Abstract
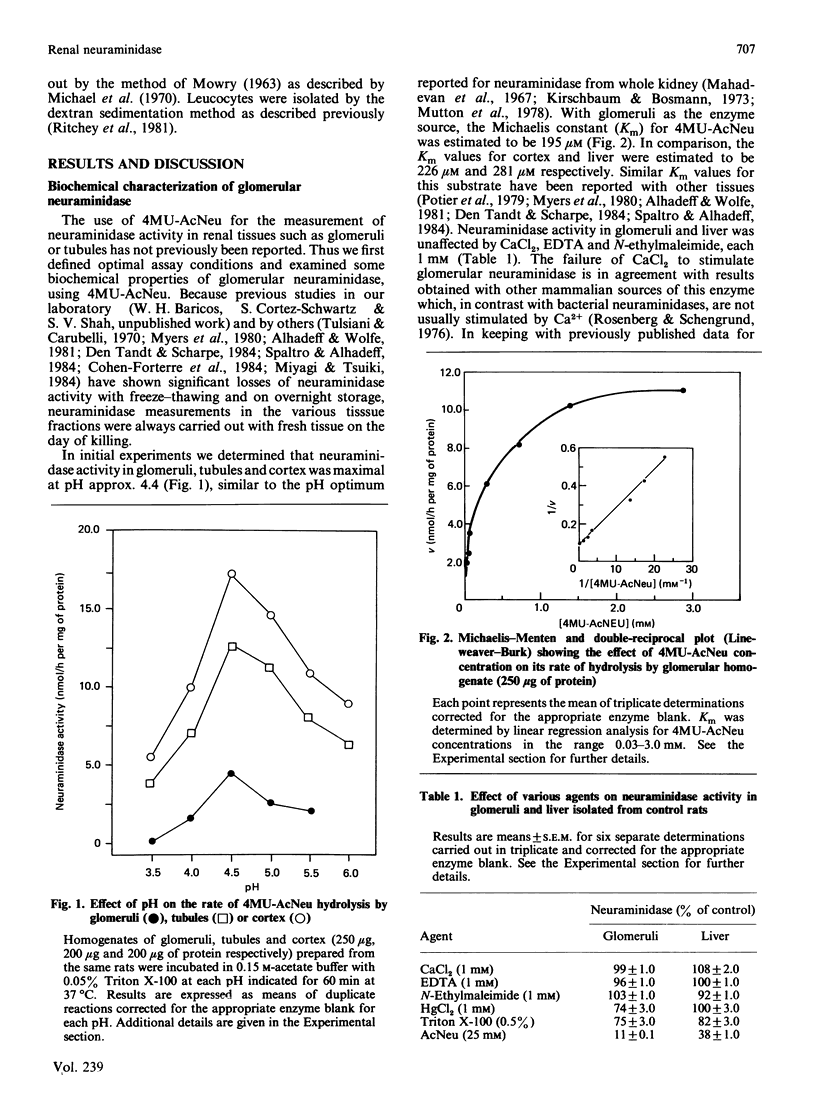
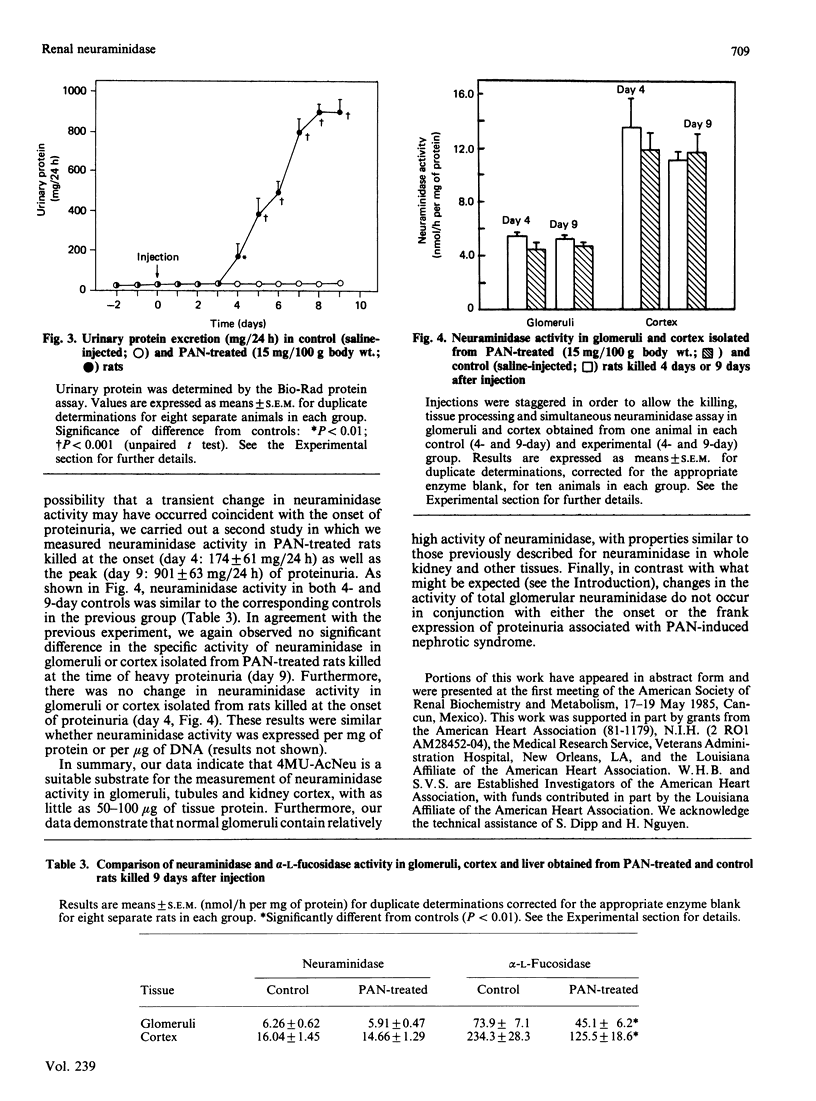
Several lines of evidence suggest that increased neuraminidase activity may be responsible for the loss of glomerular N-acetylneuraminic acid (AcNeu) observed in various glomerular diseases. However, virtually no information is available on the activity of neuraminidase in glomeruli or the potential role of this enzyme in glomerular pathophysiology. Utilizing 2'-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid (4MU-AcNeu) as substrate, we defined optimal assay conditions and characterized neuraminidase activity in glomeruli and, for comparison, in other renal fractions and liver. Neuraminidase activity in glomeruli, cortex and tubules was maximal at pH 4.4. The Km for 4MU-AcNeu was estimated to be 195 microM for glomeruli and 226 microM for cortex. Glomerular neuraminidase was inhibited by AcNeu (90% at 25 mM) and high concentrations of Triton X-100 (26% at 0.5%), but unaffected by CaCl2, EDTA or N-ethylmaleimide (each 1 mM). Neuraminidase activity (nmol/h per mg of protein; mean +/- S.E.M.) in normal rat kidney was: cortex, 14.47 +/- 0.76; medulla, 7.85 +/- 0.64; papilla, 2.64 +/- 0.11; tubules, 13.79 +/- 0.70; glomeruli, 5.57 +/- 0.28. In comparison, neuraminidase activity in rat liver was 2.58 +/- 0.14. Puromycin aminonucleoside (PAN)-induced nephrotic syndrome is a model of glomerular disease in which the loss of glomerular AcNeu is well documented. In two separate studies, we observed no change in the specific activity of neuraminidase in either glomeruli or cortex isolated from rats treated with PAN (15 mg/100 g, intraperitoneally) and killed at either the onset or the peak of proteinuria. Results were similar whether neuraminidase activity was expressed per mg of protein or per microgram of DNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud H. E., Ou S. L., Velosa J. A., Shah S. V., Dousa T. P. Dynamics of renal histamine in normal rat kidney and in nephrosis induced by aminonucleoside of puromycin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):327–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI110456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alhadeff J. A., Wolfe S. Characterization of human liver (4-mythylumbelliferyl-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid) neuraminidase activity. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(9):975–980. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. M. Glomerular epithelial alterations resulting from sialic acid surface coat removal. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):376–385. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baricos W. H., Shah S. V. Increased cathepsin D-like activity in cortex, tubules, and glomeruli isolated from rats with experimental nephrotic syndrome. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2230393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertani T., Poggi A., Pozzoni R., Delaini F., Sacchi G., Thoua Y., Mecca G., Remuzzi G., Donati M. B. Adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats: sequence of pathologic events. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B., Haas J. E. Glomerular sialic acid and proteinuria in human renal disease. Lab Invest. 