ABSTRACT
We present the results of 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing of the microbiota from preen oil and the cloaca of chipping sparrows (Spizella passerina) collected near Mountain Lake Biological Station in Pembroke, VA.
KEYWORDS: microbiome, preen oil, cloaca, chipping sparrow, Spizella passerina
ANNOUNCEMENT
New world sparrows (Passerellidae), specifically non-migratory dark-eyed juncos (Junco hyemalis carolinensis), are at the forefront of avian microbial ecology studies (1). These birds harbor symbiotic bacteria used for chemical communication through preen oil (2). In the same habitat is one overlooked species, the migratory chipping sparrow (Spizella passerina). Here, we describe microbial communities of the preen oil and cloaca of chipping sparrows to provide information for future interspecific comparative studies.
Birds were sampled as previously described (2). Microbial communities from the preen oil and cloaca were collected using a pre-moistened swab with sterile buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8, 2 mM EDTA, and 1.2% Triton X-100). We extracted DNA with the Qiagen DNeasy Powerlyzer PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit with the following modifications: (i) Swabs were soaked in a 500-µL bead solution and 200-µL phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol for 10 min before using Biospec Products MiniBeadBeater-16 run 2× for 30 sec. (ii) Samples received 100 µL each of solutions C2 and C3, plus 1-µL RNase A, and incubated at 4°C for 5 min before one-step centrifugation. (iii) Lysates were mixed with 650-µL solution C4 and 650-µL 100% ethanol instead of using 1,200-µL solution C4 alone. (iv) DNA was eluted in 60-µL solution C6, reduced from 100 µL (1). We amplified bacterial DNA using nested PCR as described previously (2). The amplified V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was prepared using the V2 500 cycle MiSeq Reagent Kit (Illumina MS102-2003) and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq platform by Michigan State University Research Technology Support Facility’s Genomics Core generating 2 × 250-bp reads.
Analyses were performed using R Statistical Software v4.3.3 (3). We used DADA2 v1.30.0 (4) to process sequencing reads. Default parameters for DADA2 were used except reads were trimmed 10 bp at the 5′ end and truncated at 240 bp (F) and 200 bp (R) at the 3′ end. Paired-end reads were merged, and chimeric sequences were removed. Table 1 tracks reads through the DADA2 pipeline. We assigned taxonomy using the SILVA 138.1 data set with species information (5). Contaminating sequences from blank and water extractions were removed using decontam v1.22.0 (6). We used phyloseq v1.46.0 (7) to analyze alpha (observed amplicon sequence variants, Shannon diversity, and Simpson’s diversity index) and beta (Bray–Curtis dissimilarity) diversity. We used vegan v2.6.6.1 (8) for statistical analyses and ggplot2 v3.5.1 (9) to generate figures.
TABLE 1.
Sample information for sequencing reads
| Bird | Sample | Site | Input | Filtered | Denoised F | Denoised R | Merged | Non-chimera | NCBI accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHSP02 | 262 | Cloaca | 23,692 | 21,166 | 20,744 | 20,850 | 19,894 | 18,729 | SRR29202452 |
| CHSP03 | 8 | Cloaca | 53,394 | 48,310 | 46,990 | 47,125 | 43,746 | 42,312 | SRR29202442 |
| CHSP04 | 39 | Cloaca | 11,372 | 9,649 | 9,344 | 9,322 | 8,763 | 8,707 | SRR29202444 |
| CHSP05 | 2 | Cloaca | 40,953 | 35,685 | 34,840 | 34,926 | 33,020 | 31,999 | SRR29202438 |
| CHSP06 | 377 | Cloaca | 58,412 | 53,359 | 52,344 | 52,381 | 50,307 | 49,818 | SRR29202445 |
| CHSP07 | 372 | Cloaca | 45,801 | 42,088 | 41,404 | 41,524 | 40,076 | 39,548 | SRR29202446 |
| CHSP08 | 20 | Cloaca | 54,567 | 45,840 | 44,686 | 44,668 | 40,451 | 39,019 | SRR29202437 |
| CHSP09 | 184 | Cloaca | 55,020 | 48,926 | 48,163 | 48,153 | 46,358 | 44,916 | SRR29202440 |
| CHSP10 | 214 | Cloaca | 19,470 | 18,049 | 17,818 | 17,853 | 17,483 | 17,483 | SRR29202435 |
| CHSP11 | 180 | Cloaca | 112,134 | 100,851 | 100,044 | 100,117 | 89,998 | 88,560 | SRR29202443 |
| CHSP12 | 186 | Cloaca | 29,577 | 25,491 | 25,041 | 25,060 | 23,672 | 22,923 | SRR29202439 |
| CHSP02 | 123 | Preen | 3,984 | 3,585 | 3,452 | 3,488 | 3,244 | 3,202 | SRR29202454 |
| CHSP03 | 298 | Preen | 9,871 | 9,269 | 9,186 | 9,208 | 9,144 | 6,304 | SRR29202450 |
| CHSP04 | 93 | Preen | 11,302 | 10,028 | 9,851 | 9,844 | 9,332 | 9,012 | SRR29202441 |
| CHSP05 | 103 | Preen | 43,007 | 38,430 | 37,808 | 37,882 | 36,601 | 35,407 | SRR29202455 |
