Abstract
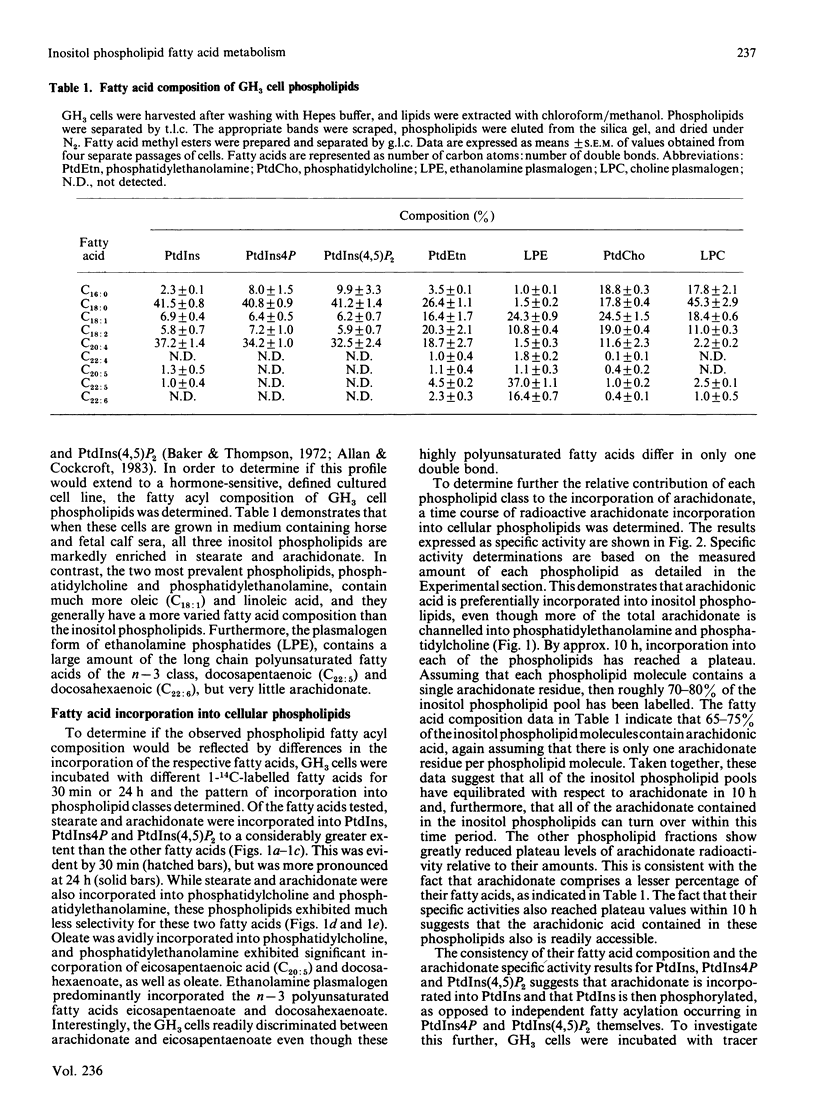
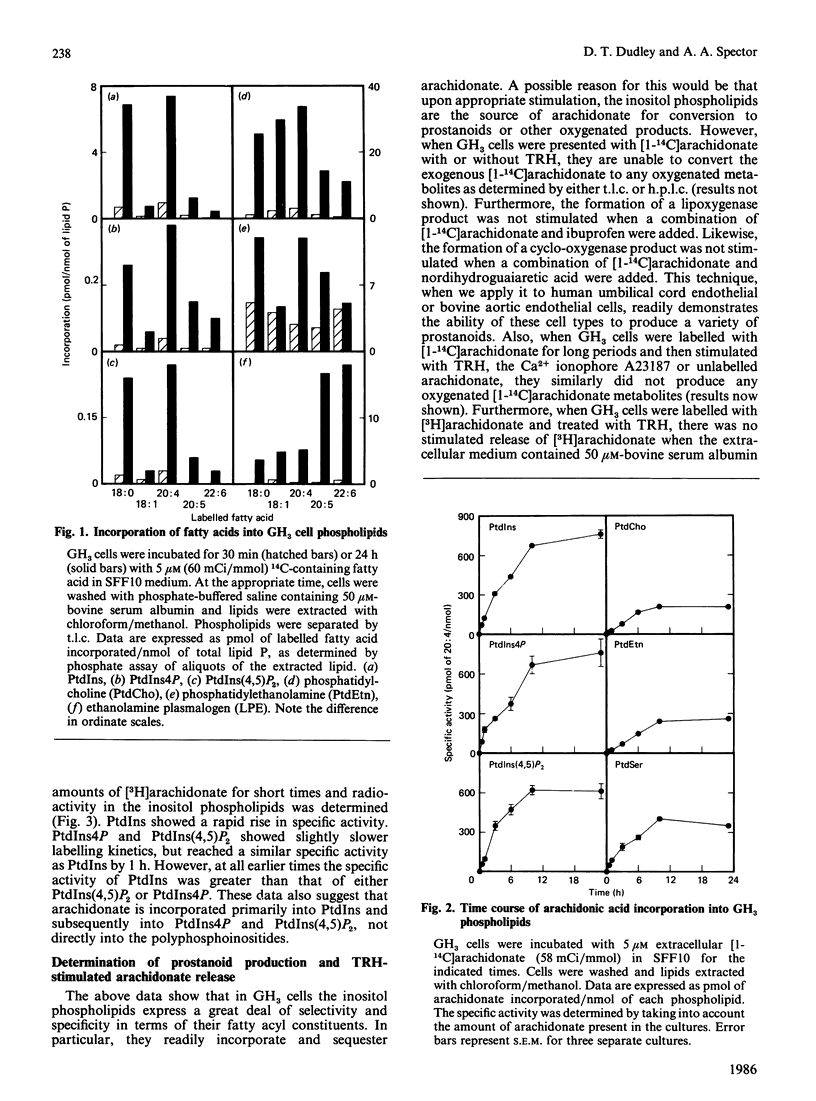
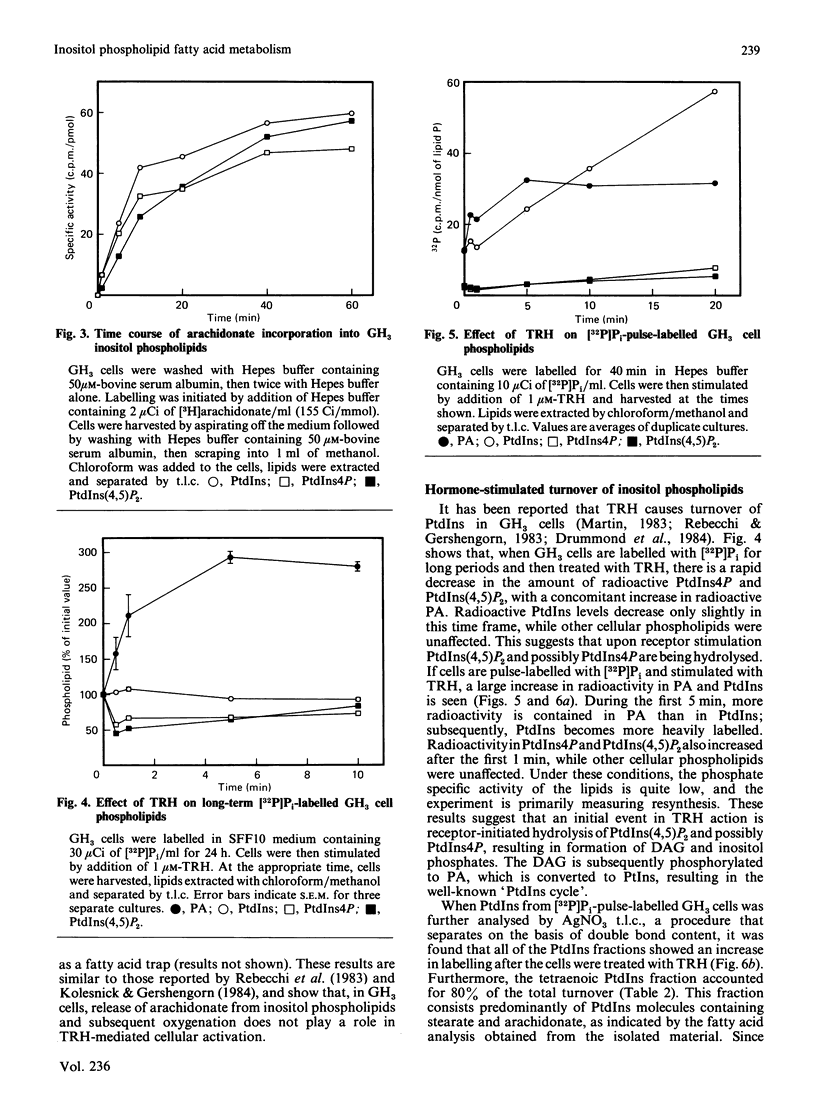
Inositol phospholipids in cultured GH3 cells, a prolactin secreting, thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) sensitive rat pituitary cell line, exhibit a preferential selectivity for incorporating arachidonic acid. Fatty acid composition data show that all inositol phospholipids are enriched in stearic and arachidonic acids to a much greater degree than other cellular phospholipids. Incubation of GH3 cells with radioactive stearate, oleate, arachidonate, eicosapentaenoate or docosahexaenoate also showed that much more stearate and arachidonate were incorporated into inositol phospholipids. In short term incubations with tracer amounts of radioactive arachidonate, incorporation was initially into phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns), with phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P), and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] being labelled at later times. During longer incubations, all of the inositol phospholipids reach equilibrium at about 10 h, and the resulting specific activities of the three fractions were similar. These findings suggest that arachidonate is incorporated initially into PtdIns and that PtdIns is then phosphorylated. There was no release of either arachidonate or eicosanoid products when GH3 cells were incubated with TRH. However, TRH stimulation of 32P-labelled GH3 cells resulted in rapid breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and PtdIns4P, with concomitant increases in [32P]phosphatidic acid and [32P]PtdIns. When the [32P]PtdIns was further analysed by argentation chromatography to separate PtdIns molecular species, it was found that tetraenoic (stearate/arachidonate) species accounted for 80% of the stimulated labelling. The selectivity for arachidonate incorporation into inositol phospholipids coupled with turnover of the arachidonate-containing molecular species suggests that inositol phospholipids containing arachidonic acid or the diacylglycerol resulting therefrom may play a vital cellular role in GH3 cells. This role may involve the operation of the PtdIns cycle itself rather than a stimulated release of arachidonate for eicosanoid formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations in pituitary cells. Relation to prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5827–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Cockcroft S. The fatty acid composition of 1,2-diacylglycerol and polyphosphoinositides from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):555–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2130555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. R., Thompson W. Positional distribution and turnover of fatty acids in phosphatidic acid, phosphinositides, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine in rat brain in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop H. H., Strickland K. P. On the specificity of cytidine diphosphate diglycerides in monophosphoinositide biosynthesis by rat brain preparations. Can J Biochem. 