1973 Apr;28(4):477–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B., Michael A. F. Rat glomerular glycoprotein composition and metabolism in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):164–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARUBELLI R., TRUCCO R. E., CAPUTTO R. Neuraminidase activity in mammalian organs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 18;60:196–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest P. M., Roth J. Localization of sialic acid in kidney glomeruli: regionalization in the podocyte plasma membrane and loss in experimental nephrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8508–8512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu J., Drummond K. N. Chemical and histochemical studies of glomerular sialoprotein in nephrotoxic nephritis in rats. Am J Pathol. 1972 Aug;68(2):391–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Forterre L., Mozere G., Andre J., Sternberg M. Studies on kidney sialidase in normal and diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 7;801(1):138–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Jermanovich N. B., Belok S., Stilmant M. M., Hoyer J. R. Effect of aminonucleoside nephrosis on immune complex localization in autologous immune complex nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):561–572. doi: 10.1172/JCI108967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENK S., ANTONOWICZ I., CRAIG J. M., METCOFF J. Experimental nephrotic syndrome induced in rats by aminonucleoside; renal lesions and body electrolyte composition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Jul;89(3):424–427. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszer-Szafarz B., Szafarz D., Guevara de Murillo A. A general, fast, and sensitive micromethod for DNA determination application to rat and mouse liver, rat hepatoma, human leukocytes, chicken fibroblasts, and yeast cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat A., Touster O. On the lysosomal occurrence and the properties of the neuraminidase of rat liver and of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4380–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Detachment of endothelium and epithelium from the glomerular basement membrane produced by kidney perfusion with neuraminidase. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Sharkey D. J., Farquhar M. G. Identification and characterization of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the renal glomerular epithelial cell. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1591–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Vernillo A. T., Farquhar M. G. Reduced sialylation of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the rat kidney glomerulus--in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):343–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum B. B., Bosmann H. B. Renal membrane biosynthesis and degradation. II. Localization and characterization of neuraminidase activity in rat kidney. Nephron. 1973;11(1):25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuratowska Z., Kubicka T. Purification and some properties of the neuraminidase from rabbit kidney. Acta Biochim Pol. 1967;14(2):255–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Kashgarian M., Sterzel R. B. Lysosomal enzymes in glomerular cells of the rat. Am J Pathol. 1982 May;107(2):161–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Nduguba J. C., Tappel A. L. Sialidase of rat liver and kidney. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4409–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. M., Lemonnier M., Bourrillon R. Human liver neuraminidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1302–1309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Blau E., Vernier R. L. Glomerular polyanion. Alteration in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;23(6):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagi T., Tsuiki S. Rat-liver lysosomal sialidase. Solubilization, substrate specificity and comparison with the cytosolic sialidase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):75–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Skoza L. Glomerular sialoprotein. Science. 1969 Jun 27;164(3887):1519–1521. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3887.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutton T., Resnick M. I., Boyce W. H. Human renal neuraminidase. Invest Urol. 1978 Mar;15(5):419–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. W., Lee R. T., Lee Y. C., Thomas G. H., Reynolds L. W., Uchida Y. The synthesis of 4-methylumbelliferyl alpha-ketoside of N-acetylneuraminic acid and its use in a fluorometric assay for neuraminidase. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 1;101(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Mameli L., Bélisle M., Dallaire L., Melançon S. B. Fluorometric assay of neuraminidase with a sodium (4-methylumbelliferyl-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminate) substrate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchey E. E., Wallin J. D., Shah S. V. Chemiluminescence and superoxide anion production by leukocytes from chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1981 Feb;19(2):349–358. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaltro J., Alhadeff J. A. Solubilization, stabilization and isoelectric focusing of human liver neuraminidase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 30;800(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. G., Price R. G., Robinson D. The distribution of some hydrolases in glomeruli and tubular fragments prepared from rat kidney by zonal centrifugation. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):641–645. doi: 10.1042/bj1220641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Carubelli R. Studies on the soluble and lysosomal neuraminidases of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1821–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Carubelli R. Studies on the soluble and lysosomal neuraminidases of rat mammary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 13;227(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuppy H., Palese P. Neuraminidase aus Schweinenieren reinigung und Eigenschaften. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Sep;349(9):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velosa J. A., Shah S. V., Ou S. L., Abboud H. E., Dousa T. P. Activities of lysosomal enzymes in isolated glomeruli. Alterations in experimental nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1981 Dec;45(6):522–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Tandt W. R., Scharpe S. Methylumbelliferyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid sialidase in human liver. Biochem Med. 1984 Jun;31(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(84)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


