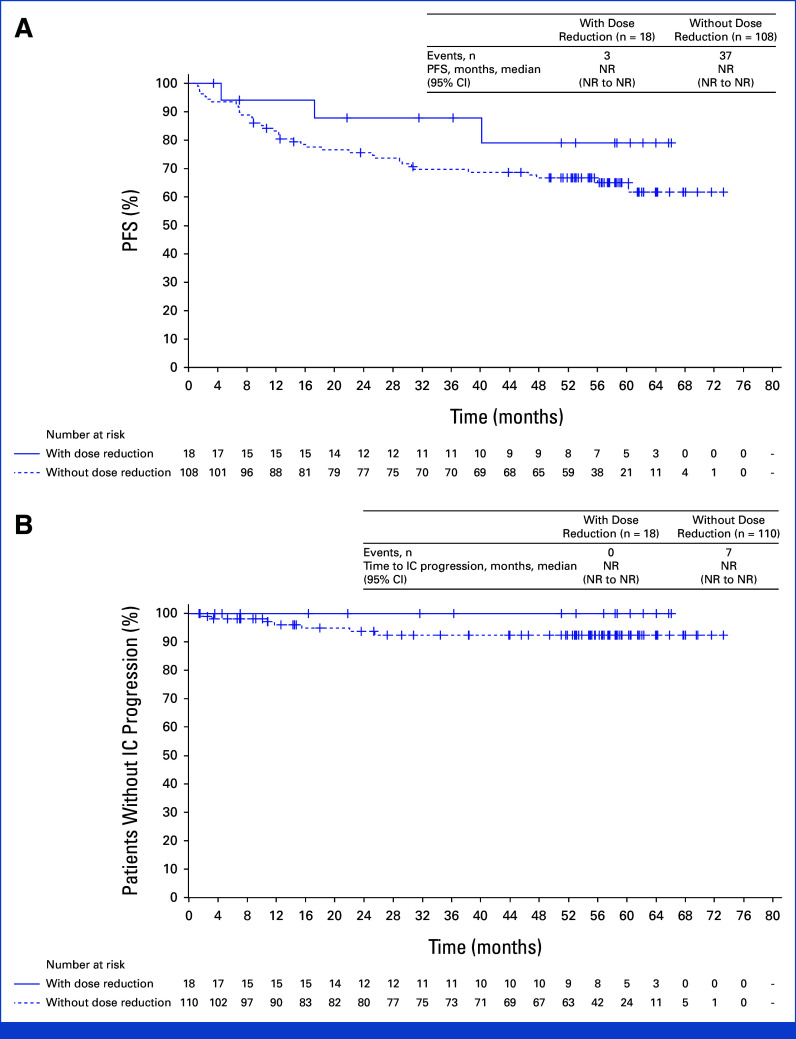
Efficacy in Patients Who Had Dose Reduction
Post hoc analyses were conducted in patients who had lorlatinib dose reduction within the first 16 weeks and in those who did not. Dose reduction did not seem to impact median PFS (Fig 4A) or time to intracranial progression (Fig 4B) in these patients.
FIG 4.
Outcomes in patients who had first lorlatinib dose reduction within 16 weeks. (A) PFS by investigator assessment and (B) time to intracranial progression by investigator assessment. PFS and time to intracranial progression were recalculated starting at the landmark time. Patients with event/censor time within the landmark time were excluded from the analysis. HR, hazard ratio; IC, intracranial; NR, not reached; PFS, progression-free survival.
Biomarker Analyses
Baseline plasma samples were available from 134 patients in the lorlatinib group and 129 in the crizotinib group. EML4::ALK variant 1 was detected in 15% of patients in the lorlatinib group and 20% in the crizotinib group; EML4::ALK variant 3a/b was detected in 13% and 18% of patients, respectively (Appendix Fig A4). The median PFS was 64.3 months (95% CI, 26.0 to NR) in patients with EML4::ALK variant 1 and 60.0 months (95% CI, 33.3 to NR) in those with EML4::ALK variant 3a/b in the lorlatinib group; in the crizotinib group, the median PFS was 7.4 months (95% CI, 5.5 to 9.0) and 5.6 months (95% CI, 5.3 to 7.6), respectively (Appendix Table A6). With lorlatinib (n = 97), the median PFS was 51.6 months (95% CI, 16.4 to NR) in the TP53 mutation–positive subgroup and NR (95% CI, 60.0 to NR) in the TP53 mutation–negative subgroup; with crizotinib (n = 100), the median PFS was 5.7 months (5.4 to 7.2) and 9.1 months (7.6 to 11.1), respectively (Appendix Table A7).
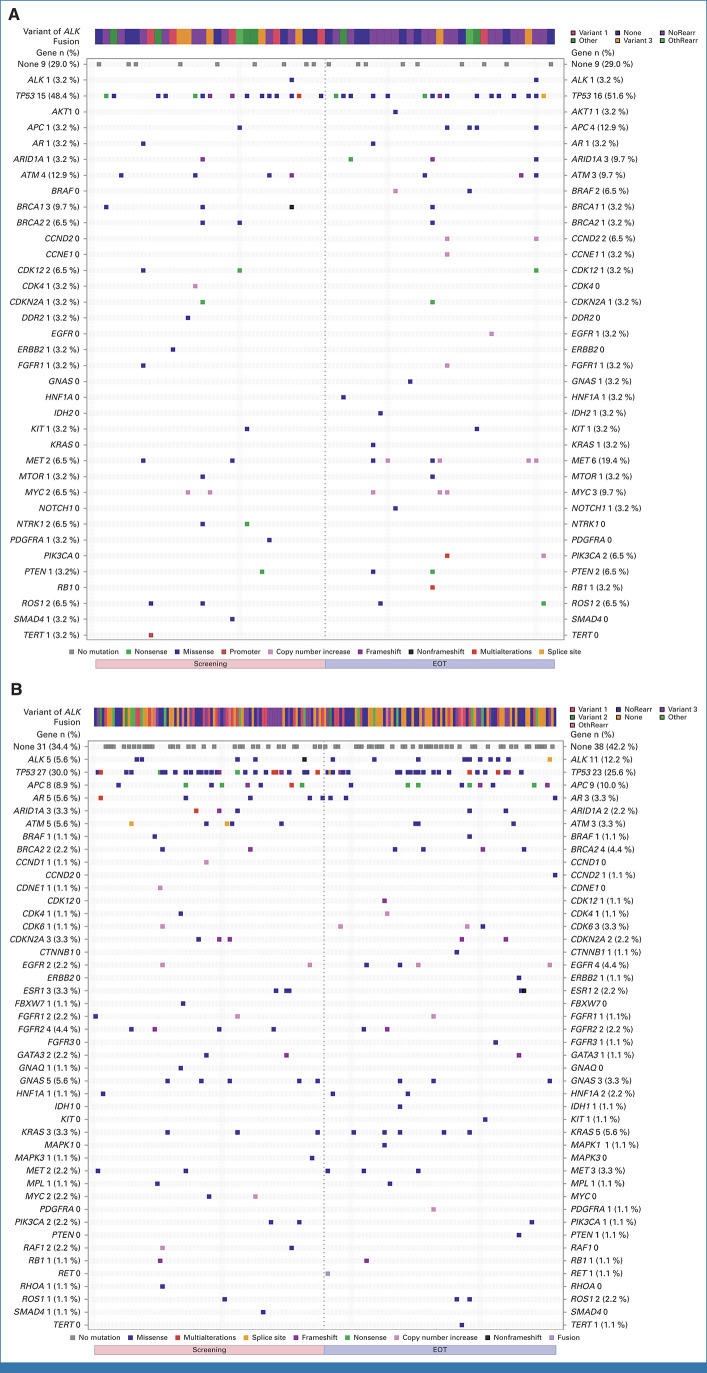
End-of-treatment ctDNA samples were available for 31 patients in the lorlatinib group and 89 patients in the crizotinib group. Emerging new ALK resistance mutations were detected at the end of crizotinib treatment, but none were detected in the ctDNA collected at the end of lorlatinib treatment (Appendix Table A8). Paired baseline and end-of-treatment ctDNA samples indicated that bypass mechanism aberrations were the main resistance mechanism in response to lorlatinib treatment (Appendix Table A9). The mutational landscape in lorlatinib and crizotinib patients is shown in Appendix Fig A5.
