Abstract
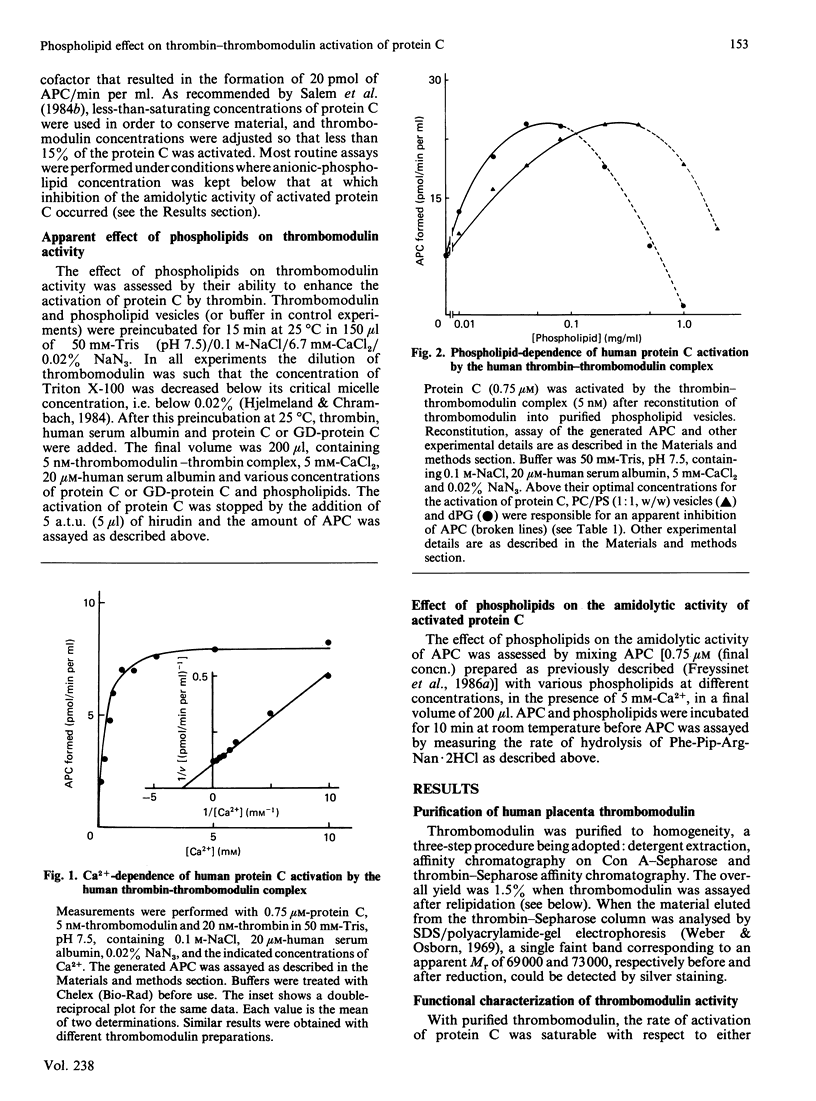
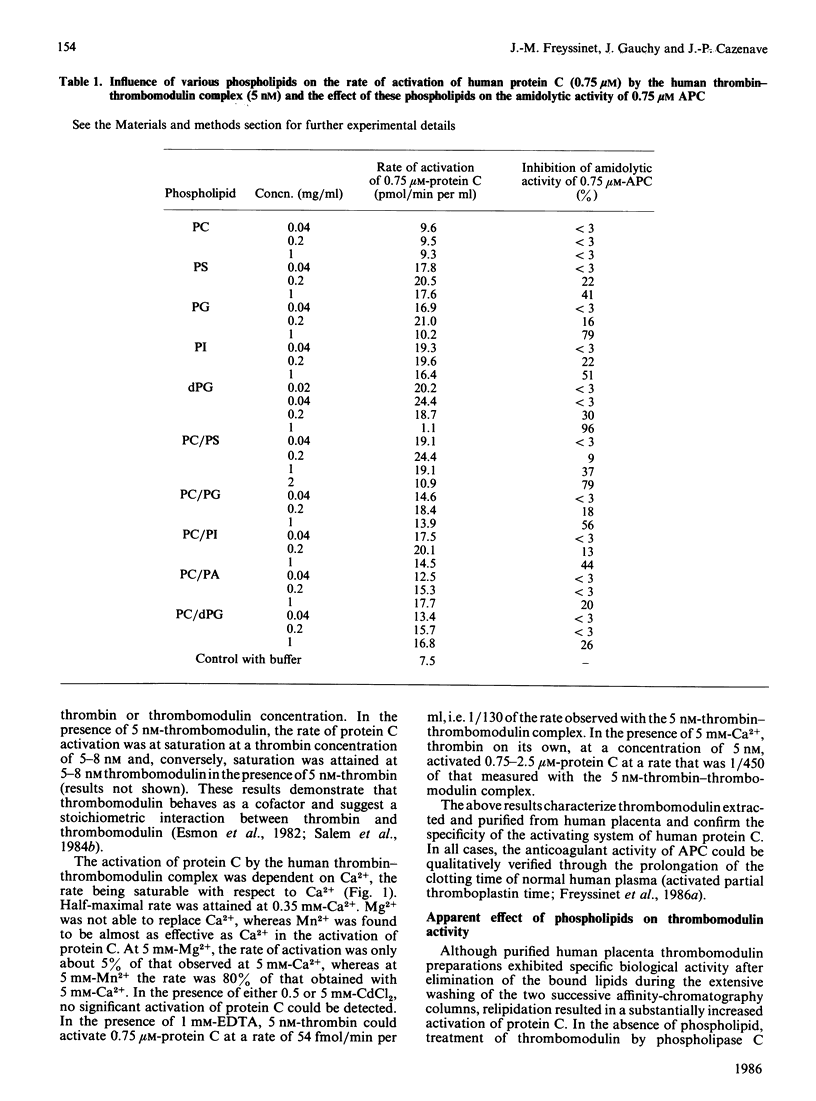
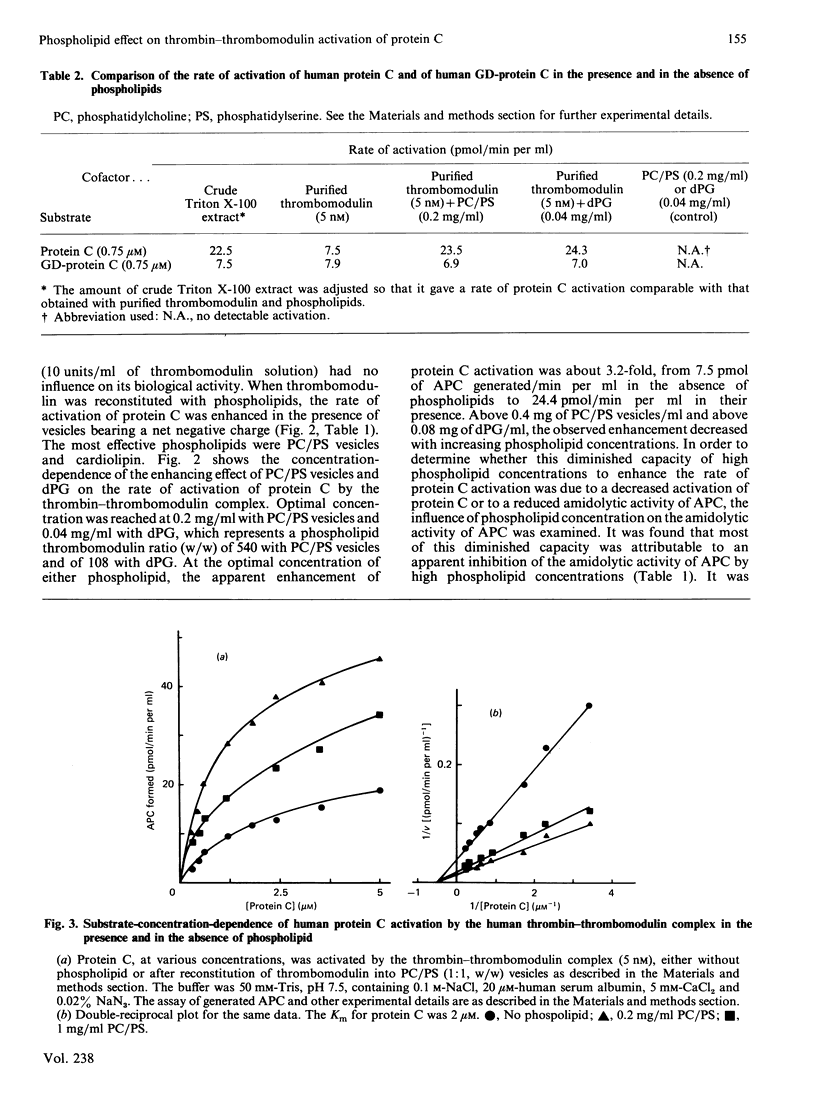
Human thrombomodulin, an endothelial-cell-membrane glycoprotein, has been purified from placenta by Triton X-100 extraction and by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose and thrombin-Sepharose. It has been characterized by its ability to promote the activation of human protein C by human alpha-thrombin in the presence of Ca2+ and fulfilled the requirements of a cofactor. Reconstitution of thrombomodulin into phospholipid vesicles containing anionic phospholipids resulted in an increased rate of activation of protein C. Cardiolipin and vesicles containing phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine (1:1, w/w) were the most effective. The apparent Km of the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex for protein C was 2 microM. It was not changed in the presence of phospholipid, whereas the Vmax. could be apparently increased up to 3.2-fold depending on the phospholipid and on its concentration, the catalytic-centre activity reaching 15.7 mol of activated protein C formed/min per mol of thrombin. Above their optimal concentrations, phospholipids inhibited the amidolytic activity of activated protein C. Phospholipids had no effect on the activation of 4-carboxyglutamic acid-domainless protein C, a proteolytic derivative of protein C lacking the 4-carboxyglutamic acid residues. These results show that the positive effect of anionic phospholipids in the activation of protein C by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex involves a Ca2+-dependent interaction between protein C and phospholipids. They suggest that the enhancement of thrombomodulin activity by such phospholipids may be of functional significance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Nemerson