Abstract
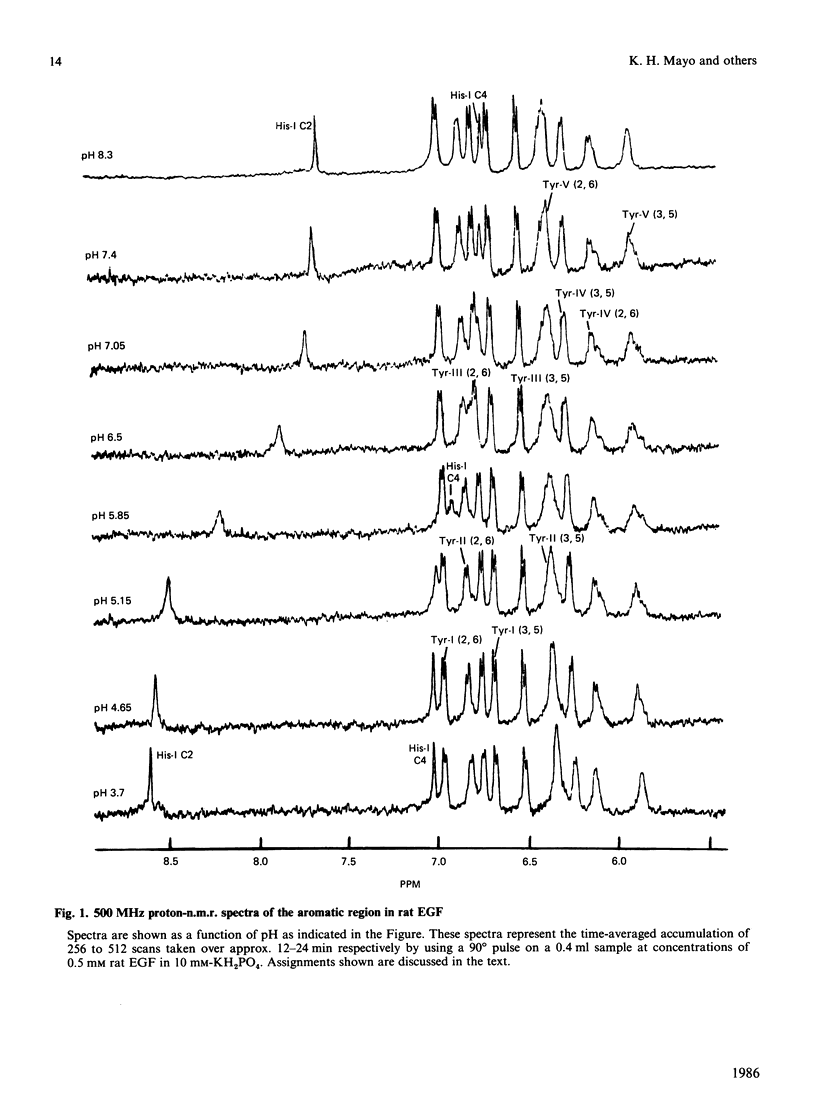
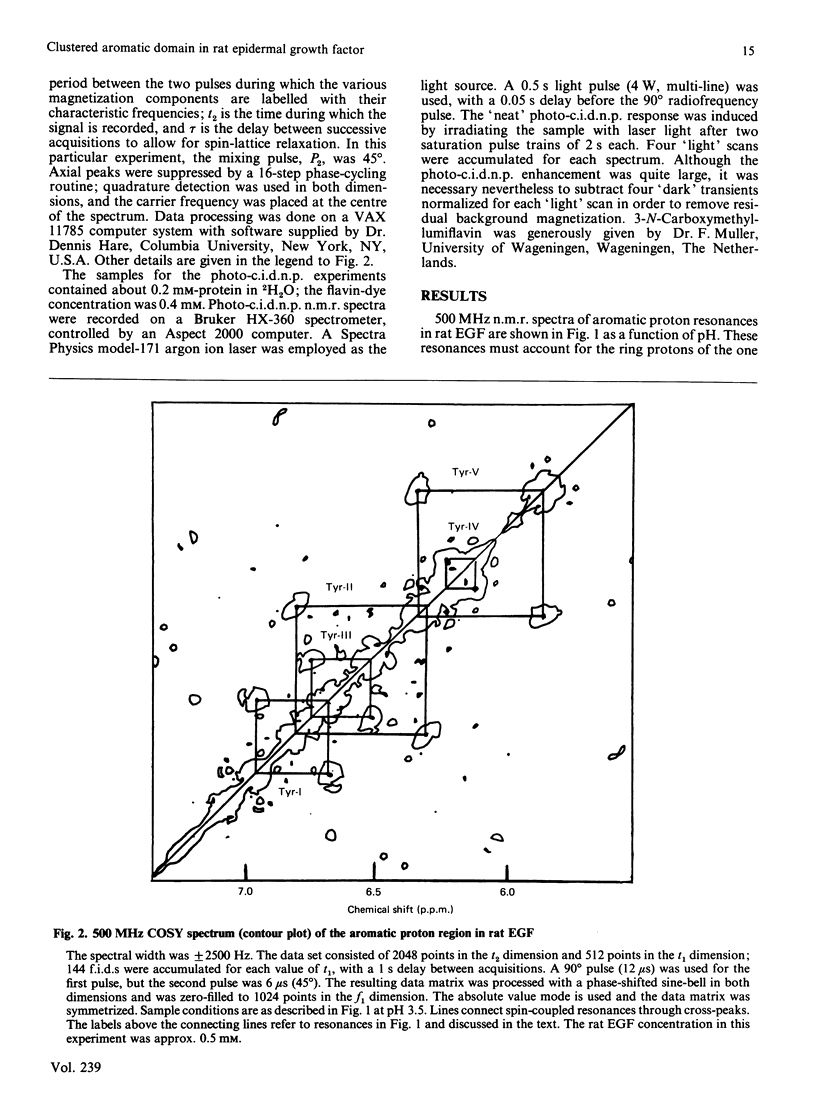
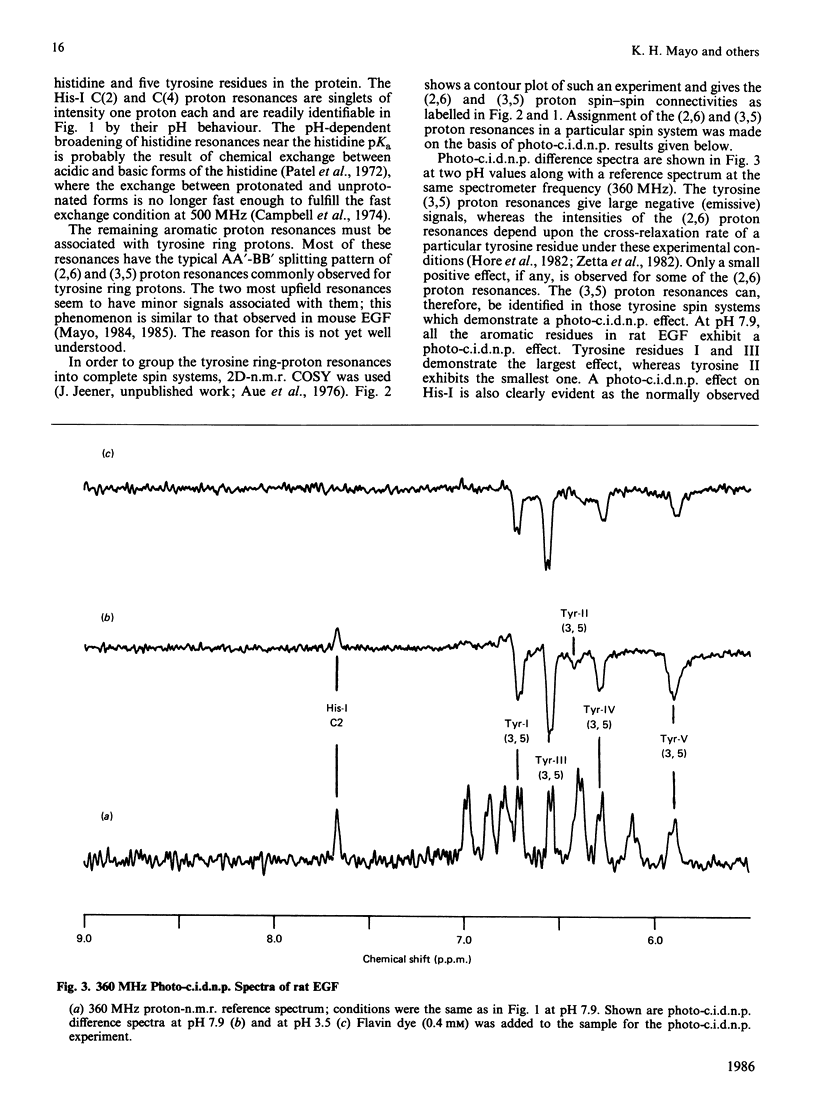
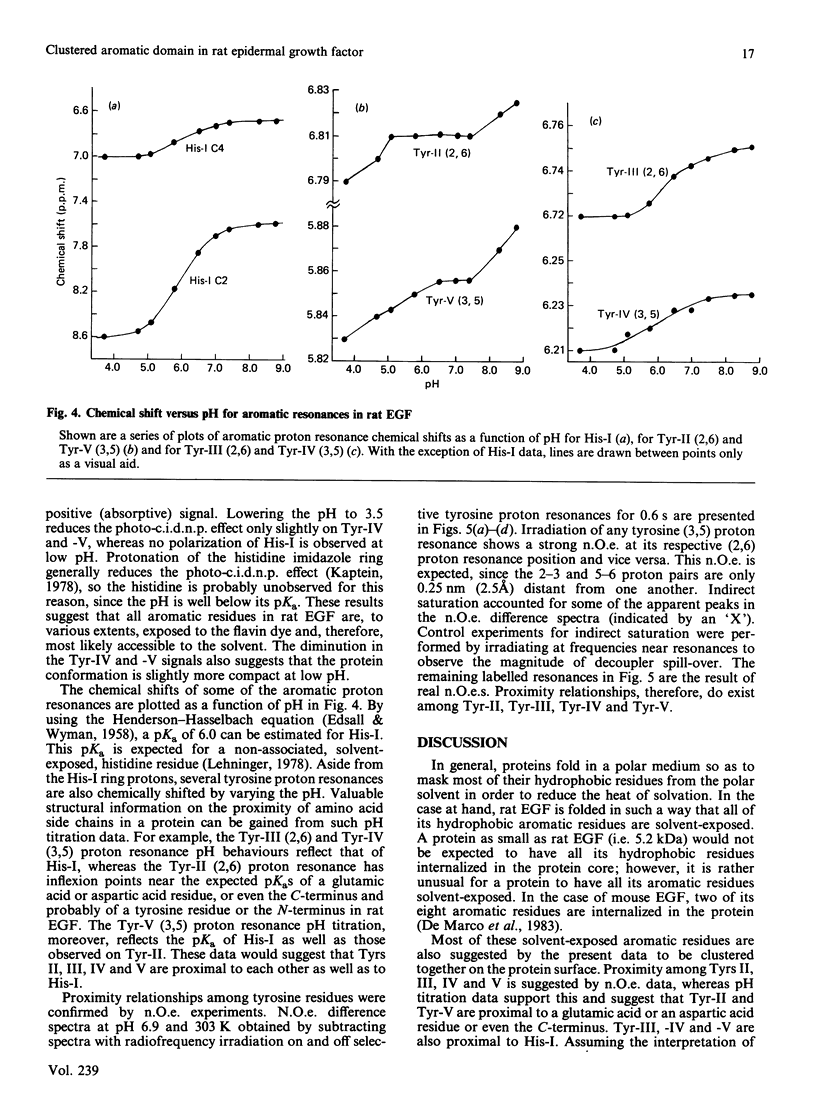
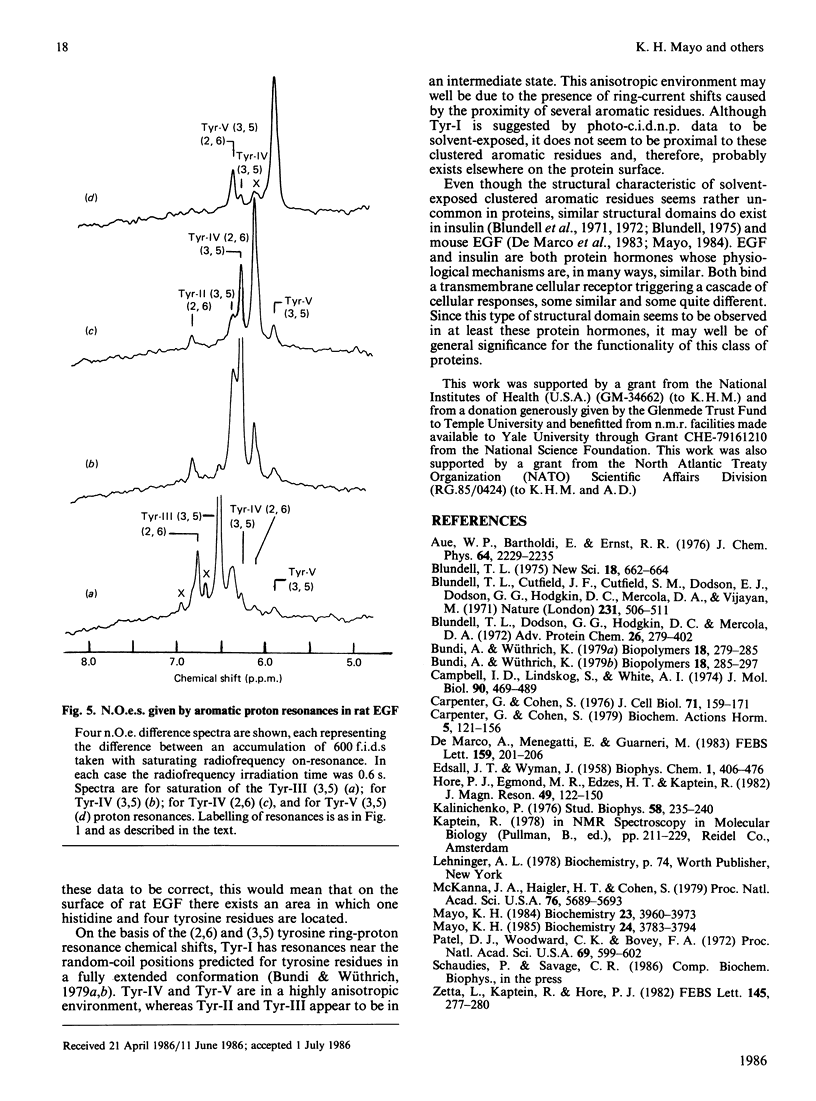
Aromatic amino acid residues in epidermal growth factor (EGF) isolated from the rat have been investigated by proton n.m.r. and nuclear Overhauser methods at 500 MHz and by photochemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization (photo-c.i.d.n.p.) experiments at 360 MHz. Rat EGF contains six aromatic residues, i.e. one histidine and five tyrosine residues. pH titration data allow identification of the