Abstract
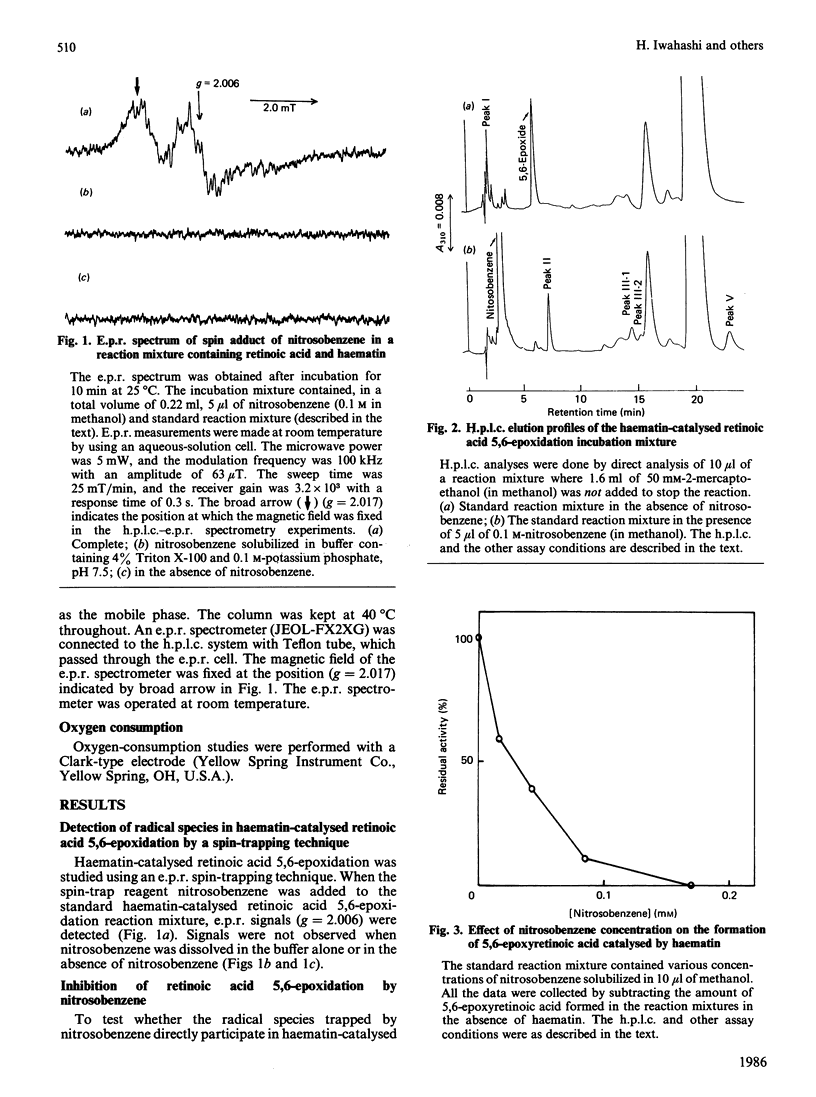
E.p.r. signals were detected in an all-trans-retinoic acid/haematin incubation mixture by using an e.p.r. spin-trapping technique. The spin adducts are presumably attributable to some intermediates in haematin-catalysed retinoic acid 5,6-epoxidation, since addition of nitrosobenzene to the reaction mixture dose-dependently inhibited the epoxidation. Analysing the reaction mixture by h.p.l.c.-e.p.r. spectrometry resulted in the detection of three peaks (III-1, III-2, IV) ascribable to the radical species. Two (peaks III-1 and -2) of the three peaks, which appeared 10 min after the reaction had started, seem to be attributable to the radical species directly participating in the epoxidation. The radicals trapped by nitrosobenzene do not appear to be derived from active oxygen, since none of these peaks were detected in a similar h.p.l.c. analysis of O2- and OH.-generating systems. They are presumably derived from retinoic acid. This view is also supported by the following results: none of these peaks were detected in the h.p.l.c. elution profile of the reaction mixture when retinoic acid was absent; peaks III-1 and 2 were detected even under anaerobic conditions, and their peak heights were unchanged under aerobic conditions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dairman W., Christenson J. G. Properties of human red blood cell 1-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylating activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 May;22(2):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demos J. J., Tuil D. G., Katz P. C., Berthelon M. A., Dautreaux B., Premont N. Diphenoloxidases in X-linked recessive (Duchenne) muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1981;59(2):154–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00293066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix T. A., Fontana R., Panthani A., Marnett L. J. Hematin-catalyzed epoxidation of 7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo[a]pyrene by polyunsaturated fatty acid hydroperoxides. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5358–5365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix T. A., Marnett L. J. Conversion of linoleic acid hydroperoxide to hydroxy, keto, epoxyhydroxy, and trihydroxy fatty acids by hematin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5351–5357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi H., Ikeda A., Kido R. Haemoglobin-catalysed retinoic acid 5,6-epoxidation. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):459–466. doi: 10.1042/bj2320459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi H., Ikeda A., Negoro Y., Kido R. Retinoic acid 5,6-epoxidation by hemoproteins. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):63–71. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John K. V., Lakshmanan M. R., Cama H. R. Preparation, properties and metabolism of 5,6-monoepoxyretinoic acid. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):539–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1030539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiese M., Renner G., Schlaeger R. Mechanism of the autocatalytic formation of ferrihemoglobin by N,N-dimethylaniline-N-oxide. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;268(3):247–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00997260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieyal J. J., Ackerman R. S., Blumer J. L., Freeman L. S. Characterization of Enzyme-like activity of human hemoglobin. Properties of the hemoglobin-P-450 reductase-coupled aniline hydroxylase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3436–3441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieyal J. J., Blumer J. L. Accleration of autooxidation of human oxyhemoglobin by aniline and its relation to hemoglobin-catalyzed aniline hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3442–3446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symms K. G., Juchau M. R. The aniline hydroxylase and nitroreductase activities of partially purified cytochromes P-450 and P-420, and cytochrome b5 solubilized from rabbit hepatic microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Mar-Apr;2(2):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPPEL A. L. The mechanism of the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids catalyzed by hematin compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jun;44(2):378–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERAYAMA H. AMINOAZO DYE AMINE-N-OXIDE AS A POSSIBLE INTERMEDIATE METABOLITE PRECEDING N-DEMETHYLATION AND ORTHO-HYDROXYLATION, AS WELL AS AZO DYE-PROTEIN BINDING. Gan. 1963 Jun;54:195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamabe H., Lovenberg W. Decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine by oxyhemoglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



