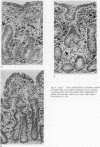
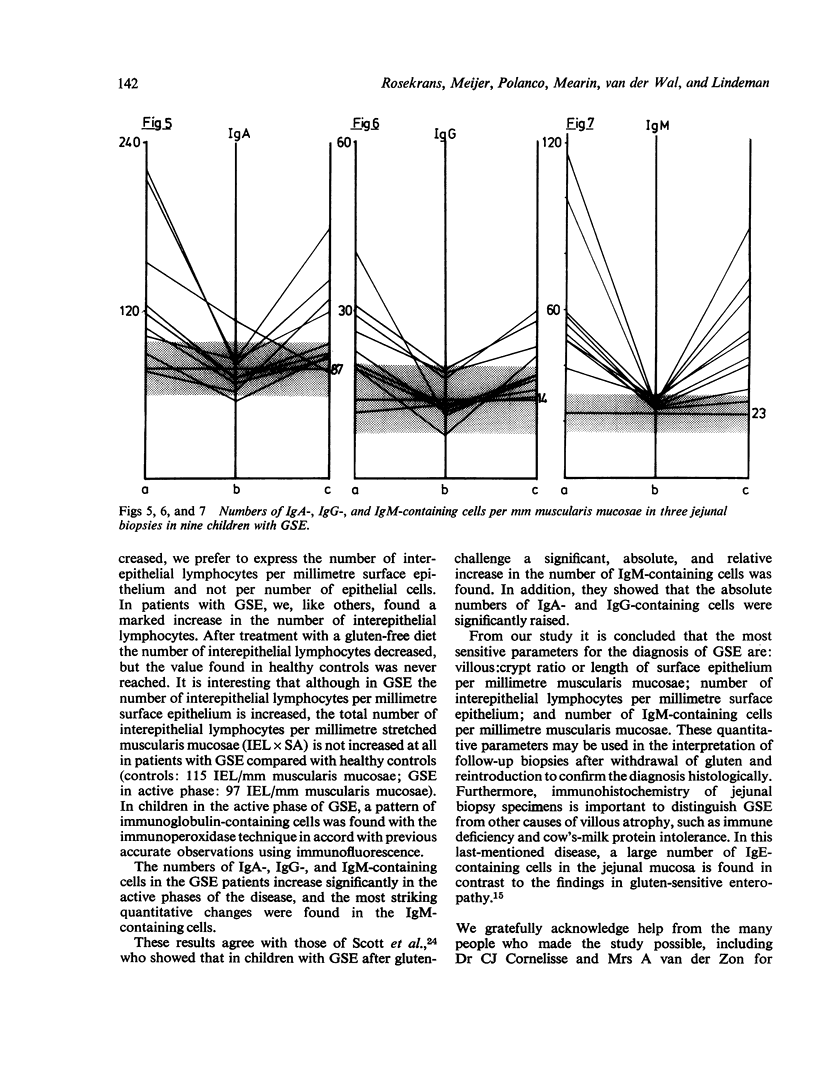
Abstract
Jejunal biopsy specimens from nine Spanish children with gluten-sensitive enteropathy were studied with morphometric and immunohistochemical techniques in three stages of the diseases: the first biopsy was taken for diagnosis, when the child had a gluten-containing diet, the second after gluten withdrawal, and the third biopsy after gluten-provocation. The findings were compared with those in 10 healthy adults. The villous:crypt ratio and the length of the surface epithelium per stretched millimetre muscularis mucosae were decreased, whereas the number of interepithelial lymphocytes per millimetre surface epithelium was increased when the child had a gluten-containing diet. Although these parameters improved after withdrawal of gluten for at least seven months, they never reached the values of the healthy control group. With the indirect immunoperoxidase technique it was shown that the numbers of IgA-, IgG-, and IgM-containing cells, expressed per "mucosal tissue unit" of 4 micrometer thick and 1 mm wide, were significantly increased during the active phases of the disease. This increase was most striking for the IgM-containing cells. The most sensitive parameters for the histological diagnosis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy are the villous:crypt ratio or the length of the surface epithelium per millimetre muscularis mucosae, the number of interepithelial lymphocytes per millimetre surface epithelium, and the number of IgM-containing cells per millimetre muscularis mucosae.
