Abstract
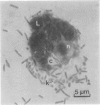
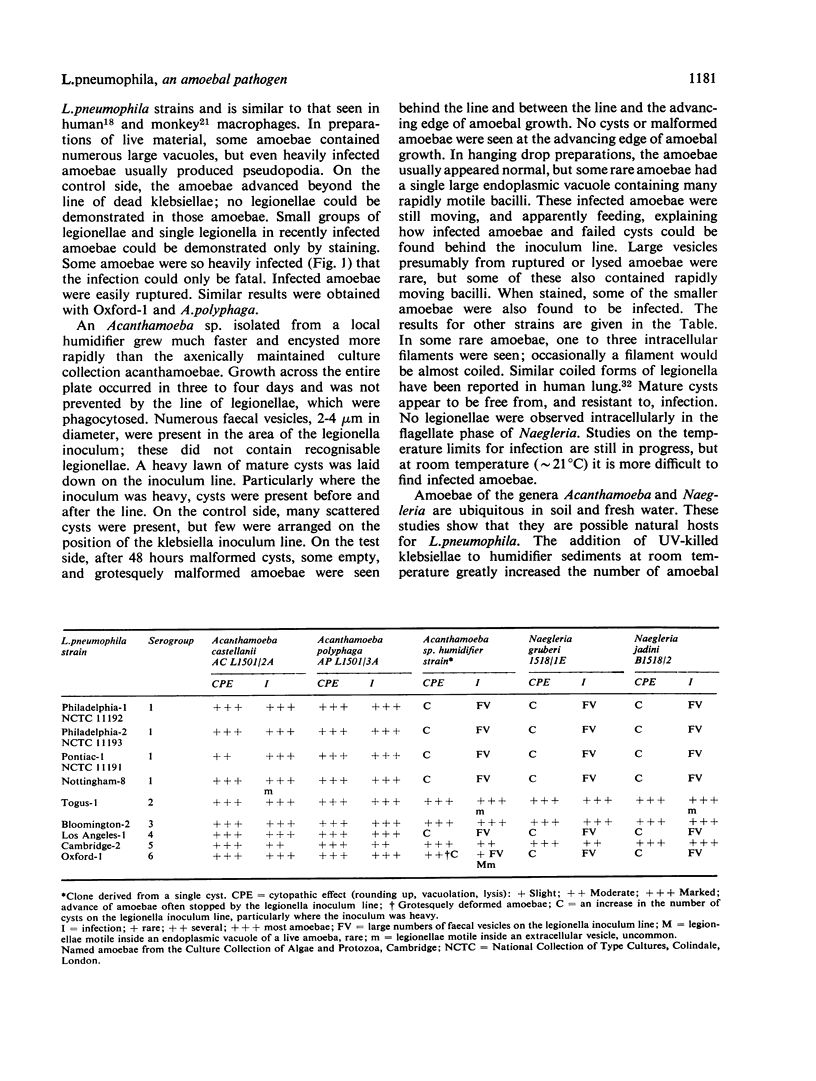
Legionella pneumophila, the causative organism of Legionnaires' disease, is pathogenic for free living, ubiquitous, freshwater, and soil amoebae of the genera Acanthamoeba and Naegleria. Some species support the growth of strains from serogroups 1 to 6, others only strains from certain serogroups. Initial studies with seeded material indicate that amoebal enrichment could be utilised for the isolation of legionellae from clinical specimens and natural habitats. It is suggested that a vacuole, or amoeba, full of legionellae, rather than free legionellae, could be the infective particle for man.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome C. V., Fraser D. W. Epidemiologic aspects of legionellosis. Epidemiol Rev. 1979;1:1–16. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Cole R. M., Hicklin M. D., Blackmon J. A., Callaway C. S. Ultrastructure of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. A study using transmission electron microscopy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):642–647. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., McDade J. E., Hicklin M. D., Blackmon J. A., Thomason B. M., Ewing E. P., Jr Pathologic findings in guinea pigs inoculated intraperitoneally with the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):671–675. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Fraser D. W., Skaliy P., Perlino C. A., Elsea W. R., Mallison G. F., Hayes P. S. Legionnaires' disease outbreak at an Atlanta, Georgia, Country Club: evidence for spread from an evaporative condenser. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):425–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Wilkinson H. W., Gorman G. W., Fikes B. J., Fraser D. W. Atypical Legionella-like organisms: fastidious water-associated bacteria pathogenic for man. Lancet. 1979 Nov 3;2(8149):927–930. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92623-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Abraham W. H. Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3. Lancet. 1979 Aug 11;2(8137):304–304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher-Hoch S., Hudson M. J., Thompson M. H. Identification of a clinical isolate as Legionella pneumophila by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry of cellular fatty acids. Lancet. 1979 Aug 18;2(8138):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. R., Pine L., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Amino acid requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.286-291.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavin F. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Craighead J. E. Ultrastructure of lung in Legionnaires' disease. Observations of three biopsies done during the Vermont epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):555–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves P. G., Sharp G., Macrae A. D. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila. Lancet. 1979 Mar 10;1(8115):551–552. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90969-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez F. J., Kirby B. D., Stanley T. M., Edelstein P. H. Legionnaires' disease. Postmortem pathologic findings of 20 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Apr;73(4):488–495. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Pesanti E., Elliott J. Serospecificity and opsonic activity of antisera to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):698–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.698-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Kastello M. D., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro interaction between normal cynolmolgus monkey alveolar macrophages and Legionnaires disease bacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):761–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.761-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewallen K. R., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Dail D. H., Thomason B. M., Bright R. A. A newly identified bacterium phenotypically resembling, but genetically distinct from, Legionella pneumophila: an isolate in a case of pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Dec;91(6):831–834. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. P. Cooling towers and evaporative condensers. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):667–670. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Patton C. M., Feeley J. C., Johnson S. E., Gorman G., Martin W. T., Skaliy P., Mallison G. F., Politi B. D., Mackel D. C. Isolation of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium from environmental samples. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):664–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G. Ultrastructure of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;32(12):1195–1202. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.12.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter D. A., Maber H. B. Culture of Legionella pneumophila. Lancet. 1979 Mar 31;1(8118):723–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., McEachern H. V. Survival of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium in water. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):662–663. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. G., Harrison T. G. Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3. Lancet. 1979 Jul 7;2(8132):47–47. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Blaser M. J., Cravens J., Johnson M. A. Growth, survival, and resistance of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):614–618. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]