Abstract
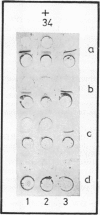
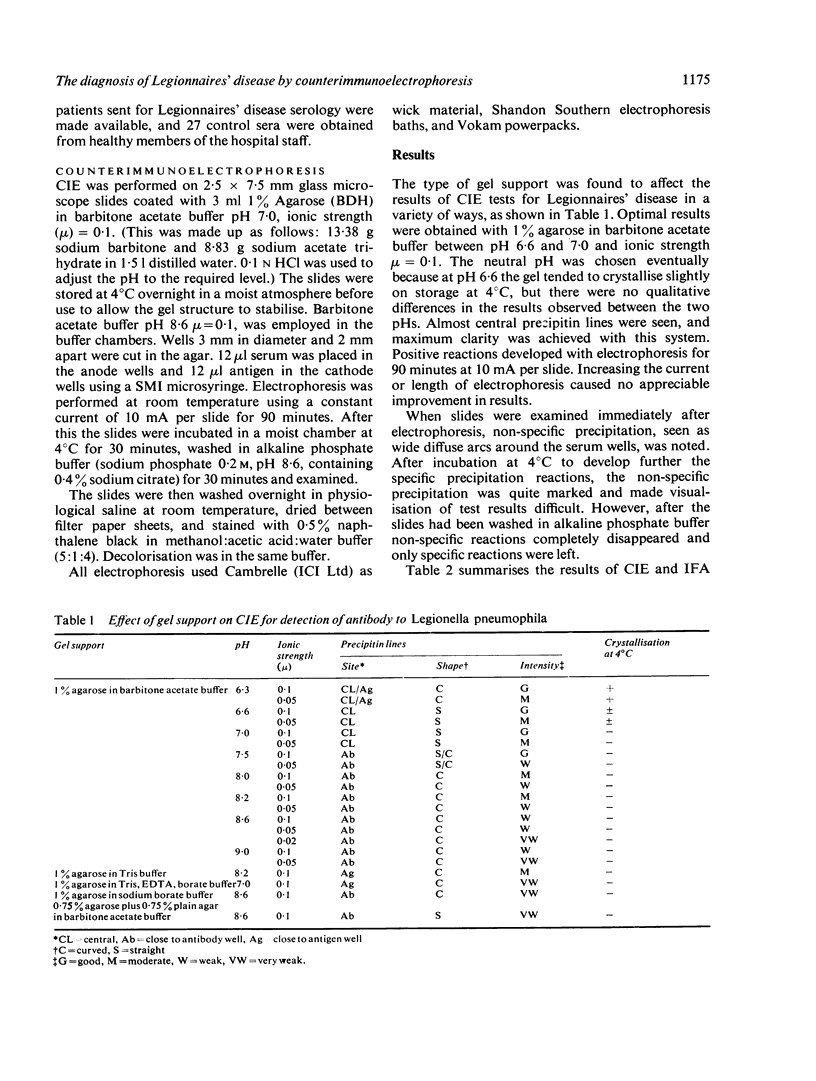
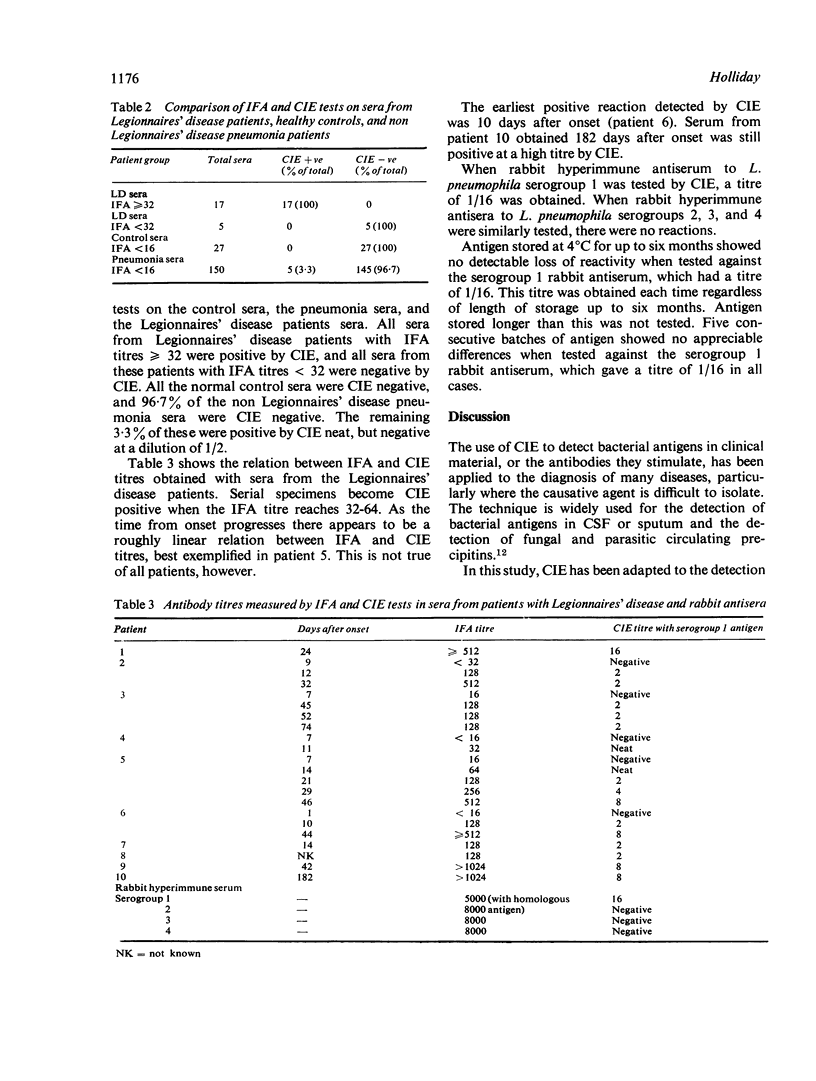
Counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE) was found to be a rapid, specific method for detecting circulating antibodies to Legionella pneumophila, the aetiologic agent of Legionnaires' disease in human sera. Optimum conditions for performing the test are given. Better precipitin lines are observed when the gel support is neutral, and a result may be obtained in 90 to 180 minutes. Comparison of results of CIE and indirect fluorescent antibody tests on 22 sera from patients with Legionnaires' disease and on 27 sera from healthy control subjects showed 100% correlation, and 75 paired sera from patients with pneumonia of unknown aetiology showed 96.7% correlation. Laboratory diagnosis may be made quickly and accurately by CIE. The method is simple and easily performed in the routine laboratory. The antigen is stable at 4 degrees C for at least six months.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Abraham W. H. Scottish experience with the serologic diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):684–686. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: clinical features of 24 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):297–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Harris P. P., Lewallen K. R., Hebert G. A., Edelstein P. H., Thomason B. M. Four serogroups of Legionnaires' disease bacteria defined by direct immunofluorescence. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):621–624. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai T. F., Fraser D. W. The diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):413–414. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]