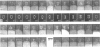Abstract
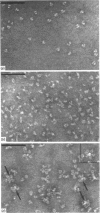
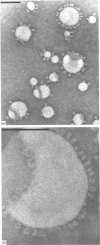
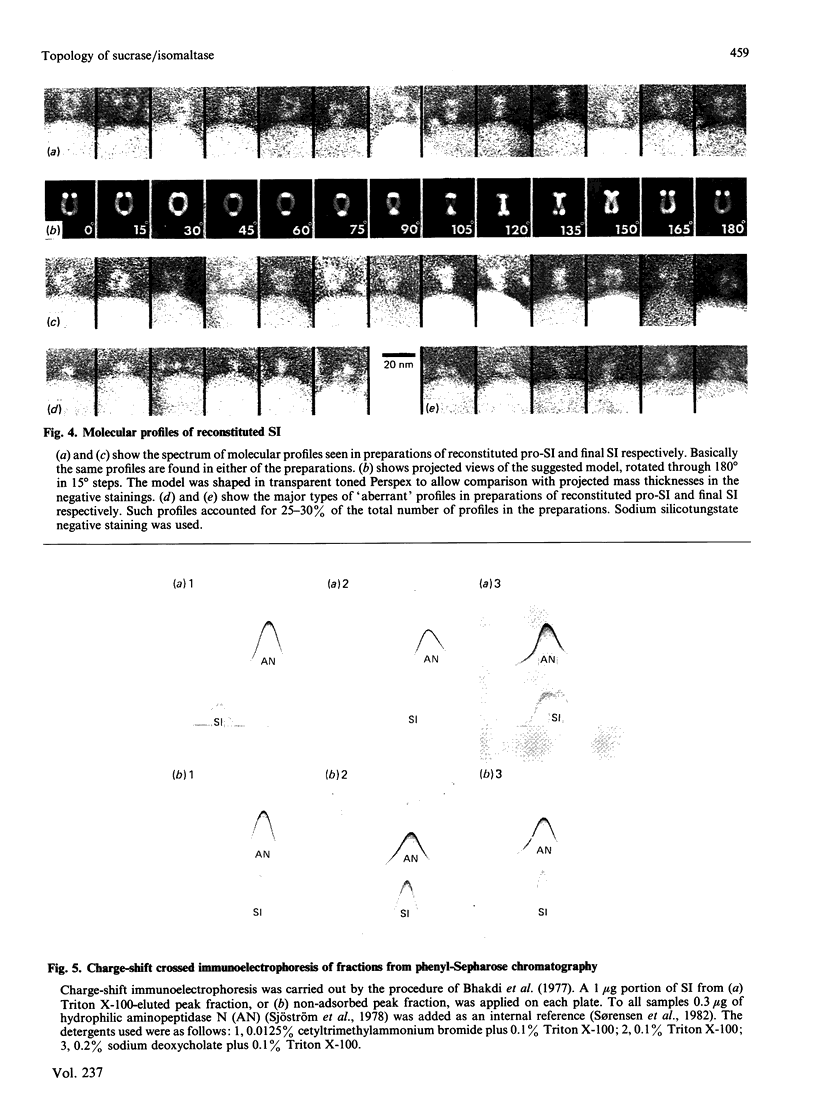
Pig sucrase/isomaltase (EC 3.2.1.48/10) was purified from intestinal microvillar vesicles prepared from animals with and without pancreatic-duct ligation to obtain the single-chain pro form and the proteolytically cleaved final form respectively. The purified enzymes were re-incorporated into phosphatidylcholine vesicles and analysed by electron microscopy after negative staining. The two forms of the enzyme were observed as identical series of characteristic projected views that could be unified in a single dimeric model, containing two sucrase and two isomaltase units. This shows a homodimeric functional organization similar to that of other microvillar hydrolases. The bulk of the dimer was separated from the membrane by a maximal gap of 3.5 nm, representing a junctional segment connecting the intramembrane section of the anchor to the catalytically active domain of sucrase/isomaltase. The enzyme complex protrudes from the membrane for a distance of up to 17 nm. From charge-shift immunoelectrophoresic studies of hydrophilic prosucrase/isomaltase and from electron microscopy of reconstituted pro-sucrase/isomaltase, there was no evidence to suggest the presence of anchoring sequences between the sucrase and isomaltase subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J. Detection of amphiphilic proteins and peptides in complex mixtures. Charge-shift crossed immunoelectrophoresis and two-dimensional charge-shift electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Hauser H., Braun H., Wilson K. J., Wacker H., O'Neill B., Semenza G. The mode of association of the enzyme complex sucrase.isomaltase with the intestinal brush border membrane. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1821–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Cowell G. M., Norén O., Sjöström H. Biosynthesis of microvillar proteins. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2210001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G., Brunner J., Hauser H., Wacker H., Semenza G., Zuber H. The hydrophobic anchor of small-intestinal sucrase--isomaltase: N-terminal sequence of isomaltase subunit. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The 130 kDa protein in pig kidney, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK5C1, is an ectoenzyme with aminopeptidase activity. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):753–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2300753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitzelmann R., Bächi T., Binz H., Lindenmann J., Semenza G. Localization of rabbit intestinal sucrase with ferritin-antibody conjugates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):20–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Quaroni A., Isselbacher K. J. Biogenesis of intestinal plasma membrane: posttranslational route and cleavage of sucrase-isomaltase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5183–5186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Quaroni A., Isselbacher K. J. Monoclonal antibodies to sucrase/isomaltase: probes for the study of postnatal development and biogenesis of the intestinal microvillus membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6629–6633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. M. Reconstitution of purified dipeptidyl peptidase IV. A comparison with aminopeptidase N with respect to morphology and influence of anchoring peptide on function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 14;815(2):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. M., Tranum-Jensen J., Norén O., Sjöström H., Christiansen K. Reconstitution of purified amphiphilic pig intestinal microvillus aminopeptidase. Mode of membrane insertion and morphology. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):179–186. doi: 10.1042/bj1990179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., McGill K. A., Kershaw D. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Reconstitution of endopeptidase in liposomes shows that it is a short-stalked protein. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2110755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann H., Semenza G., Sund H. Hydrodynamic properties of the sucrase-isomaltase complex from rabbit small intestine. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi Y., Takesue Y. Localization of intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex on the microvillous membrane by electron microscopy using nonlabeled antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):516–525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi Y., Tamura R., Takesue Y. Intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex: morphological identification of the subunit directly bound to the microvillar membrane. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Dec;73(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi Y., Yoshida T. O., Takesue Y. Electron microscope studies on the structure of rabbit intestinal sucrase. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G., Brunner J., Wacker H. Biosynthesis and assembly of the largest and major intrinsic polypeptide of the small intestinal brush borders. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:92–112. doi: 10.1002/9780470720769.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Christiansen L., Wacker H., Semenza G. A fully active, two-active-site, single-chain sucrase.isomaltase from pig small intestine. Implications for the biosynthesis of a mammalian integral stalked membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11332–11338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Danielsen E. M., Skovbjerg H. Structure of microvillar enzymes in different phases of their life cycles. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:50–72. doi: 10.1002/9780470720769.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Jeppesen L., Staun M., Svensson B., Christiansen L. Purification of different amphiphilic forms of a microvillus aminopeptidase from pig small intestine using immunoadsorbent chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):503–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovbjerg H., Sjöström H., Norén O. Does sucrase-isomaltase always exist as a complex in human intestine? FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80572-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Hauser H., Rosenbusch J. P., Semenza G. Hydrodynamic properties of phospholipid vesicles and of sucrase isomaltase-phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8977–8982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen S. H., Norén O., Sjöström H., Danielsen E. M. Amphiphilic pig intestinal microvillus maltase/glucoamylase. Structure and specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):559–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]