DISCUSSION
In this updated analysis from the CROWN study, after 5 years of follow-up, lorlatinib continued to show superior efficacy over crizotinib in patients with previously untreated, advanced, ALK-positive NSCLC, with remarkable PFS benefit and intracranial efficacy. At a median follow-up of 60.2 months, median PFS was still NR with lorlatinib. The PFS benefit, which exceeds 5 years, is the longest reported PFS in advanced NSCLC to date; to our knowledge, this represents the longest reported PFS outcome with any molecular targeted therapy across metastatic solid tumors (Data Supplement, online only).
The long-term efficacy of lorlatinib in the CROWN study surpassed that of other currently approved ALK TKIs. In the global phase III ALEX trial, after a median follow-up of 37.8 months, the investigator-assessed median PFS was 34.8 months (95% CI, 17.7 to not evaluable) and the 3-year PFS was 46% with alectinib.15 In the phase III ALTA-1L trial, at a median follow-up of 40.4 months, the median PFS by investigator was 30.8 months (95% CI, 21.3 to 40.6) and the 3-year PFS was 45% with brigatinib.16 In the phase III eXalt3 study, with a median follow-up of 23.8 months, the median PFS by BICR was 25.8 months (95% CI, 21.8 to NR) with ensartinib.17 Acknowledging the absence of head-to-head trials comparing second-generation ALK TKIs with lorlatinib and the limitations of cross-trial comparisons, findings from this study represent the longest reported PFS in ALK-positive NSCLC. Most (76%) PFS events occurred in the first 2 years with lorlatinib in the CROWN study, with only six additional PFS events occurring between 3 years and 5 years.
Brain metastases in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC remain a key clinical challenge.18,19 Although second-generation ALK TKIs have shown significant improvement in terms of intracranial efficacy versus crizotinib, prognosis in patients with brain metastases remains poor.15,16 In patients with baseline brain metastases after 5 years of follow-up in the CROWN study, lorlatinib resulted in high intracranial response, the majority of which were complete and durable responses; only five of 35 patients overall experienced intracranial progression, all within 30 months. Consistent with these results, only four patients developed intracranial lesions of the 114 without baseline brain metastases in the lorlatinib group, notwithstanding discrepancies between investigator and independent radiologic review. These results indicate that lorlatinib was effective in controlling preexisting brain metastases and in protecting against the development of new brain metastases.
At the time of this analysis, the required number of OS events for a protocol-specified second interim analysis was not met. OS follow-up is currently ongoing in the CROWN study, and the results will be reported in the future. In the pivotal phase I/II study, with a median follow-up for OS of 72.7 months (95% CI, 69.3 to 76.3), median OS was NR (95% CI, NR to NR) with lorlatinib, and 5-year OS was 76% (95% CI, 57 to 88) in patients with treatment-naїve ALK-positive NSCLC (n = 30; data on file). In the ALEX trial, 5-year OS was 62.5% with alectinib.15 In the ALTA-1L trial, 4-year OS was 66% with brigatinib.16
The safety profile of lorlatinib remains similar to that reported in previous analyses of the CROWN study, with no new safety signals detected after additional treatment exposure and longer follow-up.4,5 Lorlatinib was associated with a higher incidence of grade 3/4 AEs (77% v 57% with crizotinib), mostly due to an increase in blood lipid values; however, cardiovascular AEs (28%) were similar between the treatment groups. A subsequent assessment in patients who had hyperlipidemia at baseline or during the study showed that although a higher number of patients in the lorlatinib group had hyperlipidemia (134 v 32 in the crizotinib group), the incidence of cardiovascular AEs was lower with lorlatinib than with crizotinib (28% v 47%, respectively), mostly due to fewer occurrences of ischemic heart disease and embolic and thrombotic events. Management of hyperlipidemia should include monitoring for cholesterol and triglyceride levels while on lorlatinib treatment.20-22 The pragmatic guide recommends treatment with statins (eg, rosuvastatin or pravastatin) at the first sign of hyperlipidemia. For hyperlipidemia that persists despite treatment, increasing the dosage or inclusion of an additional lipid-lowering therapy is recommended.23
Among patients who developed CNS AEs, most had grade 1/2 events, which frequently could be managed by dose interruption and dose reduction.24 Long-term observations showed that the frequency of CNS AEs was higher among patients who had prior brain radiotherapy than those without prior brain radiotherapy; however, the number of patients who underwent brain radiotherapy was small, which may have affected the results. Despite higher incidences of grade 3/4 AEs with lorlatinib than with crizotinib, permanent discontinuations because of AEs were similar.
As reported previously, AEs with lorlatinib were manageable with dose reduction without affecting systemic or intracranial efficacy.25,26 These findings were confirmed with longer follow-up. PFS and time to intracranial progression were similar in patients who had lorlatinib dose reduction within the first 16 weeks and those who had no dose reductions, indicating that dose reduction may be an effective strategy to mitigate toxicity without compromising systemic or intracranial efficacy.
Patients with poor prognostic factors such as EML4::ALK variant 3a/b or TP53 mutation–positive status are associated with worse outcomes than those with EML4::ALK variant 1 or TP53 mutation–negative status.14,16,27 With long-term follow-up, the median PFS with lorlatinib was 60.0 months in EML4::ALK variant 3a/b subgroup and 51.6 months in TP53 mutation–positive subgroup. In the 3-year analysis, the median PFS by BICR was 33.3 months in EML4::ALK variant 3a/b subgroup.14 The discordance between the 3- and 5-year analyses was due to disagreement between BICR and investigator assessments in a few patients, resulting in the differences in median PFS because of the small number of patients (n = 18) in this subgroup. In the ALEX trial, the median PFS with alectinib was 17.7 months for EML4::ALK variant 3.27 In the ALTA-1L trial, the median PFS with brigatinib was 16.0 months in patients with EML4::ALK variant 3 and 18.0 months in those with TP53 mutation.16 The results from this study emphasize that lorlatinib treatment can benefit patients with poor prognostic biomarkers or difficult-to-treat alterations such as EML4::ALK variant 3 or TP53 comutation relatively more than other second-generation ALK TKIs. ctDNA samples at the end of lorlatinib treatment indicated that lorlatinib was effectively able to suppress the emergence of new ALK kinase domain mutations; instead, aberrations in bypass signaling pathways were the main resistance mechanism in patients who did develop lorlatinib resistance. By delaying the emergence of on-target resistance, lorlatinib is able to improve the durability of treatment outcomes.
A limitation of this study is that this is a post hoc analysis. The results provided are consequently descriptive in nature, with no statistical comparisons performed. In addition, end point evaluation by BICR stopped after the 3-year analysis, and only investigator assessments were conducted.
