Abstract
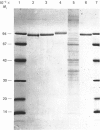
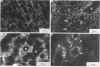
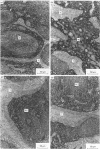
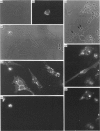
Endopeptidase-24.11 (EC 3.4.24.11), a widely distributed cell-surface endopeptidase in pig tissues, was purified by immunoaffinity chromatography from its second most abundant source, lymph nodes. The detergent-solubilized enzyme is a glycoprotein with an apparent subunit Mr of 91,000, by electrophoresis in the presence of SDS. This value is intermediate between those observed in preparations from kidney and intestine. The specific activity (125I-labelled insulin B-chain as substrate) was similar to that prepared from other sources. Immuno-peroxidase and immunofluorescent cytochemical methods with either a monoclonal antibody, GK7C2, or an affinity-purified polyclonal antiserum, RP109, were used to establish the distribution and localization of the antigen in lymph nodes. Examination of many nodes confirmed the variability of endopeptidase-24.11 content from node to node. Pig lymph nodes are composed of functionally discrete nodelets and are anatomically inverted, with medulla being located peripheral to the cortex. Endopeptidase-24.11 was present in medulla, paracortex and cortex. The medulla, containing relatively few lymphocytes, stained more intensely than other zones. Lymphocyte-rich areas stained only weakly, but antigen was detectable in the centres of follicles and more strongly in a band surrounding them. The pattern of staining was reticular in appearance in all zones. In primary cell cultures, set up after enzymic disruption of nodes, the immuno-positive cells were found to be adherent to glass or plastic and to exhibit a fibroblastic morphology. Diffuse surface immunofluorescence and brighter intracellular immunofluorescence in