Abstract
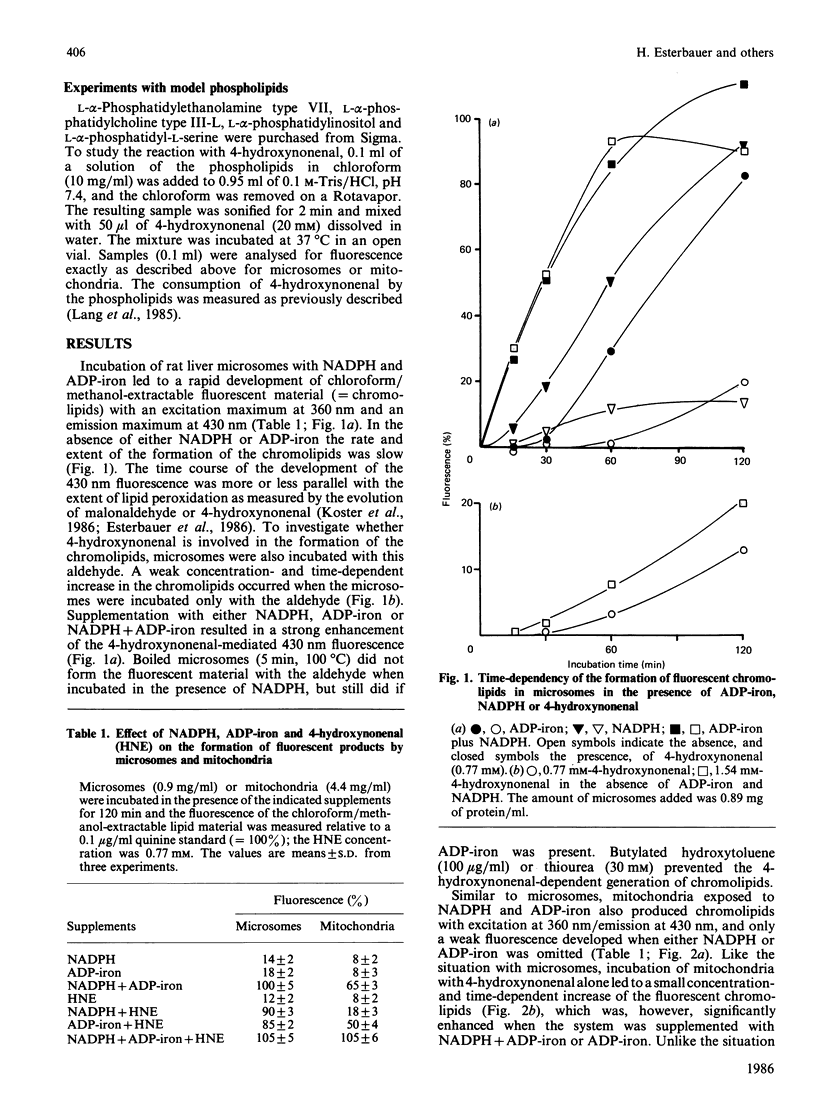
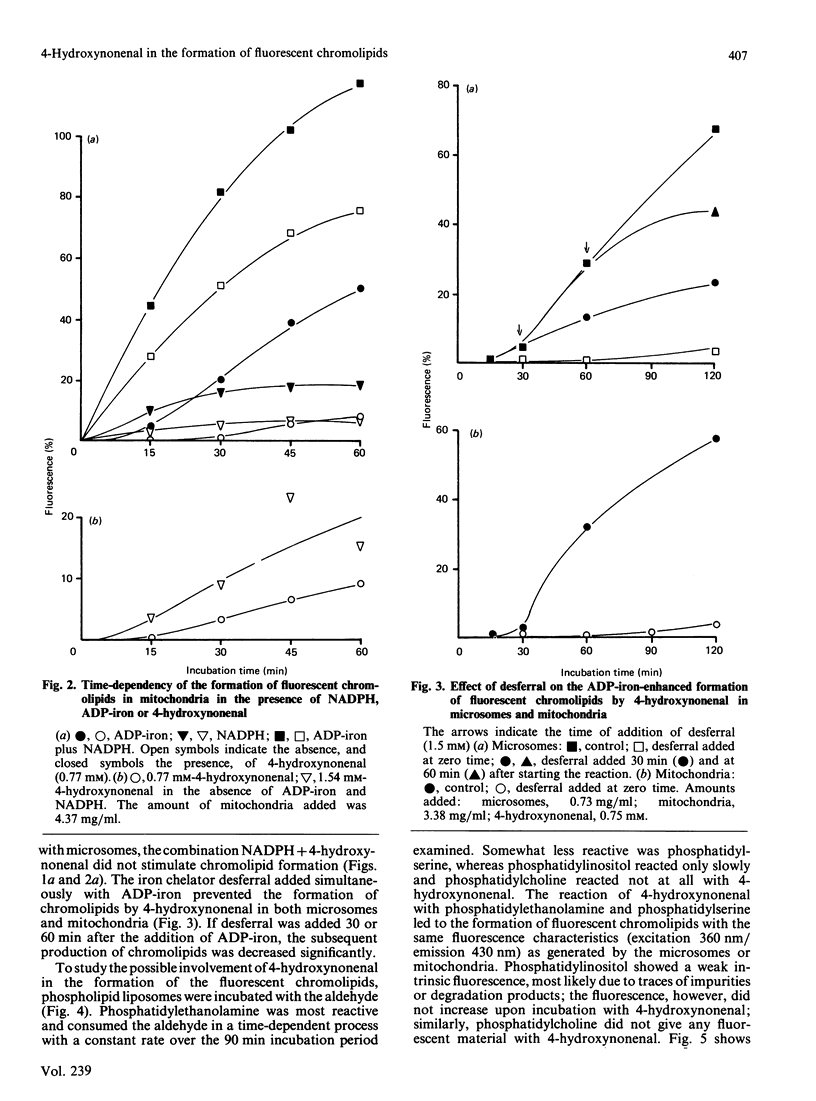
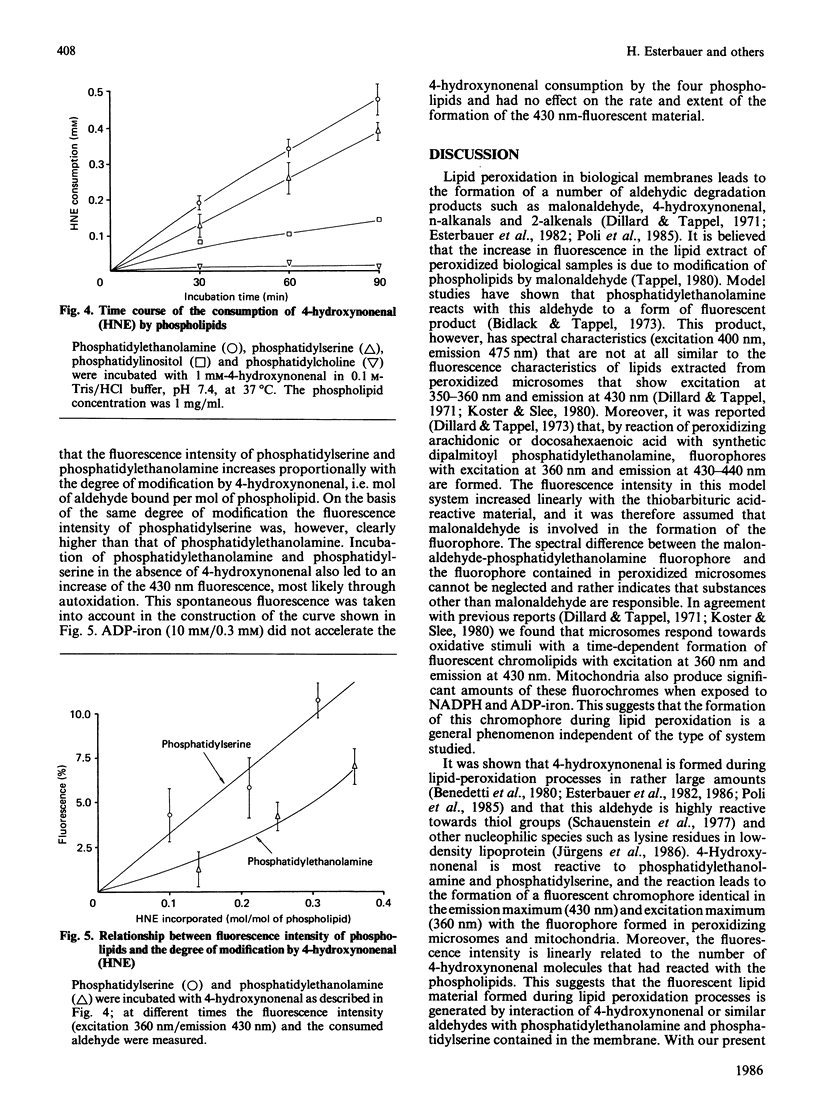
The effects of the lipid-peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal on the formation of fluorescent chromolipids from microsomes, mitochondria and phospholipids were studied. Incubation of freshly prepared rat liver microsomes or mitochondria with 4-hydroxynonenal results in a slow formation of a fluorophore with an excitation maximum at 360 nm and an emission maximum at 430 nm. The rate and extent of the development of the 430 nm fluorescence can be significantly enhanced by ADP-iron (Fe3+). With microsomes, yet not with mitochondria. NADPH has a catalytic effect similar to that of ADP-iron. Fluorescent chromolipids with maximum excitation and emission at 360/430 nm are also formed during the NADPH-linked ADP-iron-stimulated lipid peroxidation. Phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine react with 4-hydroxynonenal revealing a fluorophore with the same spectral characteristics as that obtained in the microsomal and mitochondrial system. The findings suggest that the fluorescent chromolipids formed by lipid peroxidation are not derived from malonaldehyde, but are formed from 4-hydroxynonenal or similar reactive aldehydes via a NADPH and/or ADP-iron-catalysed reaction with phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine contained in the membrane.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedetti A., Barbieri L., Ferrali M., Casini A. F., Fulceri R., Comporti M. Inhibition of protein synthesis by carbonyl compounds (4-hydroxyalkenals) originating from the peroxidation of liver microsomal lipids. Chem Biol Interact. 