In summary, after 5 years of follow-up, the median PFS has yet to be reached in the lorlatinib group, corresponding to the longest PFS ever reported with any single-agent molecular targeted treatment not only in advanced NSCLC but across all metastatic solid tumors. These systemic efficacy results coupled with prolonged intracranial efficacy and the absence of new safety signals represent unprecedented outcomes for patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC and set a new benchmark for targeted therapies in cancer.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank the participating patients and their families, investigators, subinvestigators, research nurses, study coordinators, and operations staff. Editorial and medical writing support was provided by Kakoli Parai, PhD, of Nucleus Global and was funded by Pfizer.
APPENDIX 1. RESULTS
Patients Without Baseline Brain Metastases Who Developed Intracranial Lesion(s) in the Lorlatinib Group
In the lorlatinib group, according to investigator assessment only 4 of 114 patients without baseline brain metastases developed intracranial lesion(s), which occurred during the first 16 months of treatment. The first patient had intracranial progression after 1.6 months of treatment with lorlatinib, which was consistent with findings reported by blinded independent central review (BICR). In contrast, findings from investigator assessment in the remaining three patients were discordant with the BICR provided by independent neuroradiologists. The second patient, who had undergone brain radiotherapy 1 month before start of treatment, had intracranial progression at 5.6 months. This patient had a nontarget brain lesion at baseline with intracranial progression documented by BICR. The third patient had intracranial progression at 14.7 months. This patient was classified as having baseline brain metastases but had no documentation of intracranial progression by BICR. The fourth patient had intracranial progression at 15.7 months. This patient was categorized as without baseline brain metastases and did not have intracranial progression by BICR.
FIG A1.
PFS by investigator assessment in patients with baseline brain metastases. HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached; PFS, progression-free survival.
FIG A2.
PFS by investigator assessment in patients without baseline brain metastases. HR, hazard ratio; NR, not reached; PFS, progression-free survival.
FIG A3.
Cumulative incidence of progression of brain metastases as first event in (A) the intention-to-treat population, (B) patients with baseline brain metastases, and (C) patients without baseline brain metastases.
FIG A4.
Baseline plasma ctDNA samples available in the lorlatinib and crizotinib groups. ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA.
FIG A5.
Mutational landscape in (A) lorlatinib and (B) crizotinib patients at screening and EOT. None indicates no mutation, which includes no ctDNA samples and failed samples. If all mutations detected are SILENT, the column corresponding to the sample is blank. One crizotinib patient had no screening visit sample and was not included in the plot for screening. EOT, end of treatment; NoRearr, no rearrangement; OthRearr, other rearrangement.
TABLE A1.
All-Causality AEs Occurring in ≥10% of Patients in Any Treatment Group
| Event | Lorlatinib (n = 149) | Crizotinib (n = 142) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Gradea | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Any Gradeb | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Any AE, No. (%) | 149 (100) | 95 (64) | 20 (13) | 140 (99) | 69 (49) | 12 (8) |
| Hypercholesterolemiac | 108 (72) | 30 (20) | 2 (1) | 5 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertriglyceridemiac | 99 (66) | 25 (17) | 12 (8) | 8 (6) | 0 | 0 |
| Edemac | 85 (57) | 6 (4) | 0 | 61 (43) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Peripheral neuropathyc | 65 (44) | 2 (1) | 0 | 23 (16) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Weight increased | 65 (44) | 34 (23) | 0 | 18 (13) | 3 (2) | 0 |
| Fatiguec | 45 (30) | 2 (1) | 0 | 47 (33) | 4 (3) | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 41 (28) | 1 (1) | 0 | 20 (14) | 0 | 0 |
| Cognitive effectsc | 41 (28) | 5 (3) | 0 | 10 (7) | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 39 (26) | 18 (12) | 0 | 6 (4) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Anemia | 37 (25) | 6 (4) | 0 | 14 (10) | 4 (3) | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 34 (23) | 3 (2) | 0 | 75 (53) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 34 (23) | 5 (3) | 0 | 26 (18) | 4 (3) | 0 |
| Headache | 33 (22) | 0 | 0 | 28 (20) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Mood effectsc | 31 (21) | 2 (1) | 0 | 9 (6) | 0 | 0 |
| Cough | 30 (20) | 0 | 0 | 27 (19) | 0 | 0 |
| Pyrexia | 30 (20) | 1 (1) | 0 | 19 (13) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| ALT increased | 29 (19) | 4 (3) | 0 | 49 (35) | 5 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Back pain | 29 (19) | 2 (1) | 0 | 20 (14) | 0 | 0 |
| Constipation | 29 (19) | 0 | 0 | 43 (30) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Vision disorderc | 29 (19) | 0 | 0 | 57 (40) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Pain in extremity | 28 (19) | 0 | 0 | 14 (10) | 0 | 0 |
| Gamma-glutamyltransferase increased | 27 (18) | 8 (5) | 1 (1) | 22 (15) | 6 (4) | 0 |
| Nausea | 25 (17) | 1 (1) | 0 | 75 (53) | 3 (2) | 0 |
| SARS-CoV-2 test positive | 25 (17) | 0 | 0 | 3 (2) | 0 | 0 |
| AST increased | 24 (16) | 3 (2) | 0 | 39 (27) | 5 (4) | 0 |
| Lipase increased | 22 (15) | 8 (5) | 1 (1) | 18 (13) | 4 (3) | 1 (1) |
| Hyperglycemia | 21 (14) | 8 (5) | 0 | 5 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 21 (14) | 0 | 0 | 6 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 20 (13) | 1 (1) | 0 | 56 (39) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 19 (13) | 4 (3) | 0 | 25 (18) | 5 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Dizziness | 19 (13) | 0 | 0 | 21 (15) | 0 | 0 |
| Sleep effectsc | 19 (13) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 14 (10) | 0 | 0 |
| Chest pain | 18 (12) | 2 (1) | 0 | 20 (14) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Rash | 18 (12) | 0 | 0 | 12 (8) | 0 | 0 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 18 (12) | 1 (1) | 0 | 11 (8) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Amylase increased | 17 (11) | 0 | 0 | 19 (13) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Pneumonia | 17 (11) | 5 (3) | 1 (1) | 13 (9) | 4 (3) | 1 (1) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 16 (11) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hyperuricemia | 16 (11) | 0 | 1 (1) | 6 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| Blood creatine increased | 11 (7) | 2 (1) | 0 | 22 (15) | 3 (2) | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 11 (7) | 1 (1) | 0 | 21 (15) | 13 (9) | 0 |
| Blood alkaline phosphatase increased | 9 (6) | 0 | 0 | 17 (12) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Dysgeusia | 9 (6) | 0 | 0 | 23 (16) | 0 | 0 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 8 (5) | 1 (1) | 0 | 18 (13) | 6 (4) | 0 |
| Decreased appetite | 6 (4) | 0 | 0 | 35 (25) | 4 (3) | 0 |
| Sinus bradycardia | 6 (4) | 0 | 0 | 16 (11) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Blood lactate dehydrogenase increased | 5 (3) | 1 (1) | 0 | 16 (11) | 0 | 0 |
| Bradycardia | 4 (3) | 0 | 0 | 20 (14) | 0 | 0 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 3 (2) | 0 | 0 | 18 (13) | 8 (6) | 4 (3) |
Abbreviation: AE, adverse event.
