Abstract
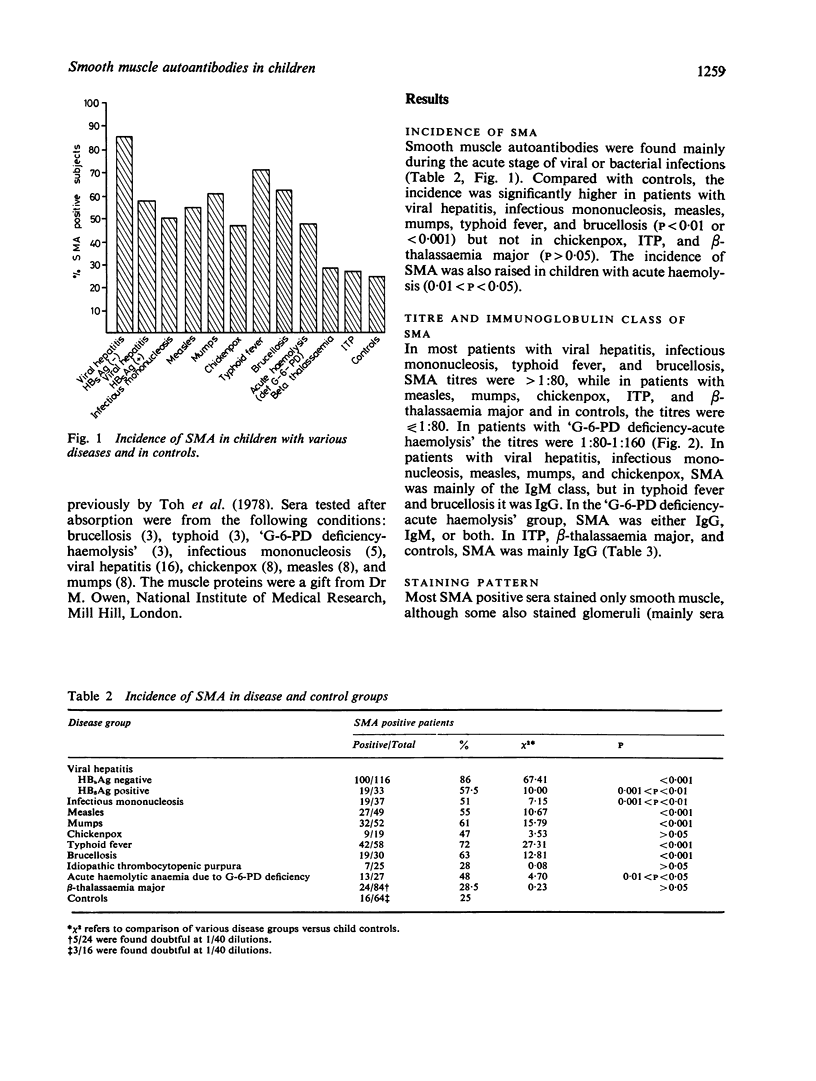
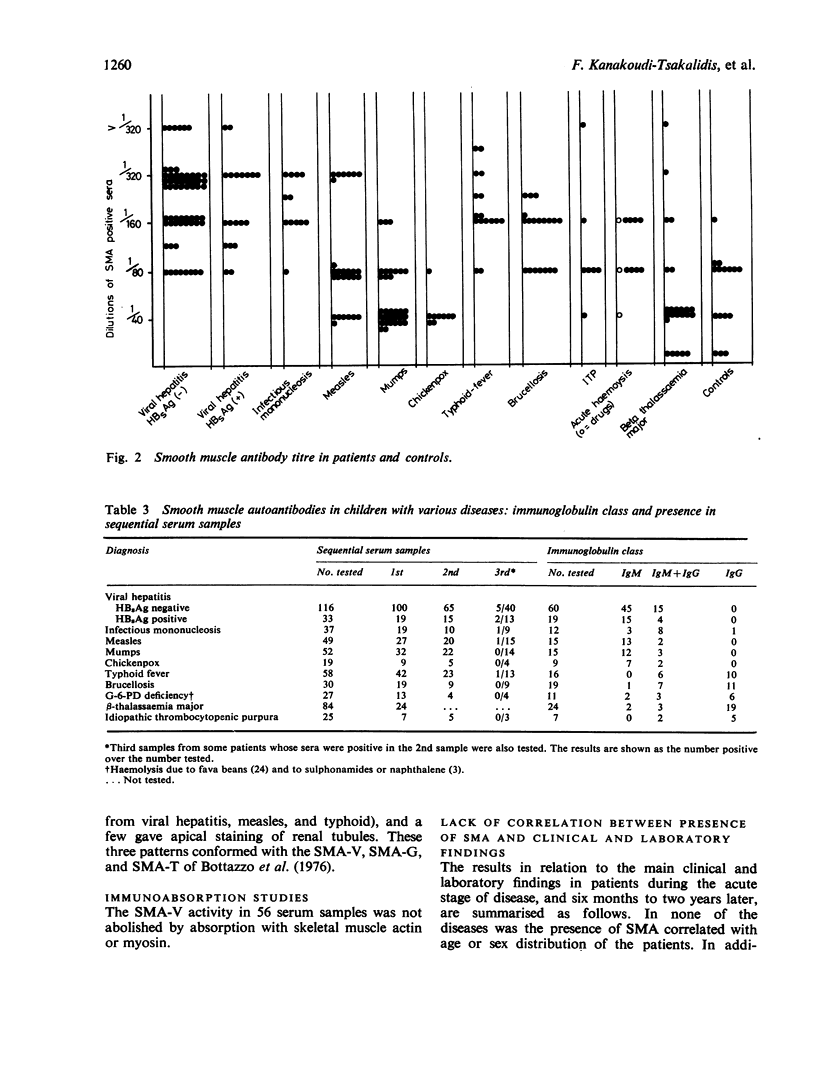
Sera from 530 children suffering from various diseases and from 64 controls were tested for smooth muscle autoantibodies (SMA) by indirect immunofluorescence. A high incidence of SMA (51-86%) was found in patients with viral and bacterial infections (viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, measles, mumps, chickenpox, typhoid fever, and brucellosis), independently of liver invovlvement, and in patients with acute haemolytic anaemia due to G-6-PD deficiency (48%). By contrast, the incidence of SMA from patients with beta-thalassaemia major and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura was no higher than in the controls. The discrepancy in incidence in haemolytic anaemias due to different causes may reflect the effect of endogenous and extrinsic agents. In the viral infections, SMA were mainly of the IgM class and gave an 'SMA-V' staining pattern. In bacterial infections (typhoid fever and brucellosis), SMA were either IgG only or IgM and IgG, and the staining pattern was also mainly 'SMA-V'. In infections which affect or may affect the liver (viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, typhoid fever, and brucellosis), SMA was present at high titres (1:80-1:320), whereas in infections not affecting the liver (measles, mumps, and chickenpox) the titres were lower (less than or equal to 1:80). In most patients SMA occurred transiently and without apparent pathogenetic significance. The antigen against which infection-induced SMA is directed is not actin; its nature has yet to be identified.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajdukiewicz A. B., Fox R. A., Dudley F. J., Doniach D., Sherlock S. Immunological studies in an epidemic of infective, short-incubation hepatitis. Lancet. 1972 Apr 15;1(7755):803–805. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90795-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and other tissue antibodies in cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):22–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the specificity of smooth-muscle antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):57–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Sterner G. Smooth muscle antibodies in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):287–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Fairfax A., Swana G., Doniach D., Groeschel-Stewart U. Classification of smooth muscle autoantibodies detected by immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):403–410. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Roitt I. M., Walker J. G., Sherlock S. Tissue antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis, active chronic (lupoid) hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis and other liver diseases and their clinical implications. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):237–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax A. J., Gröschel-Stewart U. Myosin autoantibodies detected by immunofluorescence. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):27–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow L. J., Holborow E. J., Brighton W. D. Reaction of human smooth muscle antibody with liver cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 11;232(2):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio232186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow L. J., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D., Lamb S. G., Stewart J. S., Taylor P. E., Zuckerman A. J. Autoantibodies and the hepatitis-associated antigen in acute infective hepatitis. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):693–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Lamelin J. P., Vassalli P., Majno G., Bouvier C. A., Cruchaud A., Lüscher E. F. Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to "nonmuscular" cells. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Hemsted E. H., Mead S. V. Smooth muscle autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 11;3(5875):323–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5875.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper B., Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Mackay I. R., Curnow D. H. Autoimmunity in a rural community. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):79–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J., Glynn L. E. Antibody to smooth muscle in patients with liver disease. Lancet. 1965 Oct 30;2(7418):878–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudi F., Nikolaidis A., Daniilidis B., Manios S., Zurukzoglu S. S., Cassimos C. Immunological studies in children with acute viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):78–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Linder E., Miettinen A., Alfthan O. Smooth muscle antibodies of actin and "non-actin" specificity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Apr;9(4):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidman K., Biberfeld G., Fagraeus A., Norberg R., Torstensson R., Utter G., Carlsson L., Luca J., Lindberg U. Anti-actin specificity of human smooth muscle antibodies in chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):266–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcmillan S. A., Haire M. Smooth muscle antibody in patients with warts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Aug;21(2):339–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. Selective chemotherapy of macrophages in the treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 18;298(20):1139–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805182982009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu S., Nisengard R. J., Hale W. L., Beutner E. H. Incidence and titers of antinuclear, antismooth muscle, and other autoantibodies in blood donors. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. N., Emond R. T., Thomas D. B., Doniach D. The occurrence of autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):427–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. N., Marston S. D., Almond E. J., Reynolds K., Pounds F. J. Asymptomatic infection with EB virus. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Feb;27(2):97–100. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Clarke F. M., Ceredig R. Reaction of human smooth muscle autoantibody with skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and thymic myoid cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jan;9(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vittal S. B., Dourdourekas D., Shobassy N., Ainis H., Clowdus B. F., Steigmann F. Immunoglobulin and autoantibody response in acute and chronic liver disease. Am J Med. 1974 Oct;57(4):546–550. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse J. M., Holborow E. J. Smooth muscle antibody in malignant disease. Br Med J. 1971 Nov 27;4(5786):511–513. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5786.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


