Abstract
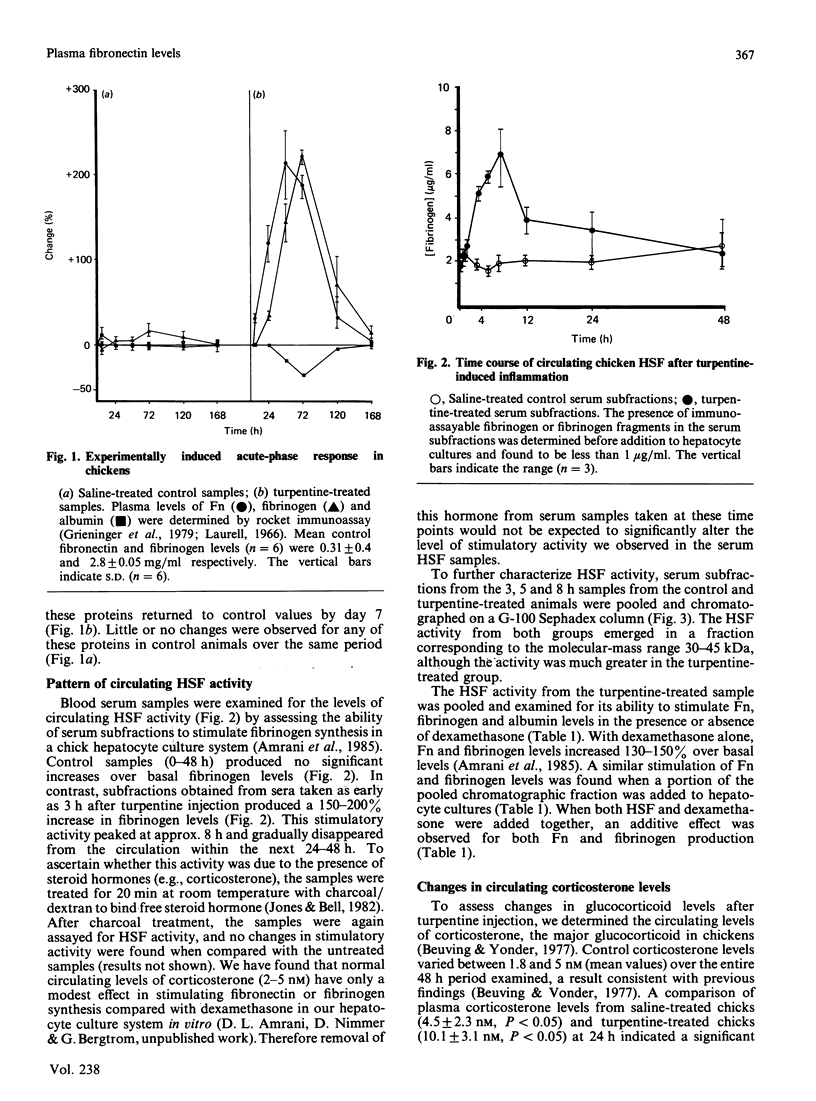
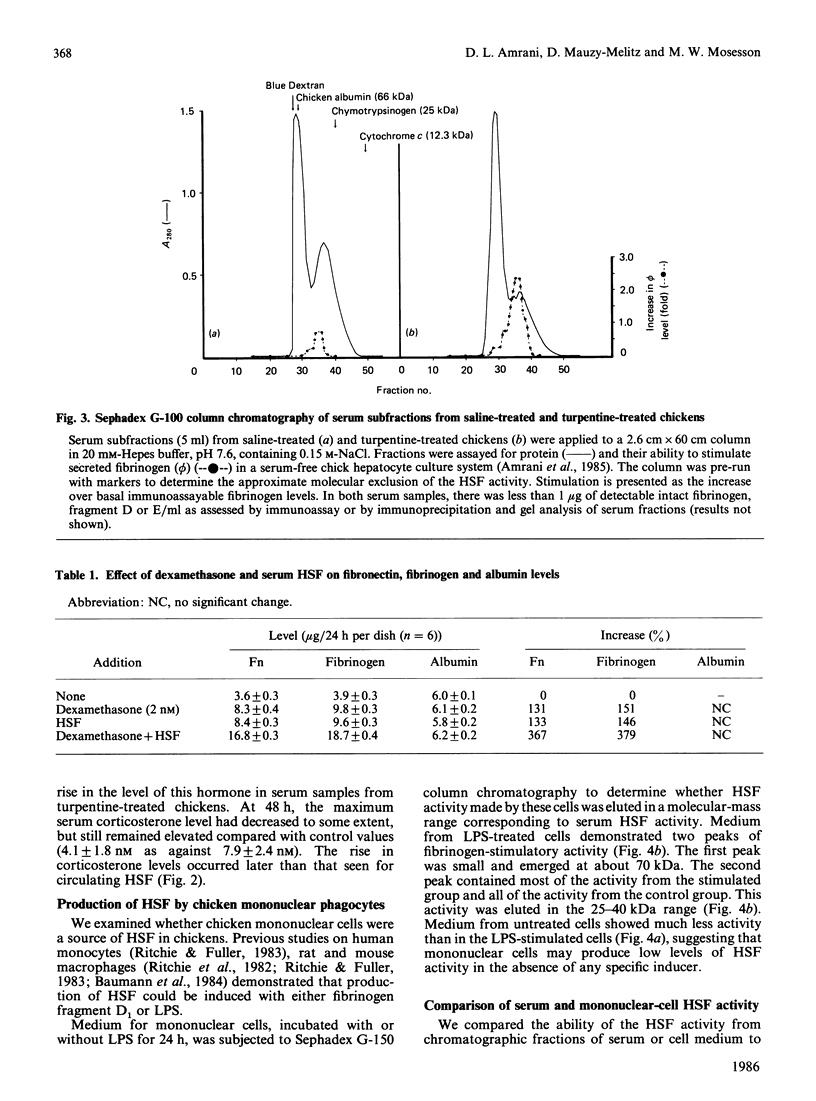
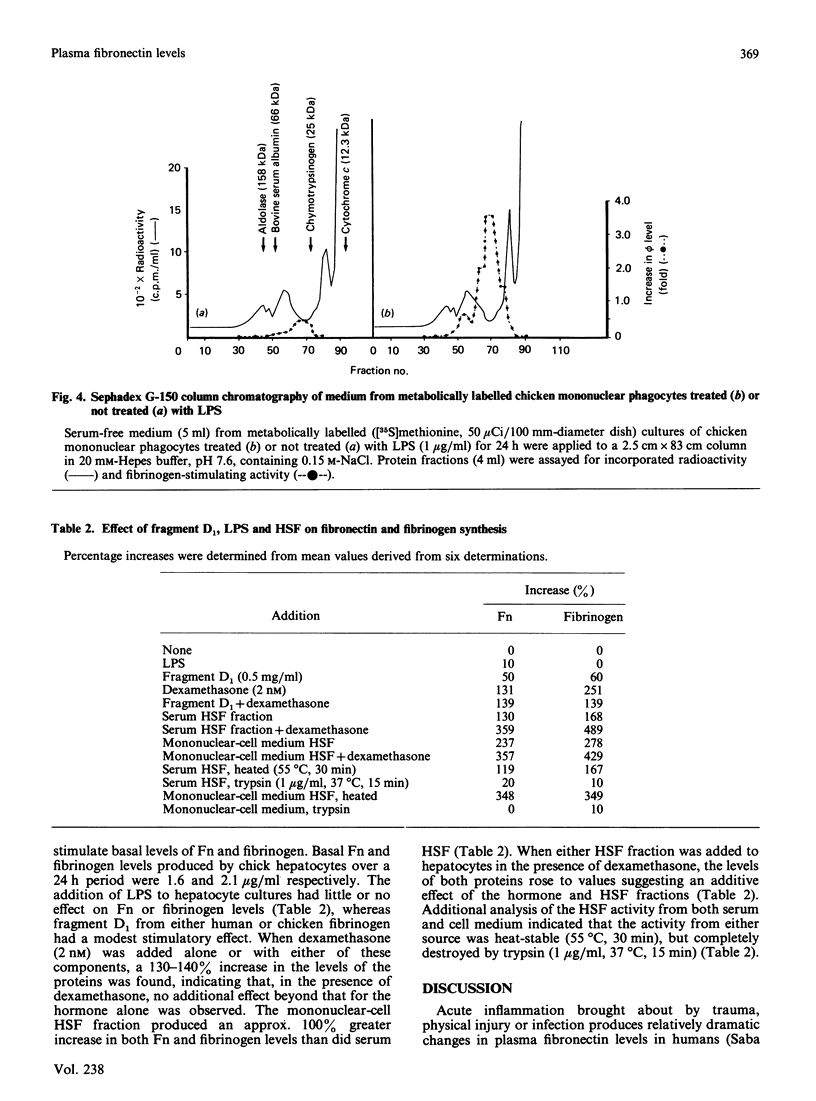
We evaluated the effects of hepatocyte-stimulating factor (HSF) and a glucocorticoid (dexamethasone) on changes in the levels, in vivo and in vitro, of plasma fibronectin (Fn), a glycoprotein that is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. In turpentine-treated chickens, plasma levels of Fn, which peaked at 48 h (whereas fibrinogen levels were maximum at 72 h) rose 200-250% over basal levels, whereas albumin levels decreased by 20-40%. Corticosterone levels in serum samples taken between 5 and 48 h after injection revealed a 124% increase in hormone levels at 24 h in turpentine-treated chickens. We also showed that circulating HSF levels were maximal 8 to 12 h after injection and that HSF activity, as assessed by molecular-exclusion chromatography, was eluted in the 30-45 kDa range. Addition of either serum-derived HSF or dexamethasone (2 nM) to chick hepatocyte cultures resulted in a 130-150% increase in secreted Fn as well as in fibrinogen. When HSF and dexamethasone were added together, a 360-489% increase in the secreted levels of both proteins was found. Chicken mononuclear phagocytic cells treated with lipopolysaccharide secreted an HSF activity that was eluted in two peaks, a minor peak at approximately 70 kDa and a major peak in the 25-40 kDa range. Addition of mononuclear-cell-derived HSF resulted in a greater increase in Fn levels than did the addition of serum HSF. These findings indicate that Fn, like fibrinogen, is an acute-phase protein, the production of which, at least in chickens, is stimulated by HSF and glucocorticoids in an additive manner.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrani D. L., Falk M. J., Mosesson M. W. Studies of fibronectin synthesized by cultured chick hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Sep;160(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Eldredge D. Dexamethasone increases the synthesis and secretion of a partially active fibronectin in rat hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):29–40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Firestone G. L., Burgess T. L., Gross K. W., Yamamoto K. R., Held W. A. Dexamethasone regulation of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and other acute phase reactants in rat liver and hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):563–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Gaines K. C. Synthesis and regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in primary cultures of mouse hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):866–876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Sauder D. N., Koj A. Human keratinocytes and monocytes release factors which regulate the synthesis of major acute phase plasma proteins in hepatic cells from man, rat, and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7331–7342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuving G., Vonder G. M. Effect of stressing factors on corticosterone levels in the plasma of laying hens. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1978 Jun;35(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(78)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Bianco C. Receptors for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):42–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L., Black C. M., Lloyd C. W. Microtubule nucleating sites in higher plant cells identified by an auto-antibody against pericentriolar material. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):319–324. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtoy P. J., Lombart C., Feldmann G., Moguilevsky N., Rogier E. Synchronous increase of four acute phase proteins synthesized by the same hepatocytes during the inflammatory reaction: a combined biochemical and morphologic kinetics study in the rat. Lab Invest. 1981 Feb;44(2):105–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann G. Morphologic aspects of hepatic synthesis and secretion of plasma proteins. Prog Liver Dis. 1979;6:23–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouad F. M., Abd-El-Fattah M., Scherer R., Ruthenstroth-Bauer G. Effect of glucocorticoids, insulin and a growth promoting tripeptide on the biosynthesis of plasma proteins in serum-free hepatocyte cultures. Z Naturforsch C. 1981 Mar-Apr;36(3-4):350–352. doi: 10.1515/znc-1981-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieninger G., Hertzberg K. M., Pindyck J. Fibrinogen synthesis in serum-free hepatocyte cultures: stimulation by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5506–5510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieninger G., Pindyck J., Hertzberg K. M., Mosesson M. W. Application of electroimmunoassay to the study of plasma protein synthesis in cultured hepatocytes. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1979 Nov-Dec;9(6):511–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Bell P. A. Glucocorticoid-receptor interactions. Discrimination between glucocorticoid agonists and antagonists by means of receptor-binding kinetics. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):721–729. doi: 10.1042/bj2040721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Gauldie J., Regoeczi E., Sauder D. N., Sweeney G. D. The acute-phase response of cultured rat hepatocytes. System characterization and the effect of human cytokines. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):505–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2240505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L. The structure and biologic activities of plasma fibronectin. Blood. 1980 Aug;56(2):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Galanakis D. K. The essential covalent structure of human fibrinogen evinced by analysis of derivatives formed during plasmic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7913–7929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Physiology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:561–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver N., Newby R. F., Furcht L. T., Bourgeois S. Regulation of fibronectin biosynthesis by glucocorticoids in human fibrosarcoma cells and normal fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens M. R., Cimino C. D. Synthesis of fibronectin by the isolated perfused rat liver. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1305–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piovella F., Giddings J. C., Ricetti M. M., Almasio P., Ascari E. The effect of dexamethasone on formation of intra and extracellular fibronectin matrix by human endothelial cells in culture. Haematologica. 1982 Feb;67(1):58–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P. S., Saba T. M. Effect of endotoxin on fibronectin and Kupffer cell activity. Hepatology. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P. S., Saba T. M. Fibronectin levels during intraperitoneal inflammation. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1411–1418. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1411-1418.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. O., Scovill W. A., Shin B. Opsonic fibronectin deficiency in patients with intra-abdominal infection. Surgery. 1983 Aug;94(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Fuller G. M. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor: a monocyte-derived acute-phase regulatory protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:490–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Levy B. A., Adams M. A., Fuller G. M. Regulation of fibrinogen synthesis by plasmin-derived fragments of fibrinogen and fibrin: an indirect feedback pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1530–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubli E., Büssard S., Frei E., Lundsgaard-Hansen P., Pappova E. Plasma fibronectin and associated variables in surgical intensive care patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):310–317. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198303000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. G., Fuller G. M. The effects of leucocytic and serum factors on fibrinogen biosynthesis in cultured hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jan;118(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90579-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Blumenstock F. A., Weber P., Kaplan J. E. Physiologic role of cold-insoluble globulin in systemic host defense: implications of its characterization as the opsonic alpha 2-surface-binding glycoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Plasma fibronectin is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Fuller G. M. Identification and partial characterization of hepatocyte-stimulating factor from leukemia cell lines: comparison with interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Smith E. M., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Fuller G. M., Blalock J. E. Corticotropin-releasing activity of monokines. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1035–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2997929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