1981 Jun;35(3):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(81)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti A., Comporti M., Esterbauer H. Identification of 4-hydroxynonenal as a cytotoxic product originating from the peroxidation of liver microsomal lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 7;620(2):281–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlack W. R., Tappel A. L. Fluorescent products of phospholipids during lipid peroxidation. Lipids. 1973 Apr;8(4):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF02544636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillard C. J., Tappel A. L. Fluorescent products from reaction of peroxidizing polyunsaturated fatty acids with phosphatidyl ethanolamine and phenylalanine. Lipids. 1973 Apr;8(4):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02544632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillard C. J., Tappel A. L. Fluorescent products of lipid peroxidation of mitochondria and microsomes. Lipids. 1971 Oct;6(10):715–721. doi: 10.1007/BF02531296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Benedetti A., Lang J., Fulceri R., Fauler G., Comporti M. Studies on the mechanism of formation of 4-hydroxynonenal during microsomal lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 21;876(1):154–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Cheeseman K. H., Dianzani M. U., Poli G., Slater T. F. Separation and characterization of the aldehydic products of lipid peroxidation stimulated by ADP-Fe2+ in rat liver microsomes. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj2080129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Modification of human low-density lipoprotein by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster J. F., Slee R. G. Lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 5;620(3):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster J. F., Slee R. G., Montfoort A., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Comparison of the inactivation of microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase by in situ lipid peroxidation-derived 4-hydroxynonenal and exogenous 4-hydroxynonenal. Free Radic Res Commun. 1986;1(4):273–287. doi: 10.3109/10715768609051637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster J. F., Slee R. G., Van Berkel T. J. On the lipid peroxidation of rat liver hepatocytes, the formation of fluorescent chromolipids and high molecular weight protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 15;710(2):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J., Celotto C., Esterbauer H. Quantitative determination of the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90525-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Dianzani M. U., Cheeseman K. H., Slater T. F., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Separation and characterization of the aldehydic products of lipid peroxidation stimulated by carbon tetrachloride or ADP-iron in isolated rat hepatocytes and rat liver microsomal suspensions. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):629–638. doi: 10.1042/bj2270629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappel A. L. Protection against free radical lipid peroxidation reactions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;97:111–131. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7793-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida M., Miura T., Mizutani K., Aibara K. Fluorescent substances in mouse and human sera as a parameter of in vivo lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 25;834(2):196–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