| CHSP06 | 237 | Preen | 38,532 | 34,316 | 33,689 | 33,706 | 32,041 | 30,803 | SRR29202453 |
| CHSP07 | 207 | Preen | 8,057 | 7,037 | 6,860 | 6,878 | 6,591 | 6,542 | SRR29202436 |
| CHSP08 | 283 | Preen | 1,655 | 1,461 | 1,379 | 1,374 | 1,308 | 1,308 | SRR29202451 |
| CHSP09 | 319 | Preen | 20,659 | 18,642 | 18,256 | 18,305 | 17,466 | 17,133 | SRR29202449 |
| CHSP10 | 326 | Preen | 44,570 | 40,618 | 39,818 | 39,740 | 37,751 | 37,589 | SRR29202448 |
| CHSP11 | 22 | Preen | 59,017 | 53,469 | 52,934 | 52,982 | 48,990 | 48,558 | SRR29202434 |
| CHSP12 | 329 | Preen | 40,065 | 36,088 | 35,652 | 35,645 | 34,274 | 33,466 | SRR29202447 |
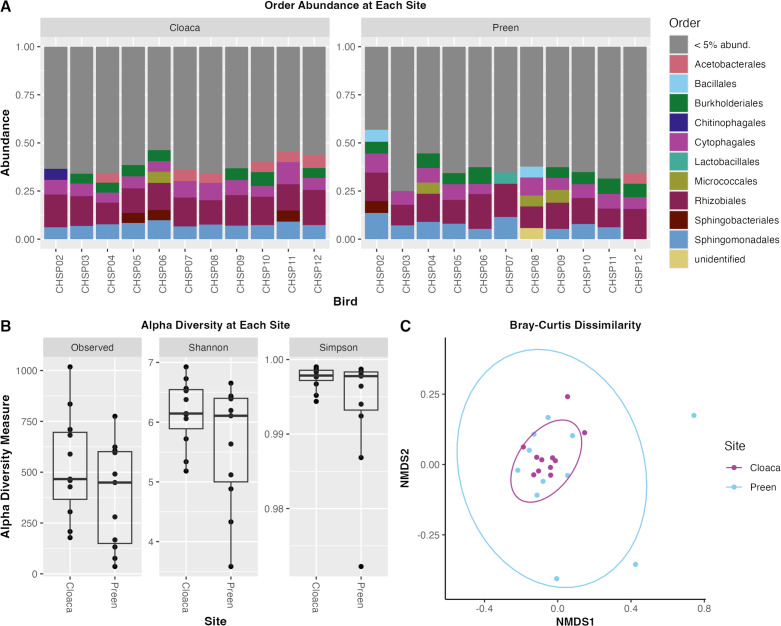
A column chart comparing relative order abundance between preen oil and cloaca showed no noticeable differences (Fig. 1A). The Similarity Percentages function (simper) did not identify any statistically significantly different taxa in preen oil compared to cloaca. Alpha diversity analysis showed that the preen oil community was less diverse than that of the cloaca, though not significantly (Fig. 1B). We saw no significant difference in Bray–Curtis dissimilarity between the preen oil and cloaca communities (Fig. 1C).
Fig 1.
Microbial diversity and community composition in cloaca and preen gland samples from chipping sparrows. (A) Relative abundance of orders obtained from 16S rRNA gene sequencing of preen oil and the cloaca. Orders with less than 5% abundance were grouped together as were orders that were unidentified. (B) Alpha diversity of cloaca and preen oil communities. (C) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plot of Bray–Curtis dissimilarity.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the University of Virginia, Mountain Lake Biological Station, and the Mountain Lake Lodge.
This work was supported by the BEACON Center for the Study of Evolution in Action (National Science Foundation DBI-0939454).
Contributor Information
Joel W. G. Slade, Email: joelslade@csufresno.edu.
Elinne Becket, California State University, San Marcos, California, USA.
DATA AVAILABILITY
The 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences have been deposited in the GenBank Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1117373 under the SRA accession numbers SRR29202434- SRR29202455.
ETHICS APPROVAL
This study was conducted in compliance with the Indiana University Bloomington Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines (15–026), US Fish and Wildlife Service (MB093279-1), and Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries (058772).
REFERENCES
- 1. Whittaker DJ, Slowinski SP, Greenberg JM, Alian O, Winters AD, Ahmad MM, Burrell MJE, Soini HA, Novotny MV, Ketterson ED, Theis KR. 2019. Experimental evidence that symbiotic bacteria produce chemical cues in a songbird. J Exp Biol 222:jeb202978. doi: 10.1242/jeb.202978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Whittaker Danielle J., Atyam A, Burroughs NA, Greenberg JM, Hagey TJ, Novotny MV, Soini HA, Theis KR, Van Laar TA, Slade JWG. 2023. Effects of short-term experimental manipulation of captive social environment on uropygial gland microbiome and preen oil volatile composition. Front Ecol Evol 10. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.1027399 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3. R Core Team . 2024. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. 2016. DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. McLaren MR, Callahan BJ. 2021. Silva 138.1 prokaryotic SSU taxonomic training data formatted for DADA2 [Data set]. Zenodo [Google Scholar]
- 6. Davis NM, Proctor DM, Holmes SP, Relman DA, Callahan BJ. 2018. Simple statistical identification and removal of contaminant sequences in marker-gene and metagenomics data. Microbiome 6:226. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0605-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. McMurdie PJ, Holmes S. 2013. Phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One 8:e61217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Oksanen J, Simpson G, Kindt R, Legendre P, Michin P, O’Hara R, Solymos P, Stevens M, Szoecs E, Wagner H, et al. 2024. Vegan: community ecology package (2.6-6.1)
- 9. Wickham H. 2016. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer-Verlag New York. Available from: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org. Retrieved 27 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences have been deposited in the GenBank Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1117373 under the SRA accession numbers SRR29202434- SRR29202455.