Abstract
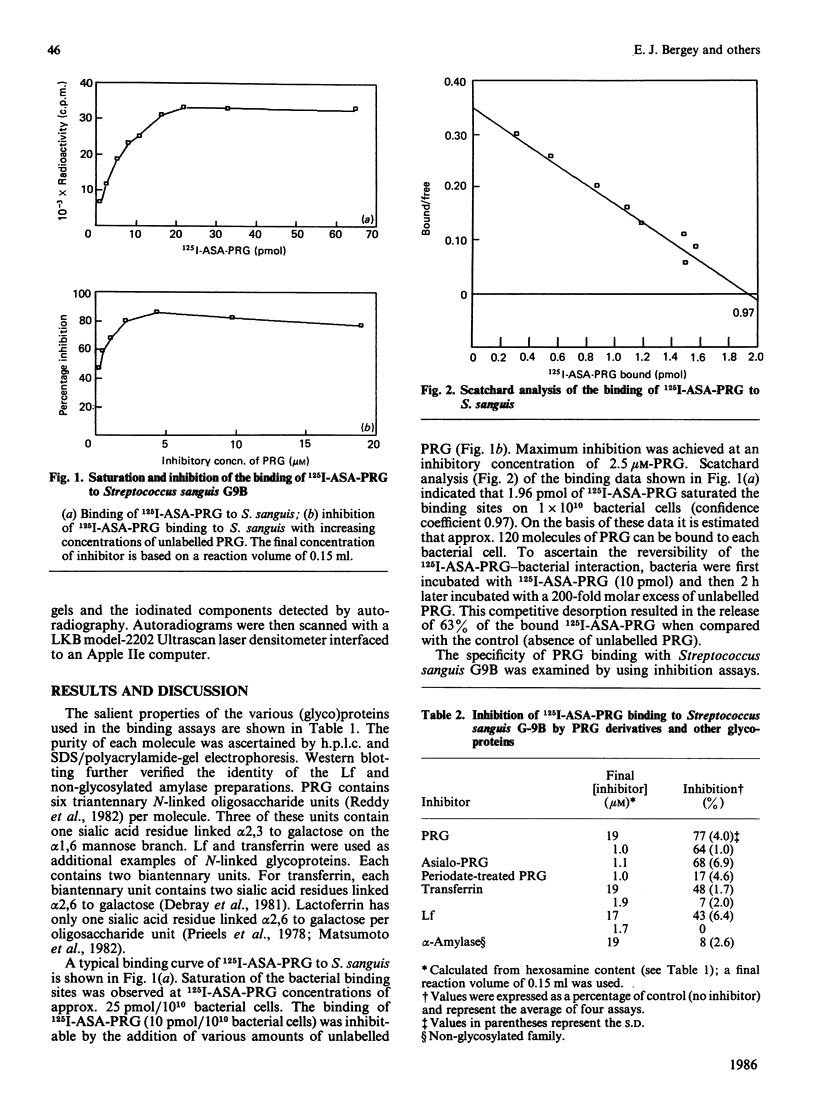
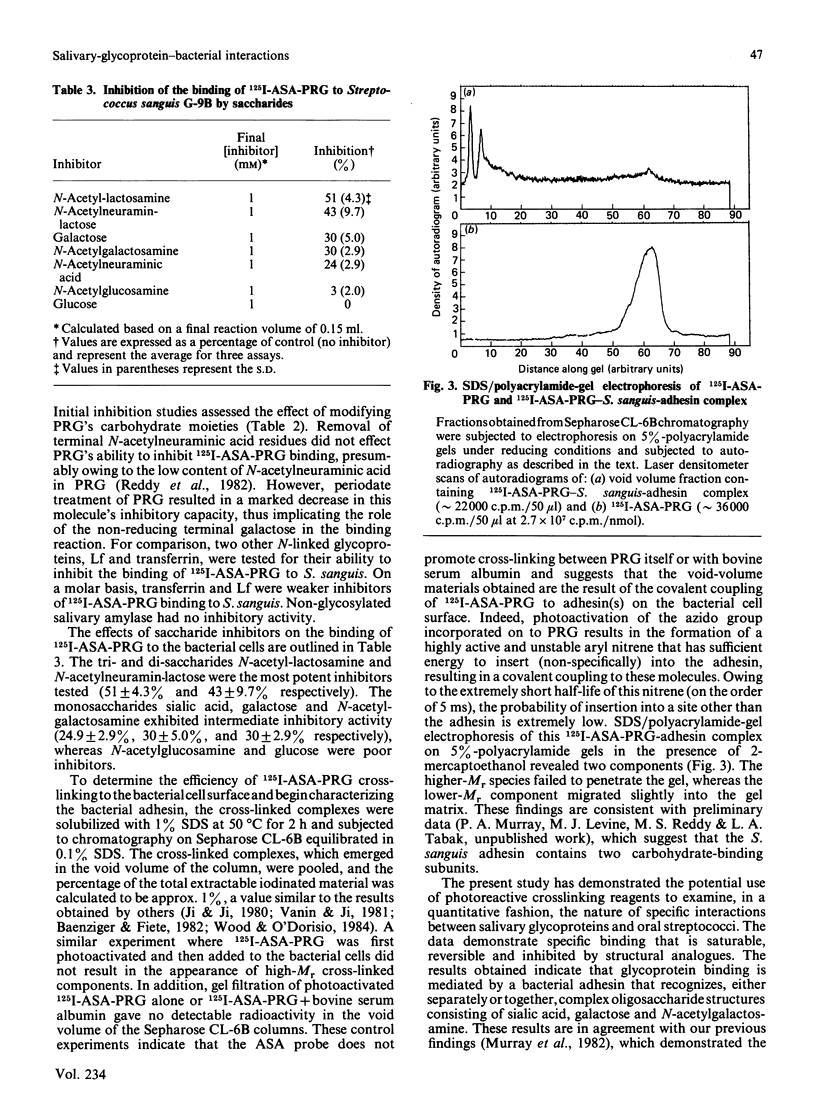
The present study has utilized the iodinatable cross-linking agent N-hydroxysuccinimidyl-4-azidosalicylic acid (ASA) to examine the specific interaction between the proline-rich glycoprotein (PRG) of human parotid saliva and Streptococcus sanguis G9B. The binding of 125I-ASA-PRG to Streptococcus sanguis G9B displayed saturation kinetics, reversibility and was inhibited by unlabelled PRG. Inhibition studies with other glycoproteins and saccharides indicated that binding was mediated by a bacterial adhesin with specificity towards N-acetylneuraminic acid, galactose, and N-acetylgalactosamine. After cross-linking, the 125I-ASA-PRG-adhesin complex could be extracted with SDS and separated from uncoupled 125I-ASA-PRG by gel filtration on Sepharose CL-6B. Approx. 1% of the 125I-ASA-PRG was cross-linked to the bacterial surface. Examination of the 125I-ASA-PRG-adhesin complex by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis/fluorography on 5% -(w/v)-polyacrylamide gels revealed that PRG was bound to two bacterial components. These findings support our previous suggestion that human salivary glycoproteins can specifically interact with oral streptococci and that these interactions occur between the glycoprotein's carbohydrate units and lectin(s) on the bacterial cell surface.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Photoactivatable glycopeptide reagents for site-specific labeling of lectins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4421–4425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beppu M., Terao T., Osawa T. Photoaffinity labeling of concanavalin A. Preparation of a concanavalin A derivative with reduced valence. J Biochem. 1975 Nov;78(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Grahnén H., Jonsson G. Lactobacilli and streptococci in the mouth of children. Caries Res. 1975;9(5):333–339. doi: 10.1159/000260166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray H., Decout D., Strecker G., Spik G., Montreuil J. Specificity of twelve lectins towards oligosaccharides and glycopeptides related to N-glycosylproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. R., Hemperly J. J., Wang J. L., Edelman G. M. Monovalent derivatives of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):790–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Enzymatic modification of bacterial receptors on saliva-treated hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.52-58.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Moreno E. C. Association of neuraminidase-sensitive receptors and putative hydrophobic interactions with high-affinity binding sites for Streptococcus sanguis C5 in salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1006-1012.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Handley P. S., Embery G. Surface fibrils may be responsible for the salivary glycoprotein-mediated aggregation of the oral bacterium Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(11):945–949. