Abstract
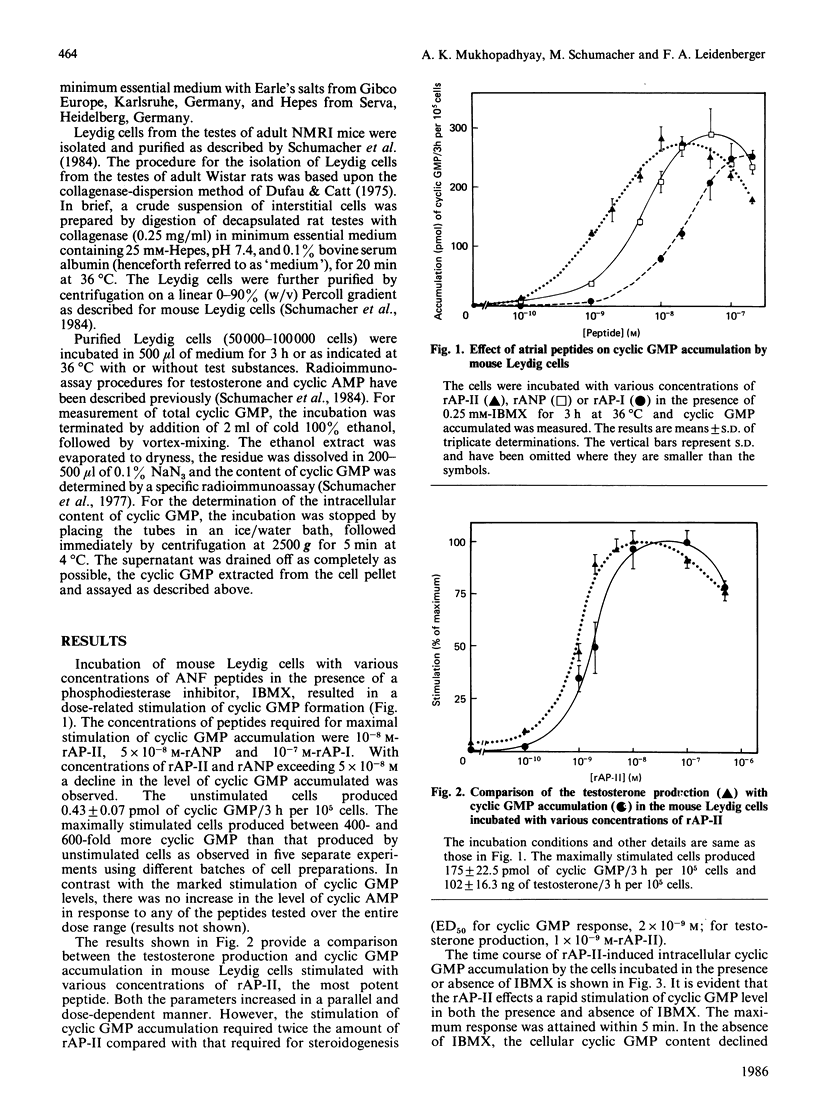
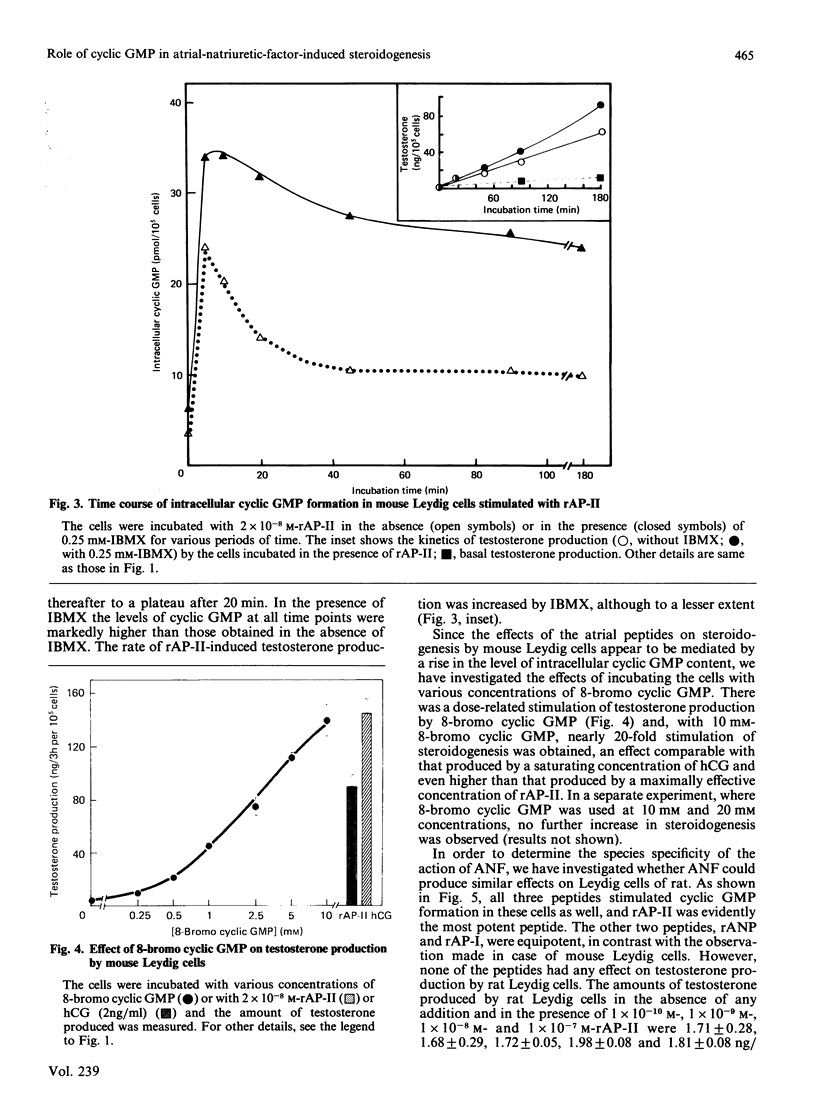
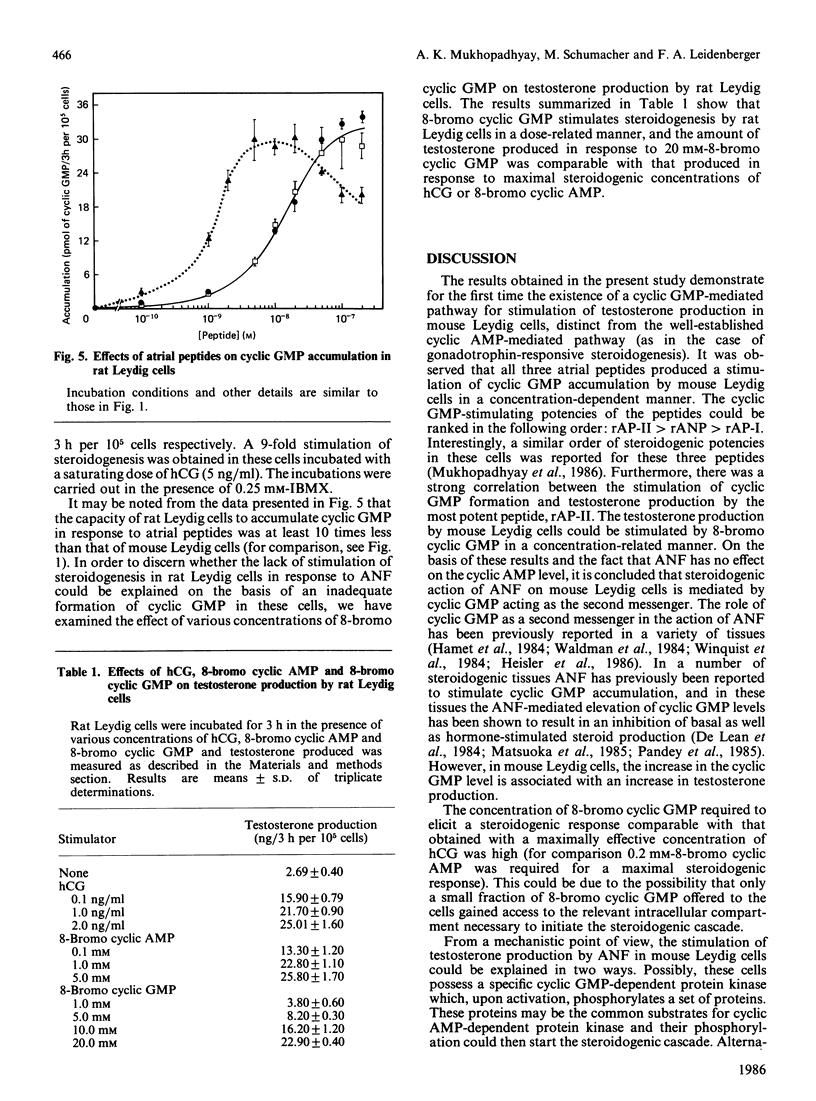
The effects of different atrial natriuretic peptides on cyclic GMP formation and steroidogenesis have been studied in Percoll-purified mouse Leydig cells. Rat atrial peptides rANP (rat atrial natriuretic peptide), rAP-I (rat atriopeptin I) and rAP-II (rat atriopeptin II), in the presence of a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, stimulated cyclic GMP formation in a concentration-dependent manner. In the presence of saturating concentrations of the peptides, a 400-600 fold stimulation of cyclic GMP accumulation was observed. Among the peptides, rAP-II appeared to be the most potent. ED50 values (concentration causing half-maximal effect) for rAP-II, rANP and rAP-I were 1 X 10(-9) M, 2 X 10(-9) M and 2 X 10(-8) M respectively. A parallel stimulation of cyclic GMP formation and testosterone production by the cells was observed after incubation of the cells with various concentrations of rAP-II. In the presence of a saturating concentration of rAP-II (2 X 10(-8) M), maximum stimulation of intracellular cyclic GMP content was obtained within 5 min of incubation. Testosterone production by mouse Leydig cells could be stimulated by 8-bromo cyclic GMP in a concentration-related manner. At a 10 mM concentration of the cyclic nucleotide, steroidogenesis was stimulated to a similar extent as that obtained with a saturating concentration of human chorionic gonadotrophin (5 ng/ml). On the basis of these results we conclude that cyclic GMP acts as a second messenger in atrial-peptide-stimulated steroidogenesis in mouse Leydig cells. The steroidogenic effect of atrial peptides appears to be species-specific, since none of these peptides stimulated testosterone production by purified Leydig cells of rats, though in these cells a 40-60-fold stimulation of cyclic GMP formation in response to each of the three peptides was observed. However, 8-bromo cyclic GMP could stimulate testosterone production in rat Leydig cells. Therefore we conclude that the lack of steroidogenic response in rat Leydig cells to atrial-natriuretic-factor-stimulation results from an insufficient formation of cyclic GMP in these cells. This species difference would appear to result from a lower guanylate cyclase activity in rat Leydig cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atarashi K., Mulrow P. J., Franco-Saenz R., Snajdar R., Rapp J. Inhibition of aldosterone production by an atrial extract. Science. 