Abstract
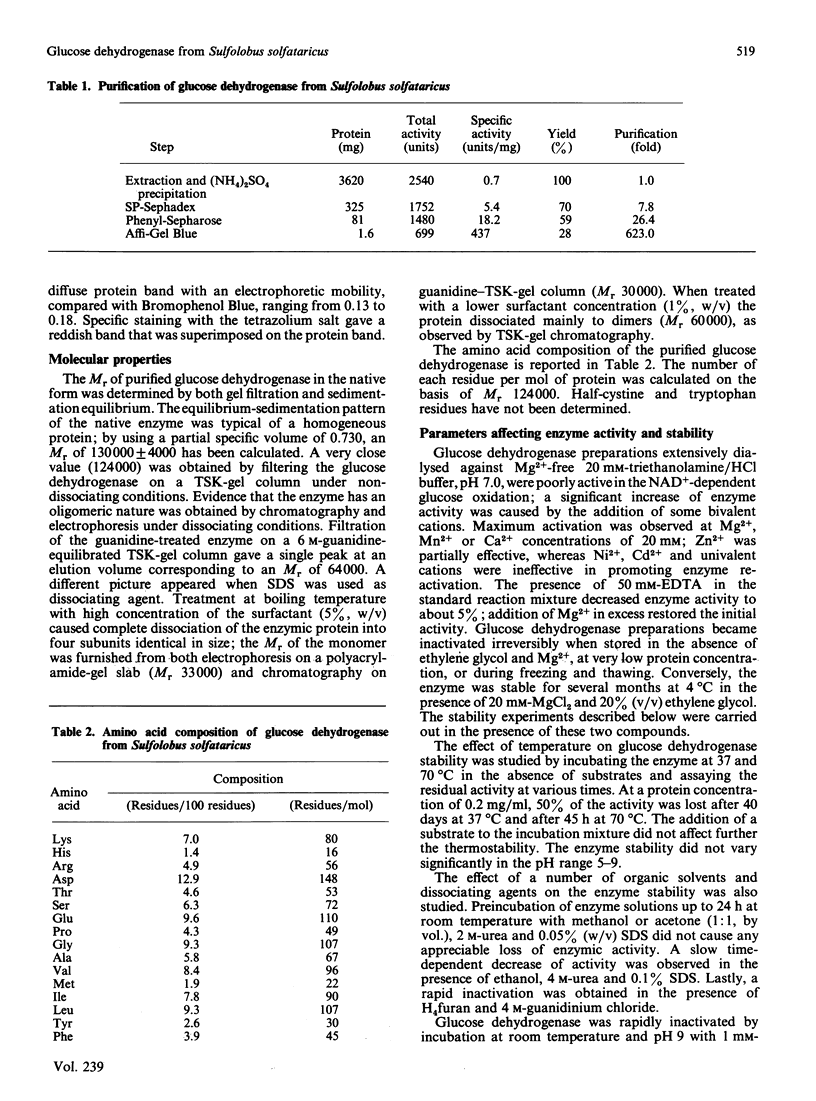
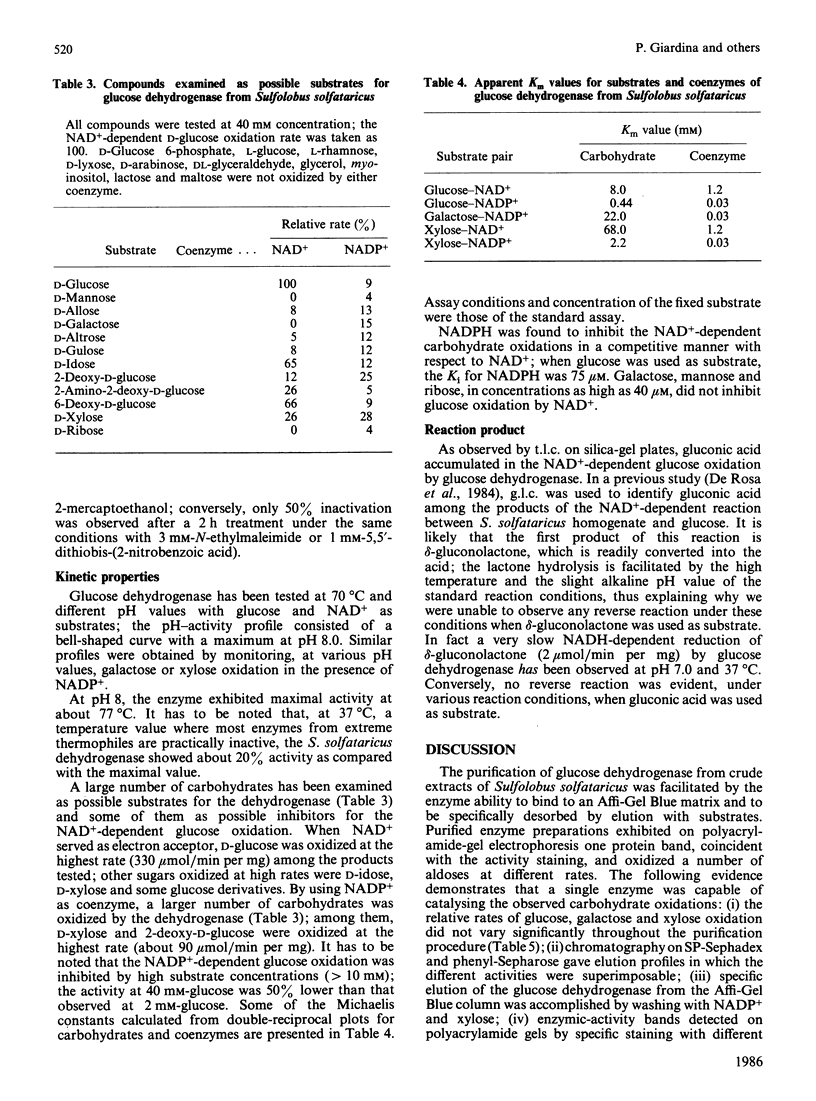
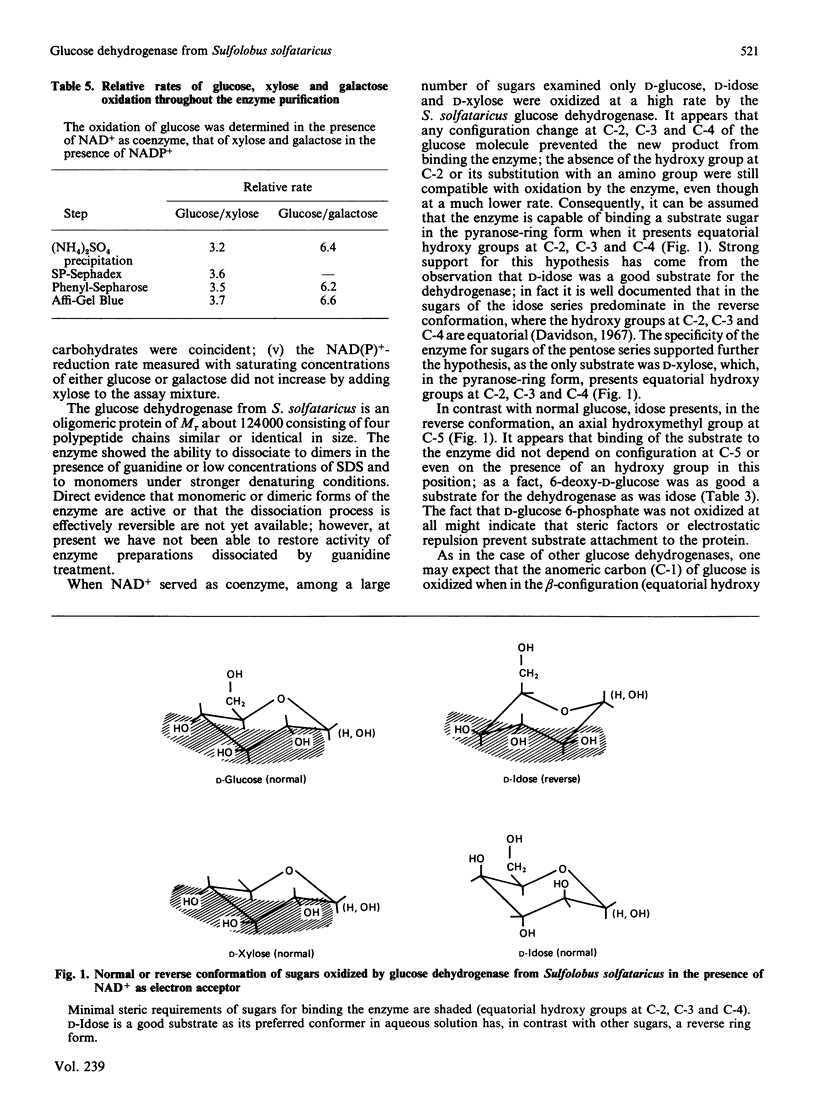
Glucose dehydrogenase has been purified to homogeneity from cell extracts of the extreme thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. The enzyme utilizes both NAD+ and NADP+ as coenzyme and catalyses the oxidation of several monosaccharides to the corresponding glyconic acid. Substrate specificity and oxidation rate depend on the coenzyme present; when NAD+ is used, the enzyme binds and oxidizes specifically sugars presenting equatorial orientation of hydroxy groups at C-2, C-3 and C-4. The Mr of the native enzyme is 124,000 and decreases to about 60,000 in the presence of 6 M-guanidinium chloride and to about 30,000 in the presence of 5% (w/v) SDS. The enzyme shows maximal activity at pH 9, 77 degrees C and 20 mM-Mg2+, -Mn2+ or -Ca2+ and is fairly stable in the presence of chaotropic agents and water-miscible organic solvents such as methanol or acetone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avigad G., Alroy Y., Englard S. Purification and properties of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked aldohexose dehydrogeanse from Gluconobacter cerinus. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1936–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACH J. A., SADOFF H. L. Aerobic sporulating bacteria. I. Glucose dehydrogenase of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:699–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.699-707.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. P., Carper W. R., Thompson R. E. Bovine liver glucose dehydrogenase: isolation and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Nicolaus B., Giardina P., Poerio E., Buonocore V. Glucose metabolism in the extreme thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):407–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2240407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Ramaley R., Freese E. Location and properties of glucose dehydrogenase in sporulating cells and spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):282–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.282-293.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein L. I. The metabolism of carbohydrates by extremely halophilic bacteria: glucose metabolism via a modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1085–1091. doi: 10.1139/m74-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly H. E., Pfleiderer G. D-glucose dehydrogenase from Bacillus megaterium M 1286: purification, properties and structure. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Oct;356(10):1613–1623. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. P., Spencer K. A rapid kinetic assay for glucose using glucose dehydrogenase. Ann Clin Biochem. 1979 Mar;16(2):100–105. doi: 10.1177/000456327901600120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulich W. M., Baalen C. Purification and characterization of glucose dehydrogenase from a heterotrophically grown blue-green alga. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):393–397. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram P. V., Blumenberg B., Hinsch W. Routine glucose determination in serum by use of an immobilized glucose dehydrogenase nylon-tube reactor. Clin Chem. 1979 Aug;25(8):1436–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Uratani B., Ramaley R. F., Freese E. Isolation of a developmental gene of Bacillus subtilis and its expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):785–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):156–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