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji I., Ji T. H. Macromolecular photoaffinity labeling of the lutropin receptor on granulosa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7167–7170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji T. H., Ji I. Macromolecular photoaffinity labeling with radioactive photoactivable heterobifunctional reagents. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., MacAndrew V. I., Jr, Pilch P. F. Identification of the glucagon receptor in rat liver membranes by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):875–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J., Kauffman D. L., Allan B. J., Williams B. L. Further studies on the structural differences between the isoenzymes of human parotid -amylase. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4867–4874. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Weill J. C., Ellison S. A. The isolation and analysis of a glycoprotein from parotid saliva. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):165–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Yoshima H., Takasaki S., Kobata A. Structural study of the sugar chains of human lactoferrin: finding of four novel complex-type asparagine-linked sugar chains. J Biochem. 1982 Jan;91(1):143–155. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite: evidence for two binding sites. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Nakao M., Shibata S., Shizukuishi S., Nakamura R., Tsunemitsu A. Purification and characterization of galactosephilic component present on the cell surfaces of Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557. J Periodontol. 1983 Mar;54(3):163–172. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieels J. P., Pizzo S. V., Glasgow L. R., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Hepatic receptor that specifically binds oligosaccharides containing fucosyl alpha1 leads to 3 N-acetylglucosamine linkages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2215–2219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querinjean P., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Molecular weight, single-chain structure and amino acid composition of human lactoferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):420–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROE J. H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. S., Levine M. J., Prakobphol A. Oligosaccharide structures of the low-molecular-weight salivary mucin from a normal individual and one with cystic fibrosis. J Dent Res. 1985 Jan;64(1):33–36. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640010601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. S., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A. Structure of the carbohydrate chains of the proline-rich glycoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 11;104(3):882–888. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Nagata K., Nakamura R., Tsunemitsu A., Misaki A. Interaction of parotid saliva basic glycoprotein with Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557. J Periodontol. 