Abstract
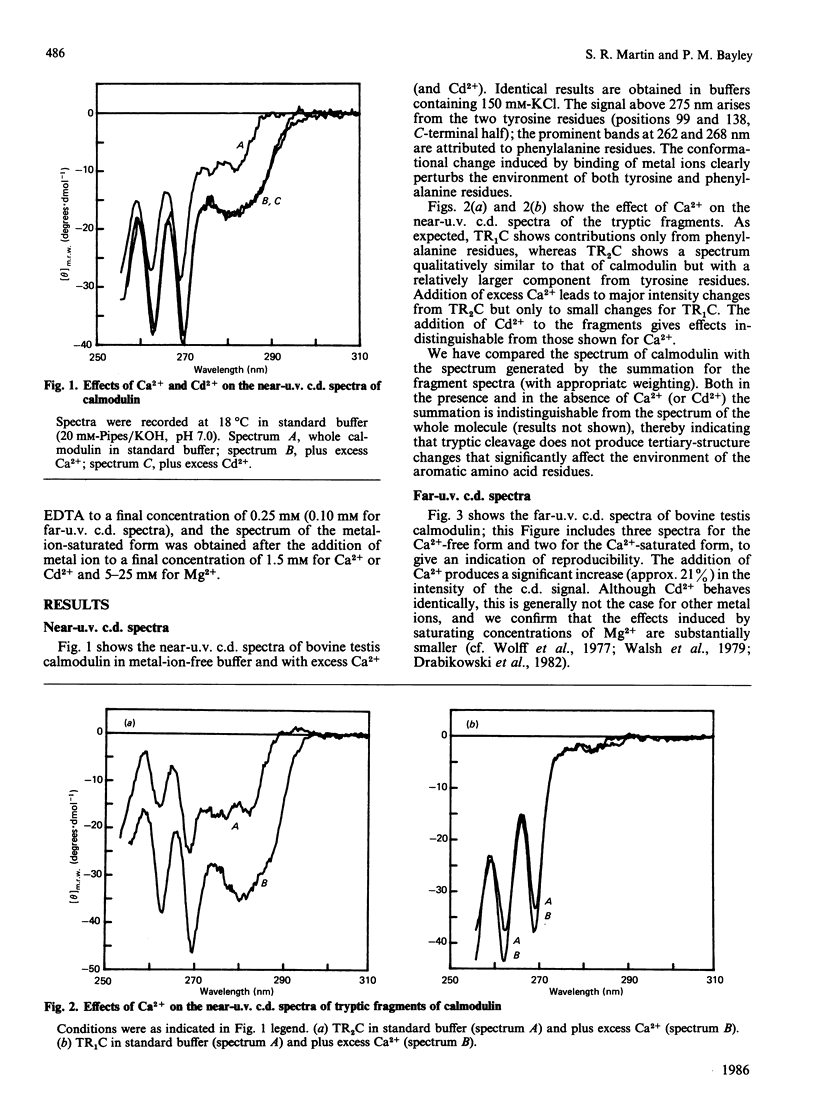
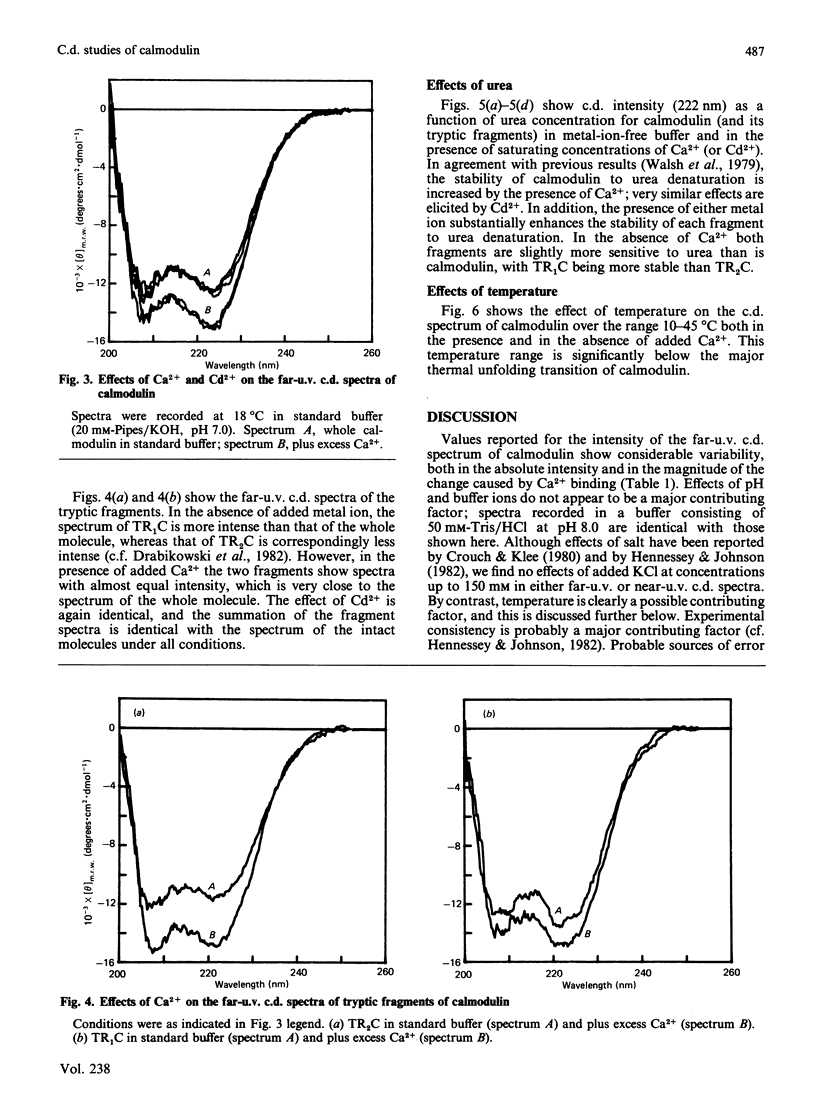
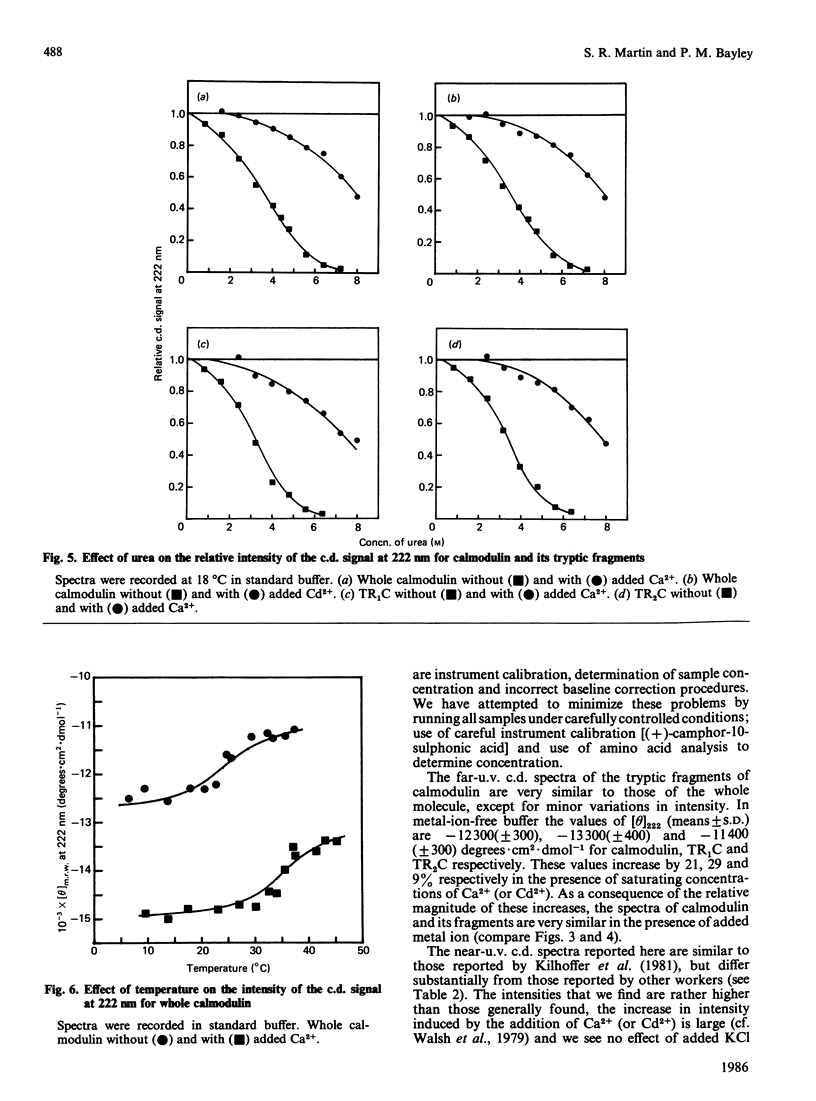
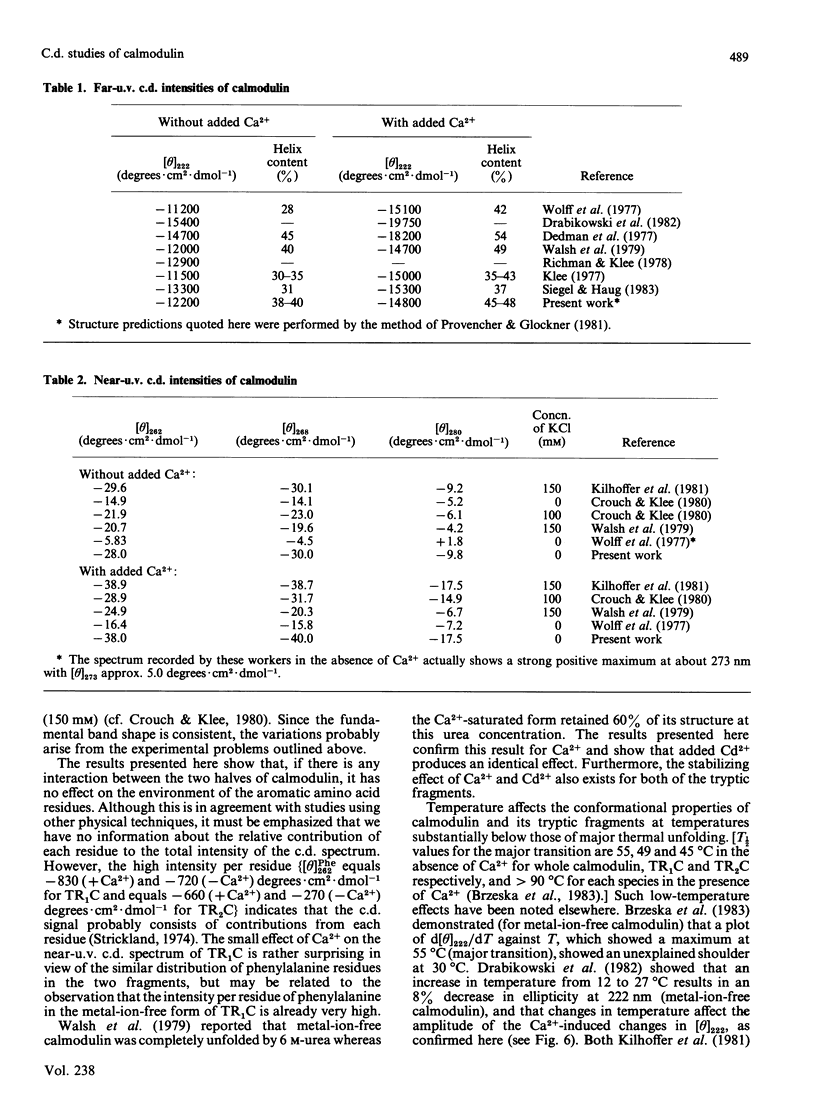
Near-u.v. and far-u.v. c.d. spectra of bovine testis calmodulin and its tryptic fragments (TR1C, N-terminal half, residues 1-77, and TR2C, C-terminal half, residues 78-148) were recorded in metal-ion-free buffer and in the presence of saturating concentrations of Ca2+ or Cd2+ under a range of different solvent conditions. The results show the following: if there is any interaction between the N-terminal and C-terminal halves of calmodulin, it has not apparent effect on the secondary or tertiary structure of either half; the conformational changes induced by Ca2+ or Cd2+ are substantially greater in TR2C than they are in TR1C; the presence of Ca2+ or Cd2+ confers considerable stability with respect to urea-induced denaturation, both for the whole molecule and for either of the tryptic fragments; a thermally induced transition occurs in whole calmodulin at temperatures substantially below the temperature of major thermal unfolding, both in the presence and in the absence of added metal ion; the effects of Cd2+ are identical with those of Ca2+ under all conditions studied.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A., Forsén S., Thulin E., Vogel H. J. Cadmium-113 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of proteolytic fragments of calmodulin: assignment of strong and weak cation binding sites. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2309–2313. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Drakenberg T., Forsén S., Thulin E. Characterization of the Ca2+ binding sites of calmodulin from bovine testis using 43Ca and 113Cd NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):501–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeska H., Venyaminov SVu, Grabarek Z., Drabikowski W. Comparative studies on thermostability of calmodulin, skeletal muscle troponin C and their tryptic fragments. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch T. H., Klee C. B. Positive cooperative binding of calcium to bovine brain calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3692–3698. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Potter J. D., Jackson R. L., Johnson J. D., Means A. R. Physicochemical properties of rat testis Ca2+-dependent regulator protein of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Relationship of Ca2+-binding, conformational changes, and phosphodiesterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8415–8422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabikowski W., Brzeska H., Venyaminov SYu Tryptic fragments of calmodulin. Ca2+- and Mg2+-induced conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11584–11590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabikowski W., Kuznicki J., Grabarek Z. Similarity in Ca2+-induced changes between troponic-C and protein activator of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and their tryptic fragments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 23;485(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsén S., Thulin E., Drakenberg T., Krebs J., Seamon K. A 113Cd NMR study of calmodulin and its interaction with calcium, magnesium and trifluoperazine. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangola P., Pant H. C. Temperature dependent conformational changes in calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):301–305. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey J. P., Jr, Johnson W. C., Jr Experimental errors and their effect on analyzing circular dichroism spectra of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilhoffer M. C., Demaille J. G., Gérard D. Tyrosine fluorescence of ram testis and octopus calmodulins. Effects of calcium, magnesium, and ionic strength. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4407–4414. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Conformational transition accompanying the binding of Ca2+ to the protein activator of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):1017–1024. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Andersson Teleman A., Bayley P. M., Drakenberg T., Forsen S. Kinetics of calcium dissociation from calmodulin and its tryptic fragments. A stopped-flow fluorescence study using Quin 2 reveals a two-domain structure. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman P. G., Klee C. B. Conformation-dependent nitration of the protein activator of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):928–935. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel N., Haug A. Aluminum interaction with calmodulin. Evidence for altered structure and function from optical and enzymatic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 14;744(1):36–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulin E., Andersson A., Drakenberg T., Forsén S., Vogel H. J. Metal ion and drug binding to proteolytic fragments of calmodulin: proteolytic, cadmium-113, and proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1862–1870. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M., Stevens F. C. Characterization of tryptic fragments obtained from bovine brain protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7440–7443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M., Stevens F. C., Oikawa K., Kay C. M. Circular dichroism studies of native and chemically modified Ca2+-dependent protein modulator. Can J Biochem. 1979 Mar;57(3):267–278. doi: 10.1139/o79-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Poirier P. G., Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A. Divalent cation binding properties of bovine brain Ca2+-dependent regulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4108–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


