Abstract
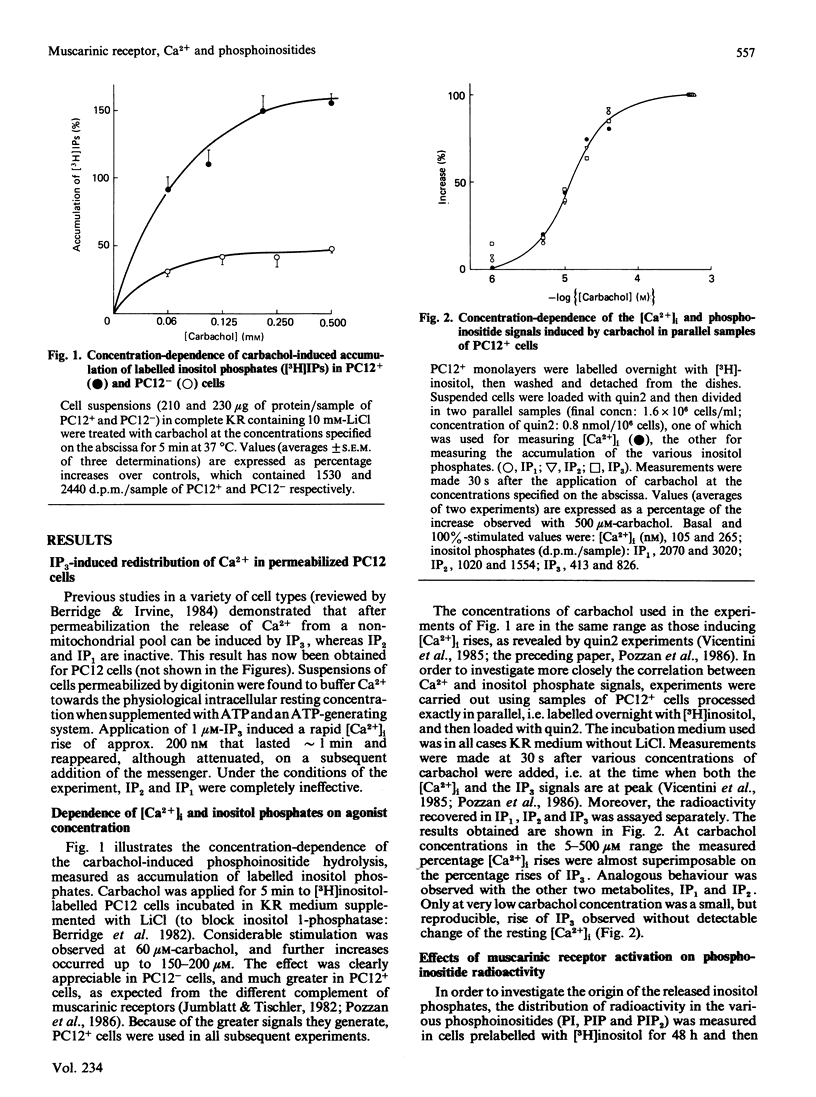
The intracellular signals generated by carbachol activation of the muscarinic receptor [release of inositol phosphates as a consequence of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and rise of the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i, measured by quin2)] were studied in intact PC12 pheochromocytoma cells that had been differentiated by treatment with nerve growth factor. When measured in parallel samples of the same cell preparation 30 s after receptor activation, the release of inositol trisphosphate and of its possible metabolites, inositol bis- and mono-phosphate, and the [Ca2+]i rise were found to occur with almost superimposable carbachol concentration curves. At the same time carbachol caused a decrease in the radioactivity of preloaded phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, the precursor of inositol trisphosphate. Neither the inositol phosphate nor the [Ca2+]i signal was modified by preincubation of the cells with either purified Bordetella pertussis toxin or forskolin, the direct activator of adenylate cyclase. Both signals were partially inhibited by dibutyryl cyclic AMP, especially when the nucleotide analogue was applied in combination with the phosphodiesterase inhibitors RO 201724 and theophylline. The latter drug alone profoundly inhibited the carbachol-induced [Ca2+]i rise, with only minimal effect on phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Because of the diverging results obtained with forskolin on the one hand, dibutyryl cyclic AMP and phosphodiesterase inhibitors on the other, the effects of the latter drugs are considered to be pharmacological, independent of the intracellular cyclic AMP concentration. Two further drugs tested, mepacrine and MY5445, inhibited phosphoinositide hydrolysis at the same time as the 45Ca2+ influx stimulated by carbachol. Taken together, our results concur with previous evidence obtained with permeabilized cells and cell fractions to indicate phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis and [Ca2+]i rise as two successive events in the intracellular transduction cascade initiated by receptor activation. The strict correlation between the carbachol concentration curves for inositol trisphosphate generation and [Ca2+]i rise, and the inhibition by theophylline of the Ca2$ signal without major effects on inositol phosphate generation, satisfy important requirements of the abovementioned interpretation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler S. K., Brown R. D., Taylor P. The relationship between phosphatidylinositol metabolism and mobilization of intracellular calcium elicited by alpha1-adrenergic receptor stimulation in BC3H-1 muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Moore J. P., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. The calcium signal and phosphatidylinositol breakdown in 2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7137–7142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Prentki M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ from permeabilized insulin-secreting cells. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2230467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase-C of platelets: association with 1,2-diacyglycerol-kinase and inhibition by cyclic-AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic factor-induced phospholipase C stimulation and lysosomal enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80801-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Dougherty R. W., Lapetina E. G., Niedel J. E. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic peptide-stimulated generation of inositol phosphates and lysosomal enzyme secretion in human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3277–3280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate formation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, adrenaline and angiotensin II and its relationship to changes in cytosolic free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):79–90. doi: 10.1042/bj2270079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M., Gomperts B. D. Breakdown and synthesis of polyphosphoinositides in fMetLeuPhe-stimulated neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Vicentini L. M., Treves S., Riz G., Pozzan T. Inositol phosphate formation in fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated human neutrophils does not require an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2290361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Reconstitution of resolved muscarinic cholinergic receptors with purified GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3477–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Endo T., Kanayama T., Hidaka H. Effect of 1-(3-chloroanilino)-4-phenylphthalazine (MY-5445), a specific inhibitor of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase, on human platelet aggregation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):467–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. The effects of mepacrine and p-bromophenacyl bromide on arachidonic acid release in human platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. The rapid polyphosphoinositide metabolism may