1980 Sep;51(9):499–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1980.51.9.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura H., Kanai Y., Sanada K. Amino acid sequences of glycopeptides obtained from basic proline-rich glycoprotein of human parotid saliva. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):857–863. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shomers J. P., Tabak L. A., Levine M. J., Mandel I. D., Hay D. I. Properties of cysteine-containing phosphoproteins from human submandibular-sublingual saliva. J Dent Res. 1982 Feb;61(2):397–399. doi: 10.1177/00220345820610020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorr R. G., Heald S. L., Jeffs P. W., Lavin T. N., Strohsacker M. W., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. The beta-adrenergic receptor: rapid purification and covalent labeling by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2778–2782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Application of a novel radioimmunoassay to identify baculovirus structural proteins that share interspecies antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):125–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.125-137.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Levine M. J., Cavese J. M., Prakobphol A., Murray P. A., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to salivary mucin bound to glass. J Dent Res. 1982 Dec;61(12):1390–1393. doi: 10.1177/00220345820610120101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowell C. P., Lee R. T., Lee Y. C. Studies on the specificity of rabbit hepatic carbohydrate-binding protein using neoglycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4904–4908. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak L. A., Levine M. J., Mandel I. D., Ellison S. A. Role of salivary mucins in the protection of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol. 1982 Feb;11(1):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1982.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Ji T. H. Synthesis and application of cleavable photoactivable heterobifunctional reagents. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6754–6760. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H., Schnaar R. L., Kuhlenschmidt M. S., Schmell E., Lee R. T., Lee Y. C., Roseman S. Adhesion of hepatocytes to immobilized sugars. A threshold phenomenon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10830–10838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G. Ionic interaction of oral streptococcal bacteria studied by partition in an aqueous polymer two-phase system. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(12):1035–1039. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. L., O'Dorisio M. S. Covalent cross-linking of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide to its receptors on intact human lymphoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


