Abstract
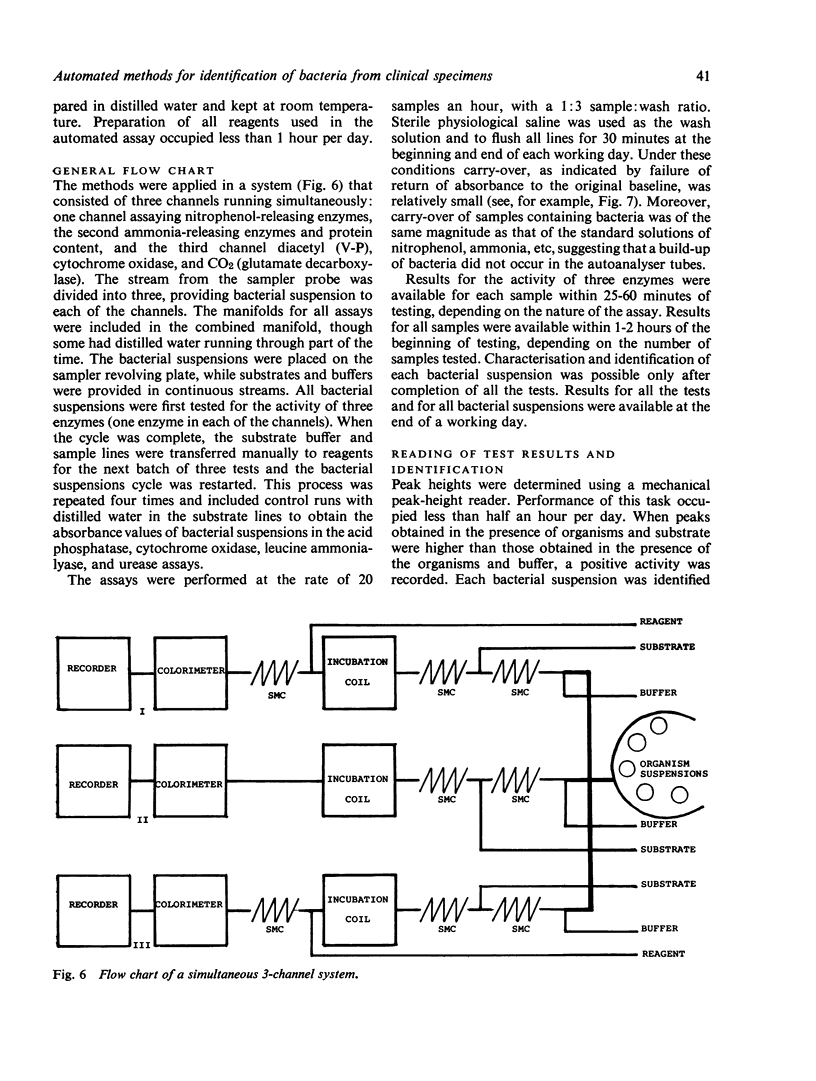
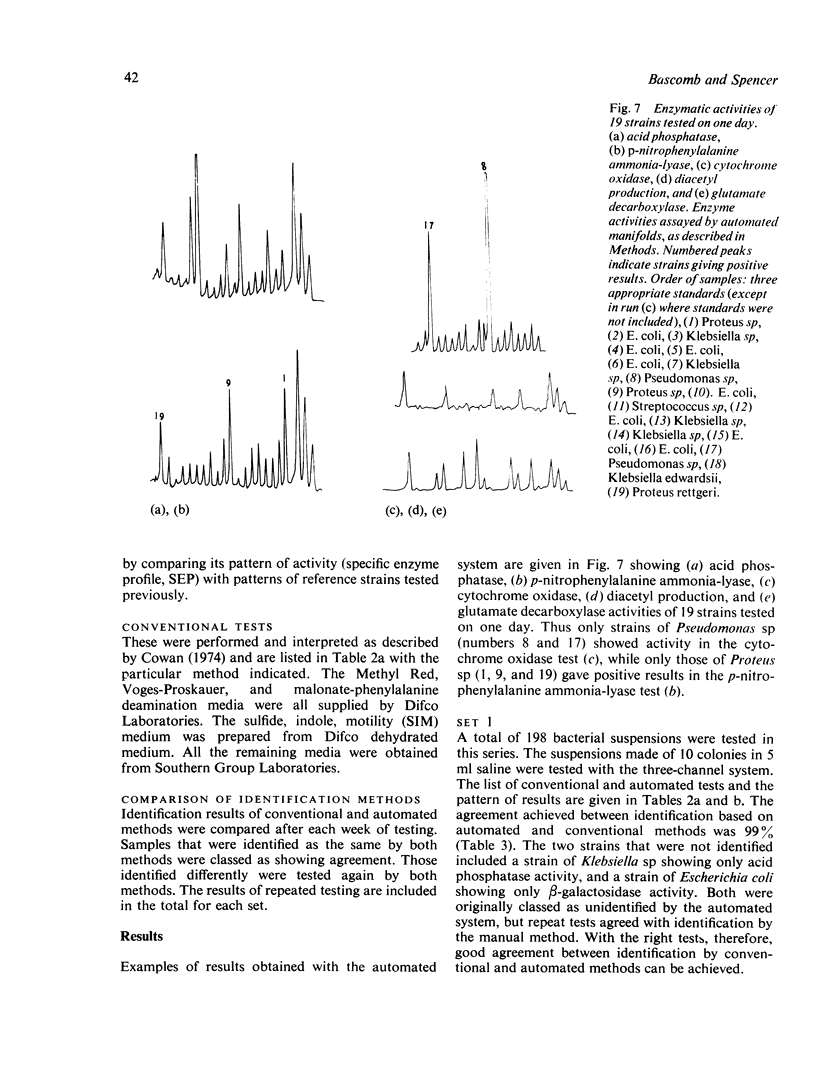
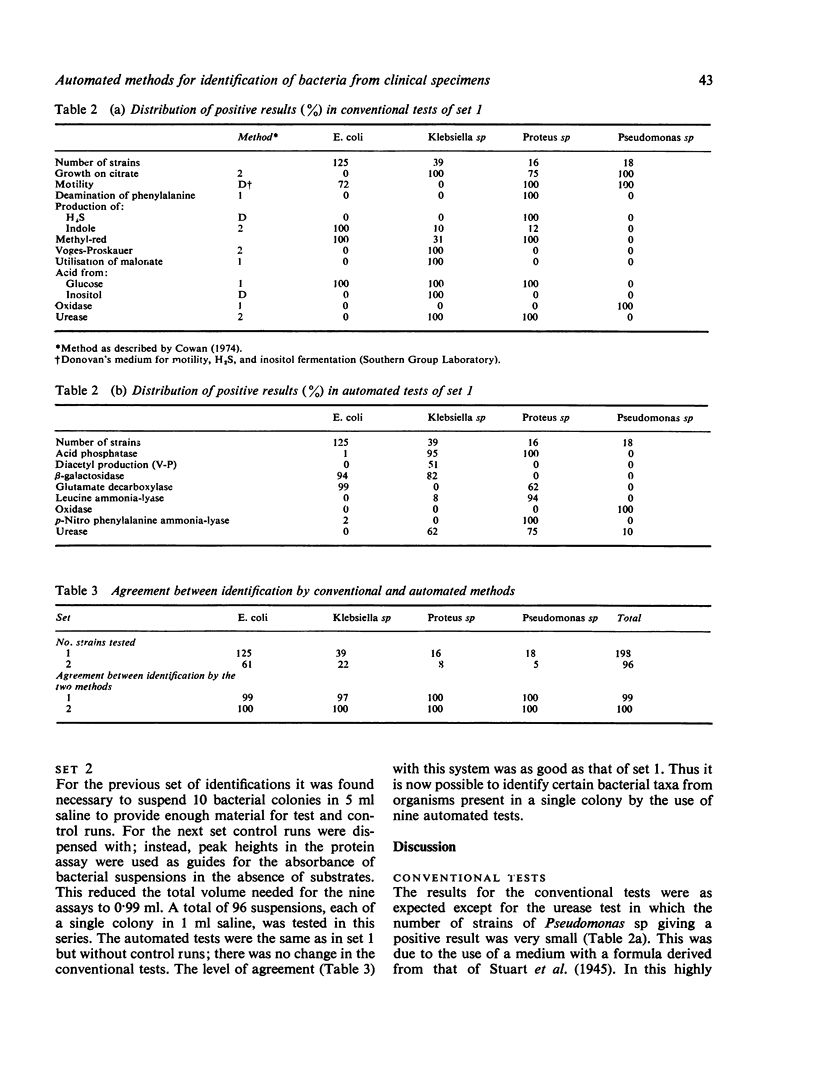
Automated methods for measuring enzyme activities of bacterial suspensions in saline are described. The methods were applied to bacteria cultured from urine specimens, and specific enzyme profiles characteristic for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp, Proteus sp, and Pseudomonas sp were established. Identification of 294 freshly isolated strains by automated and conventional methods were compared. Results from automated identification based on eight enzyme tests and assay of protein content, all performed on a bacterial suspension made from one colony in 1 ml of saline, agreed 100% with those obtained by conventional methods. Identification was achieved in 6 hours.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buissière J., Fourcard A., Colobert L. Usage de substrats synthétiques pour l'étude de l'équipement enzymatique de microorganismes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jan 9;264(2):415–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dealy J. D., Umbreit W. W. The application of automated procedures for studying enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Nov 9;130(2):745–750. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb12618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humble M. W., King A., Phillips I. API ZYM: a simple rapid system for the detection of bacterial enzymes. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Mar;30(3):275–277. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun P. P., Pleau J. M., Man N. K. Semiautomated method for measurement of guanidinosuccinic acid in serum. Clin Chem. 1972 Apr;18(4):355–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Bülow P. Rapid diagnosis of Enterobacteriaceae. I. Detection of bacterial glycosidases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Oct;84B(5):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc H. Mise en évidence de la décarboxylase de l'acide glutamique chez les bactéries à l'aide d'une technique automatique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Jun;112(6):713–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Van Stratum E., Rustigian R. Further Studies on Urease Production by Proteus and Related Organisms. J Bacteriol. 1945 May;49(5):437–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.5.437-444.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade H. E., Robinson H. K., Phillips B. W. Asparaginase and glutaminase activities of bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):299–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