Fourteen patients in the lorlatinib group died due to COVID-19 pneumonia (n = 2), respiratory failure (n = 2), pneumonia (n = 1), cardiac failure (n = 1), pulmonary embolism (n = 1), lower respiratory tract infection (n = 1), basal ganglia hemorrhage (n = 1), cardiac arrest (n = 1), cardiac failure acute (n = 1), death (n = 1; reason unknown), disease progression (n = 1), or lung neoplasm malignant (n = 1). Two treatment-related deaths occurred due to cardiac failure acute and respiratory failure (n = 1 each).
Seven patients in the crizotinib group died due to malignant neoplasm progression (n = 2), pericardial effusion (n = 1), death (n = 1; reason unknown), disease progression (n = 1), neoplasm progression (n = 1), or Clostridium difficile colitis (n = 1).
This category comprised a cluster of AEs that may represent similar clinical symptoms or syndromes.
TABLE A2.
Summary of All-Causality Cardiovascular AEs
| Event | Lorlatinib (n = 149) | Crizotinib (n = 142) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Gradea | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Any Grade | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Any AEs, No. (%) | 42 (28) | 19 (13) | 8 (5) | 10 (7) | 1 (1) | 40 (28) | 15 (11) | 13 (9) | 11 (8) | 1 (1) |
| SMQ ischemic heart disease, No. (%) | 21 (14) | 14 (9) | 1 (1) | 6 (4) | 0 | 25 (18) | 15 (11) | 3 (2) | 6 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 19 (13) | 14 (9) | 1 (1) | 4 (3) | 0 | 25 (18) | 16 (11) | 3 (2) | 5 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Arteriosclerosis coronary artery | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ECG T wave abnormal | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Troponin increased | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase MB increased | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| ECG ST segment elevation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ECG T wave inversion | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SMQ embolic and thrombotic events, No. (%) | 13 (9) | 4 (3) | 4 (3) | 4 (3) | 0 | 16 (11) | 3 (2) | 8 (6) | 5 (4) | 0 |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 6 (4) | 2 (1) | 4 (3) | 0 | 0 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 3 (2) | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (4) | 0 | 3 (2) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Embolic cerebral infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Monoparesis | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sigmoid sinus thrombosis | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Ischemic stroke | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Retinal vein occlusion | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Superior vena cava syndrome | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombophlebitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Cluster cardiac failure, No. (%) | 7 (5) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure | 3 (2) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Ejection fraction decreased | 2 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure acute | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure chronic | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure congestive | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SMQ ischemic CNS vascular conditions, No. (%) | 5 (3) | 0 | 1 (1) | 4 (3) | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Carotid artery disease | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Embolic cerebral infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Ischemic stroke | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 |
| SMQ hemorrhagic CNS vascular conditions, No. (%) | 4 (3) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Basal ganglia hemorrhage | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subdural hematoma | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Thalamus hemorrhage | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
NOTE. Cardiovascular events were cardiac death; sudden cardiac death; sudden death; and the SMQ embolic and thrombotic events of cluster cardiac failure, SMQ ischemic heart disease, SMQ ischemic CNS vascular conditions, and SMQ hemorrhagic CNS vascular conditions.
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; SMQ, Standardized MedDRA Queries.
Four patients in the lorlatinib group died due to pulmonary embolism, cardiac failure, cardiac failure acute, and basal ganglia hemorrhage (n = 1 each).
TABLE A3.
Summary of Cardiovascular AEs in Patients With Hyperlipidemia At Baseline and/or Developed During the Study
| Event | Lorlatinib (n = 134) | Crizotinib (n = 32) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Gradea | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Any Grade | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Any CV AEs, No. (%) | 37 (28) | 18 (13) | 7 (5) | 8 (6) | 1 (1) | 15 (47) | 8 (25) | 4 (13) | 3 (9) | 0 |
| SMQ ischemic heart disease | 21 (16) | 14 (10) | 1 (1) | 6 (4) | 0 | 10 (31) | 7 (22) | 2 (6) | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 19 (14) | 14 (10) | 1 (1) | 4 (3) | 0 | 10 (31) | 8 (25) | 2 (6) | 0 | 0 |
| Arteriosclerosis coronary artery | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ECG T wave abnormal | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Troponin increased | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase MB increased | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 |
| ECG ST segment elevation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ECG T wave inversion | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SMQ embolic and thrombotic events, No. (%) | 10 (7) | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | 4 (3) | 0 | 6 (19) | 2 (6) | 2 (6) | 2 (6) | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 2 (1) | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (6) | 0 | 2 (6) | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Embolic cerebral infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sigmoid sinus thrombosis | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Thrombophlebitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Cluster cardiac failure, No. (%) | 6 (4) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure | 2 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ejection fraction decreased | 2 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure acute | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure chronic | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac failure congestive | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SMQ hemorrhagic CNS vascular conditions, No. (%) | 4 (3) | 0 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Basal ganglia hemorrhage | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subdural hematoma | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thalamus hemorrhage | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SMQ ischemic CNS vascular conditions, No. (%) | 4 (3) | 0 | 1 (1) | 3 (2) | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral ischemia | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Embolic cerebral infarction | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cerebral infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3) | 0 |
NOTE. Cardiovascular events were cardiac death; sudden cardiac death; sudden death; and SMQ embolic and thrombotic events of cluster cardiac failure, SMQ ischemic heart disease, SMQ ischemic CNS vascular conditions, and SMQ hemorrhagic CNS vascular conditions.
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; CV, cardiovascular; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; SMQ, Standardized MedDRA Queries.
Three patients in the lorlatinib group died due to cardiac failure, cardiac failure acute, and basal ganglia hemorrhage (n = 1 each).
TABLE A4.
Summary of CNS AEs in the Lorlatinib Group
| Cluster Term | Lorlatinib (n = 149) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Grade | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Any AEs, No. (%) | 63 (42) | 36 (24) | 18 (12) | 8 (5) | 1 (1) |
| Cognitive effectsa | 41 (28) | 25 (17) | 11 (7) | 5 (3) | 0 |
| Mood effectsb | 31 (21) | 17 (11) | 12 (8) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Speech effectsc | 9 (6) | 6 (4) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Psychotic effectsd | 8 (5) | 5 (3) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; HLGT, High-Level Group Term; HLT, High-Level Term; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; NEC, not elsewhere classified; PT, preferred term; SMQ, Standardized MedDRA Queries.
Cognitive effects were any event from HLGT cognitive and attention disorders and disturbances, deliria (including confusion), or mental impairment disorders.
Mood effects were any event from HLGT anxiety disorders and symptoms, depressed mood disorders and disturbances, manic and bipolar mood disorders and disturbances, mood disorders and disturbances NEC, or personality disorders and disturbances in behavior.
Speech effects were any event from HLT speech and language abnormalities.
Psychotic effects were any event from SMQ narrow psychosis and psychotic disorders or PT of psychotic symptom.
TABLE A5.