be a triggering event for thrombin-mediated stimulation of human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jumblatt J. E., Tischler A. S. Regulation of muscarinic ligand binding sites by nerve growth factor in PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):152–154. doi: 10.1038/297152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Ogawa Y., Kimura S., Nishizuka Y., Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Ichihara A. Inhibitory action of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on phosphatidylinositol turnover: difference in tissue response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91946-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Harden T. K., Brown J. H. Relationships between phosphoinositide and calcium responses to muscarinic agonists in astrocytoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Marsh M. L., Kermode J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits the rise in the intracellular concentration of free calcium that is induced by chemotactic factors in rabbit neutrophils: possible role of the "G proteins" in calcium mobilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91603-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. E., Johnson P. C., Houlihan M. J., Saluja A. K., Steer M. L. Intracellular Ca2+ levels and amylase secretion in Quin 2-loaded mouse pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C535–C541. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. E., Saluja A. K., Houlihan M. J., Steer M. L. Inositol trisphosphate production and amylase secretion in mouse pancreatic acini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91800-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Di Virgilio F., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Activation of muscarinic receptors in PC12 cells. Stimulation of Ca2+ influx and redistribution. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):547–553. doi: 10.1042/bj2340547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Della Bianca V., Grzeskowiak M., De Togni P., Cabrini G. Relationships between phosphoinositide metabolism, Ca2+ changes and respiratory burst in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated human neutrophils. The breakdown of phosphoinositides is not involved in the rise of cytosolic free Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Hasegawa-Sasaki H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in a T-cell leukaemia line stimulated by phytohaemagglutinin is not dependent on Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):971–979. doi: 10.1042/bj2270971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Wuarin F., Zbaren C., Wollheim C. B., Zahnd G. R. Pertussis toxin selectively abolishes hormone induced lowering of cytosolic calcium in GH3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80835-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. F., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Activation of phospholipase C in thrombin-stimulated platelets does not depend on cytoplasmic free calcium concentration. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81365-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P. Mitogens increase phosphorylation of phosphoinositides in thymocytes. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):462–465. doi: 10.1038/312462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Alexander J., Williamson J. R. Relationship between inositol polyphosphate production and the increase of cytosolic free Ca2+ induced by vasopressin in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5574–5584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tou J. S., Maier C. Phospholipid metabolism and lysosomal enzyme secretion by leukocytes. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 21;451(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Smith C. D., Snyderman R. Potential role for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in chemoattractant receptor mediated polyphosphoinositide metabolism, Ca++ mobilization and cellular responses by leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Ambrosini A., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Muscarinic receptor-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis at resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1330–1333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. alpha Latrotoxin of black widow spider venom binds to a specific receptor coupled to phosphoinositide breakdown in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):538–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Yassin R., Tao W., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Leukotriene B4 mobilizes calcium without the breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and the production of phosphatidic acid in rabbit neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5966–5969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walenga R., Vanderhoek J. Y., Feinstein M. B. Serine esterase inhibitors block stimulus-induced mobilization of arachidonic acid and phosphatidylinositide-specific phospholipase C activity in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6024–6027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


