Abstract
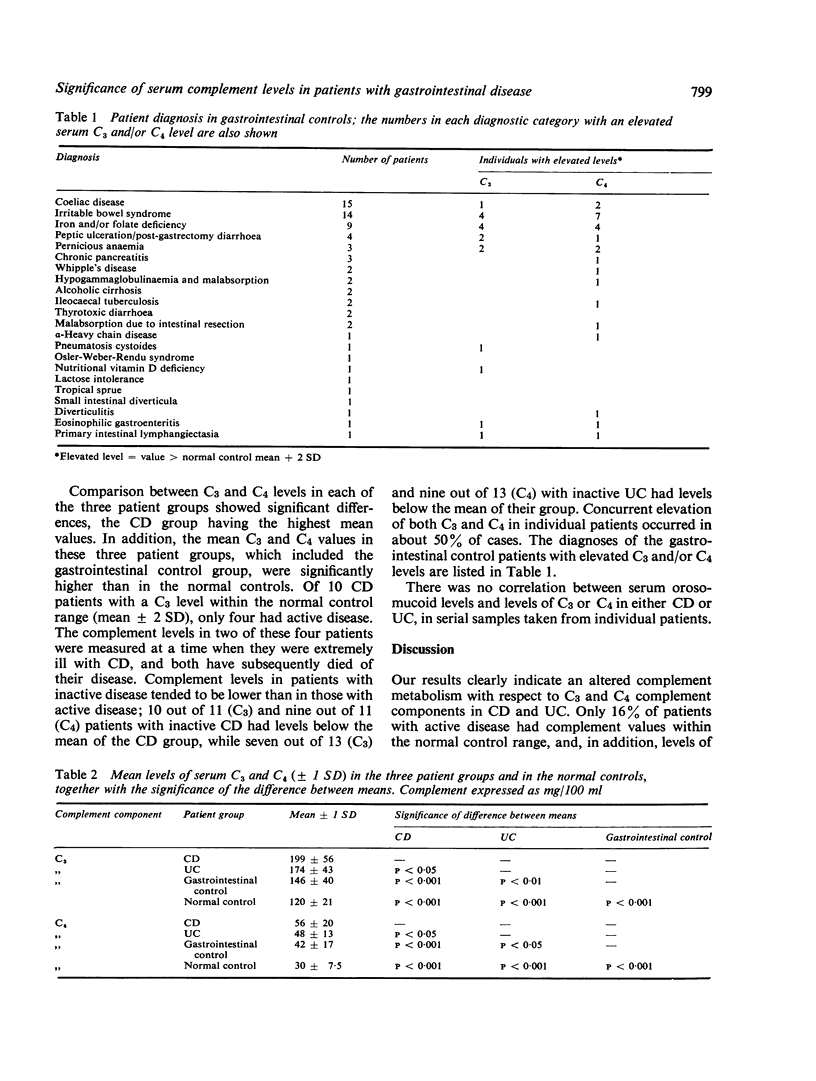
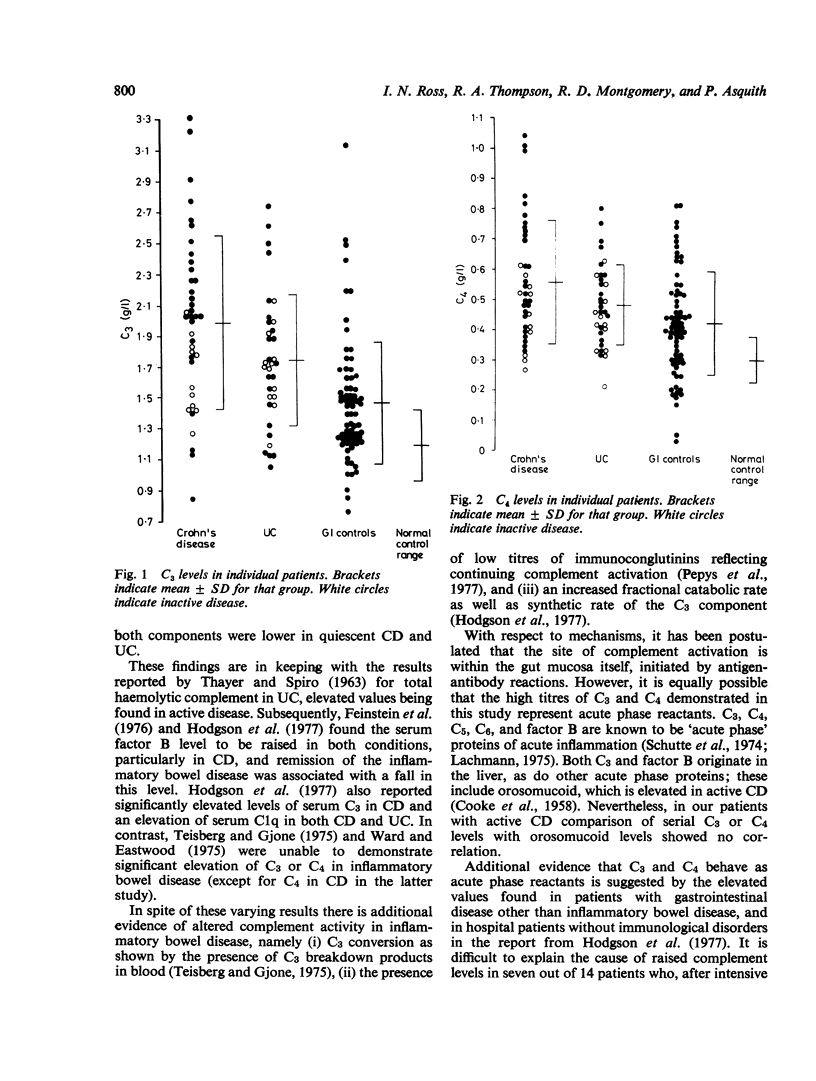
Levels of the serum complement components, C3 and C4, in patients with Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and miscellaneous gastrointestinal disorders were compared with those of normal blood donors. Significant increases of both components were found in all three patient groups, the highest being in patients with Crohn's disease. Generally, levels of C3 and C4 were lower in patients with inactive rather than active Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These results provide some evidence in support of an immunological basis for inflammatory bowel disease. However, in view of the frequent elevation of C3 and C4 in other gastrointestinal diseases, it is equally possible that the complement components are behaving as acute phase proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard J., Shiner M. Evidence of cytotoxicity in ulcerative colitis from immunofluorescent staining of the rectal mucosa. Lancet. 1974 May 25;1(7865):1014–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90416-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE W. T., FOWLER D. I., COX E. V., GADDIE R., MEYNELL M. J. The clinical significance of seromucoids in regional ileitis and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1958 May;34(5):910–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Booth C. C., Brown D. L. Evidence for complement-binding immune complexes in adult coeliac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):402–403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein P. A., Kaplan S. R., Thayer W. R., Jr The alternate complement pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. Quantitation of the C3 proactivator (factor B) protein. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel B. J., Hook W. A., Polish E. A note on serum complement activity with particular reference to ulcerative colitis. Mil Med. 1967 Apr;132(4):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. Humoral immune system in inflammatory bowel disease: I. Complement levels. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):749–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte M., DiCamelli R., Murphy P., Sadove M., Gewurz H. C3 proactivator (C3PA) as an acute phase reactant. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Oct;18(2):251–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAYER W. R., Jr, SPIRO H. M. Persistence of serum complement in sera of patients with ulcerative colitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teisberg P., Gjone E. Humoral immune system activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(5):545–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M., Eastwood M. A. Serum C3 and C4 complement components in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Digestion. 1975;13(1-2):100–103. doi: 10.1159/000197698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