1984 Jun 1;224(4652):992–994. doi: 10.1126/science.6326267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bex F., Corbin A. Atrial natriuretic factor stimulates testosterone production by mouse interstitial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 10;115(1):125–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Genest J. The heart and the atrial natriuretic factor. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):107–127. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier L., Schiffrin E., Thibault G., Garcia R. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits the stimulation of aldosterone secretion by angiotensin II, ACTH and potassium in vitro and angiotensin II-induced steroidogenesis in vivo. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):2026–2028. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-2026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Léan A., Racz K., Gutkowska J., Nguyen T. T., Cantin M., Genest J. Specific receptor-mediated inhibition by synthetic atrial natriuretic factor of hormone-stimulated steroidogenesis in cultured bovine adrenal cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1636–1638. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Catt K. J. Gonadotropic stimulation of interstitial cell functions of the rat testis in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:252–271. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Horner K. A., Hayashi K., Tsuruhara T., Conn P. M., Catt K. J. Actions of choleragen and gonadotropin in isolated Leydig cells. Functional compartmentalization of the hormone-activated cyclic AMP response. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3721–3729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Tremblay J., Pang S. C., Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of native and synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic GMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisler S., Simard J., Assayag E., Mehri Y., Labrie F. Atrial natriuretic factor does not affect basal, forskolin- and CRF-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity, cAMP formation or ACTH secretion, but does stimulate cGMP synthesis in anterior pituitary. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Feb;44(2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. G., Sullivan M. H., Dix C. J., Aldred L. F., Cooke B. A. Stimulation and inhibition by LHRH analogues of cultured rat Leydig cell function and lack of effect on mouse Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Jun;27(1):31–44. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Baird A. Inhibition of aldosterone production in the adrenal glomerulosa by atrial natriuretic factor. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):756–757. doi: 10.1038/312756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka H., Ishii M., Sugimoto T., Hirata Y., Sugimoto T., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Inhibition of aldosterone production by alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide is associated with an increase in cGMP production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):1052–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay A. K., Bohnet H. G., Leidenberger F. A. Testosterone production by mouse Leydig cells is stimulated in vitro by atrial natriuretic factor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 23;202(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80659-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey K. N., Kovacs W. J., Inagami T. The inhibition of progesterone secretion and the regulation of cyclic nucleotides by atrial natriuretic factor in gonadotropin responsive murine Leydig tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):800–806. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90975-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Schwarz M., Brändle W. Desensitization of the cAMP system in mouse Leydig cells by hCG, cholera toxin, dibutyryl cAMP and cAMP: localization of the 'lesion' to the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein-adenylate cyclase complex. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Jan;34(1):67–80. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Schäfer G., Lichtenberg V., Hilz H. Maximal steroidogenic capacity of mouse leydig cells. Kinetic analysis and dependence on protein kinase activation and cAMP accumulation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Seidel I., Strätling W. H. Elevated cyclic GMP concentrations during estrogen induced differentiation of the chick oviduct. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Murad F., Rapoport R. M. Atrial natriuretic factor elicits an endothelium-independent relaxation and activates particulate guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7661–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