Y., Konigsberg W. Purification and characterization of bovine tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8324–8331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Leykam J. E., Schwartz B. D., Miletich J. P. Purification of human brain tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10917–10920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L. Protein C activation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):122–130. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., DeBault L. E., Esmon C. T. Proteolytic formation and properties of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-domainless protein C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5548–5553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnouf M. P. Biochemistry of blood coagulation. Br Med Bull. 1977 Sep;33(3):213–218. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4673–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Brami B., Gauchy J., Cazenave J. P. Coextraction of thrombomodulin and tissue factor from human placenta: effects of concanavalin A and phospholipid environment on activity. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Feb 28;55(1):112–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Thevenon D., Souque A., Suscillon M. Reversible inhibition of the in vitro coagulation of human plasma by lectins. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Oct 29;48(2):120–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H. Clinical studies of protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):162–166. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M., Chrambach A. Solubilization of functional membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:305–318. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Thompson T. E. Preparation of homogeneous, single-walled phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:485–489. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Thrombomodulin is present in human plasma and urine. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2178–2181. doi: 10.1172/JCI112225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G. Membrane-bound enzyme complexes in blood coagulation. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Salem H. H., Majerus P. W. Coagulation factor Va binds to human umbilical vein endothelial cells and accelerates protein C activation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):224–230. doi: 10.1172/JCI111405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls P. Liposomes-as artificial organelles, topochemical matrices, and therapeutic carrier systems. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1981;12:327–388. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364373-5.50018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T., Majerus P. W. Effects of thrombomodulin and coagulation Factor Va-light chain on protein C activation in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):968–972. doi: 10.1172/JCI111321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent formation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:157–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Protein S and the regulation of activated protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):131–138. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. Blood cell membranes and haemostasis. Haemostasis. 1982;11(1):12–39. doi: 10.1159/000214638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F. Membrane and lipid involvement in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):163–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


