Abstract
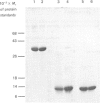
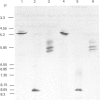
Three fractions of rye-grass (Lolium perenne) pollen extract have been isolated by preparative isoelectric focusing (i.e.f.) and characterized in terms of physicochemical and immunochemical properties. The purified components were designated 'R7' and 'R14' on the basis of their positions in relation to other rye-grass pollen extract components on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and their apparent molecular masses were assessed as 31 and 11 kDa respectively. On i.e.f., R14 split into two components, one acidic (pI 5.0) and one basic (pI 9.0), termed 'R14a' and 'R14b' respectively, and R7 focused at pI 5.8. R7 and R14a were shown to be allergenic by skin-prick test and all three components were recognized by rye-grass-pollen-specific human IgE. On SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and i.e.f., R7 behaved in a manner identical with that shown by an authentic sample of Rye I and gave an amino acid analysis similar to published data [Johnson & Marsh (1966) Immunochemistry 3, 91-100] for Rye group-I isoallergens; the amino acid sequence of the first 27 N-terminal amino acids was also determined. Physicochemical analysis revealed that R14a was equivalent to Rye II and 14b to Rye III. Preparative i.e.f. followed by gel-permeation chromatography proved to be a rapid and efficient method for purifying the allergenic components of Rye I (R7), Rye II (R14a) and Rye III (R14b) from rye-grass pollen extract.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter P. E., Dunbar B., Fothergill J. E. The serine proteinase chain of human complement component C1s. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and N-terminal sequences of the fragments. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):565–571. doi: 10.1042/bj2150565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Eriksson R., Varga J. M. Radioimmunosorbent assay of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Jan;49(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty S., Ekramoddoullah A. K., Kisil F. T., Sehon A. H. Isolation and partial characterization of allergen C from Kentucky blue grass pollen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(4):377–389. doi: 10.1159/000232779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekramoddoullah A. K., Kisil F. T., Sehon A. H. Isolation of allergenically active cytochrome c from Kentucky blue grass pollen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(4):367–376. doi: 10.1159/000232778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Larson J. B., Jones R. T., Baer H. Measurement of the potency of allergy extracts by their inhibitory capacities in the radioallergosorbent test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Mar;53(3):158–169. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett B. J., Clarke A. E. Isolation and partial characterization of two antigenic glycoproteins from rye-grass (Lolium perenne) pollen. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):695–706. doi: 10.1042/bj1970695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Bennich H., Berg T. In vitro diagnosis of atopic allergy. 3. Quantitative estimation of circulating IgE antibodies by the radioallergosorbent test. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(2):443–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Marsh D. G. Allergens from common rye grass pollen (Lolium perenne). I. Chemical composition and structure. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Haddad Z. H., Campbell D. H. A new method for determining the distribution of allergenic fractions in biological materials: its applications to grann pollen extracts. J Allergy. 1970 Aug;46(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(70)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Milner F. H., Johnson P. The allergenic activity and stability of purified allergens from the pollen of common rye grass (lolium perenne). Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(6):521–535. doi: 10.1159/000229739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran D. M., Dupe B. E., Gauntlett S. A micro immunoassay method for measuring IgG antibodies using staphylococcal protein-A. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(1-2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran D. M., Standring R., Henderson D. C. Antibody response profiles to components of rye grass pollen extract in various strains of mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;69(2):120–126. doi: 10.1159/000233158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Gerrie L. M., Dunbar B., Fothergill J. E. Primary structure of bovine complement activation fragment C4a, the third anaphylatoxin. Purification and complete amino acid sequence. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):253–260. doi: 10.1042/bj2070253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Wrigley C. W., Baldo B. A. Detection of IgE- and IgG-binding proteins after electrophoretic transfer from polyacrylamide gels. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jul 30;52(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping M. D., Brighton W. D., Stokell M., Patterson J. M. Fractionation of cocksfoot (Dactylis glomerata) pollen by preparative isoelectric focussing. J Immunol Methods. 1978;19(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]