Full text
PDF

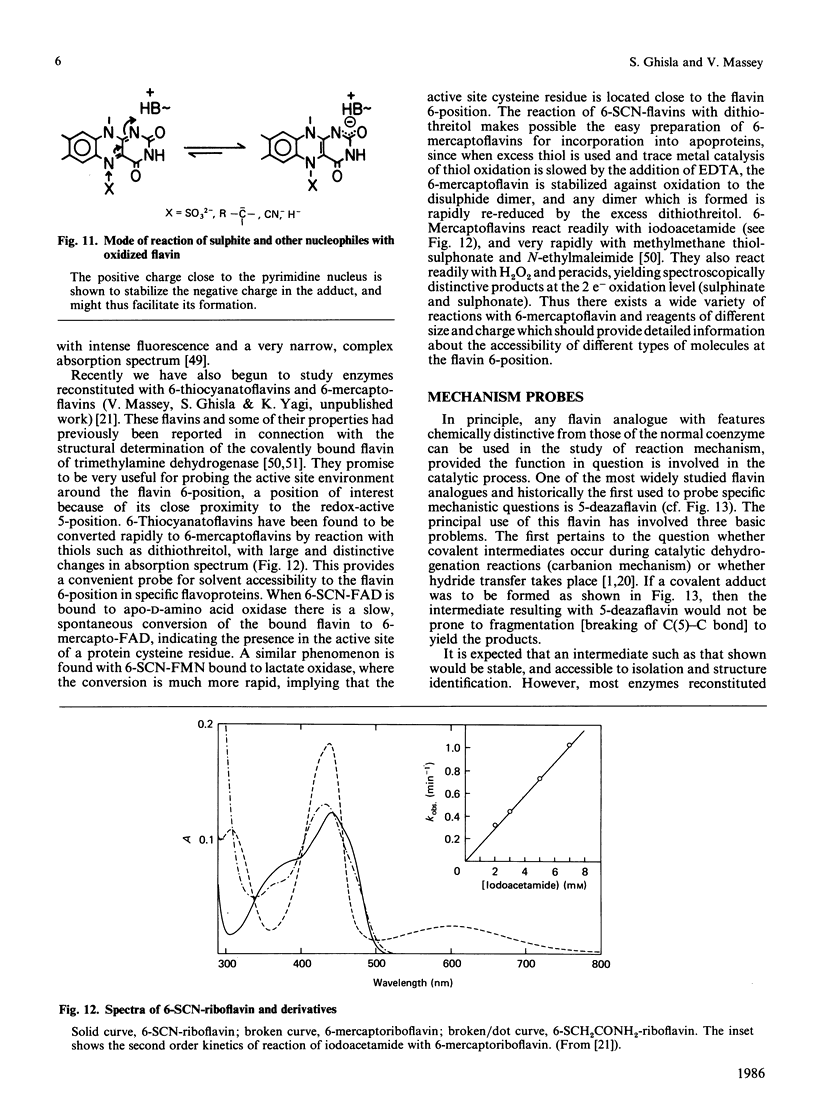
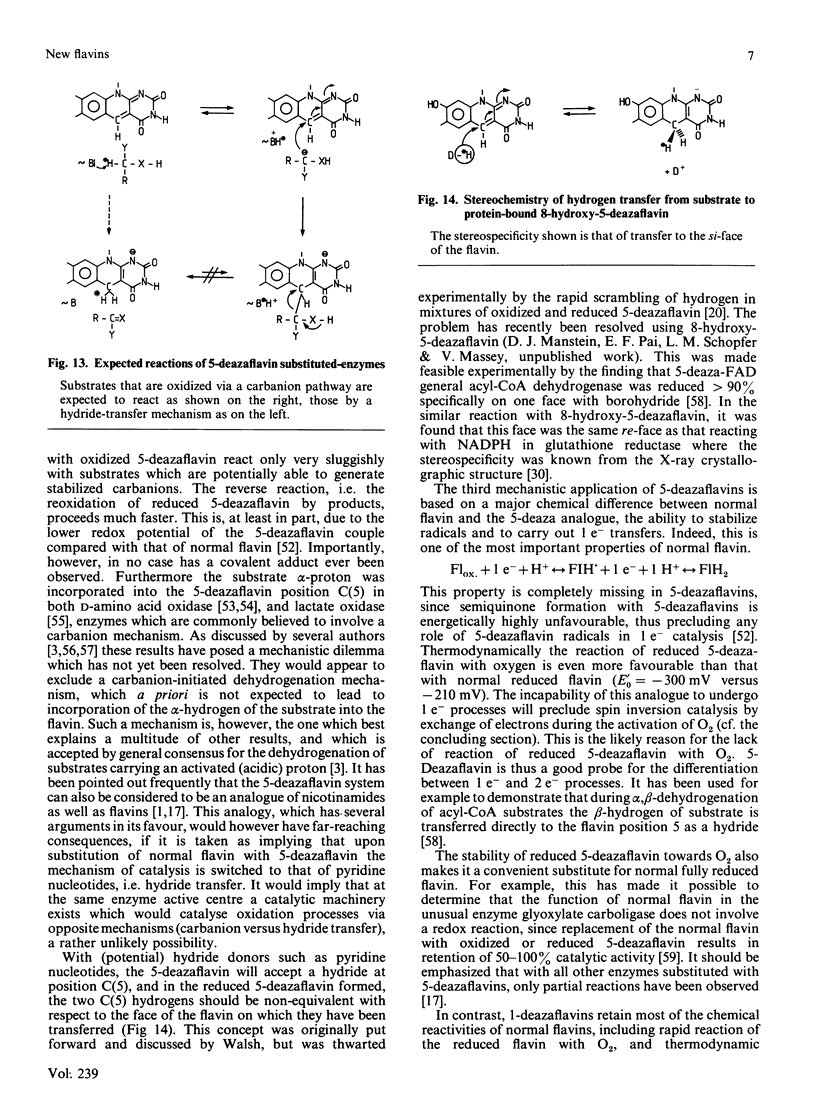
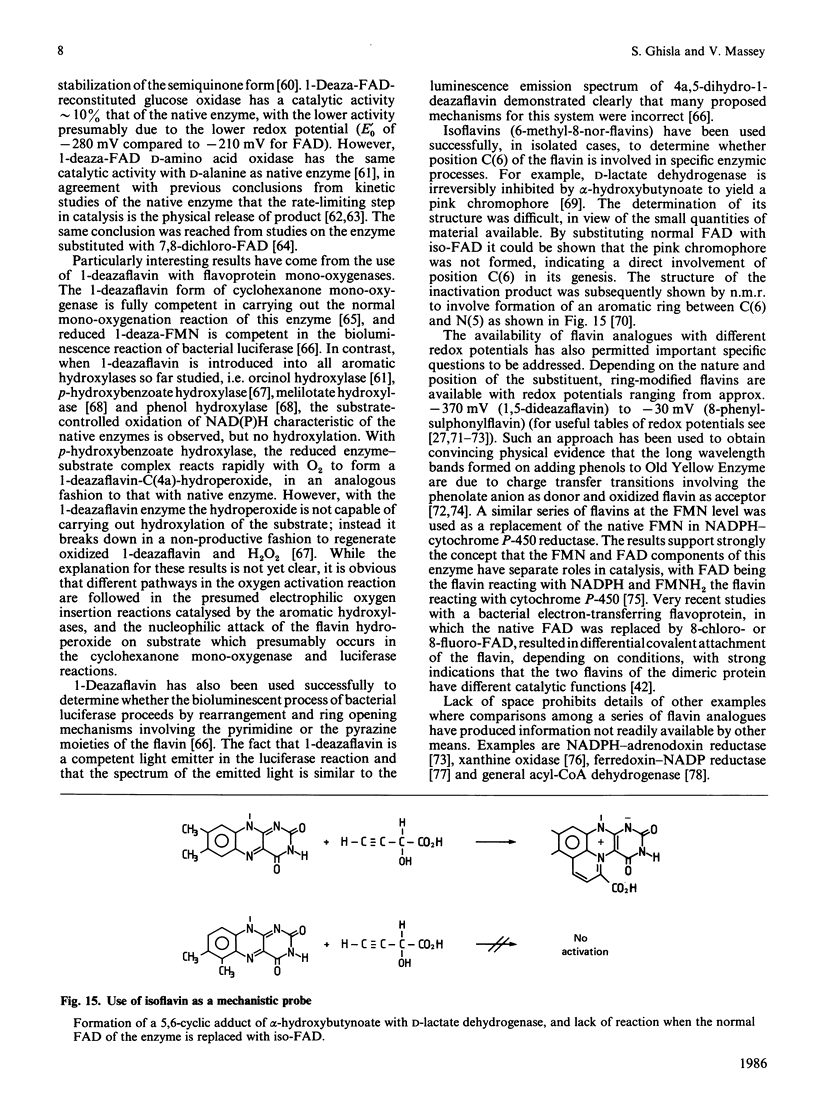
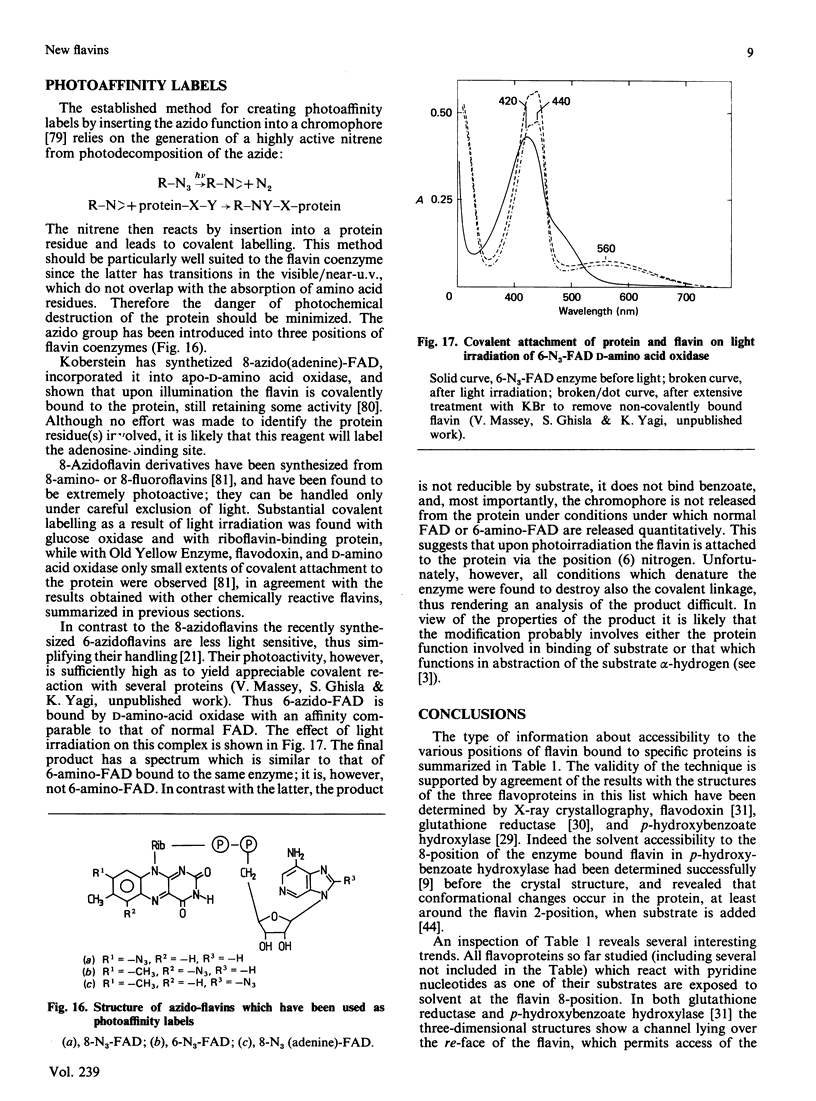


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovitz A. S., Massey V. Interaction of phenols with old yellow enzyme. Physical evidence for charge-transfer complexes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5327–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemann M., Claiborne A., Ghisla S., Massey V. 4-Thioflavins as active site probes of flavoproteins. Reactions with sulfite. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13355–13362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemann M., Claiborne A., Ghisla S., Massey V., Hemmerich P. Oxidation of 2-thioflavins by peroxides. Formation of flavin 2-S-oxides. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5440–5448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenhorn G. Nicotinamide-dependent one-electron and two-electron (flavin) oxidoreduction: thermodynamics, kinetics, and mechanism. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):67–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J. D., McCormick D. B. The interaction of flavins with egg white riboflavin-binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne A., Massey V., Fitzpatrick P. F., Schopfer L. M. 2-Thioflavins as active site probes of flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):174–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie T. H., Walsh C. T. Escherichia coli glyoxalate carboligase. Properties and reconstitution with 5-deazaFAD and 1,5-dihydrodeazaFADH2. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmer K., Schopfer L. M., Massey V. Reactions of 1-deaza-FAD-substituted phenol hydroxylase and melilotate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1532–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. D., Ingraham L. L. A potentiometric study of the flavin semiquinone equilibrium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jun;125(3):802–808. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. E., Barman B., Tollin G. On the importance of the N-5 position in flavin coenzymes. Properties of free and protein-bound 5-deaza analogs. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1133–1138. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg A., Müller F., Hemmerich P. Basicity, visible spectra, and electron spin resonance of flavosemiquinone anions. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Oct;2(3):286–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entsch B., Husain M., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Walsh C. Oxygen reactivity of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase containing 1-deaza-FAD. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1420–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Spencer R., Walsh C. Enzyme-catalyzed redox reactions with the flavin analogues 5-deazariboflavin, 5-deazariboflavin 5'-phosphte, and 5-deazariboflavin 5'-diphosphate, 5' leads to 5'-adenosine ester. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1054–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick P. F., Ghisla S., Massey V. 8-Azidoflavins as photoaffinity labels for flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8483–8491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick P. F., Massey V. The reaction of 8-mercaptoflavins and flavoproteins with sulfite. Evidence for the role of an active site arginine in D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9700–9705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Kenney W. C., Knappe W. R., McIntire W., Singer T. P. Chemical synthesis and some properties of 6-substituted flavins. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2537–2544. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Massey V., Choong Y. S. Covalent adducts of lactate oxidase. Photochemical formation and structure identification. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10662–10669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Massey V., Lhoste J. M., Mayhew S. G. Fluorescence and optical characteristics of reduced flavines and flavoproteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):589–597. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Massey V. Mechanism of inactivation of the flavoenzyme lactate oxidase by oxalate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Massey V., Yagi K. Preparation and some properties of 6-substituted flavins as active site probes for flavin enzymes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3282–3289. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Mayhew S. G. Identification and properties of 8-hydroxyflavin--adenine dinucleotide in electron-transferring flavoprotein from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):373–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Olson S. T., Massey V., Lhoste J. M. Structure of the flavin adduct formed in the suicide reaction of alpha-hydroxybutynoate with D-lactate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4733–4742. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Thorpe C., Massey V. Mechanistic studies with general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase: evidence for the transfer of the beta-hydrogen to the flavin N(5)-position as a hydride. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3154–3161. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerich P., Massey V. Flavin and 5-deazaflavin: a chemical evaluation of 'modified' flavoproteins with respect to the mechanisms of redox biocatalysis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 1;84(1):5–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Jorns M. S. Use of 5-deazaFAD to study hydrogen transfer in the D-amino acid oxidase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8728–8734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille R., Fee J. A., Massey V. Equilibrium properties of xanthine oxidase containing FAD analogs of varying oxidation-reduction potential. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8933–8940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Vereijken J. M., Weijer W. J., Beintema J. J., Wierenga R. K., Drenth J. Primary and tertiary structure studies of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Isolation and alignment of the CNBr peptides; interactions of the protein with flavin adenine dinucleotide. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):141–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Massey V. Reversible resolution of flavoproteins into apoproteins and fee flavins. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:429–437. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koberstein R. 8-Azidoacenine analogs of NAD+ and FAD. Synthesis and coenzyme properties with NAD+-dependent and FAD-dependent enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauth-Siegel R. L., Schirmer R. H., Ghisla S. FAD analogues as prosthetic groups of human glutathione reductase. Properties of the modified enzyme species and comparisons with the active site structure. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):335–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambooy J. P., Lambooy J. P. Syntheses and biological activities of 7-ethyl-8-chloro-10-(1'-D-ribityl) isoalloxazine and 7-chloro-8-ethyl-10(1'-D-ribityl) isoalloxazine, analogs of riboflavin. J Med Chem. 1973 Jul;16(7):765–770. doi: 10.1021/jm00265a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. R., Walsh C. Flavin analogs as mechanistic probes of adrenodoxin reductase-dependent electron transfer to the cholesterol side chain cleavage cytochrome P-450 of the adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4264–4277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V., GIBSON Q. H. ROLE OF SEMIQUINONES IN FLAVOPROTEIN CATALYSIS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:18–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORMICK D. B., CHASSY B. M., TSIBRIS J. C. COENZYME SPECIFICITY OF D-AMINO ACID OXIDASE FOR THE ADENYLATE MOIETY OF FAD. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 18;89:447–452. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Claiborne A., Biemann M., Ghisla S. 4-Thioflavins as active site probes of flavoproteins. General properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9667–9678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Ganther H. On the interpretation of the absorption spectra of flavoproteins with special reference to D-amino acid oxidase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1161–1173. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Ghisla S., Moore E. G. 8-Mercaptoflavins as active site probes of flavoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9640–9650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Hemmerich P. Active-site probes of flavoproteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):246–257. doi: 10.1042/bst0080246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Müller F., Feldberg R., Schuman M., Sullivan P. A., Howell L. G., Mayhew S. G., Matthews R. G., Foust G. P. The reactivity of flavoproteins with sulfite. Possible relevance to the problem of oxygen reactivity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):3999–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Palmer G. On the existence of spectrally distinct classes of flavoprotein semiquinones. A new method for the quantitative production of flavoprotein semiquinones. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3181–3189. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Stankovich M., Hemmerich P. Light-mediated reduction of flavoproteins with flavins as catalysts. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):1–8. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Strickland S., Mayhew S. G., Howell L. G., Engel P. C., Matthews R. G., Schuman M., Sullivan P. A. The production of superoxide anion radicals in the reaction of reduced flavins and flavoproteins with molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 10;36(6):891–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G., Foust G. P., Massey V. Oxidation-reduction properties of flavodoxin from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):803–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G. Studies on flavin binding in flavodoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 12;235(2):289–302. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G., Whitfield C. D., Ghisla S., Schuman-Jörns M. Identification and properties of new flavins in electron-transferring flavoprotein from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii and pig-liver glycolate oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):579–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, Lambeth J. D., Edmondson D. E., McCormick D. B. Formation and mode of action of flavoproteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:281–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzer J. P., Thorpe C. Stabilization of the red semiquinone form of pig kidney general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by acyl coenzyme A derivatives. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4965–4970. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. G., Cardemil E., Massey V. Production of a covalent flavin linkage in lipoamide dehydrogenase. Reaction with 8-Cl-FAD. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6413–6422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. G., Ghisla S., Massey V. Properties of flavins where the 8-methyl group is replaced by mercapto- residues. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8173–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Mayhew S. G., Massey V. On the effect of temperature on the absorption spectra of free and protein-bound flavines. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4654–4662. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F. On the interaction of flavins with phosphine-derivatives. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Sep;27(9):1023–1026. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Massey V., Ghisla S., Whitfield C. D. Suicide inactivation of the flavoenzyme D-lactate dehydrogenase by alpha-hydroxybutynoate. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4724–4732. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. J., Voet J. G., Bright H. J. Mechanistic features of the D-amino acid oxidase reaction studied by double stopped flow spectrophotometry. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4464–4473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Chassy B. M., McCormick D. B. Coenzymatic activities of 2-anilino and 2-morpholino derivatives of FMN with yeast NADPH diaphorase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 5;118(2):429–431. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryerson C. C., Ballou D. P., Walsh C. Mechanistic studies on cyclohexanone oxygenase. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2644–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer L. M., Massey V., Claiborne A. Active site probes of flavoproteins. Determination of the solvent accessibility of the flavin position 8 for a series of flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7329–7337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E., Schirmer R. H., Pai E. F. FAD-binding site of glutathione reductase. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):287–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöllnhammer G., Hemmerich P. Nucleophilic addition at the photoexcited flavin cation: synthesis and properties of 6- and 9-hydroxy-flavocoenzyme chromophores. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):561–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R., Fisher J., Walsh C. One-and two-electron redox chemistry of 1-carba-1-deazariboflavin. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3586–3594. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R., Fisher J., Walsh C. Preparation, characterization, and chemical properties of the flavin coenzyme analogues 5-deazariboflavin, 5-deazariboflavin 5'-phosphate, and 5-deazariboflavin 5'-diphosphate, 5'leads to5'-adenosine ester. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1043–1053. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R., Fisher J., Walsh C. Reconstitution of flavin enzymes with 1-carba-1 -deazaflavin coenzyme analogues. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3594–3602. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., McIntire W., Kenney W. C. Structure of the covalently bound coenzyme of trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Evidence for a 6-substituted flavin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2818–2824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. C., Massey V. Potentiometric studies of native and flavin-substituted Old Yellow Enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13639–13647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe C., Massey V. Flavin analogue studies of pig kidney general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2972–2978. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsibris J. C., McCormick D. B., Wright L. D. Studies on the binding and function of flavin phosphates with flavin mononucleotide-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1138–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargo D., Pokora A., Wang S. W., Jorns M. S. Formation of epoxide intermediates in the reaction of enzyme-bound 5-deazaflavin with peroxides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6027–6033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermilion J. L., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Coon M. J. Separate roles for FMN and FAD in catalysis by liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):266–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. Chemical approaches to the study of enzymes catalyzing redox transformations. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:881–931. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Fisher J., Spencer R., Graham D. W., Ashton W. T., Brown J. E., Brown R. D., Rogers E. F. Chemical and enzymatic properties of riboflavin analogues. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1942–1951. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Drenth J., Schulz G. E. Comparison of the three-dimensional protein and nucleotide structure of the FAD-binding domain of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase with the FAD- as well as NADPH-binding domains of glutathione reductase. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):725–739. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti G., Beretta C., Malandra D. Properties of rabbit liver glutathione reductase reconstituted with FAD analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):831–837. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90652-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti G., Massey V., Curti B. FAD analogues as mechanistic and 'binding-domain' probes of spinach ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):201–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