1970 Mar;48(3):269–277. doi: 10.1139/o70-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., Cronin M. J., MacLeod R. M. Diacylglycerol lipase and pituitary prolactin release in vitro: studies employing RHC 80267. Life Sci. 1985 Mar 11;36(10):997–1002. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. L., Judd A. M., Koike K., Valdenegro C. A., MacLeod R. M. Arachidonate stimulates prolactin release in vitro: a role for the fatty acid and its metabolites as intracellular regulator(s) in mammotrophs. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):218–225. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalvardjian A., Rudnicki E. Determination of lipid phosphorus in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau L. Y., Tai H. H. Resolution into two different forms and study of the properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from human platelet cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., Ellis J. M., Olson S. C., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. A common source of platelet-activating factor and arachidonate in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12014–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Bushfield M., Macphee C. H. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated [3H]inositol metabolism in GH3 pituitary tumor cells. Studies with lithium. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):201–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. B., Sprecher H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):660–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Thaw C. Calcium influx is not required for TRH to elevate free cytoplasmic calcium in GH3 cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1522–1524. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitler C. Use of ANS to detect phospholipids and apolar molecules in chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):324–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Lewis D. G., Greer T. L. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-receptor interaction in GH3 pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1980 Mar;106(3):1000–1005. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-3-1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone in prolactin producing rat pituitary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6180–6186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A. Metabolism of molecular species of diacylglycerophospholipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1978;16:1–125. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024916-9.50007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A. Resolution of intact phosphatidylinositols by argentation thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):510–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Kuksis A., Thompson W. Molecular species of mono-, di-, and triphosphoinositides of bovine brain. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Piekarski J. Biosynthesis of molecular species of CDP-diglyceride from endogenously-labeled phosphatidate in rat liver microsomes. Lipids. 1976 Apr;11(4):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02544050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Piekarski J. Substrate selectivity of diacylglycerol kinase in guinea pig brain. Lipids. 1979 Mar;14(3):309–311. doi: 10.1007/BF02533920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub B. J., Piekarski Suitability of different molecular species of 1,2-diacylglycerols as substrates for diacylglycerol kinase in rat brain microsomes. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):903–908. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Deykin D. The activation of phosphatidylinositol-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 during prostaglandin synthesis in transformed mouse BALB/3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5215–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Zwiers H., Dekker A., Wirtz K. W., Gispen W. H. Corticotropin-(1--24)-tetracosapeptide affects protein phosphorylation and polyphosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):283–291. doi: 10.1042/bj1940283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R. N., Gershengorn M. C. Ca2+ ionophores affect phosphoinositide metabolism differently than thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9514–9519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra M. G., Sheltawy A. The metabolic turnover of molecular species of phosphatidylinositol and its precursor phosphatidic acid in guinea-pig cerebral hemispheres. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1501–1511. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. R., SMITH L. M. PREPARATION OF FATTY ACID METHYL ESTERS AND DIMETHYLACETALS FROM LIPIDS WITH BORON FLUORIDE--METHANOL. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:600–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Drummond A. H. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in GH3 pituitary tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. Degradation of different molecular species of phosphatidylinositol in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5337–5339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. The molecular species composition of individual diacyl phospholipids in human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 14;713(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P. J., Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Evidence for a role in stimulus--secretion coupling of prostaglandins derived from release of arachidonoyl residues as a result of phosphatidylinositol breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3292–3296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly activates the phosphodiester hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in GH3 pituitary cells. Evidence for the role of a polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14816–14822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Formation of lysophosphatidylcholine by human platelets in response to thrombin. Support for the phospholipase A2 pathway for the liberation of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1522–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Gershengorn M. C. Thyroliberin stimulates rapid hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by a phosphodiesterase in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. Evidence for an early Ca2+-independent action. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Kolesnick R. N., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates rapid loss of phosphatidylinositol and its conversion to 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. Association with calcium mobilization and prolactin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Differential activation of platelet phospholipases by thrombin and ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4153–4155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Hasegawa-Sasaki H. Molecular species of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol in a phytohemagglutinin-stimulated T-cell leukemia line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 8;833(2):316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Extraction and purification of polyphosphoinositides. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:626–631. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura T., Waku K. Enhanced turnover of arachidonic acid-containing species of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid of concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 14;796(2):190–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. M., Hullin F., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Phosphatidylcholine is the major phospholipid providing arachidonic acid for prostacyclin synthesis in thrombin-stimulated human endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1984 Apr 15;34(2):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. II. The effects of glucose and of inhibitors of arachidonate metabolism on insulin secretion and metabolite synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Colca J. R., McDaniel M. L. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. III. Effects of exogenous lipoxygenase products and inhibitors on insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 27;834(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waku K., Shibata T., Kato H., Tsutsui K., Nakazawa Y. The turnover of molecular species of phosphatidylinositol in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 15;710(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]