Summary of CNS AEs in Patients With and Without Prior Brain Radiotherapy in the Lorlatinib Group
| Cluster Term | Lorlatinib | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Grade | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Prior brain radiotherapy (n = 9) | |||||
| Any AEs, No. (%) | 6 (67) | 5 (56) | 1 (11) | 0 | 0 |
| Cognitive effectsa | 4 (44) | 3 (33) | 1 (11) | 0 | 0 |
| Mood effectsb | 2 (22) | 2 (22) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Speech effectsc | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Psychotic effectsd | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No prior brain radiotherapy (n = 140) | |||||
| Any AEs, No. (%) | 57 (41) | 31 (22) | 17 (12) | 8 (6) | 1 (1) |
| Cognitive effectsa | 37 (26) | 22 (16) | 10 (7) | 5 (4) | 0 |
| Mood effectsb | 29 (21) | 15 (11) | 12 (9) | 2 (1) | 0 |
| Speech effectsc | 9 (6) | 6 (4) | 2 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| Psychotic effectsd | 8 (6) | 5 (4) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) |
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; HLGT, High-Level Group Term; HLT, High-Level Term; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; NEC, not elsewhere classified; PT, preferred term; SMQ, Standardized MedDRA Queries.
Cognitive effects were any event from HLGT cognitive and attention disorders and disturbances, deliria (including confusion), or mental impairment disorders.
Mood effects were any event from HLGT anxiety disorders and symptoms, depressed mood disorders and disturbances, manic and bipolar mood disorders and disturbances, mood disorders and disturbances NEC, or personality disorders and disturbances in behavior.
Speech effects were any event from HLT speech and language abnormalities.
Psychotic effects were any event from SMQ narrow psychosis and psychotic disorders or PT of psychotic symptom.
TABLE A6.
Efficacy by EML4::ALK Fusion Variant and Other ALK Rearrangements in Baseline ctDNA
| EML4::ALK Variant | Lorlatinib (n = 134) | Crizotinib (n = 129) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | ORR, % (95% CI) | DOR, Months, Median (95% CI) | PFS, Months, Median, (95% CI) | No. (%) | ORR, % (95% CI) | DOR, Months, Median (95% CI) | PFS, Months, Median, (95% CI) | |
| Variant 1 | 20 (15) | 80 (56 to 94) | 62.5 (50.0 to NR) | 64.3 (26.0 to NR) | 26 (20) | 50 (30 to 70) | 7.4 (5.6 to 9.2) | 7.4 (5.5 to 9.0) |
| Variant 2 | 7 (5) | 100 (59 to 100) | NR (32.8 to NR) | NR (34.6 to NR) | 2 (2) | 50 (1 to 99) | NR (NR to NR) | NR (3.7 to NR) |
| Variant 3a/b | 18 (13) | 83 (59 to 96) | 58.2 (38.7 to NR) | 60.0 (33.3 to NR) | 23 (18) | 70 (47 to 87) | 5.6 (3.7 to 8.5) | 5.6 (5.3 to 7.6) |
| Other | 15 (11) | 87 (60 to 98) | 27.6 (11.1 to NR) | 29.3 (11.1 to NR) | 9 (7) | 78 (40 to 97) | 7.5 (7.3 to 14.6) | 10.0 (7.2 to 16.0) |
| Other ALK fusion | 2 (1) | 100 (16 to 100) | NR (12.9 to NR) | NR (14.1 to NR) | 4 (3) | 75 (19 to 99) | 3.7 (3.7 to NR) | 8.2 (3.5 to NR) |
| ALK rearrangement not detected | 35 (26) | 69 (51 to 83) | NR (NR to NR) | NR (42.3 to NR) | 36 (28) | 64 (46 to 79) | 11.1 (7.5 to 27.4) | 11.0 (7.2 to 13.1) |
| No cell-free DNA detected | 32 (24) | 88 (71 to 97) | NR (NR to NR) | NR (NR to NR) | 25 (19) | 84 (64 to 96) | 14.8 (11.0 to 28.2) | 18.4 (12.7 to 29.3) |
| Not analyzeda | 5 (4) | 60 (15 to 95) | NR (31.3 to NR) | 32.9 (1.9 to NR) | 4 (3) | 50 (7 to 93) | 12.7 (5.3 to NR) | 21.9 (9.0 to NR) |
Abbreviations: ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; DOR, duration of response; NR, not reached; ORR, objective response rate; PFS, progression-free survival.
Sample failed analysis, was uninformative, or was not analyzed.
TABLE A7.
Efficacy by TP53 Statusa in Patients With Baseline ctDNA
| Mutation Status | Lorlatinib (n = 97) | Crizotinib (n = 100) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | ORR, % (95% CI) | DOR, Months, Median (95% CI) | PFS, Months, Median, (95% CI) | No. (%) | ORR, % (95% CI) | DOR, Months, Median (95% CI) | PFS, Months, Median, (95% CI) | |
| Positive | 41 (42) | 68 (52 to 82) | NR (50.0 to NR) | 51.6 (16.4 to NR) | 42 (42) | 60 (43 to 74) | 5.6 (5.3 to 8.5) | 5.7 (5.4 to 7.2) |
| Negative | 56 (58) | 88 (76 to 95) | NR (62.5 to NR) | NR (60.0 to NR) | 58 (58) | 66 (52 to 78) | 9.2 (7.4 to 11.1) | 9.1 (7.6 to 11.1) |
Abbreviations: ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; DOR, duration of response; NR, not reached; ORR, objective response rate; PFS, progression-free survival.
For TP53 mutation status determination, both known pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants and variants of unknown significance per the ClinVar database were taken into account.
TABLE A8.
Summary of Resistance Mechanisms in End-of-Treatment ctDNA Samples
| Resistance Mechanism | Lorlatinib (n = 31) | Crizotinib (n = 89) |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance mechanisms, No. (%) | ||
| New single ALK mutation | 0 | 8 (9) |
| ALK compound mutation | 0 | 2 (2) |
| Bypass mechanism, No. (%) | 9 (29) | 10 (11) |
| MAPK pathway aberration | 3 (10) | 1 (1) |
| PI3K/MTOR/PTEN pathway aberration | 2 (6) | 0 |
| RTK pathway aberration | 4 (13) | 5 (6) |
| Cell cycle pathway aberration | 2 (6) | 5 (6) |
| Other gene aberration, No. (%) | 11 (35) | 19 (21) |
| Unknown, No. (%) | 13 (42) | 56 (63) |
NOTE. Resistance mechanisms at EOT were not available for three patients because of results not reported at screening and for one patient because of results not reported at screening and EOT. The following aberrations were identified: MAPK pathway aberration: Lorlatinib: KRAS G12C; BRAF G466E; BRAF amplification; Crizotinib: KRAS K117N. PI3K/MTOR/PTEN pathway aberration: Lorlatinib: PIK3CA amplification; PTEN Q214*. RTK pathway aberration: Lorlatinib: MET amplification (3); EGFR amplification; Crizotinib: NCOA4-RET fusion; EGFR L858R; FGFR1/PDGFRA amplification; EGFR amplification; FGFR3 Y770F. Cell cycle pathway aberration: Lorlatinib: MYC amplification; RB1 K80*; Crizotinib: CDK4 amplification; CDK6 amplification; CDKN2A Y44fs; RB1 M695fs; CCND2 I287T. Other gene aberration: Any alteration in any of the other genes included in the G360 panel (eg, APC, AR, ARID1A, ATM, etc).
Abbreviations: ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; EOT, end of treatment.
TABLE A9.