histidine imidazole ring protons, whereas two-dimensional n.m.r. correlated spectroscopy establishes connectivities between tyrosine ring (2,6) and (3,5) proton resonances. Photo-c.i.d.n.p. data give evidence for solvent exposure of the one histidine and the five tyrosine residues in rat EGF. Nuclear Overhauser experiments and pH titration data suggest proximity relationships among four of the tyrosine residues and the histidine residue. These data indicate the presence of a clustered, aromatic, structural domain on the protein surface and may provide a clue to the understanding of the functional structure of EGF.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C., Mercola D. A., Vijayan M. Atomic positions in rhombohedral 2-zinc insulin crystals. Nature. 1971 Jun 25;231(5304):506–511. doi: 10.1038/231506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. D., Lindskog S., White A. I. A study of the histidine residues of human carbonic anhydrase B using 270 MHz proton magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 15;90(3):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H. Epidermal growth factor from the mouse. Physical evidence for a tiered beta-sheet domain: two-dimensional NMR correlated spectroscopy and nuclear Overhauser experiments on backbone amide protons. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3783–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H. Epidermal growth factor from the mouse. Structural characterization by proton nuclear magnetic resonance and nuclear overhauser experiments at 500 MHz. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3960–3973. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Woodward C. K., Bovey F. A. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of ribonuclease A in H 2 O. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):599–602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


