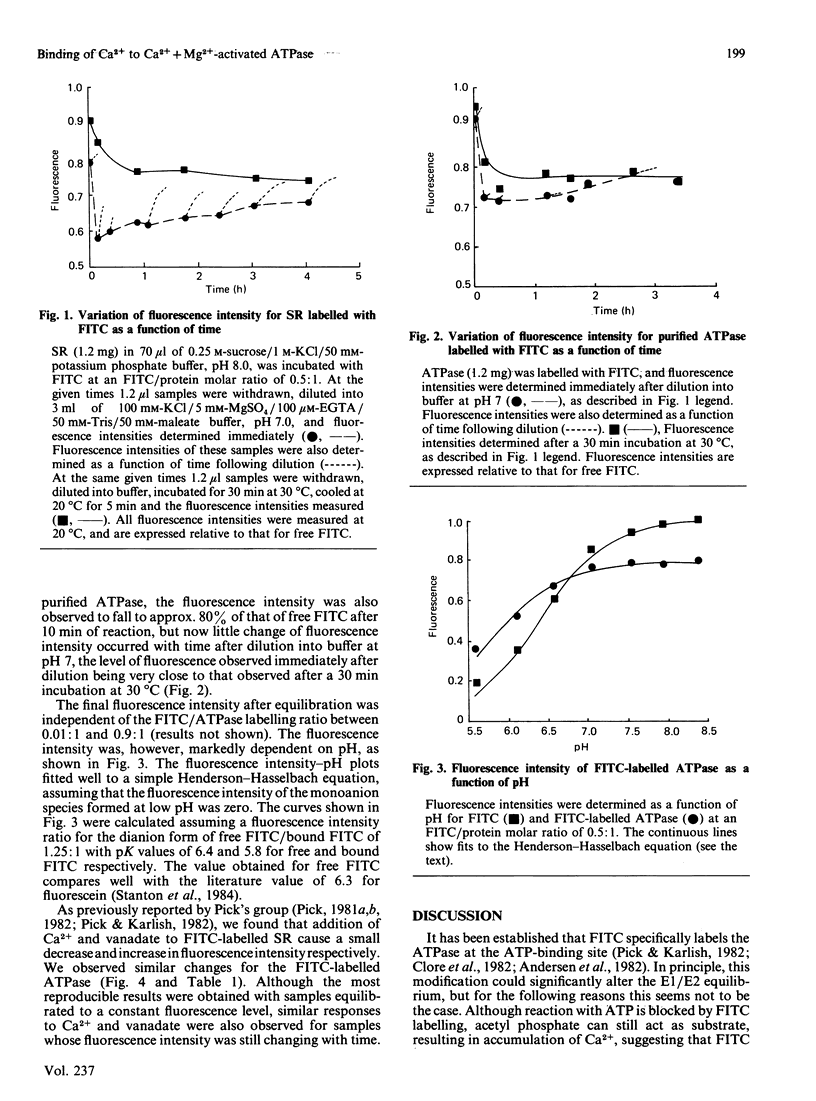
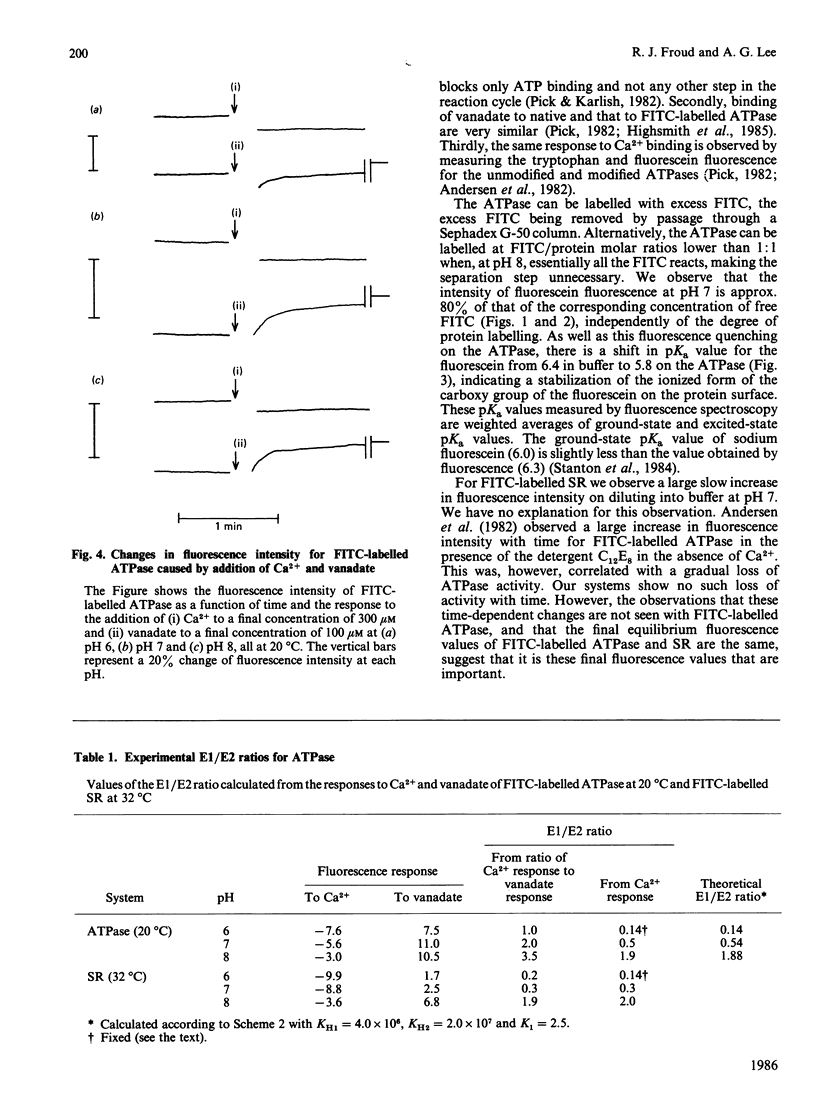
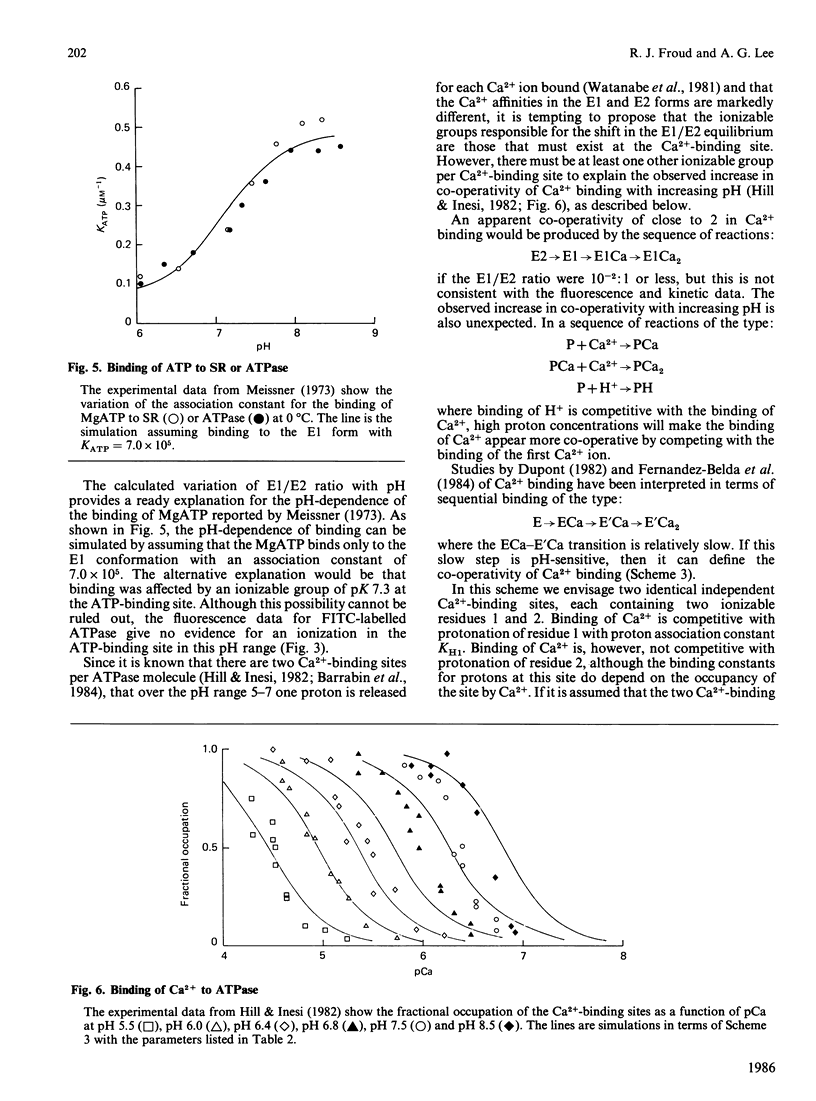
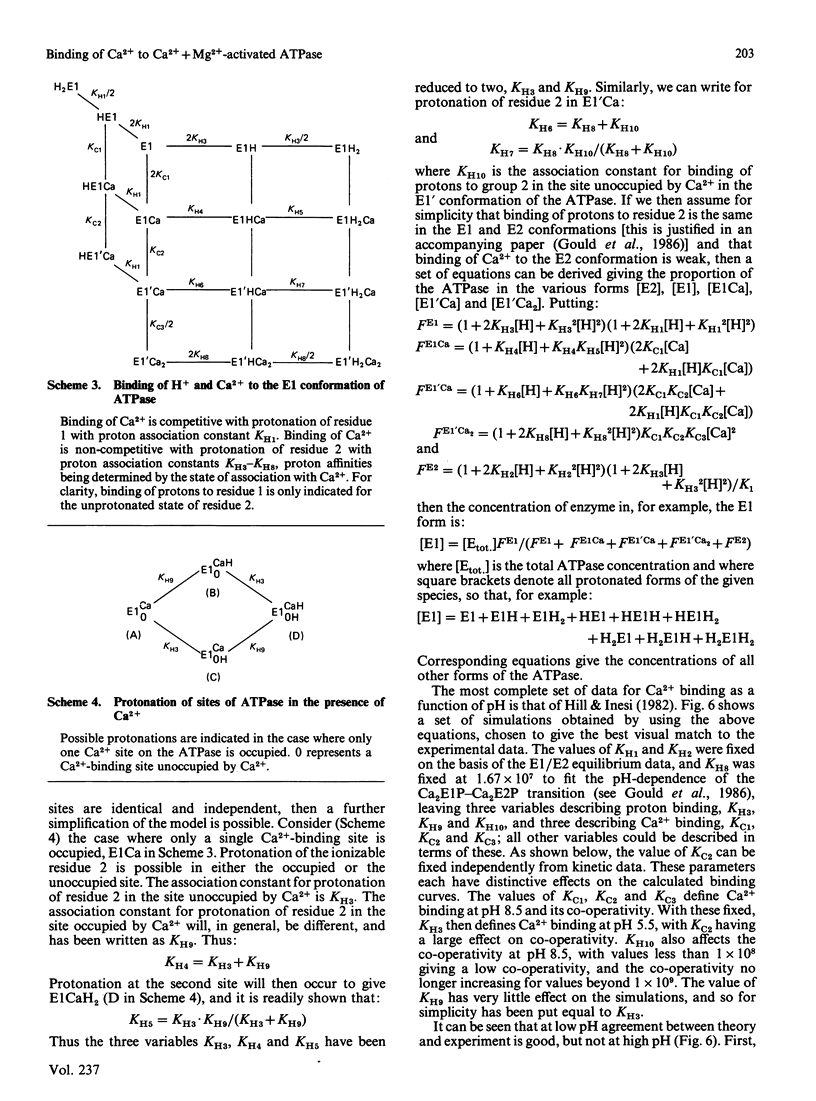
Abstract
We have studied the fluorescence of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum labelled with fluorescein isothiocyanate. The change in intensity of fluorescein fluorescence caused by addition of Ca2+ to the labelled ATPase can be interpreted in terms of a two-conformation model for the ATPase, one conformation (E1) having a high affinity for Ca2+, the other (E2) a low affinity. Effects of Ca2+ as a function of pH allow an estimate of the effect of pH on the E1/E2 ratio, consistent with kinetic studies. A model is presented for binding of Ca2+ to the ATPase as a function of pH that is consistent both with the data on the E1/E2 equilibrium and with literature data on Ca2+ binding.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. P., Møller J. V., Jørgensen P. L. The functional unit of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Active site titration and fluorescence measurements. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8300–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrabin H., Scofano H. M., Inesi G. Adenosinetriphosphatase site stoichiometry in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles and purified enzyme. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1542–1548. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha S. A simple method for derivation of rate equations for enzyme-catalyzed reactions under the rapid equilibrium assumption or combined assumptions of equilibrium and steady state. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 25;243(4):820–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaloub R. M., Guimaraes-Motta H., Verjovski-Almeida S., de Meis L., Inesi G. Sequential reactions in Pi utilization for ATP synthesis by sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9464–9468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaloub R. M., de Meis L. Effect of K+ on phosphorylation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase by either Pi or ATP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6168–6172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Mitchinson C., Green N. M. 1H-NMR studies on nucleotide binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase. Determination of the conformations of bound nucleotides by the measurement of proton-proton transferred nuclear Overhauser enhancements. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. A rapid-filtration technique for membrane fragments or immobilized enzymes: measurements of substrate binding or ion fluxes with a few-millisecond time resolution. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90496-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y., Leigh J. B. Transient kinetics of sarcoplasmic reticulum CA2+ + Mg2+ ATPase studied by fluorescence. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):396–398. doi: 10.1038/273396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Low-temperature studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Mechanisms of calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J. M., Jones O. T., Simmonds A. C., Lee A. G. Membrane fluidity is not an important physiological regulator of the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8070–8071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J. M., Lee A. G. Lipid selectivity of the calcium and magnesium ion dependent adenosinetriphosphatase, studied with fluorescence quenching by a brominated phospholipid. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4144–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Belda F., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. A comparative study of calcium transients by isotopic tracer, metallochromic indicator, and intrinsic fluorescence in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9687–9698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. A model for the phosphorylation of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase by phosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2370207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., East J. M., Froud R. J., McWhirter J. M., Stefanova H. I., Lee A. G. A kinetic model for the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2370217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillain F., Champeil P., Lacapère J. J., Gingold M. P. Stopped flow and rapid quenching measurement of the transient steps induced by calcium binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosine triphosphatase. Competition with Ca2+-independent phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6140–6147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillain F., Gingold M. P., Büschlen S., Champeil P. A direct fluorescence study of the transient steps induced by calcium binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2072–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwicke P. M., Green N. M. The effect of delipidation on the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Electron microscopy and physical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Barker D., Scales D. J. High-affinity and low-affinity vanadate binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Murphy A. J. Nd3+ and Co2+ binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum CaATPase. An estimation of the distance from the ATP binding site to the high-affinity calcium binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14651–14656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Inesi G. Equilibrium cooperative binding of calcium and protons by sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Hill T. L. Calcium and proton dependence of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Biophys J. 1983 Nov;44(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84299-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. ATP and Ca2+ binding by the Ca2+ pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):906–926. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Bassilian S. Modification of the ATP binding site of the Ca2+ -ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by fluorescein isothiocyanate. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. Dynamic interconversions of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated intermediates of the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum followed in a fluorescein-labeled enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. Interaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with nucleotide-binding sites of the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;121(1):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karlish S. J. Indications for an oligomeric structure and for conformational changes in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase labelled selectively with fluorescein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karlish S. J. Regulation of the conformation transition in the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by pH, temperature, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6120–6126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. The interaction of vanadate ions with the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6111–6119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Jencks W. P. Energetics of the calcium-transporting ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1629–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. L., Verjovski-Almeida S. Self-association and modification of calcium binding in solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):707–716. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton S. G., Kantor A. B., Petrossian A., Owicki J. C. Location and dynamics of a membrane-bound fluorescent hapten. A spectroscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):228–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90212-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Steady state of an ATP-driven calcium pump: limitations on kinetic and thermodynamic parameters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6161–6165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reversible lipid titrations of the activity of pure adenosine triphosphatase-lipid complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5501–5507. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Lewis D., Nakamoto R., Kurzmack M., Fronticelli C., Inesi G. Modulation of calcium binding in sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6617–6625. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