granules were observed in these cells in the first few days of culture, but by the fourth day no immuno-positive cells remained and the fibroblasts that grew to confluence were somewhat different in morphology. The cells expressing the endopeptidase-24.11 antigen did not express Ia antigen and were clearly distinct from antigen-presenting dendritic cells. In appearance and properties they belong to the group described as reticular cells.
Full text
PDF


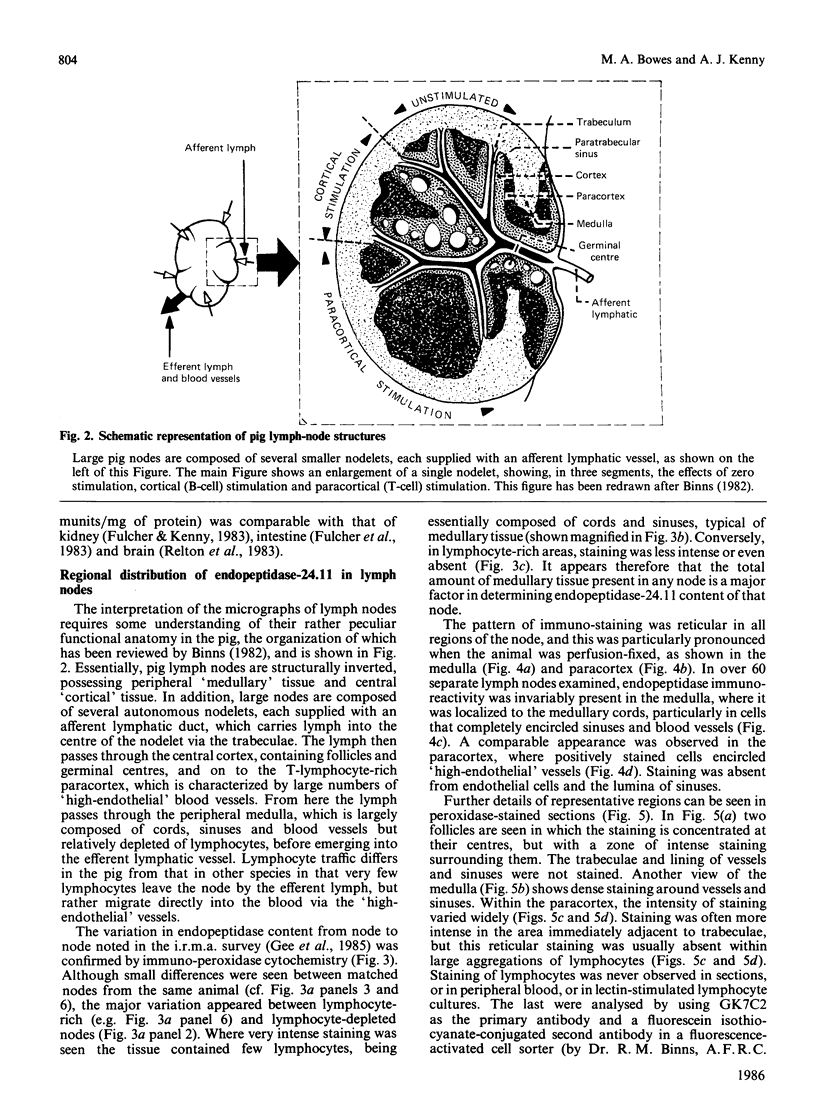
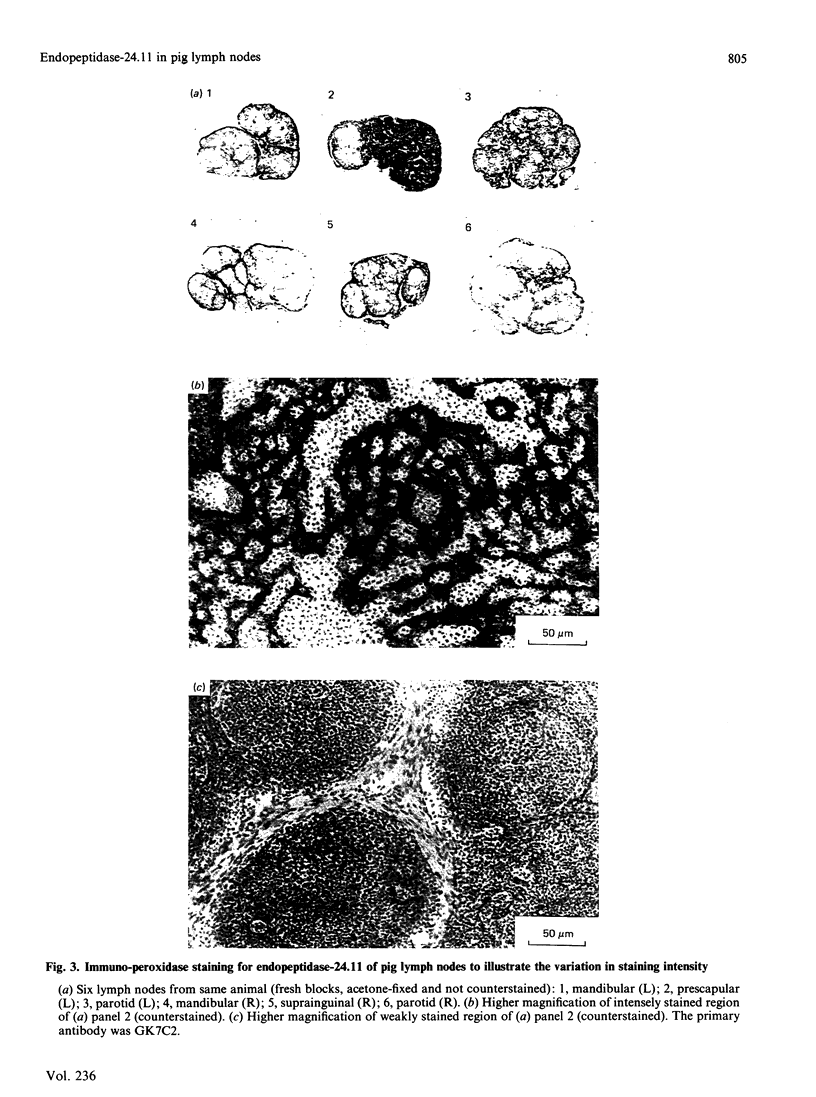
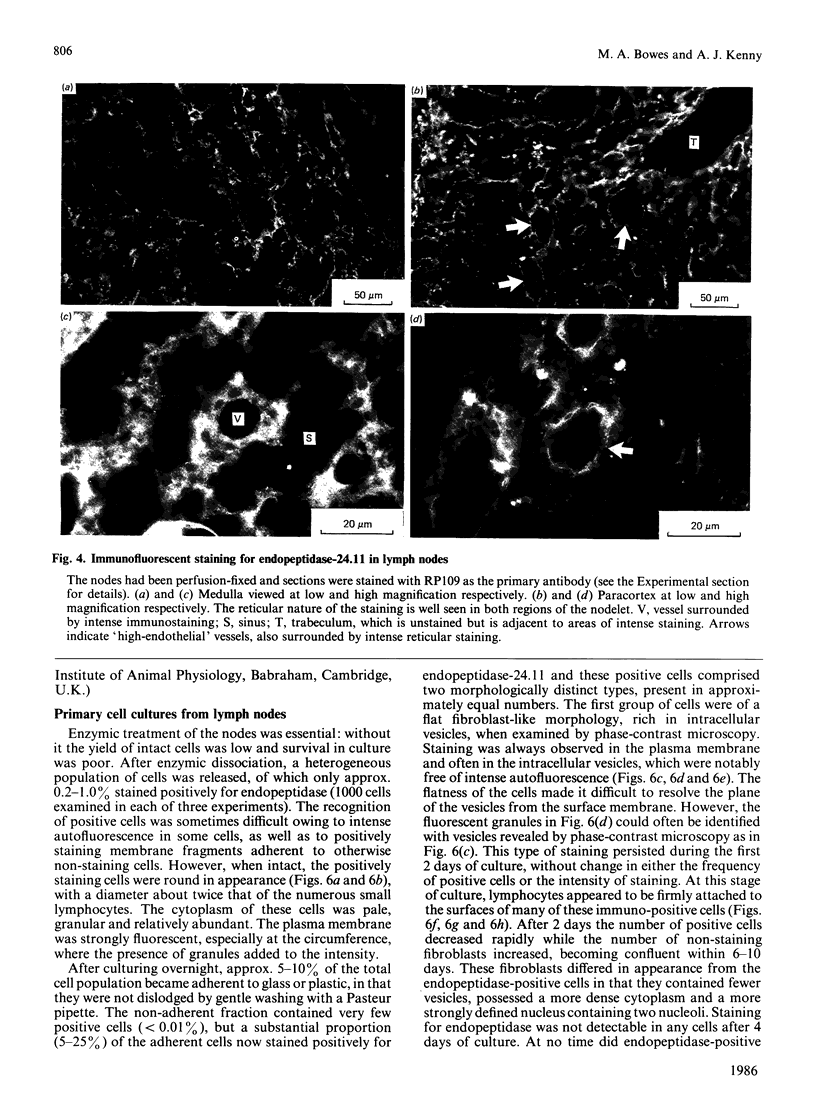
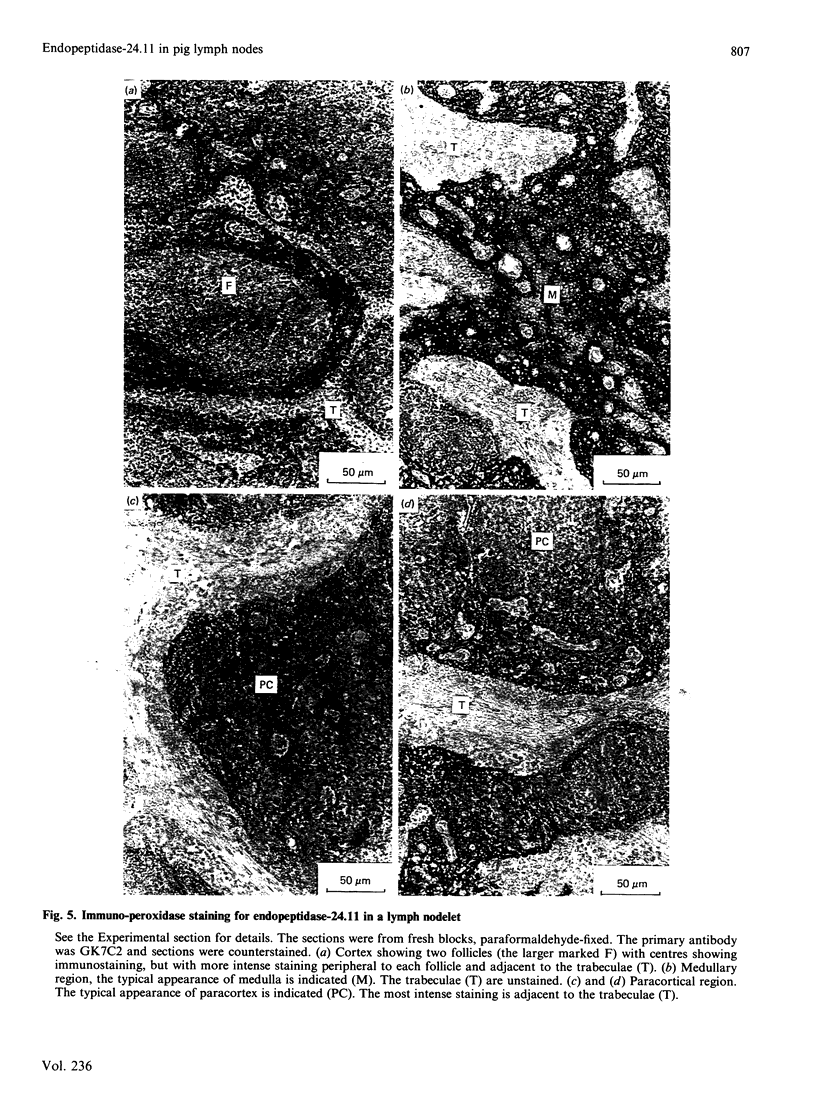



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binns R. M. Organisation of the lymphoreticular system and lymphocyte markers in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jan;3(1-2):95–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Chaplin M. F., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 purified from pig intestine is differently glycosylated from that in kidney. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2150317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic forms of endopeptidase purified from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Kidney neutral endopeptidase and the hydrolysis of enkephalin by synaptic membranes show similar sensitivity to inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2030519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Bowes M. A., Buck P., Kenny A. J. An immunoradiometric assay for endopeptidase-24.11 shows it to be a widely distributed enzyme in pig tissues. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2280119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. A monoclonal antibody to kidney endopeptidase-24.11. Its application in immunoadsorbent purification of the enzyme and immunofluorescent microscopy of kidney and intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):377–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2140377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S. A study of lymphocyte behavior in cultures of fibroblast-like lymphoreticular cells. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jun;45(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Neurokinin A (substance K) is a substrate for endopeptidase-24.11 but not for peptidyl dipeptidase A (angiotensin-converting enzyme). Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):357–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2310357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., McGill K. A., Kershaw D. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Reconstitution of endopeptidase in liposomes shows that it is a short-stalked protein. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2110755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K., Osborne B. A., Sharrow S. O., Devaux C., Pierres M., Sachs D. H. Sharing of Ia antigens between species. IV. Interspecies cross-reactivity of monoclonal antibodies directed against polymorphic mouse Ia determinants. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Rattray M., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Endopeptidase-24.11 in human synaptic membrane preparations hydrolyses substance P. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):487–492. doi: 10.1042/bj2280487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 and aminopeptidase activity in brain synaptic membranes are jointly responsible for the hydrolysis of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8). FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80583-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Devaux C., Dosseto M., Marchetto S. Clonal analysis of B- and T-cell responses to Ia antigens. I. Topology of epitope regions on I-Ak and I-Ek molecules analyzed with 35 monoclonal alloantibodies. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):481–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00350120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnizlein C. T., Kosco M. H., Szakal A. K., Tew J. G. Follicular dendritic cells in suspension: identification, enrichment, and initial characterization indicating immune complex trapping and lack of adherence and phagocytic activity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1360–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Blalock J. E. Human lymphocyte production of corticotropin and endorphin-like substances: association with leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7530–7534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Meyer W. J., Blalock J. E. Virus-induced corticosterone in hypophysectomized mice: a possible lymphoid adrenal axis. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1311–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.6183748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Kaplan G., Witmer M. D., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. V. Purification of spleen dendritic cells, new surface markers, and maintenance in vitro. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E., Davidson A. E. The human reticular cell: morphology and cytochemistry. J Pathol. 1971 Jan;103(1):41–47. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szakal A. K., Gieringer R. L., Kosco M. H., Tew J. G. Isolated follicular dendritic cells: cytochemical antigen localization, Nomarski, SEM, and TEM morphology. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1349–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]