Summary of Potential Resistance Mechanisms in ctDNA Samples Collected At the End of Treatment
| Resistance Mechanism | Lorlatinib (n = 31) | Crizotinib (n = 90) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | End of Treatment | Baseline | End of Treatment | |
| Patients with reported results, No. (%) | 29 (94) | 31 (100) | 87 (97) | 89 (99) |
| Positive status, No. (%) | ||||
| ALK fusion | 15 (48) | 6 (19) | 47 (52) | 30 (33) |
| ALK mutation | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 5 (6) | 11 (12) |
| TP53 mutation | 15 (48) | 16 (52) | 27 (30) | 23 (26) |
| MAPK pathway aberration | 0 | 3 (10) | 4 (4) | 4 (4) |
| PI3K/MTOR/PTEN pathway aberration | 1 (3) | 3 (10) | 1 (1) | 0 |
| RTK pathway aberration | 1 (3) | 6 (19) | 3 (3) | 5 (6) |
| Cell cycle pathway aberration | 4 (13) | 5 (16) | 4 (4) | 5 (6) |
| Other mutation | 12 (39) | 14 (45) | 36 (40) | 28 (31) |
| No ctDNA detected | 5 (16) | 8 (26) | 17 (19) | 29 (32) |
NOTE. Four patients were excluded from baseline because of missing sample or results not reported but were included in EOT as results were available. One patient was excluded from baseline and EOT because of results not reported. A patient could be classified in multiple categories. The following aberrations were identified: MAPK pathway aberration: BRAF V600E; V600Dup; R389C; G466E; or amplification; KRAS G12D; G12C; G12S; K117N; A146T; or amplification; NRAS G12D; or amplification. PI3K/MTOR/PTEN pathway aberration: PIK3CA E545K; E542K; K111E; R93Q; N1044K; or amplification; MTOR C1483F; PTEN Q214*. RTK pathway aberration: EGFR L858R; R1068Q; or amplification; ERBB2 A440T; R678Q; or amplification; KIT; MET; FGFR1; FGFR2; FGFR3; PDGFRA amplification; NCOA4-RET fusion. Cell cycle pathway aberration: CDK4; CDK6; CCND1; CCND2; CCNE1; or MYC amplification; CDKN2A E69* or Y44fs; RB1 M695fs; or K80*. Other gene aberration: Any alteration in any of the other genes included in the G360 panel (eg, APC, AR, ARID1A, ATM, etc).
Abbreviations: ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; EOT, end of treatment.
Benjamin J. Solomon
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Roche/Genentech, Pfizer (Inst), Amgen (Inst)
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme, AstraZeneca (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Amgen, Lilly, BeiGene, Takeda, GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Janssen (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline
Research Funding: Sanofi (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: UpToDate
Geoffrey Liu
Honoraria: Pfizer, Novartis, Merck, AstraZeneca, Takeda, AbbVie, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche Canada, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Amgen
Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, takeda, Roche Canada
Speakers' Bureau: AstraZeneca, Takeda, Pfizer
Research Funding: Roche (Inst), AstraZeneca/MedImmune (Inst), Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim
Enriqueta Felip
Consulting or Advisory Role: AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Roche, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Takeda, Turning Point Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo
Speakers' Bureau: Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Roche, Genentech, Janssen, Medical Trends, Medscape, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, PeerVoice, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, Touch Oncology
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: AstraZeneca, Janssen, Roche
Other Relationship: GRIFOLS
Uncompensated Relationships: Member of the Scientific Advisory Committee -Hospital Universitari Parc Taulí; SEOM (Sociedad Española de Oncología Médica), President from 2021 to 2023; “ETOP IBCSG Partners” Member of the Scientific Committee
Tony S.K. Mok
Employment: The Chinese University of Hong Kong
Leadership: AstraZeneca, HUTCHMED, Aurora Tele-Oncology Platform, Insighta Holdings Limited
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Aurora Tele-Oncology Platform, HUTCHMED, AstraZeneca, Biolidics, Prenetics, Alentis Therapeutics, D3 Bio, Lunit
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Alpha Biopharma, ACEA Pharmaceutical Research, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Fishawack Facilitate, InMed, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, OrigiMed, Pfizer, Prime Oncology, Roche, Sanofi Aventis GmbH, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Takeda, Lucence, Medscape, Permanyer Publications, PeerVoice, Physicans' Education Resource, Research to Practice, Shanghai BeBirds Translation & Consulting, Suzhou Liangyihui Network Technology, AbbVie, Berry Oncology, Blueprint Medicines, C4 Therapeutics, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, D3, Eisai, Gilead Sciences, Gritstone bio, Guardant Health, touchIME, Adagene, Daz Group, Janssen, Jiahui Holdings Co, Lucence, MDHealth Brazil, Merck, MiRXES, Shanghai Promedican Pharmaceuticals Co, Ltd, AVEO, GLG's Healthcare, Illumina, Hengrui Therapeutics, Novocure, Omega Therapeutics, Prenetics, Regeneron, Xencor, Qiming Development (HK) Ltd, Summit Therapeutics Sub, Inc, Da Volterra, Lakeshore Biotechnology, AnHeart Therapeutics, Simcere of America Inc, SFJ Pharmaceutical Ltd, Synergy Research, Tigermed, Vertex, Virtus Medical Group, Yuhan, Ignyta, Incyte, Inivata, IQVIA
Consulting or Advisory Role: AbbVie, ACEA Pharmaceutical Research, Alpha Biopharma, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Berry Oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Eisai, Fishawack Facilitate, Gritstone bio, Guardant Health, Hengrui Therapeutics, Ignyta, Incyte, Inivata, IQvia, Lilly, Loxo, Lunit, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Puma Biotechnology, Roche, SFJ Pharmaceuticals Group, Takeda, Vertex, Yuhan, Qiming Development (HK) Ltd, D3, C4 Therapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, geneDecode, Adagene, Bayer HealthCare Pharmacuticals, BerGenBio, Bowtie Life Insurance Company, BridgeBio, Covidien/Medtronic, Cirina, Da Volterra, Elevation Oncology, Genentech, HUTCHMED, Lakeshore Biotechnology, Lucence, Medtronic, MiRXES, Omega Therapeutics, OrigiMed, OSE Immunotherapeutics, prIME Oncology, Prenetics, Regeneron, Simcere, Summit Therapeutics, Synergy Research, Tigermed, Virtus Medical Group, Imagene AI Ltd
Research Funding: AstraZeneca (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), SFJ Pharmaceuticals Group (Inst), Roche (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Xcovery (Inst), G1 Therapeutics (Inst), Merck Serono (Inst), Takeda (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Astrazeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, MiRXES, Pfizer, Novartis, AbbVie, Roche, Zai Lab, Pfizer, LiangYiHui
Ross A. Soo
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Takeda, Yuhan, Amgen, Bayer, Merck, Merck Serono, Puma Biotechnology, J INTS BIO
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Yuhan, Takeda, Amgen, Lilly, Merck, Janssen, Puma Biotechnology, Merck Serono, Bayer, Thermo Fisher Scientific, J INTS BIO
Research Funding: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim
Julien Mazieres
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly/ImClone, MSD, AstraZeneca, Pierre Fabre, Blueprint Medicines, Hengrui Therapeutics
Research Funding: Roche (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb
Alice T. Shaw
Employment: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Filippo de Marinis
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, MSD Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck Serono
Yasushi Goto
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly Japan, Chugai Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, MSD, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Novartis, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck, Guardant Health AMEA, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Amgen, Janssen, Sandoz, Nichiiko, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca
Consulting or Advisory Role: Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Guardant Health AMEA, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Janssen, Ono Pharmaceutical
Research Funding: AbbVie (Inst), Lilly Japan (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Ono Pharmaceutical (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb Japan (Inst), Chugai Pharma (Inst), Taiho Pharmaceutical (Inst), MSD (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Merck Serono (Inst), Genomic Health (Inst), CMIC (Inst), Takeda (Inst), EPS Holdings (Inst), IQVIA (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan (Inst), Janssen (Inst), Amgen (Inst), EP Croit Co (Inst), Astellas Amgen BioPharma (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Preferred Network (Inst), Medpace (Inst), Sysmex (Inst)
Uncompensated Relationships: Cancer Net Japan, JAMT
Yi-Long Wu
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Roche, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb/China, Hengrui Pharmaceutical, BeiGene Beijing
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda
Research Funding: Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Roche (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), BMS (Inst)
Dong-Wan Kim
Research Funding: Alpha Biopharma (Inst), AstraZeneca/MedImmune (Inst), Hanmi (Inst), Janssen (Inst), Merus (Inst), Mirati Therapeutics (Inst), MSD (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Ono Pharmaceutical (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Takeda (Inst), TP Therapeutics (Inst), Xcovery (Inst), Yuhan (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical (Inst), BridgeBio Pharma (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Merck (Inst), inno.N (Inst), IMBdx (Inst)
Jean-François Martini
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer, Kiara Therapeutics
Rossella Messina
Employment: Pfizer, Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Jolanda Paolini
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Anna Polli
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Despina Thomaidou
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Francesca Toffalorio
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Todd M. Bauer
Employment: Tennessee Oncology
Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Bayer, Lilly, Sanofi, AVEO
Speakers' Bureau: Bayer, Lilly
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
See accompanying Editorial, p. 3383
PRIOR PRESENTATION
Presented in part at the ASCO annual meeting, Chicago, IL, May 31, 2024.