Full text
PDF
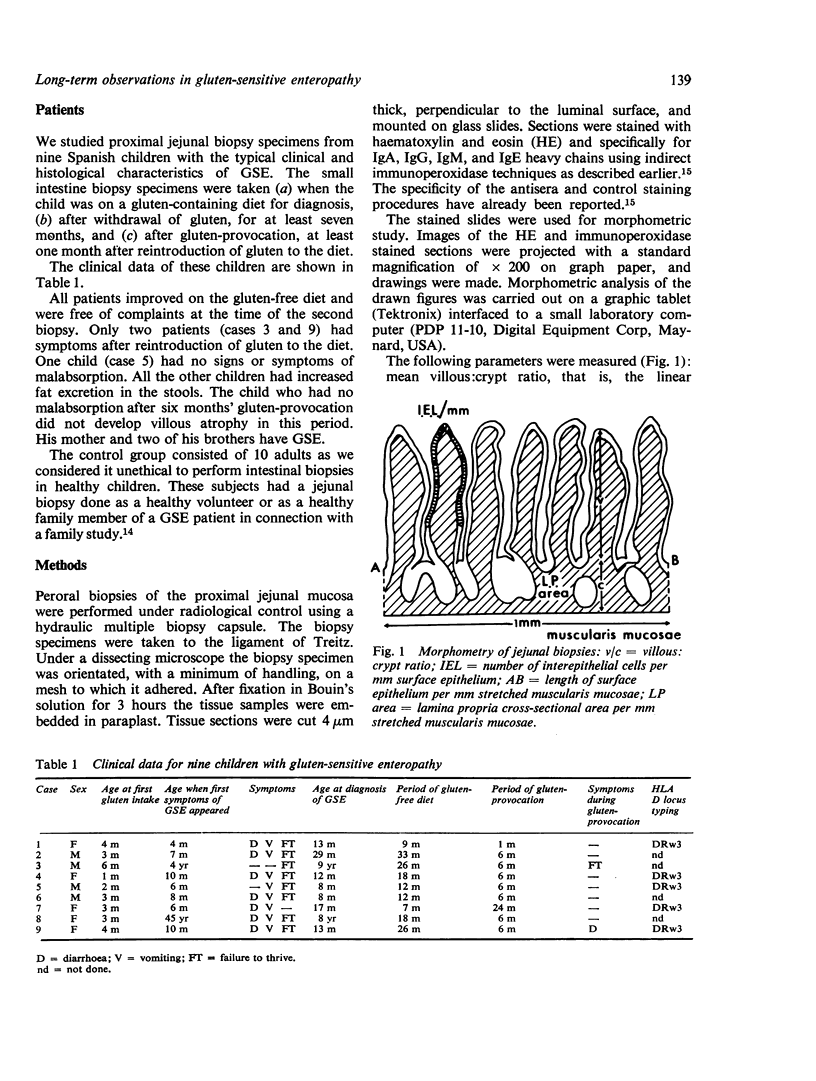


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Douglas A. P., Crabbé P. A., Hobbs J. R. Immunochemical studies on the serum, intestinal secretions and intestinal mucosa in patients with adult celiac disease and other forms of the celiac syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1970 Sep;59(3):414–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Murray D. Quantitation of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human jejunum. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):988–994. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R., Asquith P., Cooke W. T. The jejunal cellular infiltrate in coeliac disease complicated by lymphoma. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):458–461. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry L., Seah P. P., McMinn R. M., Hoffbrand A. V. Lymphocytic infiltration of epithelium in diagnosis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 12;3(5823):371–374. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5823.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasbarrini G., Miglio F., Serra M. A., Bernardi M. Immunological studies of the jejunal mucosa in normal subjects and adult celiac patients. Digestion. 1974;10(2):122–128. doi: 10.1159/000197531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Asquith P., Stokes P. L., Cooke W. T. Cellular infiltrate of jejunal biopsies in adult coeliac disease in relation to gluten withdrawal. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):278–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M., Kumar P. J., Dawson A. M. The cellular infiltrate of the jejunum in adult coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis following the reintroduction of dietary gluten. Gut. 1975 Sep;16(9):683–688. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.9.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M., Packer S., Kumar P. J., Harries J. T. Cellular infiltrate of the jejunum after re-introduction of dietary gluten in children with treated coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jul;29(7):587–591. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.7.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M., Packer S., Kumar P. J., Harries J. T. Immunological phenomena in the jejunum and serum after reintroduction of dietary gluten in children with treated coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jul;29(7):592–597. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.7.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromichalis J., Brueton M. J., McNeish A. S., Anderson C. M. Evaluation of the intraepithelial lymphocyte count in the jejunum in childhood enteropathies. Gut. 1976 Aug;17(8):600–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.8.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholl B., Egan-Mitchell B., Stevens F., Keane R., Baker S., McCarthy C. F., Fottrell P. F. Mucosal recovery in treated childhood celiac disease (gluten-sensitive enteropathy). J Pediatr. 1976 Sep;89(3):418–424. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80539-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H. F. Interepitheliale Lymphozyten bei Enteropathien. Z Gastroenterol. 1972;10(3):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN W., FAUCI A. S., MARVIN S. F., SLEISENGER M. H., JEFRIES G. H. IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STUDIES IN ADULT CELIAC DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:475–485. doi: 10.1172/JCI105161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosekrans P. C., Meijer C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van der Wal A. M., Lindeman J. Use of morphometry and immunohistochemistry of small intestinal biopsy specimens in the diagnosis of food allergy. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Feb;33(2):125–130. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHINER M., DONIACH I. Histopathologic studies in steatorrhea. Gastroenterology. 1960 Mar;38:419–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E. Intestinal immunoglobulins in children with coeliac disease. Gut. 1972 Dec;13(12):958–964. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.12.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Ek J., Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Immunoglobulin-producing cells in jejunal mucosa of children with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet and after gluten challenge. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(1):81–88. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoft J. Immunoglobulin-containing cells in non-tropical sprue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):413–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoft J., Weeke B. Immunoglobulins in serum and jejunal biopsies in non-tropical sprue. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Nov;186(5):459–464. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb01503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]