Abstract
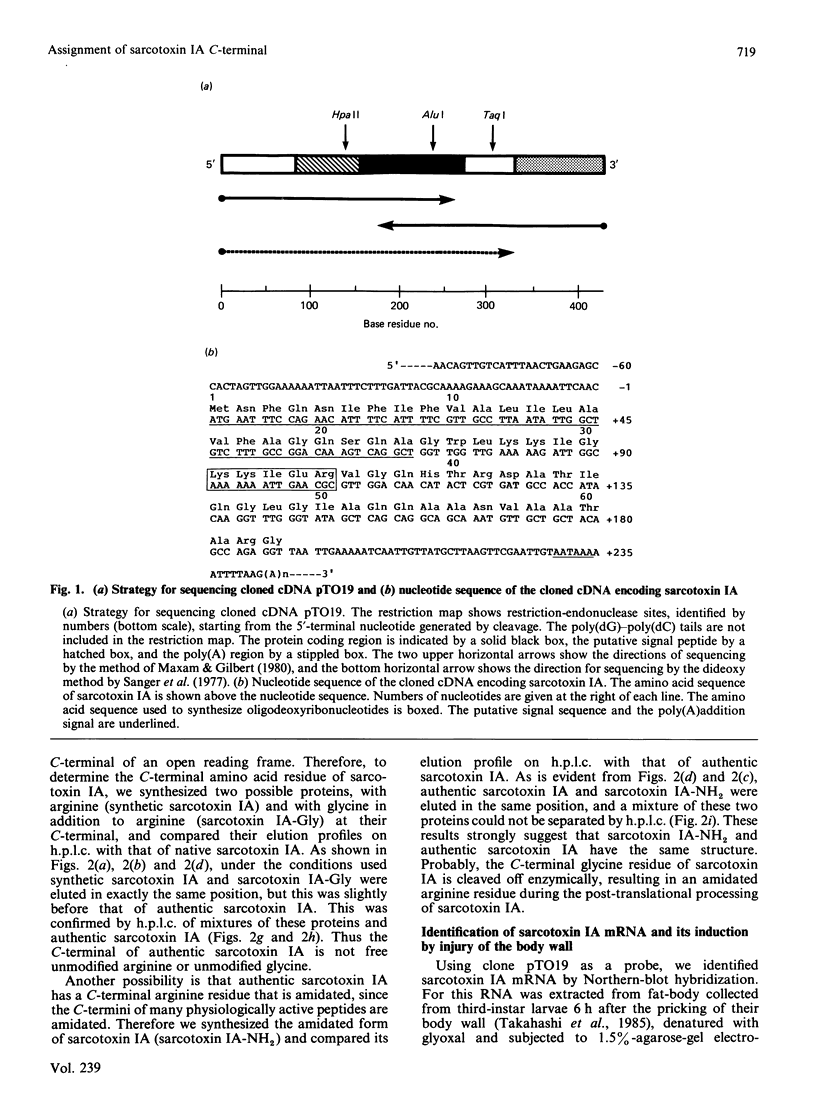
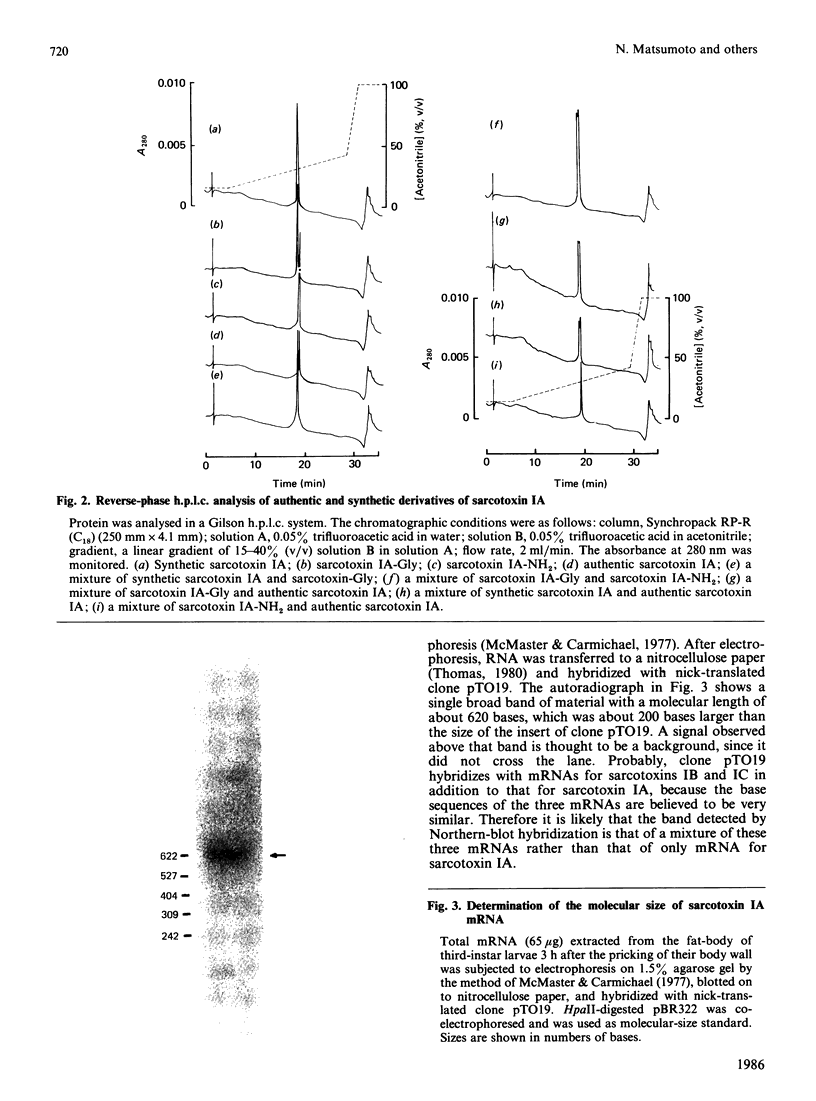
A previous paper described the complete amino acid sequences of sarcotoxins IA, IB and IC, which are a group of potent antibacterial proteins with almost identical primary structures produced by Sarcophaga peregrina (fleshfly) larvae [Okada & Natori (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260, 7174-7177]. The present paper describes the cDNA cloning and complete nucleotide sequencing of a cDNA clone for sarcotoxin IA. The C-terminal amino acid residue of sarcotoxin IA deduced from the nucleotide sequence was glycine, whereas it was found to be arginine by amino acid sequencing of purified sarcotoxin IA. Analysis of the elution profiles on h.p.l.c. of the synthetic derivatives of sarcotoxin IA showed that the C-terminal amino acid residue of authentic sarcotoxin IA is amidated arginine, which is probably produced by enzymic cleavage of terminal glycine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boman H. G., Faye I., von Hofsten P., Kockum K., Lee J. Y., Xanthopoulos K. G., Bennich H., Engström A., Merrifield R. B., Andreu D. On the primary structures of lysozyme, cecropins and attacins from Hyalophora cecropia. Dev Comp Immunol. 1985 Summer;9(3):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(85)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick J. S., Deverno P. J., Chung K. L., Aston W. P. Effects of hemolymph from immune and non-immune larvae of Galleria mellonella on the ultra-structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Summer;6(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(82)80029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glembotski C. C., Eipper B. A., Mains R. E. Characterization of a peptide alpha-amidation activity from rat anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6385–6392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizer J. S., Busby W. H., Jr, Cottle C., Youngblood W. W. Glycine-directed peptide amidation: presence in rat brain of two enzymes that convert p-Glu-His-Pro-Gly-OH into p-Glu-His-Pro-NH2 (thyrotropin-releasing hormone). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3228–3232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kockum K., Faye I., Hofsten P. V., Lee J. Y., Xanthopoulos K. G., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Isolation and sequence of two cDNA clones corresponding to acidic and basic attacins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2071–2075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano H., Natori S. Participation of Sarcophaga peregrina humoral lectin in the lysis of sheep red blood cells injected into the abdominal cavity of larvae. Dev Comp Immunol. 1985 Winter;9(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(85)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Ionophore activity of sarcotoxin I, a bactericidal protein of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):453–458. doi: 10.1042/bj2290453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Mode of action of a bactericidal protein induced in the haemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh-fly) larvae. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):119–124. doi: 10.1042/bj2220119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein from haemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh-fly) larvae. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):727–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2110727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. Sequence at the 3' end of globin mRNA shows homology with immunoglobulin light chain mRNA. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):359–362. doi: 10.1038/252359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
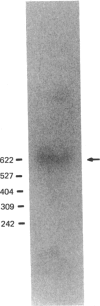
- Takahashi H., Komano H., Kawaguchi N., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Natori S. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA of Sarcophaga peregrina humoral lectin induced on injury of the body wall. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12228–12233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hofsten P., Faye I., Kockum K., Lee J. Y., Xanthopoulos K. G., Boman I. A., Boman H. G., Engström A., Andreu D., Merrifield R. B. Molecular cloning, cDNA sequencing, and chemical synthesis of cecropin B from Hyalophora cecropia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2240–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]