SUPPORT
Supported by Pfizer.
CLINICAL TRIAL INFORMATION
NCT03052608 (CROWN)
DATA SHARING STATEMENT
A data sharing statement provided by the authors is available with this article at DOI https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.24.00581. Upon request and subject to review, Pfizer will provide the data that support the findings of this study. Subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Pfizer may also provide access to the related individual deidentified participant data. See https://www.pfizer.com/science/clinical-trials/trial-data-and-results for more information.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception and design: Benjamin J. Solomon, Geoffrey Liu, Tony S.K. Mok, Alice T. Shaw, Yi-Long Wu, Dong-Wan Kim, Jean-François Martini, Anna Polli, Despina Thomaidou, Francesca Toffalorio
Provision of study materials or patients: Benjamin J. Solomon, Geoffrey Liu, Enriqueta Felip, Tony S.K. Mok, Ross A. Soo, Julien Mazieres, Alice T. Shaw, Filippo de Marinis, Dong-Wan Kim, Todd M. Bauer
Collection and assembly of data: Geoffrey Liu, Enriqueta Felip, Tony S.K. Mok, Ross A. Soo, Alice T. Shaw, Filippo de Marinis, Yi-Long Wu, Jolanda Paolini, Anna Polli, Despina Thomaidou, Francesca Toffalorio, Todd M. Bauer
Data analysis and interpretation: Geoffrey Liu, Enriqueta Felip, Tony S.K. Mok, Ross A. Soo, Julien Mazieres, Alice T. Shaw, Yasushi Goto, Yi-Long Wu, Dong-Wan Kim, Jean-François Martini, Rossella Messina, Jolanda Paolini, Anna Polli, Despina Thomaidou, Francesca Toffalorio, Todd M. Bauer
Manuscript writing: All authors
Final approval of manuscript: All authors
Accountable for all aspects of the work: All authors
AUTHORS' DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes From the Phase III CROWN Study
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/jco/authors/author-center.
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (Open Payments).
Benjamin J. Solomon
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Roche/Genentech, Pfizer (Inst), Amgen (Inst)
Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme, AstraZeneca (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Amgen, Lilly, BeiGene, Takeda, GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Janssen (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline
Research Funding: Sanofi (Inst)
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: UpToDate
Geoffrey Liu
Honoraria: Pfizer, Novartis, Merck, AstraZeneca, Takeda, AbbVie, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche Canada, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Amgen
Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, takeda, Roche Canada
Speakers' Bureau: AstraZeneca, Takeda, Pfizer
Research Funding: Roche (Inst), AstraZeneca/MedImmune (Inst), Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim
Enriqueta Felip
Consulting or Advisory Role: AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Roche, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Takeda, Turning Point Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo
Speakers' Bureau: Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Roche, Genentech, Janssen, Medical Trends, Medscape, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, PeerVoice, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, Touch Oncology
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: AstraZeneca, Janssen, Roche
Other Relationship: GRIFOLS
Uncompensated Relationships: Member of the Scientific Advisory Committee -Hospital Universitari Parc Taulí; SEOM (Sociedad Española de Oncología Médica), President from 2021 to 2023; “ETOP IBCSG Partners” Member of the Scientific Committee
Tony S.K. Mok
Employment: The Chinese University of Hong Kong
Leadership: AstraZeneca, HUTCHMED, Aurora Tele-Oncology Platform, Insighta Holdings Limited
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Aurora Tele-Oncology Platform, HUTCHMED, AstraZeneca, Biolidics, Prenetics, Alentis Therapeutics, D3 Bio, Lunit
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Alpha Biopharma, ACEA Pharmaceutical Research, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Fishawack Facilitate, InMed, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, OrigiMed, Pfizer, Prime Oncology, Roche, Sanofi Aventis GmbH, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Takeda, Lucence, Medscape, Permanyer Publications, PeerVoice, Physicans' Education Resource, Research to Practice, Shanghai BeBirds Translation & Consulting, Suzhou Liangyihui Network Technology, AbbVie, Berry Oncology, Blueprint Medicines, C4 Therapeutics, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, D3, Eisai, Gilead Sciences, Gritstone bio, Guardant Health, touchIME, Adagene, Daz Group, Janssen, Jiahui Holdings Co, Lucence, MDHealth Brazil, Merck, MiRXES, Shanghai Promedican Pharmaceuticals Co, Ltd, AVEO, GLG's Healthcare, Illumina, Hengrui Therapeutics, Novocure, Omega Therapeutics, Prenetics, Regeneron, Xencor, Qiming Development (HK) Ltd, Summit Therapeutics Sub, Inc, Da Volterra, Lakeshore Biotechnology, AnHeart Therapeutics, Simcere of America Inc, SFJ Pharmaceutical Ltd, Synergy Research, Tigermed, Vertex, Virtus Medical Group, Yuhan, Ignyta, Incyte, Inivata, IQVIA
Consulting or Advisory Role: AbbVie, ACEA Pharmaceutical Research, Alpha Biopharma, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Berry Oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Eisai, Fishawack Facilitate, Gritstone bio, Guardant Health, Hengrui Therapeutics, Ignyta, Incyte, Inivata, IQvia, Lilly, Loxo, Lunit, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Puma Biotechnology, Roche, SFJ Pharmaceuticals Group, Takeda, Vertex, Yuhan, Qiming Development (HK) Ltd, D3, C4 Therapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, geneDecode, Adagene, Bayer HealthCare Pharmacuticals, BerGenBio, Bowtie Life Insurance Company, BridgeBio, Covidien/Medtronic, Cirina, Da Volterra, Elevation Oncology, Genentech, HUTCHMED, Lakeshore Biotechnology, Lucence, Medtronic, MiRXES, Omega Therapeutics, OrigiMed, OSE Immunotherapeutics, prIME Oncology, Prenetics, Regeneron, Simcere, Summit Therapeutics, Synergy Research, Tigermed, Virtus Medical Group, Imagene AI Ltd
Research Funding: AstraZeneca (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), SFJ Pharmaceuticals Group (Inst), Roche (Inst), Merck Sharp & Dohme (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Xcovery (Inst), G1 Therapeutics (Inst), Merck Serono (Inst), Takeda (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Astrazeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, MiRXES, Pfizer, Novartis, AbbVie, Roche, Zai Lab, Pfizer, LiangYiHui
Ross A. Soo
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Takeda, Yuhan, Amgen, Bayer, Merck, Merck Serono, Puma Biotechnology, J INTS BIO
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Yuhan, Takeda, Amgen, Lilly, Merck, Janssen, Puma Biotechnology, Merck Serono, Bayer, Thermo Fisher Scientific, J INTS BIO
Research Funding: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim
Julien Mazieres
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly/ImClone, MSD, AstraZeneca, Pierre Fabre, Blueprint Medicines, Hengrui Therapeutics
Research Funding: Roche (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Pierre Fabre (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb
Alice T. Shaw
Employment: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research
Filippo de Marinis
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, MSD Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck Serono
Yasushi Goto
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly Japan, Chugai Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, MSD, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Novartis, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck, Guardant Health AMEA, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Amgen, Janssen, Sandoz, Nichiiko, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca
Consulting or Advisory Role: Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Guardant Health AMEA, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Janssen, Ono Pharmaceutical
Research Funding: AbbVie (Inst), Lilly Japan (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Ono Pharmaceutical (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb Japan (Inst), Chugai Pharma (Inst), Taiho Pharmaceutical (Inst), MSD (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Merck Serono (Inst), Genomic Health (Inst), CMIC (Inst), Takeda (Inst), EPS Holdings (Inst), IQVIA (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan (Inst), Janssen (Inst), Amgen (Inst), EP Croit Co (Inst), Astellas Amgen BioPharma (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Preferred Network (Inst), Medpace (Inst), Sysmex (Inst)
Uncompensated Relationships: Cancer Net Japan, JAMT
Yi-Long Wu
Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Roche, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb/China, Hengrui Pharmaceutical, BeiGene Beijing
Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda
Research Funding: Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Roche (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), BMS (Inst)
Dong-Wan Kim
Research Funding: Alpha Biopharma (Inst), AstraZeneca/MedImmune (Inst), Hanmi (Inst), Janssen (Inst), Merus (Inst), Mirati Therapeutics (Inst), MSD (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Ono Pharmaceutical (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Roche/Genentech (Inst), Takeda (Inst), TP Therapeutics (Inst), Xcovery (Inst), Yuhan (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical (Inst), BridgeBio Pharma (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Merck (Inst), inno.N (Inst), IMBdx (Inst)
Jean-François Martini
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer, Kiara Therapeutics
Rossella Messina
Employment: Pfizer, Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Jolanda Paolini
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Anna Polli
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Despina Thomaidou
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Francesca Toffalorio
Employment: Pfizer
Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Pfizer
Todd M. Bauer
Employment: Tennessee Oncology
Consulting or Advisory Role: Pfizer, Bayer, Lilly, Sanofi, AVEO
Speakers' Bureau: Bayer, Lilly
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pfizer
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
REFERENCES
- 1.Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, et al. : Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 29:iv192-iv237, 2018. (suppl 4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson TW, Richardson PF, Bailey S, et al. : Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(m etheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h] [2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J Med Chem 57:4720-4744, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shaw AT, Felip E, Bauer TM, et al. : Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1590-1599, 2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shaw AT, Bauer TM, de Marinis F, et al. : First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 383:2018-2029, 2020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Solomon BJ, Bauer TM, Mok TSK, et al. : Efficacy and safety of first-line lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated analysis of data from the phase 3, randomised, open-label CROWN study. Lancet Respir Med 11:354-366, 2023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.FDA approves lorlatinib for metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-lorlatinib-metastatic-alk-positive-nsclc
- 7.Lorbrena (lorlatinib) prescribing information. 2023. https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=11140
- 8.Lorviqua (lorlatinib). https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/overview/lorviqua-epar-medicine-overview_en.pdf
- 9.Lorbrena (lorlatinib) prescribing information. 2018. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000228981.pdf
- 10.Woo CG, Seo S, Kim SW, et al. : Differential protein stability and clinical responses of EML4-ALK fusion variants to various ALK inhibitors in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 28:791-797, 2017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin JJ, Zhu VW, Yoda S, et al. : Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36:1199-1206, 2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kron A, Alidousty C, Scheffler M, et al. : Impact of TP53 mutation status on systemic treatment outcome in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 29:2068-2075, 2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Felip E, Martini JF, Mazieres J, et al. : 1008P Resistance mechanisms to lorlatinib or crizotinib in treatment-naive patients (pts) with ALK+ advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol 33:S1014, 2022 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bearz A, Martini JF, Jassem J, et al. : Efficacy of lorlatinib in treatment-naive patients with ALK-positive advanced NSCLC in relation to EML4::ALK variant type and ALK with or without TP53 mutations. J Thorac Oncol 18:1581-1593, 2023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mok T, Camidge DR, Gadgeel SM, et al. : Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann Oncol 31:1056-1064, 2020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Camidge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, et al. : Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK inhibitor-naive advanced ALK-positive NSCLC: Final results of phase 3 ALTA-1L trial. J Thorac Oncol 16:2091-2108, 2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Horn L, Wang Z, Wu G, et al. : Ensartinib vs crizotinib for patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 7:1617-1625, 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guerin A, Sasane M, Zhang J, et al. : Brain metastases in patients with ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical symptoms, treatment patterns and economic burden. J Med Econ 18:312-322, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Griesinger F, Roeper J, Pottgen C, et al. : Brain metastases in ALK-positive NSCLC — time to adjust current treatment algorithms. Oncotarget 9:35181-35194, 2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bauer TM, Felip E, Solomon BJ, et al. : Clinical management of adverse events associated with lorlatinib. Oncologist 24:1103-1110, 2019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nagasaka M, Ge Y, Sukari A, et al. : A user's guide to lorlatinib. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 151:102969, 2020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Blais N, Adam JP, Nguyen J, et al. : Evaluation and management of dyslipidemia in patients treated with lorlatinib. Curr Oncol 28:265-272, 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu G, Mazieres J, Stratmann J, et al. : A pragmatic guide for management of adverse events associated with lorlatinib. Lung Cancer 191:107535, 2024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Reed M, Rosales ALS, Chioda MD, et al. : Consensus recommendations for management and counseling of adverse events associated with lorlatinib: A guide for healthcare practitioners. Adv Ther 37:3019-3030, 2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Solomon BJ, Bauer TM, Ignatius Ou SH, et al. : Post hoc analysis of lorlatinib intracranial efficacy and safety in patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer from the phase III CROWN study. J Clin Oncol 40:3593-3602, 2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bearz A, Felip E, Mazieres J, et al. : 979P Long-term intracranial safety and efficacy analyses from the phase III CROWN study. Ann Oncol 33(suppl 7):S998-S999, 2022 [Google Scholar]
- 27.Camidge DR, Dziadziuszko R, Peters S, et al. : Updated efficacy and safety data and impact of the EML4-ALK fusion variant on the efficacy of alectinib in untreated ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the global phase III ALEX study. J Thorac Oncol 14:1233-1243, 2019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
A data sharing statement provided by the authors is available with this article at DOI https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.24.00581. Upon request and subject to review, Pfizer will provide the data that support the findings of this study. Subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Pfizer may also provide access to the related individual deidentified participant data. See https://www.pfizer.com/science/clinical-trials/trial-data-and-results for more information.